最长公共子序列 LCS(模板) poj 1458
2016-04-04 13:44
567 查看
一、标准模板
#include <iostream>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <cstring>
#include <vector>
#include <cmath>
#include <algorithm>
#include <set>
#include <cassert>
#include <time.h>
#include <queue>
#include <map>
#include <stack>
#include <bitset>
#include <string>
#include <sstream>
#define INF 0x3f3f3f3f
#define PRINT(x) cout<<x<<endl;
using namespace std;
template <class Type>
Type stringToNum(const string& str)
{
istringstream iss(str);
Type num;
iss >> num;
return num;
}
//======================================================
#define MAXN 205
int dp[MAXN][MAXN];
int whLCS(char s1[],int len1,char s2[],int len2) {
for(int i=1;i<=len1;++i) {
for (int j=1;j<=len2;++j) {
if(s1[i-1]==s2[j-1])
dp[i][j]=dp[i-1][j-1]+1;
else
dp[i][j]=max(dp[i-1][j],dp[i][j-1]);
}
}
return dp[len1][len2];
}
int main()
{
freopen("input.txt","r",stdin);
char s1[MAXN],s2[MAXN];
while (scanf("%s %s",s1,s2)!=EOF) {
int res = whLCS(s1,strlen(s1),s2,strlen(s2));
PRINT(res);
}
return 0;
}当然,在内存吃紧的情况下可以用所谓的”滚动数组”,因为找子串的时候是一排一排刷的,而关系到的排只会是上一排,这样就只用保存2排就好(交替使用)。
int whLCS(char s1[],int len1,char s2[],int len2) {
int rowFlag = 1;
for(int i=1;i<=len1;++i) {
for (int j=1;j<=len2;++j) {
if(s1[i-1]==s2[j-1])
dp[rowFlag][j]=dp[!rowFlag][j-1]+1;
else
dp[rowFlag][j]=max(dp[!rowFlag][j],dp[rowFlag][j-1]);
}
rowFlag = !rowFlag;
}
return dp[!rowFlag][len2];
}AC code
#include <iostream>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <cstring>
#include <vector>
#include <cmath>
#include <algorithm>
#include <set>
#include <cassert>
#include <time.h>
#include <queue>
#include <map>
#include <stack>
#include <bitset>
#include <string>
#include <sstream>
#define INF 0x3f3f3f3f
#define PRINT(x) cout<<x<<endl;
using namespace std;
template <class Type>
Type stringToNum(const string& str)
{
istringstream iss(str);
Type num;
iss >> num;
return num;
}
//======================================================
#define MAXN 205
int same(int a,int b) {
return a==b?1:0; //相等返回1
}
int MaxOfThree(int a,int b,int c) {
return (a>=b && a>=c)?a:
((b>=a && b>=c)?b:c);
}
int dp[MAXN][MAXN];
int whLCS(char s1[],int len1,char s2[],int len2) {
memset(dp,0,sizeof(dp));
for(int i=1;i<=len1;i++){
for(int j=1;j<=len2;j++){
dp[i][j]=MaxOfThree( dp[i-1][j-1]+same(s1[i-1],s2[j-1]) , dp[i-1][j] , dp[i][j-1]); //这里简化判断
}
}
return dp[len1][len2];
}
int main()
{
//freopen("input.txt","r",stdin);
char s1[MAXN],s2[MAXN];
while (scanf("%s %s",s1,s2)!=EOF) {
int res = whLCS(s1,strlen(s1),s2,strlen(s2));
PRINT(res);
}
return 0;
}二、问题分析
1、dp
经常会遇到复杂问题不能简单地分解成几个子问题,而会分解出一系列的子问题。简单地采用把大问题分解成子问题,并综合子问题的解导出大问题的解的方法,问题求解耗时会按问题规模呈幂级数增加。为了节约重复求相同子问题的时间,引入一个数组,不管它们是否对最终解有用,把所有子问题的解存于该数组中,这就是动态规划法所采用的基本方法。
2、求解LCS
引进一个二维数组c[][],用c[i][j]记录X[i]与Y[j] 的LCS 的长度,b[i][j]记录c[i][j]是通过哪一个子问题的值求得的,以决定搜索的方向(如果需要记录路径)。我们是自底向上进行递推计算,那么在计算c[i,j]之前,c[i-1][j-1],c[i-1][j]与c[i][j-1]均已计算出来。此时我们根据X[i] = Y[j]还是X[i] != Y[j],就可以计算出c[i][j]。
问题的递归式写成:
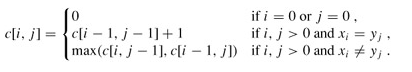
回溯输出最长公共子序列的过程:
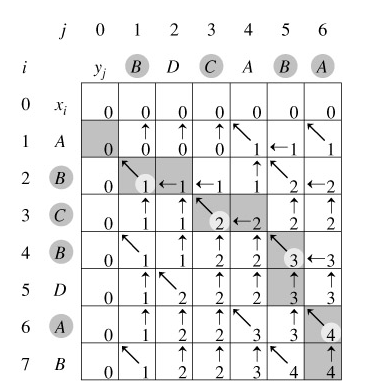
3、算法分析
由于每次调用至少向上或向左(或向上向左同时)移动一步,故最多调用(m + n)次就会遇到i = 0或j = 0的情况,此时开始返回。返回时与递归调用时方向相反,步数相同,故算法时间复杂度为Θ(m + n)。参考资料
[1] http://blog.csdn.net/yysdsyl/article/details/4226630相关文章推荐
- 杭电1019Least Common Multiple
- 学习javaEE每一天2016.4.3
- 最长上升子序列
- Scala之模式匹配(Patterns Matching)
- 学习笔记
- 追加addclass和removeclass
- HTML音频
- poj_2503(map映射)
- 刷新iframe
- poj_2503(map映射)
- HYSBZ 3196 Tyvj 1730 二逼平衡树(树套树)
- Spring mvc 配置详解
- MySQL服务基础
- TCP/IP协议之IP协议详解
- C++:标准IO(输入输出)
- iOS之使用ZbarSDK实现扫描二维码以及条形码功能
- 浅析JTable与TableModel、TableCellRenderer、TableCellEditor接口——使用JComboBox显示单元格的值
- LCD电子书项目(七)
- 分页+新建+跳转+最后页
- lintcode-medium-Permutation Sequence
