继承
2016-03-19 13:52
429 查看
[b]一.子类不继承父类构造函数,析构函数,默认私有继承或protected[/b]
[b]二.using声明可在子类把父类成员改为私有[/b]
[b]三.派生类成员与父类成员名字相同,会发生名字隐藏[/b]
[b]四.派生类可对从基类继承来的保护成员进行访问,也就是说保护成员在派生类中是可见的[/b]
[b]派生类不能访问一个基类对象的保护乘员,因为基类对象属于基类,不属于派生类[/b]
[b][b]派生类中的派生类可访问基类的保护乘员,因为派生类对象属于派生类[/b][/b]
应避免将数据成员设置成protected,而应采用私有或者相应保护类型访问函数
[b]五.创建派生类时,父类默构自动调用。父类若有带参构造,则必须有自定义默构,除非显示调用基类带参构造。[/b]
1.最先调用基类的构造函数,对基类数据成员初始化顺序取决于被继承时的说明顺序;
2.再调用数据成员是类对象的构造函数,顺序按类中定义的先后顺序;
3.最后执行派生类构造函数;
4.析构函数的调用与构造函数正好相反,由于每个类至多只有一个析构函数,调用时不会产生二义性。
[b]六.多重继承机制下的命名冲突[/b]
在多条继承路径上有一个公共基类,希望只存储一个公共基类时,可利用虚基类。
虚基类的构造函数先于非虚基类执行
虚基类由最派生类(最后一个派生类)调用构造函数初始化
[b]七.继承方式[/b]
1.公有继承:基类成员公有和保护在派生类中保持原有访问属性,私有成员仍为基类私有;
2.私有继承:基类公有和保护在派生类中成私有成员,私有成员仍为基类私有;
3.受保护继承:基类公有和保护在派生类中成保护成员,私有成员仍为基类私有。保护成员:不能被外界访问,但可被派生类成员访问
[b]八.对基类对象操作的函数,可以对子类的对象进行操作,不可逆[/b]
1.派生类对象可以赋值给基类:Base b; Derived d; b = d;
2.Derived d; Base &b = d;初始化基类引用
3.子类地址赋值给基类指针Derived d; Base *b = &d;
必须是public继承关系,protected和private不成立
[b]二.using声明可在子类把父类成员改为私有[/b]
class B
{
public:
void set(){}
};
class C: public B
{
private:
using B::set;
};[b]三.派生类成员与父类成员名字相同,会发生名字隐藏[/b]
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
class B
{
public:
void h(float x){}
};
class C: public B
{
public:
void h(string s){}
};
int main()
{
C c;
c.h("abc");//ok
c.h(1.7);//error
c.B::h(1.7);//ok
return 0;
}[b]四.派生类可对从基类继承来的保护成员进行访问,也就是说保护成员在派生类中是可见的[/b]
[b]派生类不能访问一个基类对象的保护乘员,因为基类对象属于基类,不属于派生类[/b]
[b][b]派生类中的派生类可访问基类的保护乘员,因为派生类对象属于派生类[/b][/b]
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
class B
{
protected:
int get_W() const { return 0; }
};
class C: public B
{
public:
int get_V()const { return get_W(); }
void base_W(const B &b) const { cout << b.get_W() << endl; }//error
void p(C &c)const { cout << c.get_W() << endl; } // OK
};
int main()
{
C c;
c.getW(); //error, protected
return 0;
}应避免将数据成员设置成protected,而应采用私有或者相应保护类型访问函数
[b]五.创建派生类时,父类默构自动调用。父类若有带参构造,则必须有自定义默构,除非显示调用基类带参构造。[/b]
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
class Base
{
public:
Base(int m, int n)
{
x = m;
y = n;
}
private:
int x, y;
};
class Derived: public Base
{
public:
Derived(int m, int n, int k):Base(m, n)
{
z = k;
}
private:
int z;
};
int main()
{
Derived d(1, 2, 3);
return 0;
}#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
class Base
{
public:
Base(int m, int n)
{
x = m;
y = n;
}
private:
int x, y;
};
class Derived: public Base
{
public:
Derived(int k)
{
z = k;
}
private:
int z;
};
int main()
{
Derived d(3);//error, Base没有合适的默认构造函数可用
return 0;
}1.最先调用基类的构造函数,对基类数据成员初始化顺序取决于被继承时的说明顺序;
2.再调用数据成员是类对象的构造函数,顺序按类中定义的先后顺序;
3.最后执行派生类构造函数;
4.析构函数的调用与构造函数正好相反,由于每个类至多只有一个析构函数,调用时不会产生二义性。
[b]六.多重继承机制下的命名冲突[/b]
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
class A
{
public:
void f();
};
class B
{
public:
void f();
void g();
};
class C: public A, public B
{
public:
void h();
void g();
};
int main()
{
C c;
c.g();//c中g(),B中被重写
c.f();//error,无法确定,若B:public A则c.f()不会产生二义性
c.B::g();
c.A::f();
c.B::f();
return 0;
}#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
class B
{
public:
int b;
};
class B1:public B
{};
class B2:public B
{};
class C: public B1, public B2
{};
int main()
{
C c;
c.b;//error,b不明确
c.B::b;//B不明确,在VS2015中默认为B1中的B的b
/*
C->B1->B->b
->B2->B->b
基类对象B在派生类C中存储2份
*/
return 0;
}在多条继承路径上有一个公共基类,希望只存储一个公共基类时,可利用虚基类。
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
class B
{
public:
int b;
};
class B1: virtual public B
{
public:
int b1;
};
class B2: virtual public B
{
public:
int b2;
};
class C: public B1, public B2
{
public:
int c;
};
int main()
{
C c;
c.B1::b = 1;
c.B2::b = 2;
cout << c.B1::b << endl; // 2 没有同时2个virtual则为1,存储了2个B
cout << c.B2::b << endl; // 2
/*
B1
C-> ->B
B2
C中b值只存储了一份
*/
return 0;
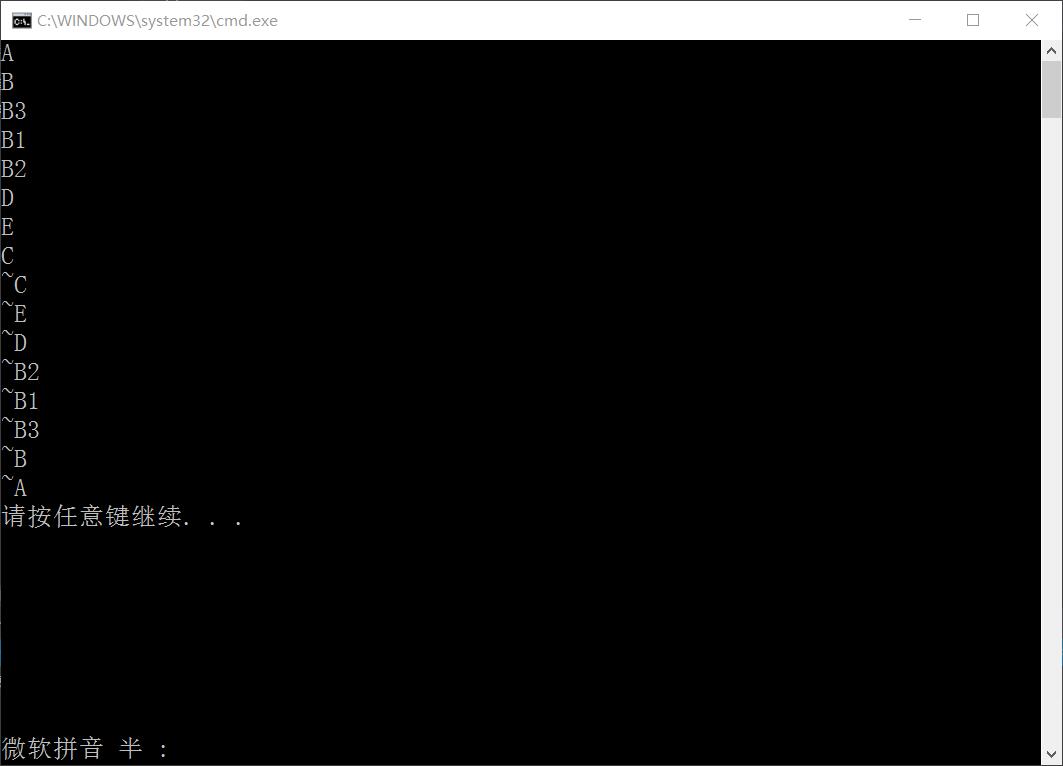
}虚基类的构造函数先于非虚基类执行
虚基类由最派生类(最后一个派生类)调用构造函数初始化
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
class A
{
public:
A()
{
cout << "A" << endl;
}
~A()
{
cout << "~A" << endl;
}
};
class B: public A
{
public:
B()
{
cout << "B" << endl;
}
~B()
{
cout << "~B" << endl;
}
int b;
};
class B3
{
public:
B3()
{
cout << "B3" << endl;
}
~B3()
{
cout << "~B3" << endl;
}
int b3;
};
class B1: public B3, virtual public B
{
public:
B1()
{
cout << "B1" << endl;
}
~B1()
{
cout << "~B1" << endl;
}
int b1;
};
class B2: virtual public B
{
public:
B2()
{
cout << "B2" << endl;
}
~B2()
{
cout << "~B2" << endl;
}
int b2;
};
class D
{
public:
D()
{
cout << "D" << endl;
}
~D()
{
cout << "~D" << endl;
}
int c;
};
class E
{
public:
E()
{
cout << "E" << endl;
}
~E()
{
cout << "~E" << endl;
}
int c;
};
class C: public B1, public B2
{
public:
C()
{
cout << "C" << endl;
}
~C()
{
cout << "~C" << endl;
}
int c;
D d; E e;
};
int main()
{
C c;
return 0;
}
[b]七.继承方式[/b]
1.公有继承:基类成员公有和保护在派生类中保持原有访问属性,私有成员仍为基类私有;
2.私有继承:基类公有和保护在派生类中成私有成员,私有成员仍为基类私有;
3.受保护继承:基类公有和保护在派生类中成保护成员,私有成员仍为基类私有。保护成员:不能被外界访问,但可被派生类成员访问
[b]八.对基类对象操作的函数,可以对子类的对象进行操作,不可逆[/b]
1.派生类对象可以赋值给基类:Base b; Derived d; b = d;
2.Derived d; Base &b = d;初始化基类引用
3.子类地址赋值给基类指针Derived d; Base *b = &d;
必须是public继承关系,protected和private不成立
相关文章推荐
- 哈希表定义
- util
- 山东省选2014 travel
- 胡谈编程语言:从C语言到Julia
- JVM的简介
- python中的静态方法和类方法
- 设计模式-五大创建型模式
- python中的静态方法和类方法
- ADT - Bundle 中的Eclipse 无法启动, 卡在loading workbench 界面无响应
- 基于多线程并发的单例模式
- 尽量减少重新绘制和重新布局
- 排它平方数--蓝桥杯
- 【问题及解决】创建Maven webapp项目后JSP 报错
- iOS开发- UICollectionView详解+实例
- Qt学习之给QPushButton添加菜单DefaultContextMenu方法
- 我的VIM配置
- nginx+tomcat均衡负载实践
- 初步使用session和cookie
- 软件工程个人作业02
- 微信浏览器禁止app下载链接的两种处理方法
