Oracle正则表达式函数
2016-01-06 13:39
579 查看
Oracle使用正则表达式离不开这4个函数:
1。regexp_like
2。regexp_substr
3。regexp_instr
4。regexp_replace
看函数名称大概就能猜到有什么用了。
regexp_like 只能用于条件表达式,和 like 类似,但是使用的正则表达式进行匹配,语法很简单:
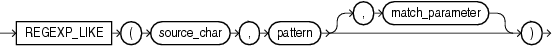
regexp_substr 函数,和 substr 类似,用于拾取合符正则表达式描述的字符子串,语法如下:
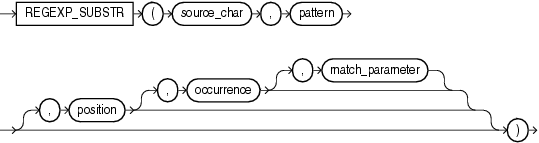
regexp_instr 函数,和 instr 类似,用于标定符合正则表达式的字符子串的开始位置,语法如下:
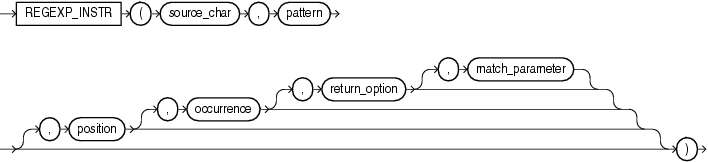
regexp_replace 函数,和 replace 类似,用于替换符合正则表达式的字符串,语法如下:
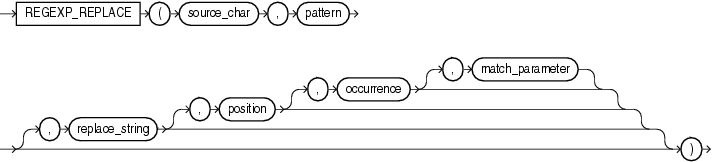
这里解析一下几个参数的含义:
1。source_char,输入的字符串,可以是列名或者字符串常量、变量。
2。pattern,正则表达式。
3。match_parameter,匹配选项。
取值范围: i:大小写不敏感; c:大小写敏感;n:点号 . 不匹配换行符号;m:多行模式;x:扩展模式,忽略正则表达式中的空白字符。
4。position,标识从第几个字符开始正则表达式匹配。
5。occurrence,标识第几个匹配组。
6。replace_string,替换的字符串。
说了一堆文绉绉的,现在开始实例演练了,在此之前先建好一个表。
01 create table tmp as
02 with data as (
03 select 'like' as id ,'a9999' as str from dual union all
04 select 'like' ,'a9c' from dual union all
05 select 'like' ,'A7007' from dual union all
06 select 'like' ,'123a34cc' from dual union all
07 select 'substr' ,'123,234,345' from dual union all
08 select 'substr' ,'12,34.56:78' from dual union all
09 select 'substr' ,'123456789' from dual union all
10 select 'instr' ,'192.168.0.1' from dual union all
11 select 'replace' ,'(020)12345678' from dual union all
12 select 'replace' ,'001517729C28' from dual
13 )
14 select * from data ;
15
16 select * from tmp ;
17 ID STR
18 ------- -------------
19 like a9999
20 like a9c
21 like A7007
22 like 123a34cc
23 substr 123,234,345
24 substr 12,34.56:78
25 substr 123456789
26 instr 192.168.0.1
27 replace (020)12345678
28 replace 001517729C28
regexp_like 例子:
01 select str from tmp where id='like' and regexp_like(str,'A\d+','i'); -- 'i' 忽略大小写
02 STR
03 -------------
04 a9999
05 a9c
06 A7007
07 123a3
4cc
08
09 select str from tmp where id='like' and regexp_like(str, 'a\d+');
10 STR
11 -------------
12 a9999
13 a9c
14 123a34cc
15
16 select str from tmp where id='like' and regexp_like(str,'^a\d+');
17 STR
18 -------------
19 a9999
20 a9c
21
22 select str from tmp where id='like' and regexp_like(str,'^a\d+$');
23 STR
24 -------------
25 a9999
regexp_substr 例子:
01 col str format a15;
02 select
03 str,
04 regexp_substr(str,'[^,]+') str,
05 regexp_substr(str,'[^,]+',1,1) str,
06 regexp_substr(str,'[^,]+',1,2) str, -- occurrence 第几个匹配组
07 regexp_substr(str,'[^,]+',2,1) str -- position 从第几个字符开始匹配
08 from tmp
09 where id='substr';
10 STR STR STR STR STR
11 --------------- --------------- --------------- --------------- ---------------
12 123,234,345 123 123 234 23
13 12,34.56:78 12 12 34.56:78 2
14 123456789 123456789 123456789 23456789
15
16 select
17 str,
18 regexp_substr(str,'\d') str,
19 regexp_substr(str,'\d+' ,1,1) str,
20 regexp_substr(str,'\d{2}',1,2) str,
21 regexp_substr(str,'\d{3}',2,1) str
22 from tmp
23 where id='substr';
24 STR STR STR STR STR
25 --------------- --------------- --------------- --------------- ---------------
26 123,234,345 1 123 23 234
27 12,34.56:78 1 12 34
28 123456789 1 123456789 34 234
29
30
31 select regexp_substr('123456789','\d',1,level) str --取出每位数字,有时这也是行转列的方式
32 from dual
33 connect by level<=9
34 STR
35 ---------------
36 1
37 2
38 3
39 4
40 5
41 6
42 7
43 8
44 9
regex_instr 例子:
01 col ind format 9999;
02 select
03 str,
04 regexp_instr(str,'\.' ) ind ,
05 regexp_instr(str,'\.',1,2) ind ,
06 regexp_instr(str,'\.',5,2) ind
07 from tmp where id='instr';
08 STR IND IND IND
09 --------------- ----- ----- -----
10 192.168.0.1 4 8 10
11
12 select
13 regexp_instr('192.168.0.1','\.',1,level) ind , -- 点号. 所在的位置
14 regexp_instr('192.168.0.1','\d',1,level) ind -- 每个数字的位置
15 from dual
16 connect by level <= 9
17 IND IND
18 ----- -----
19 4 1
20 8 2
21 10 3
22 0 5
23 0 6
24 0 7
25 0 9
26 0 11
27 0 0
regex_replace 例子:
01 select
02 str,
03 regexp_replace(str,'020','GZ') str,
04 regexp_replace(str,'(\d{3})(\d{3})','<\2\1>') str -- 将第一、第二捕获组交换位置,用尖括号标识出来
05 from tmp
06 where id='replace';
07 STR STR STR
08 --------------- --------------- ---------------
09 (020)12345678 (GZ)12345678 (020)<456123>78
10 001517729C28 001517729C28 <517001>729C28
综合应用的例子:
01 col row_line format a30;
02 with sudoku as (
03 select '020000080568179234090000010030040050040205090070080040050000060289634175010000020' as line
04 from dual
05 ),
06 tmp as (
07 select regexp_substr(line,'\d{9}',1,level) row_line,
08 level col
09 from sudoku
10 connect by level<=9
11 )
12 select regexp_replace( row_line ,'(\d)(\d)(\d)(\d)(\d)(\d)(\d)(\d)(\d)','\1 \2 \3 \4 \5 \6 \7 \8 \9') row_line
13 from tmp
14
15 ROW_LINE
16 ------------------------------
17 0 2 0 0 0 0 0 8 0
18 5 6 8 1 7 9 2 3 4
19 0 9 0 0 0 0 0 1 0
20 0 3 0 0 4 0 0 5 0
21 0 4 0 2 0 5 0 9 0
22 0 7 0 0 8 0 0 4 0
23 0 5 0 0 0 0 0 6 0
24 2 8 9 6 3 4 1 7 5
25 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 2 0
REGEXP_SUBSTR函数格式如下:
function REGEXP_SUBSTR(String, pattern, position, occurrence, modifier)
__srcstr :需要进行正则处理的字符串
__pattern :进行匹配的正则表达式
__position :起始位置,从第几个字符开始正则表达式匹配(默认为1)
__occurrence :标识第几个匹配组,默认为1
__modifier :模式('i'不区分大小写进行检索;'c'区分大小写进行检索。默认为'c'。)
__srcstr :需要进行正则处理的字符串
__pattern :进行匹配的正则表达式
__position :起始位置,从第几个字符开始正则表达式匹配(默认为1)
__occurrence :标识第几个匹配组,默认为1
__modifier :模式('i'不区分大小写进行检索;'c'区分大小写进行检索。默认为'c'。)
实际应用如下:在oracle中,使用一条语句实现将'34,56,-23'拆分成'34','56','-23'的集合。
[plain] view plaincopy
--1、查询使用正则分割后的第一个值,也就是34
SELECT REGEXP_SUBSTR('34,56,-23','[^,]+',1,1,'i') AS STR FROM DUAL;
--结果是:34
--2、查询使用正则分割后的最后一个值,也就是-23
SELECT REGEXP_SUBSTR('34,56,-23','[^,]+',1,3,'i') AS STR FROM DUAL;
--结果是:-23
--3、获取一个多个数值的列,从而能够让结果以多行的形式展示出来
SELECT LEVEL FROM DUAL CONNECT BY LEVEL <=7;
--结果是:
--1
--2
--3
--4
--5
--6
--7
--4、将上面REGEXP_SUBSTR的occurrence关联
SELECT NVL(REGEXP_SUBSTR('34,56,-23', '[^,]+', 1, LEVEL, 'i'), 'NULLL') AS STR FROM DUAL CONNECT BY LEVEL <= 7;
--结果是:
--34
--56
---23
--null
--null
--mull
--null
--5、优化上面的SQL语句,让生成的行的数量符合实际情况
SELECT REGEXP_SUBSTR('34,56,-23', '[^,]+', 1, LEVEL, 'i') AS STR FROM DUAL CONNECT BY LEVEL <= LENGTH('34,56,-23') - LENGTH(REGEXP_REPLACE('34,56,-23', ',', '')) + 1;
--结果是:
--34
--56
---23
相关文章推荐
- oracle创建表空间和用户
- oracle创建DBLINK报错:ORA-12154解决办法一
- 【DataBase】:使用Oracle遇到的几个问题及解决办法
- Oracle操作命令详解
- Oracle DBMS_OUTPUT包完全参考手册(中文版)
- oracle substr、instr以及case when 的连用截取字符串以及替换(repace)的使用
- oracle中merge into的用法
- ORACLE PL/SQL编程之八: 把触发器说透
- oracle rac cluster服务进程介绍
- QUESTION 118 You are managing an Oracle Database 11g instance with ASM storage. You lost an ASM disk
- oracle高级查询总结
- oracle rac ocr 简述
- oracle数据库密码过期报错
- ORACLE 11GR2 安装时配置了域,后期删除
- sql server 与oracle 中字段类型的对应
- over(Partition by…) 一个超级好用的特有(开窗)函数。
- oracle定时器job用法小结
- oracle中建立job定期运行存储过程总结
- Oracle执行计划详解
- Oracle执行语句跟踪(1)——使用sql trace实现语句追踪
