[置顶] Eclipse GEF UMLClass(1)
2016-05-09 20:45
706 查看
通过两篇文章对GEF进行了介绍,为了自己加深对GEF的理解和学习,从网上找了一下开源的amaterasuml的uml工具,并把其中对内容转换提取成。
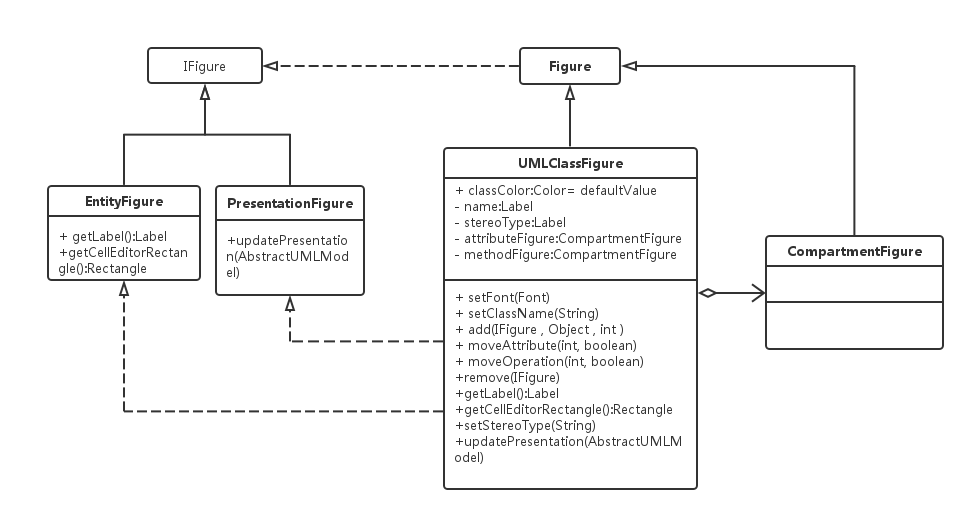
EntityFigure:实体Figure,用于获取Label和获取矩形编辑域,代码如下:
PresentaionFigure:描述Figure,用于更新模型的描述
CompartmentFigure:用于分隔的Figure,用于分隔属性和方法
UMLClassFigure:最终展示的Figure,主要的ClassFigure,包含所有相关方法
典型的模型对象包含PropertyChangeSupport类型的成员变量,用来添加监听器和通知监听器(控制器),一般来说,模型会实现一个基类,用来封装事件机制,主要包括添加监听器,删除监听器,以及模型属性改变触发的相应事件。另外,当用户希望通过属性视图编辑模型属性时,模型要实现IPropertySource接口,该接口的方法解释如下:
//得到在属性页中能编辑的值,可以返回this表示当前模型
public Object getEditableValue();
//得到IPropertyDescriptor的数组,其中每一项是属性页中能编辑的项
public IPropertyDescriptor[] getPropertyDescriptors();
//通过id得到某个属性值,在添加每一项IPropertyDescriptor都会指定id
public Object getPropertyValue(Object id);
//表示特定属性id值是否改变
public boolean isPropertySet(Object id);
public void resetPropertyValue(Object id);//通过id重置属性
public void setPropertyValue(Object id, Object value);//通过id和值设置某一项属性的值
类图如下:

我们定义一个AbstractUMLModel 封装事件机制和属性编辑
AbstractUMLEntityModel代码如下:
AbstractUMLConnectionModel,分析方法跟上面的都类似:
ConnectionBendpoint类如下:
UMLColorRegistry类如下:
BooleanPropertyDescriptor类如下:
现在对于UML的抽象类已经大致看到了外貌,主要是把Figure与Model做了较详细的介绍,以及详细的代码,但是还是停留在抽象层面,下一篇文章主要针对UMLClass类图的具体类进行分析。
Figure:
第一篇文章其实是对amaterasuml中ClassFigure的简化,真实的UML类图如下:
EntityFigure:实体Figure,用于获取Label和获取矩形编辑域,代码如下:
import org.eclipse.draw2d.IFigure;
import org.eclipse.draw2d.Label;
import org.eclipse.draw2d.geometry.Rectangle;
public interface EntityFigure extends IFigure{
Label getLabel();
Rectangle getCellEditorRectangle();
}PresentaionFigure:描述Figure,用于更新模型的描述
public interface PresentationFigure {
void updatePresentation(AbstractUMLModel model);
}CompartmentFigure:用于分隔的Figure,用于分隔属性和方法
import org.eclipse.draw2d.AbstractBorder;
import org.eclipse.draw2d.Figure;
import org.eclipse.draw2d.Graphics;
import org.eclipse.draw2d.IFigure;
import org.eclipse.draw2d.ToolbarLayout;
import org.eclipse.draw2d.geometry.Insets;
public class CompartmentFigure extends Figure {
public CompartmentFigure() {
ToolbarLayout layout = new ToolbarLayout();
layout.setMinorAlignment(ToolbarLayout.ALIGN_TOPLEFT);
layout.setStretchMinorAxis(false);
layout.setSpacing(2);
setLayoutManager(layout);
setBorder(new CompartmentFigureBorder());
}
public class CompartmentFigureBorder extends AbstractBorder {
public Insets getInsets(IFigure figure) {
return new Insets(1, 0, 2, 0);
}
public void paint(IFigure figure, Graphics graphics, Insets insets) {
graphics.drawLine(getPaintRectangle(figure, insets).getTopLeft(),
tempRect.getTopRight());
}
}
}UMLClassFigure:最终展示的Figure,主要的ClassFigure,包含所有相关方法
import org.eclipse.draw2d.ColorConstants;
import org.eclipse.draw2d.Figure;
import org.eclipse.draw2d.IFigure;
import org.eclipse.draw2d.Label;
import org.eclipse.draw2d.LineBorder;
import org.eclipse.draw2d.MarginBorder;
import org.eclipse.draw2d.PositionConstants;
import org.eclipse.draw2d.ToolbarLayout;
import org.eclipse.draw2d.geometry.Rectangle;
import org.eclipse.swt.graphics.Color;
import org.eclipse.swt.graphics.Font;
import org.eclipse.swt.graphics.Image;
public class UMLClassFigure extends Figure implements EntityFigure, PresentationFigure {
public static Color classColor = new Color(null, 255, 255, 206);
private Label name;
private Label stereoType;
private Image icon;
private CompartmentFigure attributeFigure = new CompartmentFigure();
private CompartmentFigure methodFigure = new CompartmentFigure();
private Figure nameFigure;
public UMLClassFigure(Image icon, Figure nameFigure) {
this.nameFigure = nameFigure;
this.name = new Label();
this.name.setForegroundColor(ColorConstants.darkGray);
this.name.setBorder(new MarginBorder(5));
this.name.setIcon(icon);
this.icon = icon;
this.stereoType = new Label();
this.stereoType.setTextAlignment(PositionConstants.CENTER);
ToolbarLayout layout = new ToolbarLayout();
setLayoutManager(layout);
setBorder(new LineBorder(1));
setBackgroundColor(classColor);
setOpaque(true);
nameFigure.setLayoutManager(new ToolbarLayout());
//
// nameFigure.add(this.stereoType);
nameFigure.add(this.name);
add(nameFigure);
add(attributeFigure);
add(methodFigure);
}
public void setFont(Font font){
this.name.setFont(font);
}
public void setClassName(String className){
this.name.setText(className);
}
public void add(IFigure figure, Object constraint, int index) {
if(figure instanceof AttributeLabel){
attributeFigure.add(figure);
} else if(figure instanceof OperationLabel){
methodFigure.add(figure);
} else {
super.add(figure,constraint,index);
}
}
public void moveAttribute(int index, boolean up){
@SuppressWarnings("rawtypes")
List children = attributeFigure.getChildren();
IFigure obj = (IFigure)children.get(index);
attributeFigure.remove(obj);
if(up){
attributeFigure.add(obj, index - 1);
} else {
attributeFigure.add(obj, index + 1);
}
}
public void moveOperation(int index, boolean up){
@SuppressWarnings("rawtypes")
List children = methodFigure.getChildren();
IFigure obj = (IFigure)children.get(index);
methodFigure.remove(obj);
if(up){
methodFigure.add(obj, index - 1);
} else {
methodFigure.add(obj, index + 1);
}
}
public void remove(IFigure figure) {
if(figure instanceof AttributeLabel){
attributeFigure.remove(figure);
} else if(figure instanceof OperationLabel){
methodFigure.remove(figure);
} else {
super.remove(figure);
}
}
public Label getLabel(){
return name;
}
public Rectangle getCellEditorRectangle() {
Rectangle rect = name.getBounds().getCopy();
if (name.getIcon() != null) {
return new Rectangle(rect.x + 16, rect.y, rect.width - 16, rect.height);
}
return new Rectangle(rect.x, rect.y, rect.width, rect.height);
}
public void updatePresentation(AbstractUMLModel model) {
if (model.isShowIcon()) {
name.setIcon(icon);
} else {
name.setIcon(null);
}
}
public void setStereoType(String stereoType) {
if (stereoType == null || "".equals(stereoType)) {
if (nameFigure.getChildren().contains(this.stereoType)) {
nameFigure.remove(this.stereoType);
}
} else {
this.stereoType.setText("<<" + stereoType + ">>");
if (!nameFigure.getChildren().contains(this.stereoType)) {
nameFigure.add(this.stereoType, 0);
}
}
}
}Modal :
在GEF框架中,Modal是非常简单的一部分,用户可以把Modal理解成一个简单的可持久化的实体。但为了能让控制器知道模型的变化,应该控制器作为事件监听者注册到Modal中,当模型发生变化时,就触发相应的事件给控制器,后者负责通知各个视图进行更新。典型的模型对象包含PropertyChangeSupport类型的成员变量,用来添加监听器和通知监听器(控制器),一般来说,模型会实现一个基类,用来封装事件机制,主要包括添加监听器,删除监听器,以及模型属性改变触发的相应事件。另外,当用户希望通过属性视图编辑模型属性时,模型要实现IPropertySource接口,该接口的方法解释如下:
//得到在属性页中能编辑的值,可以返回this表示当前模型
public Object getEditableValue();
//得到IPropertyDescriptor的数组,其中每一项是属性页中能编辑的项
public IPropertyDescriptor[] getPropertyDescriptors();
//通过id得到某个属性值,在添加每一项IPropertyDescriptor都会指定id
public Object getPropertyValue(Object id);
//表示特定属性id值是否改变
public boolean isPropertySet(Object id);
public void resetPropertyValue(Object id);//通过id重置属性
public void setPropertyValue(Object id, Object value);//通过id和值设置某一项属性的值
类图如下:

我们定义一个AbstractUMLModel 封装事件机制和属性编辑
public abstract class AbstractUMLModel implements Serializable, IPropertySource {
//定义属性的常量ID
public static final String P_BACKGROUND_COLOR = "_background";
public static final String P_FOREGROUND_COLOR = "_foreground";
public static final String P_SHOW_ICON = "_showicon";
private RGB backgroundColor;
private RGB foregroundColor;
private boolean showIcon = true;
private AbstractUMLEntityModel parent;
private PropertyChangeSupport listeners = new PropertyChangeSupport(this);
public void addPropertyChangeListener(PropertyChangeListener listener) {
listeners.addPropertyChangeListener(listener);
}
public void firePropertyChange(String propName, Object oldValue,Object newValue) {
listeners.firePropertyChange(propName, oldValue, newValue);
}
public void removePropertyChangeListener(PropertyChangeListener listener) {
listeners.removePropertyChangeListener(listener);
}
public Object getEditableValue() {
return this;
}
public void setParent(AbstractUMLEntityModel parent) {
this.parent = parent;
}
public AbstractUMLEntityModel getParent() {
return parent;
}
public IPropertyDescriptor[] getPropertyDescriptors() {
//定义属性的编辑项
return new IPropertyDescriptor[] {
new ColorPropertyDescriptor(P_BACKGROUND_COLOR, "Background Color"),
new ColorPropertyDescriptor(P_FOREGROUND_COLOR, "Foreground Color"),
//自定义的PropertyDescriptor
new BooleanPropertyDescriptor(P_SHOW_ICON, "Show Icon") };
}
public Object getPropertyValue(Object id) {
if (id.equals(P_BACKGROUND_COLOR)) {
return backgroundColor;
} else if (P_FOREGROUND_COLOR.equals(id)) {
return foregroundColor;
} else if (P_SHOW_ICON.equals(id)) {
return new Boolean(isShowIcon());
}
return null;
}
public boolean isPropertySet(Object id) {
return P_BACKGROUND_COLOR.equals(id) || P_FOREGROUND_COLOR.equals(id)
|| P_SHOW_ICON.equals(id);
}
//设置属性的值
public void setPropertyValue(Object id, Object value) {
if (P_BACKGROUND_COLOR.equals(id)) {
setBackgroundColor((RGB) value);
} else if (P_FOREGROUND_COLOR.equals(id)) {
setForegroundColor((RGB) value);
} else if (P_SHOW_ICON.equals(id)) {
setShowIcon(((Boolean) value).booleanValue());
}
}
public void resetPropertyValue(Object id) {
}
public Color getBackgroundColor() {
//调用自定义生成颜色对象
return UMLColorRegistry.getColor(backgroundColor);
}
public void setBackgroundColor(RGB backgroundColor) {
this.backgroundColor = backgroundColor;
//当backgroundColor改变后,触发属性改变的事件
firePropertyChange(P_BACKGROUND_COLOR, null, backgroundColor);
}
public Color getForegroundColor() {
return UMLColorRegistry.getColor(foregroundColor);
}
public void setForegroundColor(RGB foregroundColor) {
this.foregroundColor = foregroundColor;
//当foregroundColor改变后,触发属性改变的事件
firePropertyChange(P_FOREGROUND_COLOR, null, foregroundColor);
}
public boolean isShowIcon() {
return showIcon;
}
public void setShowIcon(boolean showIcon) {
this.showIcon = showIcon;
//当SHOW_ICON改变后,触发属性改变的事件
firePropertyChange(P_SHOW_ICON, null, new Boolean(showIcon));
}
public void copyPresentation(AbstractUMLModel model) {
if (backgroundColor != null) {
model.setBackgroundColor(backgroundColor);
}
if (foregroundColor != null) {
model.setForegroundColor(foregroundColor);
}
model.setShowIcon(showIcon);
}
}AbstractUMLEntityModel代码如下:
public abstract class AbstractUMLEntityModel extends AbstractUMLModel {
private Rectangle constraint;
//定义模型连线的列表
private List<AbstractUMLConnectionModel> sourceConnections = new ArrayList<AbstractUMLConnectionModel>();
private List<AbstractUMLConnectionModel> targetConnections = new ArrayList<AbstractUMLConnectionModel>();
private List<AbstractUMLModel> children = new ArrayList<AbstractUMLModel>();
private Map<String, Boolean> filterProperty = new HashMap<String, Boolean>();
//定义属性的常量ID
public static final String P_CONSTRAINT = "_constraint";
public static final String P_SOURCE_CONNECTION = "_source_connection";
public static final String P_TARGET_CONNECTION = "_target_connection";
public static final String P_CHILDREN = "_children";
public static final String P_FILTER = "_filter";
public static final String P_FORCE_UPDATE = "_force_update";
public Map<String, Boolean> getFilterProperty() {
return filterProperty;
}
public void setFilterProperty(Map<String, Boolean> filterProperty) {
this.filterProperty = filterProperty;
firePropertyChange(P_FILTER, null, filterProperty);
}
public Rectangle getConstraint() {
return constraint;
}
public void addChild(AbstractUMLModel model) {
children.add(model);
model.setParent(this);
//当增加子模型时,触发属性改变的事件
firePropertyChange(P_CHILDREN,null,model);
}
public void removeChild(AbstractUMLModel model) {
children.remove(model);
model.setParent(this);
//当删除子模型时,触发属性改变的事件
firePropertyChange(P_CHILDREN,null,model);
}
public void forceUpdate() {
firePropertyChange(P_FORCE_UPDATE, null ,null);
}
public List<AbstractUMLModel> getChildren(){
return this.children;
}
public void setConstraint(Rectangle constraint) {
if(constraint.x < 0){
constraint.x = 0;
}
if(constraint.y < 0){
constraint.y = 0;
}
this.constraint = constraint;
firePropertyChange(P_CONSTRAINT, null, constraint);
}
public void addSourceConnection(AbstractUMLConnectionModel connx) {
sourceConnections.add(connx);
//当输入的连线改变后,触发属性改变的事件
firePropertyChange(P_SOURCE_CONNECTION, null, connx);
}
public void addTargetConnection(AbstractUMLConnectionModel connx) {
targetConnections.add(connx);
//当输入的连线改变后,触发属性改变的事件
firePropertyChange(P_TARGET_CONNECTION, null, connx);
}
public List<AbstractUMLConnectionModel> getModelSourceConnections() {
return sourceConnections;
}
public List<AbstractUMLConnectionModel> getModelTargetConnections() {
return targetConnections;
}
public void removeSourceConnection(AbstractUMLConnectionModel connx) {
sourceConnections.remove(connx);
//当输入的连线改变后,触发属性改变的事件
firePropertyChange(P_SOURCE_CONNECTION, connx, null);
}
public void removeTargetConnection(AbstractUMLConnectionModel connx) {
targetConnections.remove(connx);
//当输入的连线改变后,触发属性改变的事件
firePropertyChange(P_TARGET_CONNECTION, connx, null);
}
public void setBackgroundColor(RGB backgroundColor) {
for (Iterator<AbstractUMLModel> iter = children.iterator(); iter.hasNext();) {
AbstractUMLModel element = (AbstractUMLModel) iter.next();
element.setBackgroundColor(backgroundColor);
}
super.setBackgroundColor(backgroundColor);
}
public void setForegroundColor(RGB foregroundColor) {
for (Iterator<AbstractUMLModel> iter = children.iterator(); iter.hasNext();) {
AbstractUMLModel element = (AbstractUMLModel) iter.next();
element.setForegroundColor(foregroundColor);
}
super.setForegroundColor(foregroundColor);
}
public void setShowIcon(boolean showIcon) {
for (Iterator<AbstractUMLModel> iter = children.iterator(); iter.hasNext();) {
AbstractUMLModel element = (AbstractUMLModel) iter.next();
element.setShowIcon(showIcon);
}
super.setShowIcon(showIcon);
}
}AbstractUMLConnectionModel,分析方法跟上面的都类似:
public abstract class AbstractUMLConnectionModel extends AbstractUMLModel {
private AbstractUMLEntityModel source;
private AbstractUMLEntityModel target;
private List<ConnectionBendpoint> bendpoints = new ArrayList<ConnectionBendpoint>();
public static final String P_BEND_POINT = "_bend_point";
public void addBendpoint(int index, ConnectionBendpoint point) {
bendpoints.add(index, point);
firePropertyChange(P_BEND_POINT, null, null);
}
public List<ConnectionBendpoint> getBendpoints() {
if (bendpoints == null) {
bendpoints = new ArrayList<ConnectionBendpoint>();
}
return bendpoints;
}
public void removeBendpoint(int index) {
bendpoints.remove(index);
firePropertyChange(P_BEND_POINT, null, null);
}
public void removeBendpoint(ConnectionBendpoint point) {
bendpoints.remove(point);
firePropertyChange(P_BEND_POINT, null, null);
}
public void replaceBendpoint(int index, ConnectionBendpoint point) {
bendpoints.set(index, point);
firePropertyChange(P_BEND_POINT, null, null);
}
public void attachSource() {
if (!source.getModelSourceConnections().contains(this)) {
source.addSourceConnection(this);
}
}
public void attachTarget() {
if (!target.getModelTargetConnections().contains(this)) {
target.addTargetConnection(this);
}
}
public void detachSource() {
if (source != null) {
source.removeSourceConnection(this);
}
}
public void detachTarget() {
if (target != null) {
target.removeTargetConnection(this);
}
}
public AbstractUMLEntityModel getSource() {
return source;
}
public AbstractUMLEntityModel getTarget() {
return target;
}
public void setSource(AbstractUMLEntityModel model) {
source = model;
}
public void setTarget(AbstractUMLEntityModel model) {
target = model;
}
public IPropertyDescriptor[] getPropertyDescriptors() {
return new IPropertyDescriptor[] {
new ColorPropertyDescriptor(P_FOREGROUND_COLOR, "Foreground Color")
};
}
}ConnectionBendpoint类如下:
public class ConnectionBendpoint implements Serializable, Bendpoint {
private float weight = 0.5f;
private Dimension d1 = null;
private Dimension d2 = null;
public ConnectionBendpoint() {
// ignore
}
public ConnectionBendpoint(Dimension dim1, Dimension dim2) {
d1 = dim1;
d2 = dim2;
}
public Dimension getFirstRelativeDimension() {
return d1;
}
public Point getLocation() {
return null;
}
public Dimension getSecondRelativeDimension() {
return d2;
}
public float getWeight() {
return weight;
}
public void setRelativeDimensions(Dimension dim1, Dimension dim2) {
d1 = dim1;
d2 = dim2;
}
public void setWeight(float w) {
weight = w;
}
}UMLColorRegistry类如下:
public class UMLColorRegistry {
private ColorRegistry registry;
private static UMLColorRegistry instance;
private UMLColorRegistry() {
registry = new ColorRegistry();
}
//单例
public static final Color getColor(RGB rgb) {
if (instance == null) {
instance = new UMLColorRegistry();
}
if (rgb == null) {
return null;
}
return instance.createColor(rgb);
}
//获取颜色对象
private Color createColor(RGB rgb) {
registry.put(rgb.toString(), rgb);
return registry.get(rgb.toString());
}
}BooleanPropertyDescriptor类如下:
public class BooleanPropertyDescriptor extends PropertyDescriptor {
public BooleanPropertyDescriptor(Object id,String displayName){
super(id,displayName);
}
public CellEditor createPropertyEditor(Composite parent) {
CellEditor editor = new ComboBoxCellEditor(
parent, new String[]{"true","false"},SWT.READ_ONLY){
public void doSetValue(Object value){
if(((Boolean)value).booleanValue()){
super.doSetValue(new Integer(0));
} else {
super.doSetValue(new Integer(1));
}
}
public Object doGetValue(){
int selection = ((Integer)super.doGetValue()).intValue();
if(selection==0){
return new Boolean(true);
} else {
return new Boolean(false);
}
}
};
if (getValidator() != null)
editor.setValidator(getValidator());
return editor;
}
}现在对于UML的抽象类已经大致看到了外貌,主要是把Figure与Model做了较详细的介绍,以及详细的代码,但是还是停留在抽象层面,下一篇文章主要针对UMLClass类图的具体类进行分析。
相关文章推荐
- Hibernate data validator in spring integration
- Maven学习4之eclipse下 maven install和test的两个错误
- SpringIOC容器-创建对象
- JAVA实现过滤掉文本中的表情
- struts2页面属性值回显
- java的ExecutorService 实现线程池
- JAVA——泛型类和泛型方法(静态方法泛型)
- 我理解的RxJava
- 重新学javaweb---文件上传1
- eclipse远程debug
- IO流----File类的常用方法
- struts2 捕获404错误的常用方法
- java推荐书籍及下载
- Java中二进制和十进制之间的相互转化
- java8之Lambda表达式 4:MapReduce开发案例
- java比较时间差
- Java 克隆
- java8之Lambda表达式 3:数据流
- java8之Lambda表达式 2:内建函数式接口
- java8之Lambda表达式 1:简介
