《Maven进阶》1.maven 项目生命周期与构建原理
2016-01-15 14:19
417 查看
maven是一个非常经典的和通用的项目管理工具,虽然现在热炒gradle将作为下一代 项目管理工具来取代maven,但是 由于maven强大和健全的功能,maven还有很强的生命力。
本文将介绍maven对于项目生命周期的设计以及原理。
读完本文,你将了解到:
一、maven对项目生命周期的抽象--三大项目生命周期
二、maven对项目默认生命周期的抽象
三、maven指令与生命周期阶段的关系
四、maven生命周期各个阶段的行为与maven默认行为
五、maven项目的目录结构
六、maven为生命周期阶段绑定特定行为动作的机制即插件原理
一、 maven对项目生命周期的抽象--三大项目生命周期
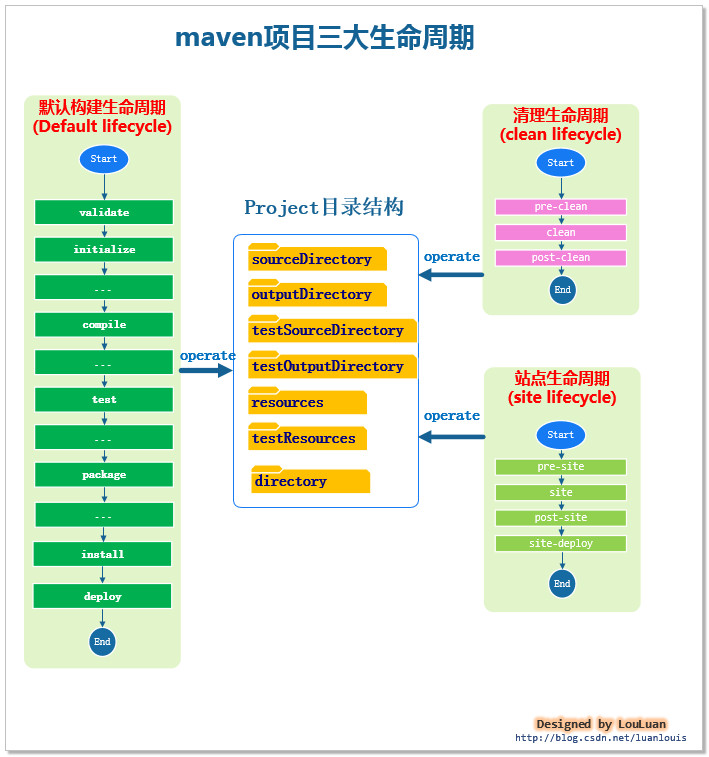
maven从项目的三个不同的角度,定义了单套生命周期,三套生命周期是相互独立的,它们之间不会相互影响。
默认构建生命周期(Default Lifeclyle):
该生命周期表示这项目的构建过程,定义了一个项目的构建要经过的不同的阶段。
清理生命周期(Clean Lifecycle): 该生命周期负责清理项目中的多余信息,保持项目资源和代码的整洁性。一般拿来清空directory(即一般的target)目录下的文件。
站点管理生命周期(Site Lifecycle) :向我们创建一个项目时,我们有时候需要提供一个站点,来介绍这个项目的信息,如项目介绍,项目进度状态、项目组成成员,版本控制信息,项目javadoc索引信息等等。站点管理生命周期定义了站点管理过程的各个阶段。
本文只介绍maven项目默认的生命周期,其他两个生命周期将另起博文介绍。
二、 maven对项目默认生命周期的抽象
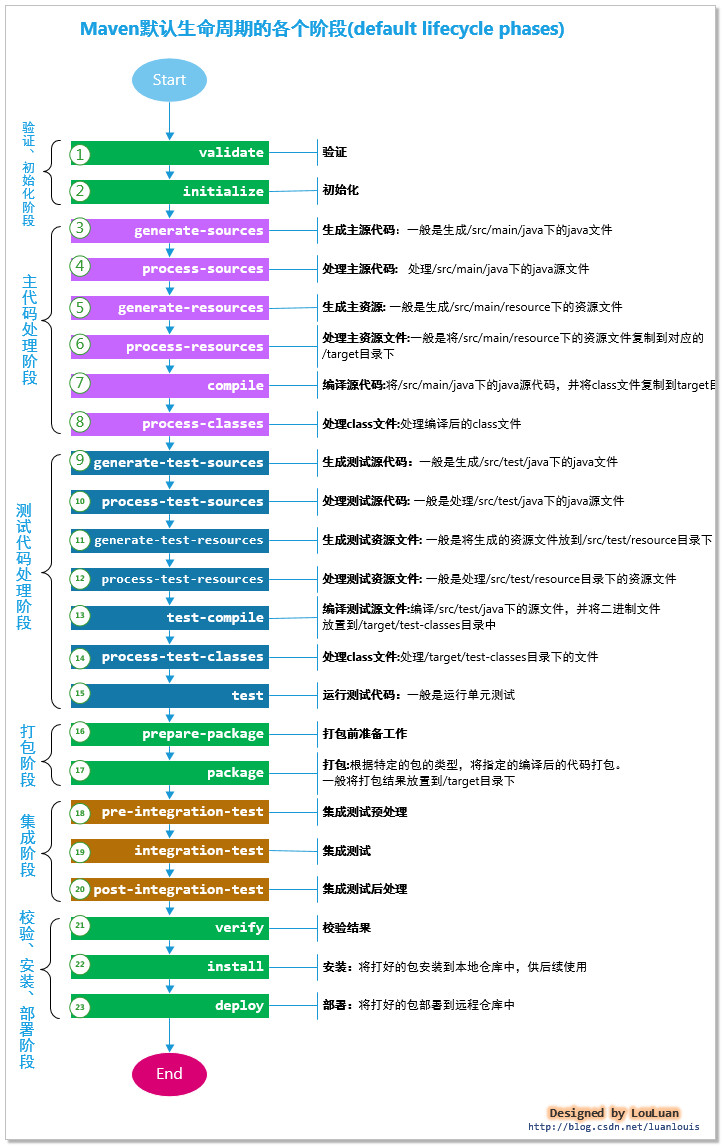
如何查看maven对默认生命周期的定义?
maven将其架构和结构的组织放置到了components.xml 配置文件中,该配置文件的路径是:
apache-maven-${version}\lib\maven-core-${version}.jar\META-INFO\plexus\conponents.xml文件中。其中,我们可以看到关于default生命周期XML节点配置信息:
maven根据一个项目的生命周期的每个阶段,将一个项目的生命周期抽象成了如上图所示的23个阶段。而每一个阶段应该干什么事情由用户决定。换句话说,maven为每一个阶段设计了接口,你可以为每一阶段自己定义一个接口,进而实现对应阶段应该有的行为。关于如何为某个生命周期阶段绑定自定义的行为,我将在后面的章节介绍。
三、 maven指令与生命周期阶段的关系
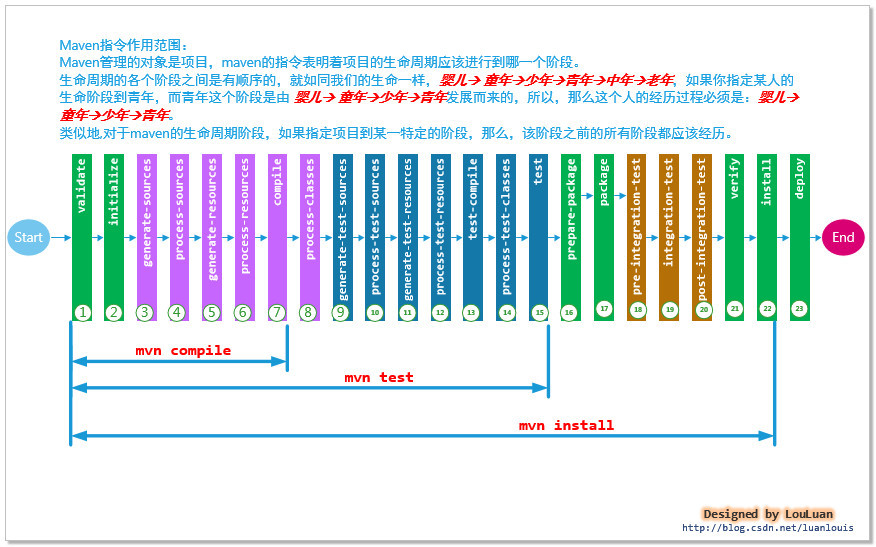
四、maven生命周期各个阶段的行为与maven默认行为
使用过maven的读者会经常使用这些maven指令:
在经历这些生命周期的阶段中,每个阶段会理论上会有相应的处理操作。但是,在实际的项目开发过程中, 并不是所有的生命周期阶段都是必须的。
然而,在实际的开发过程中,往往我们的项目的一些生命周期的阶段不需要相应的行为,我们只需要关心其中某些重要的生命周期阶段而已。下面,请看一下日常开发中,我们需要关注的生命周期阶段,即广大开发人员对项目周期阶段处理的约定:
1).应该将resource资源文件准备好,放到指定的target目录下----process-resources 阶段;
2).将java源文件编译成.class文件,然后将class 文件放置到对应的target目录下----compile阶段;
3).将test类型的resource移动到指定的 target目录下------process-test-resource阶段;
4).将test类型的java 源文件编译成class文件,然后放置到指定的target目录下------test-compile阶段;
5).运行test测试用例-------test阶段;
6).将compile阶段编译的class文件和resource资源打包成jar包或war包--------package阶段;
7).将生成的包安装到本地仓库中------install阶段
8).将生成的包部署到远程仓库中-----deploy阶段
由上面的约定可以看出,在大多数情况下,大家关心的项目生命周期阶段仅仅是上面的8个而已。跟上面maven对生命周期阶段23个的抽象相比,这就少的很多了。
基于类似的约定,maven默认地为一些不同类型的maven项目生命周期的阶段实现了默认的行为。
maven 在设计上将生命周期阶段的抽象和对应阶段应该执行的行为实现分离开,maven这些实现放到了插件中,这些插件本质上是实现了maven留在各个生命周期阶段的接口。关于插件的问题,我将另外写一篇博文介绍。
如下图所示,maven针对不同打包类型的maven项目的生命周期阶段绑定了对应的默认行为:
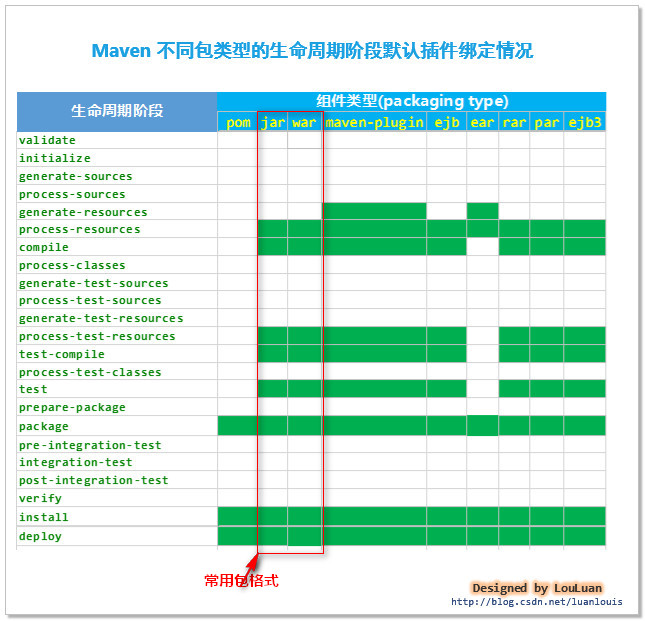
如上图所示,对于不同的打包格式的项目而言,maven为特定类型的包格式项目在不同的生命周期阶段的默认行为。
而对于我们经常使用的jar和war包格式的项目而言,maven总共为其规定了以下几个生命周期阶段的默认行为:
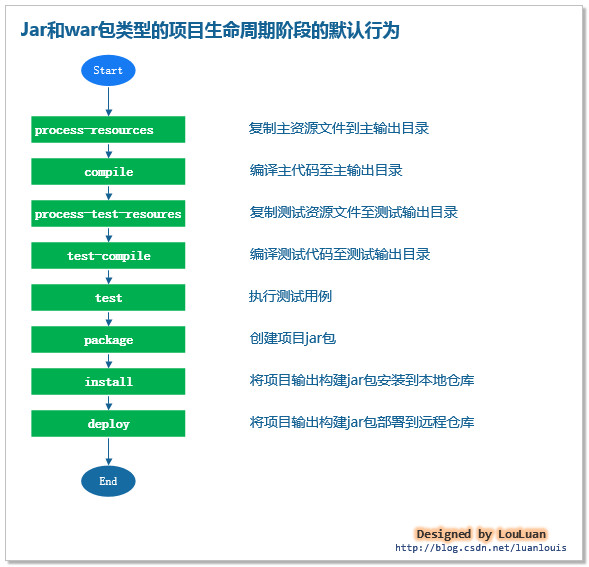
五、 maven项目的目录结构
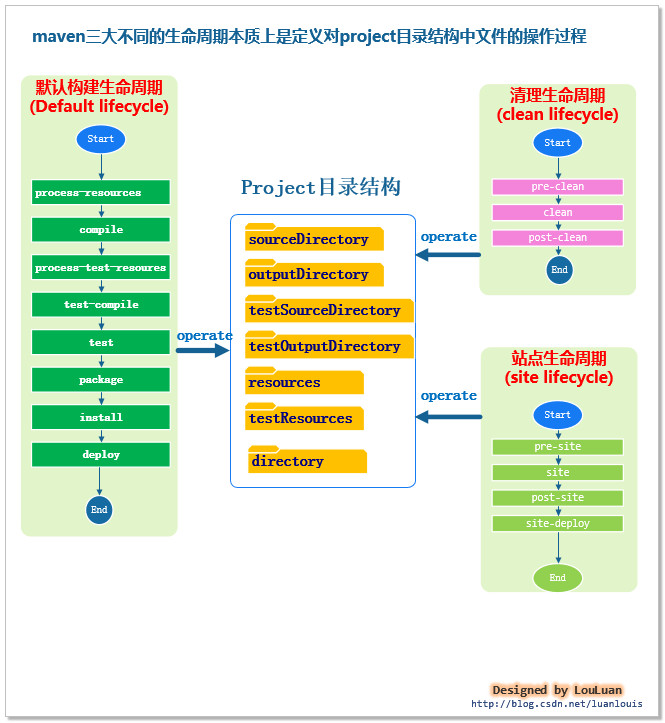
well,每个项目工程,都有非常繁琐的目录结构,每个目录都有不同的作用。请记住这一点,目录的划分是根据需要来的,每个目录有其特定的功能。目录本质上就是一个文件或文件夹路径而已。那么,我们换一个思路考虑:一个项目的文件结构需要组织什么信息呢?让我们来看一下功能的划分:

如上图所示,你会看到maven项目里不同功能类型的目录定义以及maven默认的目录的路径。
如何修改默认的目录配置
在maven项目工程对应project的 pom.xml中,在<project>--><build>节点下,你可以指定自己的目录路径信息:
请注意:对于maven管理项目工程的生命周期的操作上, 都发生在上述的几种目录中。换句话说,实质上,maven的项目管理的整个过程,就是围绕着对上述几种文件目录中内容的操作。
六、maven为生命周期阶段绑定特定行为动作的机制(即插件原理)
为maven生命周期的某些阶段绑定特定行为或动作,简单点就是调用一段代码而已,maven将需要执行的逻辑抽象成了一个接口,接口为 Mojo。Mojo是 Maven Old plain Java Object的简写,表示的意思是Mojo是maven的一个简单的对象。如下图所示:
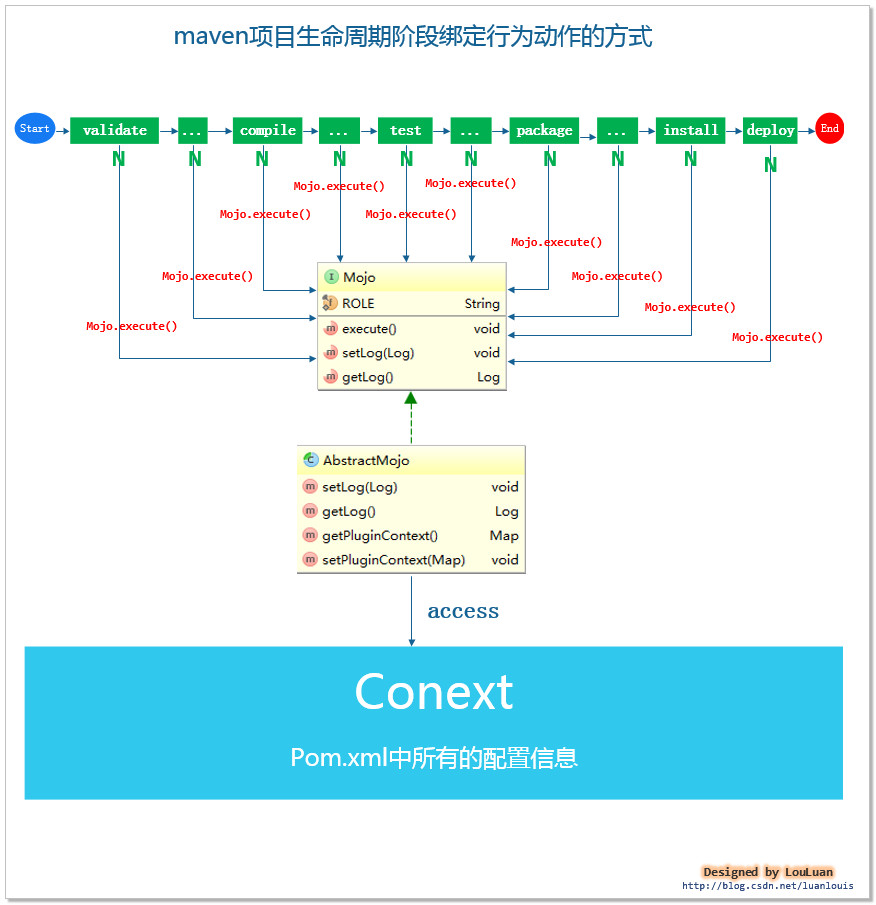
maven通过为某一个项目的生命周期阶段绑定若干个Mojo,然后依次执行Mojo.execute()方法,从而实现特定生命周期应该执行的动作。
举例:比如,对于生命周期阶段process-resources,maven默认地为其绑定了一个Mojo: org.apache.maven.plugin.resources.ResourcesMojo。
当需要经历process-resources阶段时,maven将会创建一个ResourcesMojo 实例instance,然后调用instance.execute()方法。
上面只是介绍了Maven生命周期阶段绑定执行代码的基本模式,由于maven的生命周期众多,并且每个生命周期内有可能绑定多个Mojo,如果使用上述的模式简单关联的话,会显得结构组织很乱。
maven会根据Mojo功能的划分,将具有相似功能的Mojo放到一个插件中。并且某一个特定的Mojo能实现的功能称为 goal,即目标,表明该Mojo能实现什么目标。
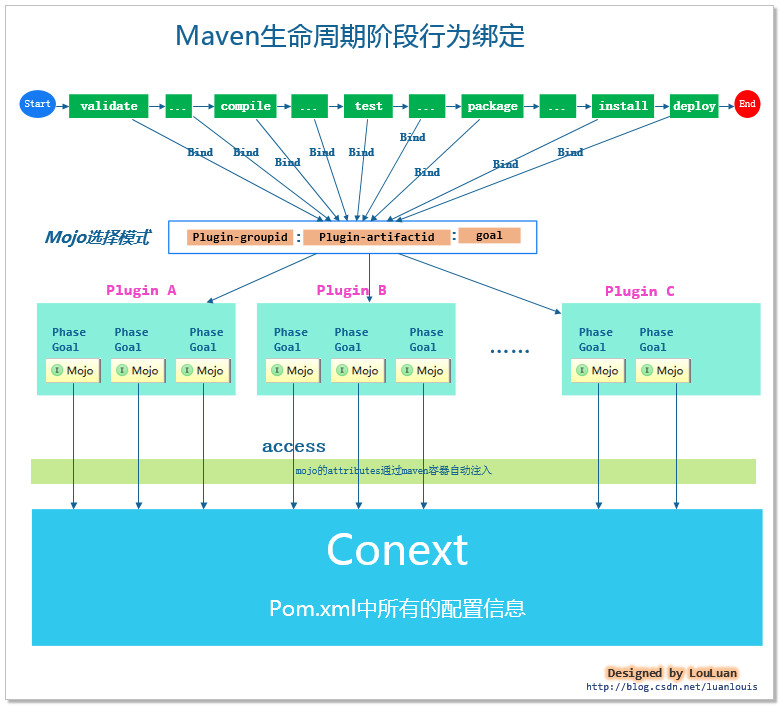
例如,我们项目生命周期有两个阶段:compile 和 test-compile,这两阶段都是需要将java源代码编译成class文件中,相对应地,compile和test-compiler分别被绑定到了org.apache.maven.plugin.compiler.CompilerMojo 和org.apache.maven.plugin.compiler.TestCompilerMojo上:
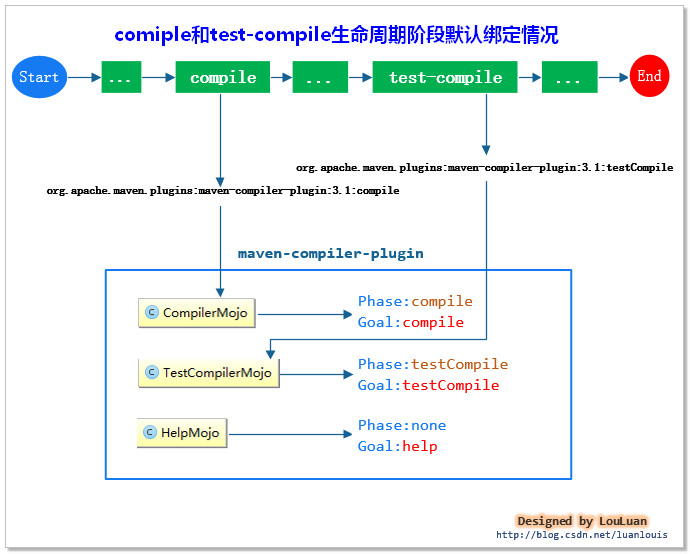
如何查看maven各个生命周期阶段和插件的绑定情况
maven默认实现上,会为各个常用的生命周期根据约定绑定特定的插件目标。maven将这些配置放置到了:
apache-maven-${version}\lib\maven-core-${version}.jar\META-INFO\plexus\default-binds.xml文件中,针对不同打包类型的项目,其默认绑定情况也会不一样,我们先看一下常用的jar包类型和war包类型的项目默认绑定情况:
如果你想查看当前maven有多少插件,每个插件都干了什么,你可以访问 maven plugin主页了解 : http://maven.apache.org/plugins/index.html
写在最后
本文旨在向读者介绍maven默认生命周期的工作机制,以及maven在项目构建过程中的基本原理和机制。
本文介绍的比较宽泛,还没有深入到maven插件底层,随后一篇博文将会详细介绍插件,解析插件的工作原理,分析当前maven默认定义的插件,并最终自己定义插件完成特定功能,敬请关注!
由于本人技术有限,如果本人有任何错误和纰漏,请读者慷慨指出,共同学习,共同进步!
2016.1.15
本文将介绍maven对于项目生命周期的设计以及原理。
读完本文,你将了解到:
一、maven对项目生命周期的抽象--三大项目生命周期
二、maven对项目默认生命周期的抽象
三、maven指令与生命周期阶段的关系
四、maven生命周期各个阶段的行为与maven默认行为
五、maven项目的目录结构
六、maven为生命周期阶段绑定特定行为动作的机制即插件原理

maven从项目的三个不同的角度,定义了单套生命周期,三套生命周期是相互独立的,它们之间不会相互影响。
默认构建生命周期(Default Lifeclyle):
该生命周期表示这项目的构建过程,定义了一个项目的构建要经过的不同的阶段。
清理生命周期(Clean Lifecycle): 该生命周期负责清理项目中的多余信息,保持项目资源和代码的整洁性。一般拿来清空directory(即一般的target)目录下的文件。
站点管理生命周期(Site Lifecycle) :向我们创建一个项目时,我们有时候需要提供一个站点,来介绍这个项目的信息,如项目介绍,项目进度状态、项目组成成员,版本控制信息,项目javadoc索引信息等等。站点管理生命周期定义了站点管理过程的各个阶段。
本文只介绍maven项目默认的生命周期,其他两个生命周期将另起博文介绍。

如何查看maven对默认生命周期的定义?
maven将其架构和结构的组织放置到了components.xml 配置文件中,该配置文件的路径是:
apache-maven-${version}\lib\maven-core-${version}.jar\META-INFO\plexus\conponents.xml文件中。其中,我们可以看到关于default生命周期XML节点配置信息:
<component> <role>org.apache.maven.lifecycle.Lifecycle</role> <implementation>org.apache.maven.lifecycle.Lifecycle</implementation> <role-hint>default</role-hint> <configuration> <id>default</id> <phases> <phase>validate</phase> <phase>initialize</phase> <phase>generate-sources</phase> <phase>process-sources</phase> <phase>generate-resources</phase> <phase>process-resources</phase> <phase>compile</phase> <phase>process-classes</phase> <phase>generate-test-sources</phase> <phase>process-test-sources</phase> <phase>generate-test-resources</phase> <phase>process-test-resources</phase> <phase>test-compile</phase> <phase>process-test-classes</phase> <phase>test</phase> <phase>prepare-package</phase> <phase>package</phase> <phase>pre-integration-test</phase> <phase>integration-test</phase> <phase>post-integration-test</phase> <phase>verify</phase> <phase>install</phase> <phase>deploy</phase> </phases> </configuration> </component>
maven根据一个项目的生命周期的每个阶段,将一个项目的生命周期抽象成了如上图所示的23个阶段。而每一个阶段应该干什么事情由用户决定。换句话说,maven为每一个阶段设计了接口,你可以为每一阶段自己定义一个接口,进而实现对应阶段应该有的行为。关于如何为某个生命周期阶段绑定自定义的行为,我将在后面的章节介绍。

使用过maven的读者会经常使用这些maven指令:
mvn compile //让当前项目经历生命周期中的1-->7 阶段 :完成编译主源代码编译 mvn package //让当前项目经历生命周期中的1-->17阶段 :完成打包 mvn install //让当前项目经历生命周期中的1-->22阶段 :完成包安装到本地仓库 mvn deploy //让当前生命经历生命周期中的1-->23阶段 :完成包部署到中心库中
在经历这些生命周期的阶段中,每个阶段会理论上会有相应的处理操作。但是,在实际的项目开发过程中, 并不是所有的生命周期阶段都是必须的。
然而,在实际的开发过程中,往往我们的项目的一些生命周期的阶段不需要相应的行为,我们只需要关心其中某些重要的生命周期阶段而已。下面,请看一下日常开发中,我们需要关注的生命周期阶段,即广大开发人员对项目周期阶段处理的约定:
1).应该将resource资源文件准备好,放到指定的target目录下----process-resources 阶段;
2).将java源文件编译成.class文件,然后将class 文件放置到对应的target目录下----compile阶段;
3).将test类型的resource移动到指定的 target目录下------process-test-resource阶段;
4).将test类型的java 源文件编译成class文件,然后放置到指定的target目录下------test-compile阶段;
5).运行test测试用例-------test阶段;
6).将compile阶段编译的class文件和resource资源打包成jar包或war包--------package阶段;
7).将生成的包安装到本地仓库中------install阶段
8).将生成的包部署到远程仓库中-----deploy阶段
由上面的约定可以看出,在大多数情况下,大家关心的项目生命周期阶段仅仅是上面的8个而已。跟上面maven对生命周期阶段23个的抽象相比,这就少的很多了。
基于类似的约定,maven默认地为一些不同类型的maven项目生命周期的阶段实现了默认的行为。
maven 在设计上将生命周期阶段的抽象和对应阶段应该执行的行为实现分离开,maven这些实现放到了插件中,这些插件本质上是实现了maven留在各个生命周期阶段的接口。关于插件的问题,我将另外写一篇博文介绍。
如下图所示,maven针对不同打包类型的maven项目的生命周期阶段绑定了对应的默认行为:

如上图所示,对于不同的打包格式的项目而言,maven为特定类型的包格式项目在不同的生命周期阶段的默认行为。
而对于我们经常使用的jar和war包格式的项目而言,maven总共为其规定了以下几个生命周期阶段的默认行为:

well,每个项目工程,都有非常繁琐的目录结构,每个目录都有不同的作用。请记住这一点,目录的划分是根据需要来的,每个目录有其特定的功能。目录本质上就是一个文件或文件夹路径而已。那么,我们换一个思路考虑:一个项目的文件结构需要组织什么信息呢?让我们来看一下功能的划分:

如上图所示,你会看到maven项目里不同功能类型的目录定义以及maven默认的目录的路径。
如何修改默认的目录配置
在maven项目工程对应project的 pom.xml中,在<project>--><build>节点下,你可以指定自己的目录路径信息:
<build> <!-- 目录信息维护,用户可以指定自己的目录路径 --> <sourceDirectory>E:\intellis\maven-principle\phase-echo\src\main\java</sourceDirectory> <scriptSourceDirectory>E:\intellis\maven-principle\phase-echo\src\main\scripts</scriptSourceDirectory> <testSourceDirectory>E:\intellis\maven-principle\phase-echo\src\test\java</testSourceDirectory> <outputDirectory>E:\intellis\maven-principle\phase-echo\target\classes</outputDirectory> <testOutputDirectory>E:\intellis\maven-principle\phase-echo\target\test-classes</testOutputDirectory> <!-- 注意,对resource而言,可以有很多个resource路径的配置,你只需要指定对应的路径是resource即可 --> <resources> <resource> <directory>E:\intellis\maven-principle\phase-echo\src\main\resources</directory> </resource> </resources> <!-- 注意,对resource而言,可以有很多个resource路径的配置,你只需要指定对应的路径是resource即可 --> <testResources> <testResource> <directory>E:\intellis\maven-principle\phase-echo\src\test\resources</directory> </testResource> </testResources> <directory>E:\intellis\maven-principle\phase-echo\target</directory> </build>
请注意:对于maven管理项目工程的生命周期的操作上, 都发生在上述的几种目录中。换句话说,实质上,maven的项目管理的整个过程,就是围绕着对上述几种文件目录中内容的操作。

为maven生命周期的某些阶段绑定特定行为或动作,简单点就是调用一段代码而已,maven将需要执行的逻辑抽象成了一个接口,接口为 Mojo。Mojo是 Maven Old plain Java Object的简写,表示的意思是Mojo是maven的一个简单的对象。如下图所示:

maven通过为某一个项目的生命周期阶段绑定若干个Mojo,然后依次执行Mojo.execute()方法,从而实现特定生命周期应该执行的动作。
举例:比如,对于生命周期阶段process-resources,maven默认地为其绑定了一个Mojo: org.apache.maven.plugin.resources.ResourcesMojo。
当需要经历process-resources阶段时,maven将会创建一个ResourcesMojo 实例instance,然后调用instance.execute()方法。
@Mojo( name = "resources", defaultPhase = LifecyclePhase.PROCESS_RESOURCES, threadSafe = true )
public class ResourcesMojo
extends AbstractMojo
implements Contextualizable
{
/**
下面若干个attribute ,maven 读取pom.xml内的配置信息,这里的attribute对应着pom.xml里的配置,如果在这里声明了,maven在创建Mojo 实例
instance的时候,会将这些值注入到instance内,供Mojo instance使用
*/
/**
* The character encoding scheme to be applied when filtering resources.
*/
@Parameter( property = "encoding", defaultValue = "${project.build.sourceEncoding}" )
protected String encoding;
/**
* The output directory into which to copy the resources.
*/
@Parameter( defaultValue = "${project.build.outputDirectory}", required = true )
private File outputDirectory;
/**
* The list of resources we want to transfer.
*/
@Parameter( defaultValue = "${project.resources}", required = true, readonly = true )
private List<Resource> resources;
/**
*
*/
@Parameter( defaultValue = "${project}", required = true, readonly = true )
protected MavenProject project;
/**
* The list of additional filter properties files to be used along with System and project
* properties, which would be used for the filtering.
* <br/>
* See also: {@link ResourcesMojo#filters}.
*
* @since 2.4
*/
@Parameter( defaultValue = "${project.build.filters}", readonly = true )
protected List<String> buildFilters;
/**
* The list of extra filter properties files to be used along with System properties,
* project properties, and filter properties files specified in the POM build/filters section,
* which should be used for the filtering during the current mojo execution.
* <br/>
* Normally, these will be configured from a plugin's execution section, to provide a different
* set of filters for a particular execution. For instance, starting in Maven 2.2.0, you have the
* option of configuring executions with the id's <code>default-resources</code> and
* <code>default-testResources</code> to supply different configurations for the two
* different types of resources. By supplying <code>extraFilters</code> configurations, you
* can separate which filters are used for which type of resource.
*/
@Parameter
protected List<String> filters;
/**
* If false, don't use the filters specified in the build/filters section of the POM when
* processing resources in this mojo execution.
* <br/>
* See also: {@link ResourcesMojo#buildFilters} and {@link ResourcesMojo#filters}
*
* @since 2.4
*/
@Parameter( defaultValue = "true" )
protected boolean useBuildFilters;
/**
*
*/
@Component( role = MavenResourcesFiltering.class, hint = "default" )
protected MavenResourcesFiltering mavenResourcesFiltering;
/**
*
*/
@Parameter( defaultValue = "${session}", required = true, readonly = true )
protected MavenSession session;
/**
* Expression preceded with the String won't be interpolated
* \${foo} will be replaced with ${foo}
*
* @since 2.3
*/
@Parameter( property = "maven.resources.escapeString" )
protected String escapeString;
/**
* Overwrite existing files even if the destination files are newer.
*
* @since 2.3
*/
@Parameter( property = "maven.resources.overwrite", defaultValue = "false" )
private boolean overwrite;
/**
* Copy any empty directories included in the Resources.
*
* @since 2.3
*/
@Parameter( property = "maven.resources.includeEmptyDirs", defaultValue = "false" )
protected boolean includeEmptyDirs;
/**
* Additional file extensions to not apply filtering (already defined are : jpg, jpeg, gif, bmp, png)
*
* @since 2.3
*/
@Parameter
protected List<String> nonFilteredFileExtensions;
/**
* Whether to escape backslashes and colons in windows-style paths.
*
* @since 2.4
*/
@Parameter( property = "maven.resources.escapeWindowsPaths", defaultValue = "true" )
protected boolean escapeWindowsPaths;
/**
* <p>
* Set of delimiters for expressions to filter within the resources. These delimiters are specified in the
* form 'beginToken*endToken'. If no '*' is given, the delimiter is assumed to be the same for start and end.
* </p><p>
* So, the default filtering delimiters might be specified as:
* </p>
* <pre>
* <delimiters>
* <delimiter>${*}</delimiter>
* <delimiter>@</delimiter>
* </delimiters>
* </pre>
* <p>
* Since the '@' delimiter is the same on both ends, we don't need to specify '@*@' (though we can).
* </p>
*
* @since 2.4
*/
@Parameter
protected List<String> delimiters;
/**
* @since 2.4
*/
@Parameter( defaultValue = "true" )
protected boolean useDefaultDelimiters;
/**
* <p>
* List of plexus components hint which implements {@link MavenResourcesFiltering#filterResources(MavenResourcesExecution)}.
* They will be executed after the resources copying/filtering.
* </p>
*
* @since 2.4
*/
@Parameter
private List<String> mavenFilteringHints;
/**
* @since 2.4
*/
private PlexusContainer plexusContainer;
/**
* @since 2.4
*/
private List<MavenResourcesFiltering> mavenFilteringComponents = new ArrayList<MavenResourcesFiltering>();
/**
* stop searching endToken at the end of line
*
* @since 2.5
*/
@Parameter( property = "maven.resources.supportMultiLineFiltering", defaultValue = "false" )
private boolean supportMultiLineFiltering;
public void contextualize( Context context )
throws ContextException
{
plexusContainer = (PlexusContainer) context.get( PlexusConstants.PLEXUS_KEY );
}
public void execute()
throws MojoExecutionException
{
try
{
if ( StringUtils.isEmpty( encoding ) && isFilteringEnabled( getResources() ) )
{
getLog().warn( "File encoding has not been set, using platform encoding " + ReaderFactory.FILE_ENCODING
+ ", i.e. build is platform dependent!" );
}
//获取资源文件过滤器配置
List filters = getCombinedFiltersList();
//根据现有配置信息创建Resources处理器对象实例
MavenResourcesExecution mavenResourcesExecution =
new MavenResourcesExecution( getResources(), getOutputDirectory(), project, encoding, filters,
Collections.<String>emptyList(), session );
//windows路径处理
mavenResourcesExecution.setEscapeWindowsPaths( escapeWindowsPaths );
// never include project build filters in this call, since we've already accounted for the POM build filters
// above, in getCombinedFiltersList().
mavenResourcesExecution.setInjectProjectBuildFilters( false );
mavenResourcesExecution.setEscapeString( escapeString );
mavenResourcesExecution.setOverwrite( overwrite );
mavenResourcesExecution.setIncludeEmptyDirs( includeEmptyDirs );
mavenResourcesExecution.setSupportMultiLineFiltering( supportMultiLineFiltering );
// if these are NOT set, just use the defaults, which are '${*}' and '@'.
if ( delimiters != null && !delimiters.isEmpty() )
{
LinkedHashSet<String> delims = new LinkedHashSet<String>();
if ( useDefaultDelimiters )
{
delims.addAll( mavenResourcesExecution.getDelimiters() );
}
for ( String delim : delimiters )
{
if ( delim == null )
{
// FIXME: ${filter:*} could also trigger this condition. Need a better long-term solution.
delims.add( "${*}" );
}
else
{
delims.add( delim );
}
}
mavenResourcesExecution.setDelimiters( delims );
}
if ( nonFilteredFileExtensions != null )
{
mavenResourcesExecution.setNonFilteredFileExtensions( nonFilteredFileExtensions );
}
mavenResourcesFiltering.filterResources( mavenResourcesExecution );
//执行Resource文件拷贝
executeUserFilterComponents( mavenResourcesExecution );
}
catch ( MavenFilteringException e )
{
throw new MojoExecutionException( e.getMessage(), e );
}
}
/**
* @since 2.5
*/
protected void executeUserFilterComponents( MavenResourcesExecution mavenResourcesExecution )
throws MojoExecutionException, MavenFilteringException
{
if ( mavenFilteringHints != null )
{
for ( Iterator ite = mavenFilteringHints.iterator(); ite.hasNext(); )
{
String hint = (String) ite.next();
try
{
mavenFilteringComponents.add(
(MavenResourcesFiltering) plexusContainer.lookup( MavenResourcesFiltering.class.getName(),
hint ) );
}
catch ( ComponentLookupException e )
{
throw new MojoExecutionException( e.getMessage(), e );
}
}
}
else
{
getLog().debug( "no use filter components" );
}
if ( mavenFilteringComponents != null && !mavenFilteringComponents.isEmpty() )
{
getLog().debug( "execute user filters" );
for ( MavenResourcesFiltering filter : mavenFilteringComponents )
{
filter.filterResources( mavenResourcesExecution );
}
}
}
protected List<String> getCombinedFiltersList()
{
if ( filters == null || filters.isEmpty() )
{
return useBuildFilters ? buildFilters : null;
}
else
{
List<String> result = new ArrayList<String>();
if ( useBuildFilters && buildFilters != null && !buildFilters.isEmpty() )
{
result.addAll( buildFilters );
}
result.addAll( filters );
return result;
}
}
/**
* Determines whether filtering has been enabled for any resource.
*
* @param resources The set of resources to check for filtering, may be <code>null</code>.
* @return <code>true</code> if at least one resource uses filtering, <code>false</code> otherwise.
*/
private boolean isFilteringEnabled( Collection<Resource> resources )
{
if ( resources != null )
{
for ( Resource resource : resources )
{
if ( resource.isFiltering() )
{
return true;
}
}
}
return false;
}
}上面只是介绍了Maven生命周期阶段绑定执行代码的基本模式,由于maven的生命周期众多,并且每个生命周期内有可能绑定多个Mojo,如果使用上述的模式简单关联的话,会显得结构组织很乱。
maven会根据Mojo功能的划分,将具有相似功能的Mojo放到一个插件中。并且某一个特定的Mojo能实现的功能称为 goal,即目标,表明该Mojo能实现什么目标。

例如,我们项目生命周期有两个阶段:compile 和 test-compile,这两阶段都是需要将java源代码编译成class文件中,相对应地,compile和test-compiler分别被绑定到了org.apache.maven.plugin.compiler.CompilerMojo 和org.apache.maven.plugin.compiler.TestCompilerMojo上:

如何查看maven各个生命周期阶段和插件的绑定情况
maven默认实现上,会为各个常用的生命周期根据约定绑定特定的插件目标。maven将这些配置放置到了:
apache-maven-${version}\lib\maven-core-${version}.jar\META-INFO\plexus\default-binds.xml文件中,针对不同打包类型的项目,其默认绑定情况也会不一样,我们先看一下常用的jar包类型和war包类型的项目默认绑定情况:
<!-- jar包格式的项目生命周期各个阶段默认绑定情况 --> <component> <role>org.apache.maven.lifecycle.mapping.LifecycleMapping</role> <role-hint>jar</role-hint> <implementation>org.apache.maven.lifecycle.mapping.DefaultLifecycleMapping</implementation> <configuration> <lifecycles> <lifecycle> <id>default</id> <!-- START SNIPPET: jar-lifecycle --> <phases> <!-- 插件绑定的格式: <plugin-groupid>:<plugin-artifactid>:<version>:goal --> <process-resources> org.apache.maven.plugins:maven-resources-plugin:2.6:resources </process-resources> <compile> org.apache.maven.plugins:maven-compiler-plugin:3.1:compile </compile> <process-test-resources> org.apache.maven.plugins:maven-resources-plugin:2.6:testResources </process-test-resources> <test-compile> org.apache.maven.plugins:maven-compiler-plugin:3.1:testCompile </test-compile> <test> org.apache.maven.plugins:maven-surefire-plugin:2.12.4:test </test> <package> org.apache.maven.plugins:maven-jar-plugin:2.4:jar </package> <install> org.apache.maven.plugins:maven-install-plugin:2.4:install </install> <deploy> org.apache.maven.plugins:maven-deploy-plugin:2.7:deploy </deploy> </phases> <!-- END SNIPPET: jar-lifecycle --> </lifecycle> </lifecycles> </configuration> </component> <!-- war包格式的项目生命周期各个阶段默认绑定情况 --> <component> <role>org.apache.maven.lifecycle.mapping.LifecycleMapping</role> <role-hint>war</role-hint> <implementation>org.apache.maven.lifecycle.mapping.DefaultLifecycleMapping</implementation> <configuration> <lifecycles> <lifecycle> <id>default</id> <!-- START SNIPPET: war-lifecycle --> <phases> <process-resources> org.apache.maven.plugins:maven-resources-plugin:2.6:resources </process-resources> <compile> org.apache.maven.plugins:maven-compiler-plugin:3.1:compile </compile> <process-test-resources> org.apache.maven.plugins:maven-resources-plugin:2.6:testResources </process-test-resources> <test-compile> org.apache.maven.plugins:maven-compiler-plugin:3.1:testCompile </test-compile> <test> org.apache.maven.plugins:maven-surefire-plugin:2.12.4:test </test> <package> org.apache.maven.plugins:maven-war-plugin:2.2:war </package> <install> org.apache.maven.plugins:maven-install-plugin:2.4:install </install> <deploy> org.apache.maven.plugins:maven-deploy-plugin:2.7:deploy </deploy> </phases> <!-- END SNIPPET: war-lifecycle --> </lifecycle> </lifecycles> </configuration> </component>
如果你想查看当前maven有多少插件,每个插件都干了什么,你可以访问 maven plugin主页了解 : http://maven.apache.org/plugins/index.html
写在最后
本文旨在向读者介绍maven默认生命周期的工作机制,以及maven在项目构建过程中的基本原理和机制。
本文介绍的比较宽泛,还没有深入到maven插件底层,随后一篇博文将会详细介绍插件,解析插件的工作原理,分析当前maven默认定义的插件,并最终自己定义插件完成特定功能,敬请关注!
由于本人技术有限,如果本人有任何错误和纰漏,请读者慷慨指出,共同学习,共同进步!
2016.1.15
相关文章推荐
- 1.15-学习概况
- Android沉浸式状态栏实现
- Qt5.5中OpenGL着色器程序编写
- (2)html学习笔记(粗略几笔)
- bitmapfactory.options 优化内存小问题
- iOS 开发 设置网络请求允许使用http
- 提交json串格式的POST请求
- (转载)iOS 开发之EXC_BAD_ACCESS异常分析
- java特种兵读书笔记(3-6)——java程序员的OS之JAVA常用工具
- Nginx中文参考手册
- Android TextWatcher使用详解
- 通过scp批量推送文件到远程目录
- 通过scp批量推送文件到远程目录
- [DGMGRL]Dgmgrl管理Dataguard(1)
- java 发送html格式邮件 样式混乱解决
- 支付 平台连接
- Clang-Format的使用及其自定义格式
- Python 模块之间传递变量
- Oracle函数和存储过程
- 《ActiveMQ In Action》Chapter 4 Connecting to ActiveMQ
