复杂链表的复制
2016-04-19 10:18
309 查看
什么是复杂链表?
复杂链表的节点包括三个成员变量:一个T类型的变量,一个指向下个节点的指针,一个随机指向的指针。
复杂链表的复制需要注意:复制之后的链表的每个节点的随机指针的指向需要和复制之前的链表的节点的随机指针指向的节点一样。
节点:
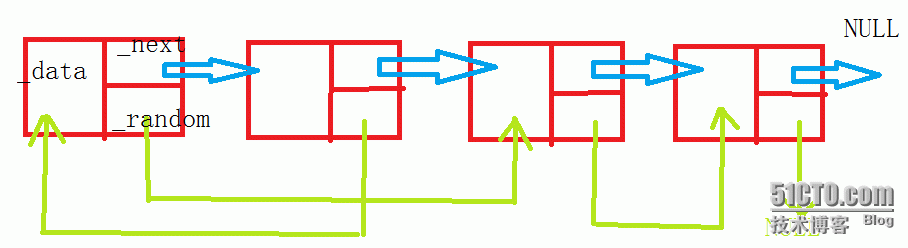
复制链表的步骤:
1、复制每个节点,将其插在原节点的后面,这样,复制节点的随机指针指向的节点是原节点的随机指针指向的节点之后的节点。
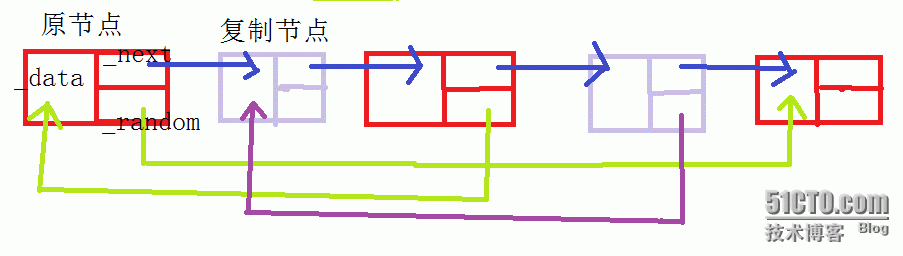
2、random指向
3、拆分链表
代码实现:
复杂链表的节点包括三个成员变量:一个T类型的变量,一个指向下个节点的指针,一个随机指向的指针。
复杂链表的复制需要注意:复制之后的链表的每个节点的随机指针的指向需要和复制之前的链表的节点的随机指针指向的节点一样。
节点:
struct ComplexNode
{
ComplexNode(int data)
:_data(data)
,_next(NULL)
,_random(NULL)
{}
int _data;
ComplexNode* _next;
ComplexNode* _random;
};实例:
复制链表的步骤:
1、复制每个节点,将其插在原节点的后面,这样,复制节点的随机指针指向的节点是原节点的随机指针指向的节点之后的节点。

2、random指向
3、拆分链表
代码实现:
ComplexNode* CopyComplexList(ComplexNode* list)
{
ComplexNode* cur=list;
while(cur)//复制节点并插到原节点的后面
{
ComplexNode* newnode = new ComplexNode(cur->_data);
newnode->_next=cur->_next;
cur->_next=newnode;
cur=newnode->_next;
}
cur=list;//cur指向头结点
while(cur)//置random
{
if(cur->_random!=NULL)
{
cur->_next->_random=cur->_random->_next;
}
cur=cur->_next->_next;
}
cur=list;
ComplexNode* tmp1=NULL;//拆分链表,tmp2为复制之后的链表
ComplexNode* tmp2=NULL;
if(cur!=NULL)
{
tmp1=tmp2=cur->_next;
cur->_next=tmp1->_next;
cur=cur->_next;
}
while(cur!=NULL)
{
tmp1->_next=cur->_next;
tmp1=tmp1->_next;
cur->_next=cur->_next->_next;
cur=cur->_next;
}
return tmp2;
}
相关文章推荐
- iOS 相册或者照相时标题是英文的问题
- 派生类与父类的初始化
- OpenCV参考手册之Mat类详解
- MySQL基础学习总结
- [Unity] Cg标准函数库
- PHP函数ip2long转换IP时数值太大产生负数的解决办法
- 七牛两个账号间空间内容迁移
- 七牛两个账号间空间内容迁移
- 七牛两个账号间空间内容迁移
- 七牛两个账号间空间内容迁移
- 七牛两个账号间空间内容迁移
- 七牛两个账号间空间内容迁移
- 七牛两个账号间空间内容迁移
- 七牛两个账号间空间内容迁移
- 七牛两个账号间空间内容迁移
- hdu1285 & hdu4857 --拓扑排序
- 【LeetCode】LeetCode——第7题:Reverse Integer
- ARM-PLC2200实验箱基础学习-1
- Jquery-UI 遮罩层
- Android客户端与服务器端数据交互之——字符串拼接
