Linux-进程间通信(二): FIFO
2016-03-20 11:09
519 查看
1. FIFO:
FIFO也被成为命名管道,因其通过路径关系绑定,可以用于任意进程间通信,而普通无名管道只能用于有共同祖先的进行直接通信;
命名管道也是半双工的,open管道的时候不要以读写方式打开,这种操作是未定义的;
2. FIFO创建:
FIFO是一种文件类型,mode参数与open函数中的mode参数相同,并且一般文件的操作函数(close, read, write, unlink等)都以用于FIFO;
3. 非阻塞标志(O_NONBLOCK):
(1) 阻塞模式:只读open要阻塞到某个进程为写而打开此FIFO,只写open要阻塞到某个进程为读而打开此FIFO;
(2) 非阻塞模式:只读立即返回,如果没有进程为读而打开FIFO,则只写open返回-1,erron=ENXIO;
4. 一端关闭:
(1) 若读一个已经关闭写端的FIFO,则读取完数据后,会读到文件结束符,read返回0;
(2) 若写一个已经关闭读端的FIFO,则产生SIGPIPE;
5. 用途:
(1) FIFO由shell命令使用以便将数据从一条管道传送到另一条,而无需创建临时文件;
(2) FIFO用于客户进程和服务器进程进行数据传递;
6. 测试代码:两个进程间通信;
fifo_writer.c -- 向fifo中写入字串
fifo_reader.c -- 从fifo中读出字串
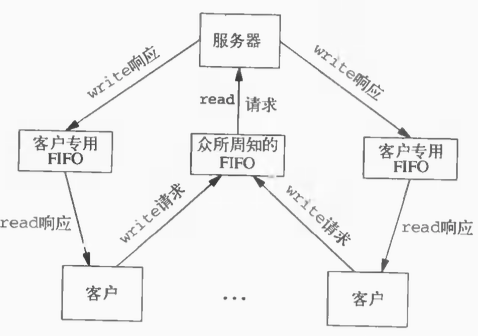
7. 测试代码:多个客户端与服务器通信
模型如下图所示:
common.h--公共头文件
fifo_server.c
fifo_client.c
FIFO也被成为命名管道,因其通过路径关系绑定,可以用于任意进程间通信,而普通无名管道只能用于有共同祖先的进行直接通信;
命名管道也是半双工的,open管道的时候不要以读写方式打开,这种操作是未定义的;
2. FIFO创建:
#include <sys/stat.h> int mkfifo(const char *pathname, mode_t mode); ret = 成功返回0,失败返回-1
FIFO是一种文件类型,mode参数与open函数中的mode参数相同,并且一般文件的操作函数(close, read, write, unlink等)都以用于FIFO;
3. 非阻塞标志(O_NONBLOCK):
(1) 阻塞模式:只读open要阻塞到某个进程为写而打开此FIFO,只写open要阻塞到某个进程为读而打开此FIFO;
(2) 非阻塞模式:只读立即返回,如果没有进程为读而打开FIFO,则只写open返回-1,erron=ENXIO;
4. 一端关闭:
(1) 若读一个已经关闭写端的FIFO,则读取完数据后,会读到文件结束符,read返回0;
(2) 若写一个已经关闭读端的FIFO,则产生SIGPIPE;
5. 用途:
(1) FIFO由shell命令使用以便将数据从一条管道传送到另一条,而无需创建临时文件;
(2) FIFO用于客户进程和服务器进程进行数据传递;
6. 测试代码:两个进程间通信;
fifo_writer.c -- 向fifo中写入字串
#include <unistd.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <limits.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#define FIFO_NAME "/var/tmp/fifo_test"
#define BUF_LEN PIPE_BUF
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
int pipeid = -1;
int fifoid = -1;
char buffer[BUF_LEN] = { 0 };
if (access(FIFO_NAME, F_OK) < 0){
fifoid = mkfifo(FIFO_NAME, 0777);
if (fifoid < 0){
perror("mkfifo error\n");
return -1;
}
}
pipeid = open(FIFO_NAME, O_WRONLY);
if (pipeid < 0){
perror("open pipeid error\n");
return -1;
}
int read_bytes = read(STDIN_FILENO, buffer, BUF_LEN);
if (read_bytes < 0){
perror("read error\n");
close(pipeid);
return -1;
}
const char * buff_send = buffer;
int no_write_bytes = read_bytes;
while (no_write_bytes > 0){
int n = write(pipeid, buff_send, no_write_bytes);
if (n < 0){
perror("write error\n");
close(pipeid);
return -1;
}
no_write_bytes -= n;
buff_send += n;
}
close(pipeid);
return 0;
}fifo_reader.c -- 从fifo中读出字串
#include <unistd.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <limits.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#define FIFO_NAME "/var/tmp/fifo_test"
#define BUF_LEN PIPE_BUF
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
int pipeid = -1;
char buffer[BUF_LEN] = { 0 };
pipeid = open(FIFO_NAME, O_RDONLY);
int n = read(pipeid, buffer, BUF_LEN - 1);
if (n < 0){
perror("read error\n");
close(pipeid);
return -1;
}
write(STDOUT_FILENO, buffer, n);
close(pipeid);
return 0;
}7. 测试代码:多个客户端与服务器通信
模型如下图所示:

common.h--公共头文件
#include <unistd.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <limits.h>
#include <string.h>
#define SERVER_FIFO_NAME "/var/tmp/fifoServer"
#define CLIENT_FIFO_NAME "/var/tmp/fifoClient%d"
#define BUFF_SIZE PIPE_BUF
#define MSG_LEN 64
#define CLIENT_FIFO_NAME_LEN 64
typedef struct fifo_msg{
pid_t client_pid;
char msg[MSG_LEN];
}fifo_msg_t;fifo_server.c
#include "common.h"
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
int fifo_id = -1;
int server_fifo_fd = -1;
if (access(SERVER_FIFO_NAME, F_OK) < 0){
fifo_id = mkfifo(SERVER_FIFO_NAME, 0777);
if (fifo_id < 0){
perror("mkfifo error\n");
return -1;
}
}
server_fifo_fd = open(SERVER_FIFO_NAME, O_RDONLY);
if (server_fifo_fd < 0){
perror("open fifo error\n");
return -1;
}
fifo_msg_t client_msg;
memset(&client_msg, 0, sizeof(client_msg));
int read_bytes = 0;
do {
read_bytes = read(server_fifo_fd, &client_msg, sizeof(client_msg));
if (read_bytes < 0){
perror("read error\n");
close(server_fifo_fd);
return -1;
}
char *tmp_msg = client_msg.msg;
while (*tmp_msg){
*tmp_msg = toupper(*tmp_msg);
tmp_msg++;
}
char client_fifo[CLIENT_FIFO_NAME_LEN] = { 0 };
snprintf(client_fifo, CLIENT_FIFO_NAME_LEN - 1, CLIENT_FIFO_NAME, client_msg.client_pid);
int client_fifo_fd = open(client_fifo, O_WRONLY);
if (client_fifo_fd < 0){
perror("open client fifo error\n");
}
write(client_fifo_fd, &client_msg, sizeof(client_msg));
printf("write to client:%d\n", client_msg.client_pid);
close(client_fifo_fd);
} while (read_bytes > 0);
close(server_fifo_fd);
return 0;
}fifo_client.c
#include "common.h"
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
pid_t client_pid = -1;
int server_fifo_fd = -1;
int client_fifo_fd = -1;
server_fifo_fd = open(SERVER_FIFO_NAME, O_WRONLY);
if (server_fifo_fd < 0){
perror("open server fifo error\n");
return -1;
}
client_pid = getpid();
char client_fifo_name[CLIENT_FIFO_NAME_LEN] = {0};
snprintf(client_fifo_name, CLIENT_FIFO_NAME_LEN - 1, CLIENT_FIFO_NAME, client_pid);
if (mkfifo(client_fifo_name, 0777) < 0){
perror("mkfifo client error\n");
close(server_fifo_fd);
return -1;
}
fifo_msg_t client_msg;
memset(&client_msg, 0, sizeof(client_msg));
client_msg.client_pid = client_pid;
#define TRY_TIMES 3
int times = 0;
for (times = 0; times < TRY_TIMES; times++){
snprintf(client_msg.msg, MSG_LEN - 1, "client_pid:%d\n", client_pid);
write(server_fifo_fd, &client_msg, sizeof(client_msg));
client_fifo_fd = open(client_fifo_name, O_RDONLY);
if (client_fifo_fd < 0){
perror("open client fifo error\n");
close(server_fifo_fd);
unlink(client_fifo_name);
return -1;
}
int n = read(client_fifo_fd, &client_msg, sizeof(client_msg));
if (n > 0){
printf("reveive msg from server:%s", client_msg.msg);
}
close(client_fifo_fd);
}
close(server_fifo_fd);
unlink(client_fifo_name);
return 0;
}
相关文章推荐
- 服务器重装之后连接不上及解决措施
- 《Linux内核设计与实现》读书笔记 第五章 系统调用
- NFS服务的搭建
- Centos7 root密码重置
- Linux程序包管理(rpm)
- VI基本操作
- linux内核分析第四次实验
- Linux的system()和popen()差异
- linux基础命令
- Linux实验四报告
- linux 配置静态IP及相关命令
- 如何在Linux python中使用tab补全
- Linux命令之touch 、mkdir 、cp
- Linux命令之ls
- linux下使用tar命令解压.tar.gz文件是参数的说明
- linux命令介绍(4)
- Linux命令之cd
- Linux命令之pwd
- Linux并发(子进程退出状态的处理)
- Linux内核分析(四)
