判断两条线段是否相交(三种算法)
2016-01-23 15:50
615 查看
算法1:
直接计算出两直线的交点,然后判断交点是不是在线段内,代码如下
算法2:
我们分两步确定两条线段是否相交:
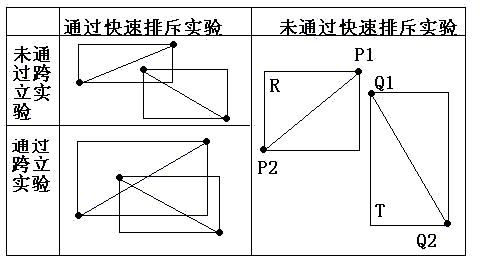
(1)快速排斥试验
设以线段 P1P2 为对角线的矩形为R, 设以线段 Q1Q2 为对角线的矩形为T,如果R和T不相交,显然两线段不会相交。
(2)跨立试验
如果两线段相交,则两线段必然相互跨立对方。若P1P2跨立Q1Q2 ,则矢量 ( P1 - Q1 ) 和( P2 - Q1 )位于矢量( Q2 - Q1 ) 的两侧,即( P1 - Q1 ) × ( Q2 - Q1 ) * ( P2 - Q1 ) × ( Q2 - Q1 ) < 0。上式可改写成( P1 - Q1 ) × ( Q2 - Q1 ) * ( Q2 - Q1 ) × ( P2 - Q1 ) > 0。当 ( P1 - Q1 ) × ( Q2 - Q1 ) = 0 时,说明 ( P1 - Q1 ) 和 ( Q2 - Q1 )共线,但是因为已经通过快速排斥试验,所以 P1 一定在线段 Q1Q2上;同理,( Q2 - Q1 ) ×(P2 - Q1 ) = 0 说明 P2 一定在线段 Q1Q2上。所以判断P1P2跨立Q1Q2的依据是:( P1 - Q1 ) × ( Q2 - Q1 ) * ( Q2 - Q1 ) × ( P2 - Q1 ) >= 0。同理判断Q1Q2跨立P1P2的依据是:( Q1 - P1 ) × ( P2 - P1 ) * ( P2 - P1 ) × ( Q2 - P1 ) >= 0。具体情况如下图所示:
算法3:
直接计算出两直线的交点,然后判断交点是不是在线段内,代码如下
struct line
{
double x1, y1, x2, y2;
bool fun(line l)
{
double xx, yy; //两直线的交点
double k1, k2; //两直线的斜率
if (fabs(this->x1-this->x2) < 1e-7 && fabs(l.x1-l.x2) < 1e-7) //两条直线都垂直于y轴
{
if (fabs(l.x1-this->x1) < 1e-7) return true;
return false;
}
else if (fabs(this->x1-this->x2) < 1e-7) //
{
if ((this->x1-l.x1)*(this->x1-l.x2) > -1e-8) return false;
k2 = (l.y1-l.y2)/(l.x1-l.x2);
xx = this->x1;
yy = k2*(xx-l.x1) + l.y1;
if ((this->y1-yy)*(yy-this->y2) >= -1e-8) return true;
return false;
}
else if (fabs(l.x1-l.x2) < 1e-7) //l垂直于y轴
{
if ((l.x1-this->x1)*(l.x1-this->x2) > -1e-8) return false;
xx = l.x1;
yy = k1*(xx-this->x1) + this->y1;
if ((l.y1-yy)*(yy-l.y2) >= 0) return true;
return false;
}
else
{
k1 = (this->y1-this->y2)/(this->x1-this->x2);
k2 = (l.y1-l.y2)/(l.x1-l.x2);
if (fabs(k1-k2) < 1e-7) return false; // 两直线平行,没交点
xx = (k1*this->x1-this->y1-k2*l.x1+l.y1)/(k1-k2);
yy = k2*(xx-l.x1) + l.y1;
if ((this->x1-xx)*(xx-this->x2)>=0 && (l.x1-xx)*(xx-l.x2)>=0) return true;//两直线的交点是不是在线段上
return false;
}
}
};算法2:
我们分两步确定两条线段是否相交:
(1)快速排斥试验
设以线段 P1P2 为对角线的矩形为R, 设以线段 Q1Q2 为对角线的矩形为T,如果R和T不相交,显然两线段不会相交。
(2)跨立试验
如果两线段相交,则两线段必然相互跨立对方。若P1P2跨立Q1Q2 ,则矢量 ( P1 - Q1 ) 和( P2 - Q1 )位于矢量( Q2 - Q1 ) 的两侧,即( P1 - Q1 ) × ( Q2 - Q1 ) * ( P2 - Q1 ) × ( Q2 - Q1 ) < 0。上式可改写成( P1 - Q1 ) × ( Q2 - Q1 ) * ( Q2 - Q1 ) × ( P2 - Q1 ) > 0。当 ( P1 - Q1 ) × ( Q2 - Q1 ) = 0 时,说明 ( P1 - Q1 ) 和 ( Q2 - Q1 )共线,但是因为已经通过快速排斥试验,所以 P1 一定在线段 Q1Q2上;同理,( Q2 - Q1 ) ×(P2 - Q1 ) = 0 说明 P2 一定在线段 Q1Q2上。所以判断P1P2跨立Q1Q2的依据是:( P1 - Q1 ) × ( Q2 - Q1 ) * ( Q2 - Q1 ) × ( P2 - Q1 ) >= 0。同理判断Q1Q2跨立P1P2的依据是:( Q1 - P1 ) × ( P2 - P1 ) * ( P2 - P1 ) × ( Q2 - P1 ) >= 0。具体情况如下图所示:

struct line
{
double x1, y1, x2, y2;
double mult(double x1, double y1, double x2, double y2, double x3, double y3) //计算叉乘
{
return (x1-x3)*(y2-y3)-(x2-x3)*(y1-y3);
}
bool fun(line l)
{
if (max(this->x1, this->x2) < min(l.x1, l.x2)) return false;
if (max(this->y1, this->y2) < min(l.y1, l.y2)) return false;
if (max(l.x1, l.x2) < min(this->x1, this->x2)) return false;
if (max(l.y1, l.y2) < min(this->y1, this->y2)) return false;
if (mult(l.x1, l.y1, this->x2, this->y2, this->x1, this->y1)*mult(this->x2, this->y2, l.x2, l.y2, this->x1, this->y1)<0) return false;
if (mult(this->x1, this->y1, l.x2, l.y2, l.x1, l.y1)*mult(l.x2, l.y2, this->x2, this->y2, l.x1, l.y1)<0) return false;
return true;
}
};算法3:
struct line
{
double x1, y1, x2, y2;
bool fun(line l)
{
double delta = (this->x2-this->x1)*(this->y2-this->y1) - (l.x1-l.x2)*(l.y1-l.y2);
if (delta >= -1e-7 && delta <= 1e-7) return false;
double namenda = ((l.x1-this->x1)*(l.y1-this->y1)-(l.x1-l.x2)*(l.y1-l.y2))/delta;
if (namenda > 1 || namenda < 0) return false;
double miu = ((this->x2-this->x1)*(this->y2-this->y1)-(l.x1-this->x1)*(l.y1-this->y1))/delta;
if (miu > 1 || miu < 0) return false;
return true;
}
};
相关文章推荐
- 书评:《算法之美( Algorithms to Live By )》
- 动易2006序列号破解算法公布
- Ruby实现的矩阵连乘算法
- C#插入法排序算法实例分析
- 超大数据量存储常用数据库分表分库算法总结
- C#数据结构与算法揭秘二
- C#冒泡法排序算法实例分析
- 算法练习之从String.indexOf的模拟实现开始
- C#算法之关于大牛生小牛的问题
- C#实现的算24点游戏算法实例分析
- c语言实现的带通配符匹配算法
- 浅析STL中的常用算法
- 算法之排列算法与组合算法详解
- C++实现一维向量旋转算法
- Ruby实现的合并排序算法
- C#折半插入排序算法实现方法
- 基于C++实现的各种内部排序算法汇总
- C++线性时间的排序算法分析
- C++实现汉诺塔算法经典实例
- PHP实现克鲁斯卡尔算法实例解析
