Spark MLlib实现的广告点击预测–Gradient-Boosted Trees
2016-01-25 00:00
633 查看
摘要: 本文尝试使用Spark提供的机器学习算法Gradient-BoostedTrees来预测一个用户是否会点击广告。训练和测试数据使用KaggleAvazuCTR比赛的样例数据,下载地址:https://www.kaggle.com/c/avazu-ct...

本文尝试使用Spark提供的机器学习算法 Gradient-Boosted Trees来预测一个用户是否会点击广告。
训练和测试数据使用Kaggle Avazu CTR 比赛的样例数据,下载地址:https://www.kaggle.com/c/avazu-ctr-prediction/data
数据格式如下:
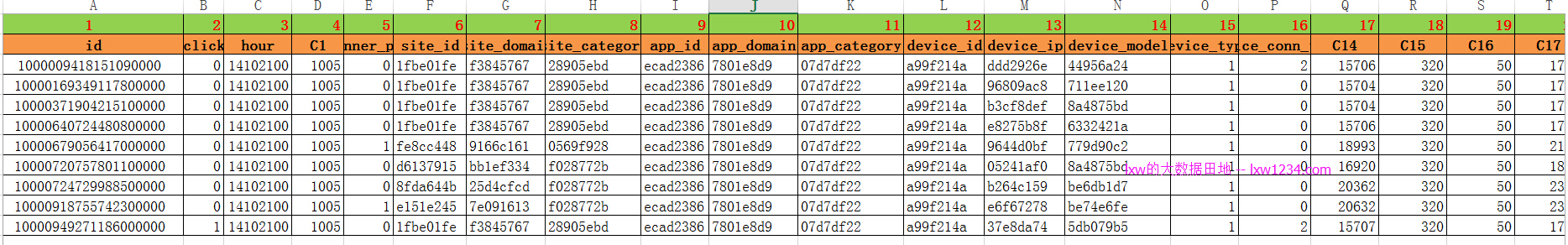
包含24个字段:
1-id: ad identifier
2-click: 0/1 for non-click/click
3-hour: format is YYMMDDHH, so 14091123 means 23:00 on Sept. 11, 2014 UTC.
4-C1 — anonymized categorical variable
5-banner_pos
6-site_id
7-site_domain
8-site_category
9-app_id
10-app_domain
11-app_category
12-device_id
13-device_ip
14-device_model
15-device_type
16-device_conn_type
17~24—C14-C21 — anonymized categorical variables
其中5到15列为分类特征,16~24列为数值型特征。
Spark代码如下:
其中,训练数据集: Train records : 104558, 测试数据集:Test records : 26510
程序主要输出:
本文转载自xw的大数据田地。转载请注明原文链接http://lxw1234.com/archives/2016/01/595.htm

本文尝试使用Spark提供的机器学习算法 Gradient-Boosted Trees来预测一个用户是否会点击广告。
训练和测试数据使用Kaggle Avazu CTR 比赛的样例数据,下载地址:https://www.kaggle.com/c/avazu-ctr-prediction/data
数据格式如下:

包含24个字段:
1-id: ad identifier
2-click: 0/1 for non-click/click
3-hour: format is YYMMDDHH, so 14091123 means 23:00 on Sept. 11, 2014 UTC.
4-C1 — anonymized categorical variable
5-banner_pos
6-site_id
7-site_domain
8-site_category
9-app_id
10-app_domain
11-app_category
12-device_id
13-device_ip
14-device_model
15-device_type
16-device_conn_type
17~24—C14-C21 — anonymized categorical variables
其中5到15列为分类特征,16~24列为数值型特征。
Spark代码如下:
package com.lxw1234.test import scala.collection.mutable.ListBuffer import scala.collection.mutable.ArrayBuffer import org.apache.spark.SparkContext import org.apache.spark.SparkContext._ import org.apache.spark.SparkConf import org.apache.spark.rdd.RDD import org.apache.spark.mllib.classification.NaiveBayes import org.apache.spark.mllib.regression.LabeledPoint import org.apache.spark.mllib.linalg.Vectors import org.apache.spark.mllib.tree.GradientBoostedTrees import org.apache.spark.mllib.tree.configuration.BoostingStrategy import org.apache.spark.mllib.tree.model.GradientBoostedTreesModel /** * By: lxw * http://lxw1234.com */ object CtrPredict { //input (1fbe01fe,f3845767,28905ebd,ecad2386,7801e8d9) //output ((0:1fbe01fe),(1:f3845767),(2:28905ebd),(3:ecad2386),(4:7801e8d9)) def parseCatFeatures(catfeatures: Array[String]) : List[(Int, String)] = { var catfeatureList = new ListBuffer[(Int, String)]() for (i <- 0 until catfeatures.length){ catfeatureList += i -> catfeatures(i).toString } catfeatureList.toList } def main(args: Array[String]) { val conf = new SparkConf().setMaster("yarn-client") val sc = new SparkContext(conf) var ctrRDD = sc.textFile("/tmp/lxw1234/sample.txt",10); println("Total records : " + ctrRDD.count) //将整个数据集80%作为训练数据,20%作为测试数据集 var train_test_rdd = ctrRDD.randomSplit(Array(0.8, 0.2), seed = 37L) var train_raw_rdd = train_test_rdd(0) var test_raw_rdd = train_test_rdd(1) println("Train records : " + train_raw_rdd.count) println("Test records : " + test_raw_rdd.count) //cache train, test train_raw_rdd.cache() test_raw_rdd.cache() var train_rdd = train_raw_rdd.map{ line => var tokens = line.split(",",-1) //key为id和是否点击广告 var catkey = tokens(0) + "::" + tokens(1) //第6列到第15列为分类特征,需要One-Hot-Encoding var catfeatures = tokens.slice(5, 14) //第16列到24列为数值特征,直接使用 var numericalfeatures = tokens.slice(15, tokens.size-1) (catkey, catfeatures, numericalfeatures) } //拿一条出来看看 train_rdd.take(1) //scala> train_rdd.take(1) //res6: Array[(String, Array[String], Array[String])] = Array((1000009418151094273::0,Array(1fbe01fe, // f3845767, 28905ebd, ecad2386, 7801e8d9, 07d7df22, a99f214a, ddd2926e, 44956a24), // Array(2, 15706, 320, 50, 1722, 0, 35, -1))) //将分类特征先做特征ID映射 var train_cat_rdd = train_rdd.map{ x => parseCatFeatures(x._2) } train_cat_rdd.take(1) //scala> train_cat_rdd.take(1) //res12: Array[List[(Int, String)]] = Array(List((0,1fbe01fe), (1,f3845767), (2,28905ebd), // (3,ecad2386), (4,7801e8d9), (5,07d7df22), (6,a99f214a), (7,ddd2926e), (8,44956a24))) //将train_cat_rdd中的(特征ID:特征)去重,并进行编号 var oheMap = train_cat_rdd.flatMap(x => x).distinct().zipWithIndex().collectAsMap() //oheMap: scala.collection.Map[(Int, String),Long] = Map((7,608511e9) -> 31527, (7,b2d8fbed) -> 42207, // (7,1d3e2fdb) -> 52791 println("Number of features") println(oheMap.size) //create OHE for train data var ohe_train_rdd = train_rdd.map{ case (key, cateorical_features, numerical_features) => var cat_features_indexed = parseCatFeatures(cateorical_features) var cat_feature_ohe = new ArrayBuffer[Double] for (k <- cat_features_indexed) { if(oheMap contains k){ cat_feature_ohe += (oheMap get (k)).get.toDouble }else { cat_feature_ohe += 0.0 } } var numerical_features_dbl = numerical_features.map{ x => var x1 = if (x.toInt < 0) "0" else x x1.toDouble } var features = cat_feature_ohe.toArray ++ numerical_features_dbl LabeledPoint(key.split("::")(1).toInt, Vectors.dense(features)) } ohe_train_rdd.take(1) //res15: Array[org.apache.spark.mllib.regression.LabeledPoint] = // Array((0.0,[43127.0,50023.0,57445.0,13542.0,31092.0,14800.0,23414.0,54121.0, // 17554.0,2.0,15706.0,320.0,50.0,1722.0,0.0,35.0,0.0])) //训练模型 //val boostingStrategy = BoostingStrategy.defaultParams("Regression") val boostingStrategy = BoostingStrategy.defaultParams("Classification") boostingStrategy.numIterations = 100 boostingStrategy.treeStrategy.numClasses = 2 boostingStrategy.treeStrategy.maxDepth = 10 boostingStrategy.treeStrategy.categoricalFeaturesInfo = Map[Int, Int]() val model = GradientBoostedTrees.train(ohe_train_rdd, boostingStrategy) //保存模型 model.save(sc, "/tmp/myGradientBoostingClassificationModel") //加载模型 val sameModel = GradientBoostedTreesModel.load(sc,"/tmp/myGradientBoostingClassificationModel") //将测试数据集做OHE var test_rdd = test_raw_rdd.map{ line => var tokens = line.split(",") var catkey = tokens(0) + "::" + tokens(1) var catfeatures = tokens.slice(5, 14) var numericalfeatures = tokens.slice(15, tokens.size-1) (catkey, catfeatures, numericalfeatures) } var ohe_test_rdd = test_rdd.map{ case (key, cateorical_features, numerical_features) => var cat_features_indexed = parseCatFeatures(cateorical_features) var cat_feature_ohe = new ArrayBuffer[Double] for (k <- cat_features_indexed) { if(oheMap contains k){ cat_feature_ohe += (oheMap get (k)).get.toDouble }else { cat_feature_ohe += 0.0 } } var numerical_features_dbl = numerical_features.map{x => var x1 = if (x.toInt < 0) "0" else x x1.toDouble} var features = cat_feature_ohe.toArray ++ numerical_features_dbl LabeledPoint(key.split("::")(1).toInt, Vectors.dense(features)) } //验证测试数据集 var b = ohe_test_rdd.map { y => var s = model.predict(y.features) (s,y.label,y.features) } b.take(10).foreach(println) //预测准确率 var predictions = ohe_test_rdd.map(lp => sameModel.predict(lp.features)) predictions.take(10).foreach(println) var predictionAndLabel = predictions.zip( ohe_test_rdd.map(_.label)) var accuracy = 1.0 * predictionAndLabel.filter(x => x._1 == x._2 ).count/ohe_test_rdd.count println("GBTR accuracy " + accuracy) //GBTR accuracy 0.8227084119200302 } }
其中,训练数据集: Train records : 104558, 测试数据集:Test records : 26510
程序主要输出:
scala> train_rdd.take(1)
res23: Array[(String, Array[String], Array[String])] = Array((1000009418151094273::0,
Array(1fbe01fe, f3845767, 28905ebd, ecad2386, 7801e8d9, 07d7df22, a99f214a, ddd2926e, 44956a24),
Array(2, 15706, 320, 50, 1722, 0, 35, -1)))
scala> train_cat_rdd.take(1)
res24: Array[List[(Int, String)]] = Array(List((0,1fbe01fe), (1,f3845767), (2,28905ebd),
(3,ecad2386), (4,7801e8d9), (5,07d7df22), (6,a99f214a), (7,ddd2926e), (8,44956a24)))
scala> println("Number of features")
Number of features
scala> println(oheMap.size)
57606
scala> ohe_train_rdd.take(1)
res27: Array[org.apache.spark.mllib.regression.LabeledPoint] = Array(
(0.0,[11602.0,22813.0,11497.0,16828.0,30657.0,23893.0,13182.0,31723.0,39722.0,2.0,15706.0,320.0,50.0,1722.0,0.0,35.0,0.0]))
scala> println("GBTR accuracy " + accuracy)
GBTR accuracy 0.8227084119200302本文转载自xw的大数据田地。转载请注明原文链接http://lxw1234.com/archives/2016/01/595.htm
相关文章推荐
- 驾照题库api 根据输入参数返回相关题目
- 程序员遇到BUG后,最好的方法是?
- 三个迹象是时候升级你的最新KVM切换器
- java导出数据到word(一)
- spring的事物管理配置
- spring4 学习4 spring MVC+mybatis+Mysql
- MySQL实现统计数据并插入数据的存储过程
- objective-c UIAlertController 提示框应用
- objective-c 图片处理机制
- objective-c 选项卡翻页效果
- objective-c 拨打电话(NSString扩展类)
- IOS sqlite3
- objective-c 加密 MD5 解密MD5
- sh文件运行
- redis和memcached区别
- 做了个方便看godoc的chrome扩展,要的拿走
- check form判定非空
- maven插件启动tomcat和jetty
- push本地项目到github上
- 移动互联网:APP开发的机遇与挑战
