【数据结构学习笔记】——二叉树的建立、交换、求宽度
2016-02-03 10:44
676 查看
要求
编写二叉树类的成员函数,分别实现以下功能:① 交换二叉树中所有节点的左右子树。
② 按层次顺序遍历二叉树:首先访问根节点,然后是它的两个孩子节点,然后是孙子节点,依此类推。(将结果输出至屏幕)
③ 求二叉树的宽度,即同一层次上最多的节点数。(将结果输出至屏幕)
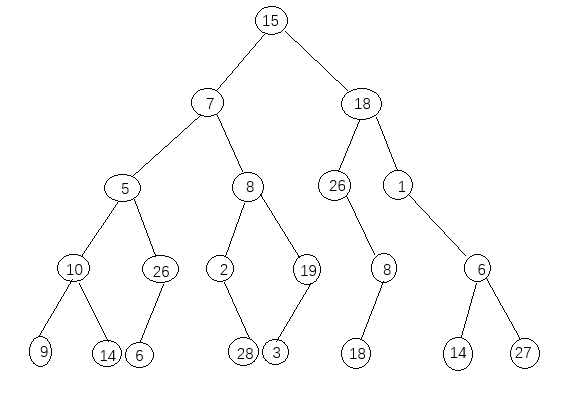
分析
观察这个二叉树,发现只是并不是完全二叉树。可以用书上makeTree的方法挨个建立,但是觉得太过麻烦。这里采用了使用数组的方法建立二叉树。发现整个树中没有数据0,我们将所有null都补位0,化成一个满二叉树,利用反中序的方法建立二叉树。对于交换,我们利用递归的方法。
放码过来
#include<queue>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Tnode //二叉树 数据结构
{
public:
int data;
Tnode *left,*right;
Tnode(){}
Tnode(const char data,Tnode *left=NULL,Tnode *right=NULL):data(data), left(left), right(right)
{}
};
Tnode *arrayTotree(int a[] , int start,int end ) //按照中序顺序的数组输入 生成二叉树
{
if(start>end)
{
return NULL;
}
int m = start+(end-start)/2; //数组中间的数就是根节点 (中序遍历)
Tnode *root = new Tnode();
root->data = a[m];
root->left=arrayTotree(a,start,m-1); //递归构建左右子树
root->right=arrayTotree(a,m+1,end);
return root; //返回根节点
}
void preOrder(Tnode*T){ //先序遍历
if(T)
{
if(T->data!=0) //0在本题中实际为NULL 因此不输出
cout<<T->data<<" ";
preOrder(T->left);
preOrder(T->right);
}
}
/*按层遍历:利用队列的特征,先输出根节点,再将它的孩子们放入队列中,再进行递归。
因此可以实现父节点肯定先于子节点输出,并且左孩子肯定先于右孩子输出,这样就实现了按层输出。*/
void levelOrder(Tnode*t){ //按层遍历 运用队列
queue<Tnode*> Q ;
while(t){
if(t->data!=0) cout<<t->data<<" ";
if(t->left) Q.push(t->left);
if(t->right) Q.push(t->right);
if(Q.empty()) return;
t=Q.front(); //返回队列头元素赋给t
Q.pop(); //删除队列头元素
}
}
int getWidth(Tnode *pRoot) //求宽度
{
if (pRoot == NULL)
{
return 0;
}
int nLastLevelWidth = 0;//记录上一层的宽度
int nTempLastLevelWidth = 0;
int nCurLevelWidth = 0;//记录当前层的宽度
int nWidth = 1;//二叉树的宽度
queue<Tnode *> myQueue;
myQueue.push(pRoot);//将根节点入队列
nLastLevelWidth = 1;
Tnode *pCur = NULL;
while (!myQueue.empty())//队列不空
{
nTempLastLevelWidth = nLastLevelWidth;
while (nTempLastLevelWidth != 0)
{
pCur = myQueue.front();//取出队列头元素
myQueue.pop();//将队列头元素出队
if (pCur->left != NULL &&pCur->left->data!=0)
{
myQueue.push(pCur->left);
}
if (pCur->right != NULL&&pCur->right->data!=0)
{
myQueue.push(pCur->right );
}
nTempLastLevelWidth--; //把上一层的元素都清出队列,并且加入下一层元素入队
}
nCurLevelWidth = myQueue.size(); //队列中只剩同一层元素
nWidth = (nCurLevelWidth > nWidth ? nCurLevelWidth : nWidth);
nLastLevelWidth = nCurLevelWidth;
}
return nWidth;
}
void exchange(Tnode * node) //利用递归 交换左右子树
{
if(node == NULL) return;
Tnode * temp = node->left;
node->left = node->right;
node->right = temp;
exchange(node->left);
exchange(node->right);
}
int main(){
int inOrderarray[]={9,10,14,5,6,26,0,7,0,2,28,8,3,19,0,15,
4000
0,0,0,26,18,8,0,18,0,0,0,1,14,6,27}; //将树补成满二叉树
Tnode*tree;
tree=arrayTotree(inOrderarray,0,30);
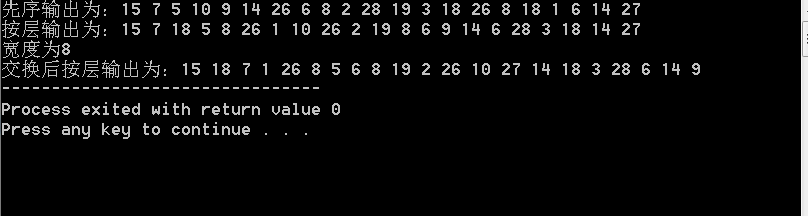
cout<<"先序输出为:";
preOrder(tree);
cout<<endl;
cout<<"按层输出为:";
levelOrder(tree);
int wide= getWidth(tree);
cout<<endl<<"宽度为" <<wide<<endl;
exchange(tree);
cout<<"交换后按层输出为:";
levelOrder(tree);
}结果
相关文章推荐
- AVL树-自平衡二叉查找树(Java实现)
- C#数据结构之顺序表(SeqList)实例详解
- Lua教程(七):数据结构详解
- 解析从源码分析常见的基于Array的数据结构动态扩容机制的详解
- C#数据结构之队列(Quene)实例详解
- C#数据结构揭秘一
- C#数据结构之单链表(LinkList)实例详解
- 数据结构之Treap详解
- C语言二叉树的非递归遍历实例分析
- 使用C语言构建基本的二叉树数据结构
- C++非递归队列实现二叉树的广度优先遍历
- C#使用前序遍历、中序遍历和后序遍历打印二叉树的方法
- C#数据结构之堆栈(Stack)实例详解
- C#数据结构之双向链表(DbLinkList)实例详解
- JavaScript数据结构和算法之图和图算法
- Java数据结构及算法实例:冒泡排序 Bubble Sort
- Java数据结构及算法实例:插入排序 Insertion Sort
- Java数据结构及算法实例:考拉兹猜想 Collatz Conjecture
- java数据结构之java实现栈
- java数据结构之实现双向链表的示例
