哈希表
2016-05-10 20:57
337 查看
哈希表:不同的Key值经过哈希函数Hash(Key)处理以后可能产生相同的值哈希地址,我们称这种情况为哈希冲突。所以用哈希冲突的开链法(哈希桶)进行处理,其结构如下:
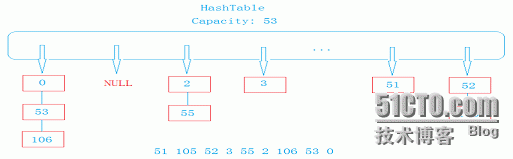
代码如下:

代码如下:
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
using namespace std;
template<class k,class v>
struct HashTableNode
{
k _key;
v _value;
HashTableNode<k, v>* _next;
HashTableNode<k,v>(const k& key, const v& value) //构造函数
:_key(key)
, _value(value)
, _next(NULL)
{}
HashTableNode() //构造无参函数
:_key(0)
, _value(0)
, _next(NULL)
{}
};
template<class k, class v>
class HashTable
{
typedef HashTableNode<k, v> Node;
public:
HashTable<k,v>()
:_size(0)
, _tables(NULL)
{}
HashTable<k,v>(const HashTable<k,v>& ht) //拷贝构造函数
{
_tables.resize(ht._size);
_size = ht._size;
for (size_t i = 0; i < _size; i++)
{
Node* cur1 = ht._tables[i];
Node* cur2 = NULL;
while (cur1)
{
if (_tables[i] == NULL)
{ //当链表为空,则开辟新节点,并将地址返回给_tables[i]
_tables[i] = new Node(cur1->_key, cur1->_value);
cur2 = _tables[i];
}
else
{ //其他情况则将新开辟的节点地址返回给cur2的next
cur2->_next = new Node(cur1->_key, cur1->_value);
}
cur1 = cur1->_next;
}
}
}
~HashTable()
{
if (_size != 0)
{
for (size_t i = 0; i < _size; i++)
{
Node* del = _tables[i];
while (del) //del不为空,则将del后的节点删除
{
Node* next = del->_next;
delete del;
del = next;
_size--;
}
_tables[i] = NULL;
}
}
}
HashTable<k, v> &operator=(HashTable<k, v> ht) //现代写法
{ //函数传参时会构造一个对象,此时只需将对象中的_tables和_size相互交换就行了
if (this != &ht)
{
if (&ht != this)
{
swap(_tables, ht._tables);
swap(_size, ht._size);
}
return *this;
}
}
bool Insert(const k& key, const v& value)
{
if (_size == _tables.size())
{
_CheckExpand(); //先进行检查容量,如若不够则需扩容
}
size_t index = _HashFunc(key); //将下标赋值给index
Node* begin = _tables[index];
while (begin)
{
if (begin->_key == key)
{
return false; //查找key,如若有则返回false
}
begin = begin->_next;
}
Node* tmp = new Node(key, value);
tmp->_next = _tables[index];
_tables[index] = tmp;
_size++;
return true;
}
size_t _HashFunc(const k&key) //返回key所在的下标
{
return key%_tables.size();
}
void _CheckExpand() //检查扩容
{
size_t newsize = _GetNextPrime();
if (newsize == _size)//若果当前容量等于newsize,函数返回
{
return;
}
vector<Node*> newTables;
newTables.resize(newsize); //开辟newsize大小的容量
for (size_t i = 0; i < _tables.size(); i++)
{ //将空间的每个节点都初始化
Node* cur = _tables[i];
while (cur)
{
Node* tmp = cur;
cur = cur->_next;
size_t index = _HashFunc(tmp->_key);
tmp->_next = newTables[index];
newTables[index] = tmp;
}
_tables[i] =NULL;
}
_tables.swap(newTables);
}
size_t _GetNextPrime() //定义28个素数表,因为素数有利于降低载荷因子
{
static const int _PrimeSize = 28;
static const unsigned long _PrimeList[_PrimeSize] =
{
53ul, 97ul, 193ul, 389ul, 769ul,
1543ul, 3079ul, 6151ul, 12289ul, 24593ul,
49157ul, 98317ul, 196613ul, 393241ul, 786433ul,
1572869ul, 3145739ul, 6291469ul, 12582917ul, 25165843ul,
50331653ul, 100663319ul, 201326611ul, 402653189ul, 805306457ul,
1610612741ul, 3221225473ul, 4294967291ul
};
for (int i = 0; i < _PrimeSize; i++)
{
if (_PrimeList[i]> _tables.size())
{
return _PrimeList[i];
}
}
return _PrimeList[_PrimeSize - 1];
}
Node* Find(const k& key) //查找节点 并返回该节点地址
{
size_t index = _HashFunc(key);
Node* cur = _tables[index];
while (cur)
{
if (cur->_key == key)
{
return cur;
}
cur = cur->_next;
}
return NULL;
}
bool Remove(const k& key) //删除某个节点
{
size_t index = _HashFunc(key);
Node* cur = _tables[index];
Node* prev = NULL;
while (cur)
{
if (cur->_key == key)
{
break;
}
prev = cur;
cur = cur->_next;
}
if (cur == _tables[index])
{
_tables[index] = cur->_next;
return true;
}
else
{
prev->_next = cur->_next;
delete cur;
return true;
}
return false;
}
void PrintTables()
{
printf("哈希表如下:\n");
for (size_t i = 0; i < _tables.size(); i++)
{
Node* cur = _tables[i];
while (cur)
{
/*cout << cur->_key << " ";
cur = cur->_next;*/
printf("[%d]=%c & %d ", i, cur->_value,cur->_key);
cur = cur->_next;
if (cur==NULL)
{
printf("\n");
}
}
}
printf("\n");
}
protected:
size_t _size;
vector<Node*> _tables;
};
测试代码如下:
void Test()
{
typedef HashTableNode<int, char> Node;
HashTable<int, char> ht;
ht.Insert(1, 'a');
ht.Insert(2, 'b');
ht.Insert(3, 'c');
ht.Insert(4, 'd');
ht.Insert(5, 'e');
ht.Insert(54, 'x');
ht.Insert(55, 'y');
ht.Insert(56, 'z');
ht.PrintTables();
HashTable<int, char> ht2;
ht2.Insert(54, 'x');
ht2.Insert(55, 'y');
ht2.Insert(56, 'z');
ht2.Insert(1, 'a');
ht2.Insert(2, 'b');
ht2.Insert(3, 'c');
ht2.Insert(4, 'd');
ht2.Insert(5, 'e');
ht2.PrintTables();
ht=ht2;
ht.PrintTables();
/*Node* ret = ht.Find(55);
cout << ret->_value << endl;*/
/*ht.Remove(4);
ht.PrintTables();*/
/*HashTable<int, char> ht1(ht);
ht1.PrintHashTable();*/
}
int main()
{
Test();
system("pause");
return 0;
}
相关文章推荐
- Ruby中require、load、include、extend的区别介绍
- vbscript include的办法实现代码第1/2页
- 解析C++编程中的#include和条件编译
- PHP脚本中include文件出错解决方法
- Flex include和import ActionScript代码
- 简单谈谈PHP中的include、include_once、require以及require_once语句
- set_include_path在win和linux下的区别
- php include加载文件两种方式效率比较
- How to Auto Include a Javascript File
- 浅谈ASP.NET的include的使用方法
- java/jsp中 中文问题详解
- php相对当前文件include其它文件的方法
- JSP计数器的制作
- php include和require的区别深入解析
- PHP include_path设置技巧分享
- JS 实现完美include载入实现代码
- JS实现完美include加载功能代码
- JSP开发入门(四)--JSP的内部对象
- 实战 J2EE 开发购物网站 二
- php 中include()与require()的对比
