hdu 2736 Average distance
2016-03-06 09:45
357 查看
传送门
Total Submission(s): 682 Accepted Submission(s): 244
Special Judge
[align=left]Problem Description[/align]
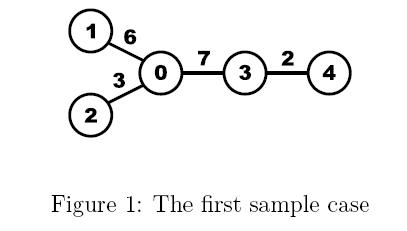
Given a tree, calculate the average distance between two vertices in the tree. For example, the average distance between two vertices in the following tree is (d01 + d02 + d03 + d04 + d12 +d13 +d14 +d23 +d24 +d34)/10 = (6+3+7+9+9+13+15+10+12+2)/10 = 8.6.
[align=left]Input[/align]
On the first line an integer t (1 <= t <= 100): the number of test cases. Then for each test case:
One line with an integer n (2 <= n <= 10 000): the number of nodes in the tree. The nodes are numbered from 0 to n - 1.
n - 1 lines, each with three integers a (0 <= a < n), b (0 <= b < n) and d (1 <= d <= 1 000). There is an edge between the nodes with numbers a and b of length d. The resulting graph will be a tree.
[align=left]Output[/align]
For each testcase:
One line with the average distance between two vertices. This value should have either an absolute or a relative error of at most 10-6
[align=left]Sample Input[/align]
1
5
0 1 6
0 2 3
0 3 7
3 4 2
[align=left]Sample Output[/align]
8.6
[align=left]Source[/align]
bapc2007
[align=left]Recommend[/align]
lcy | We have carefully selected several similar problems for you: 2378 2379 2377 2380 2381
哎,思路想复杂了,其实蛮简单的:
转一发题解:
引:如果暴力枚举两点再求距离是显然会超时的。转换一下思路,我们可以对每条边,求所有可能的路径经过此边的次数:设这条边两端的点数分别为A和B,那 么这条边被经过的次数就是A*B,它对总的距离和的贡献就是(A*B*此边长度)。我们把所有边的贡献求总和,再除以总路径数N*(N-1)/2,即为最 后所求。
每条边两端的点数的计算,实际上是可以用一次dfs解决的。任取一点为根,在dfs的过程中,对每个点k记录其子树包含的点数(包括其自身),设点数为a[k],则k的父亲一侧的点数即为N-a[k]。这个统计可以和遍历同时进行。故时间复杂度为O(n)。
Average distance
Time Limit: 1000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 32768/32768 K (Java/Others)Total Submission(s): 682 Accepted Submission(s): 244
Special Judge
[align=left]Problem Description[/align]
Given a tree, calculate the average distance between two vertices in the tree. For example, the average distance between two vertices in the following tree is (d01 + d02 + d03 + d04 + d12 +d13 +d14 +d23 +d24 +d34)/10 = (6+3+7+9+9+13+15+10+12+2)/10 = 8.6.

[align=left]Input[/align]
On the first line an integer t (1 <= t <= 100): the number of test cases. Then for each test case:
One line with an integer n (2 <= n <= 10 000): the number of nodes in the tree. The nodes are numbered from 0 to n - 1.
n - 1 lines, each with three integers a (0 <= a < n), b (0 <= b < n) and d (1 <= d <= 1 000). There is an edge between the nodes with numbers a and b of length d. The resulting graph will be a tree.
[align=left]Output[/align]
For each testcase:
One line with the average distance between two vertices. This value should have either an absolute or a relative error of at most 10-6
[align=left]Sample Input[/align]
1
5
0 1 6
0 2 3
0 3 7
3 4 2
[align=left]Sample Output[/align]
8.6
[align=left]Source[/align]
bapc2007
[align=left]Recommend[/align]
lcy | We have carefully selected several similar problems for you: 2378 2379 2377 2380 2381
哎,思路想复杂了,其实蛮简单的:
转一发题解:
引:如果暴力枚举两点再求距离是显然会超时的。转换一下思路,我们可以对每条边,求所有可能的路径经过此边的次数:设这条边两端的点数分别为A和B,那 么这条边被经过的次数就是A*B,它对总的距离和的贡献就是(A*B*此边长度)。我们把所有边的贡献求总和,再除以总路径数N*(N-1)/2,即为最 后所求。
每条边两端的点数的计算,实际上是可以用一次dfs解决的。任取一点为根,在dfs的过程中,对每个点k记录其子树包含的点数(包括其自身),设点数为a[k],则k的父亲一侧的点数即为N-a[k]。这个统计可以和遍历同时进行。故时间复杂度为O(n)。
| 16447376 | 2016-03-06 09:40:59 | Accepted | 2376 | 312MS | 4540K | 2093 B | C++ | czy |
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <stack>
#include <cctype>
#include <vector>
#include <cmath>
#include <map>
#include <queue>
#define ll long long
#define N 10005
#define eps 1e-8
using namespace std;
int T;
double tot
;
double cou
;
double num;
int n;
struct PP
{
int to;
double val;
};
vector<PP>Edge
;
PP te;
void add_adge(int from,int to,double val)
{
te.to = to;te.val = val;
Edge[from].push_back(te);
te.to = from;te.val = val;
Edge[to].push_back(te);
}
void dfs(int now,int fa)
{
unsigned int i;
PP nt;
cou[now] = 1;
for(i = 0;i < Edge[now].size();i++){
nt.to = Edge[now][i].to;
nt.val = Edge[now][i].val;
if(nt.to == fa){
continue;
}
dfs(nt.to,now);
tot[now] = tot[now] + tot[nt.to] + (n-cou[nt.to]) * cou[nt.to] * nt.val;
cou[now] = cou[now] + cou[nt.to];
//printf(" now = %d i=%d to=%d tot=%.6f cou=%.6lf\n",now,i,nt.to,tot[now],cou[now]);
}
//printf(" i=%d tot=%.6f cou=%.6f\n",now,tot[now],cou[now]);
}
int main()
{
//freopen("in.txt","r",stdin);
scanf("%d",&T);
int i;
int from,to;
double val;
for(int ccnt=1;ccnt<=T;ccnt++){
//while(scanf("%lf%lf%lf%lf",&a[0],&a[1],&a[2],&a[3])!=EOF){
scanf("%d",&n);
memset(tot,0,sizeof(tot));
memset(cou,0,sizeof(cou));
num = 1.0 *n*(n-1)/2;
for(i=0;i<=n;i++){
Edge[i].clear();
}
for(i=1;i<=n-1;i++){
scanf("%d%d%lf",&from,&to,&val);
add_adge(from,to,val);
}
dfs(0,-1);
//for(i=0;i<n;i++){
// for(int j=0;j<Edge[i].size();j++){
// printf(" i=%d to=%d val=%.6lf\n",i,Edge[i][j].to,Edge[i][j].val);
// }
// }
for(i=0;i<n;i++){
//printf(" i=%d tot=%.6f cou=%.6f\n",i,tot[i],cou[i]);
}
printf("%lf\n",tot[0]/num);
}
return 0;
}
相关文章推荐
- 科目一2013年
- HOG
- java之jms简介
- 本学期阅读计划
- 合理规划硬盘分区 fdisk命令的使用
- ExtJs学习笔记一
- 软件工程始发随想
- //子集生成总结
- gif动画生成工具
- 创建一个Cordova完整应用
- MATLAB 绘制函数曲线图
- Android Studio中新建library项目。
- 207. Course Schedule
- paper 35 :交叉验证(CrossValidation)方法思想
- ViewPager实现页卡的3种方法(谷歌组件)
- 想使用“本地项目” 的钥匙串
- 异步task处理
- 在Yii2中使用Pjax导致Yii2内联脚本载入失败的原因分析
- codeforcces 623A - Graph and String Note that 构造
- SVN 取消版本控制并添加至忽略列表
