codeforces 424D. Biathlon Track(dp+ brute force)
2015-12-22 16:37
429 查看
http://codeforces.com/problemset/problem/424/D
Recently an official statement of the world Olympic Committee said that the Olympic Winter Games 2030 will be held in Tomsk. The city officials decided to prepare for the Olympics thoroughly and to build all the necessary Olympic facilities as early as possible.
First, a biathlon track will be built.
To construct a biathlon track a plot of land was allocated, which is a rectangle divided into
n × m identical squares. Each of the squares has two coordinates: the number of the row (from 1 to
n), where it is located, the number of the column (from 1 to
m), where it is located. Also each of the squares is characterized by its height. During the sports the biathletes will have to move from one square to another. If a biathlete moves from a higher square to a lower one,
he makes a descent. If a biathlete moves from a lower square to a higher one, he makes an ascent. If a biathlete moves between two squares with the same height, then he moves on flat ground.
The biathlon track should be a border of some rectangular area of the allocated land on which biathletes will move in the clockwise direction. It is known that on one move on flat ground an average biathlete spends
tp seconds, an ascent takes
tu seconds, a descent takes
td seconds. The Tomsk Administration wants to choose the route so that the average biathlete passes it in as close to
t seconds as possible. In other words, the difference between time
ts of passing the selected track and
t should be minimum.
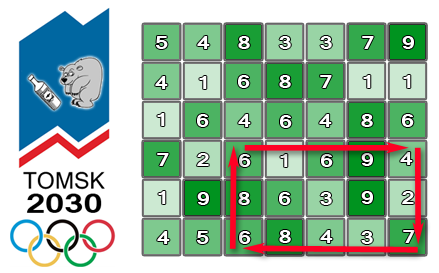
For a better understanding you can look at the first sample of the input data. In this sample
n = 6, m = 7, and the administration wants the track covering time to be as close to
t = 48 seconds as possible, also,
tp = 3,
tu = 6 and
td = 2. If we consider the rectangle shown on the image by arrows, the average biathlete can move along the boundary in a clockwise direction in exactly
48 seconds. The upper left corner of this track is located in the square with the row number
4, column number 3 and the lower right corner is at square with row number
6, column number 7.
Among other things the administration wants all sides of the rectangle which boundaries will be the biathlon track to consist of no less than three squares and to be completely contained within the selected land.
You are given the description of the given plot of land and all necessary time values. You are to write the program to find the most suitable rectangle for a biathlon track. If there are several such rectangles, you are allowed to print any of them.
Input
The first line of the input contains three integers n,
m and t (3 ≤ n, m ≤ 300,
1 ≤ t ≤ 109) — the sizes of the land plot and the desired distance covering time.
The second line also contains three integers tp,
tu and
td (1 ≤ tp, tu, td ≤ 100)
— the time the average biathlete needs to cover a flat piece of the track, an ascent and a descent respectively.
Then n lines follow, each line contains
m integers that set the heights of each square of the given plot of land. Each of the height values is a positive integer, not exceeding
106.
Output
In a single line of the output print four positive integers — the number of the row and the number of the column of the upper left corner and the number of the row and the number of the column of the lower right corner of the rectangle that is chosen for
the track.
Sample test(s)
Input
Output
分析:

行走的四个方向有不同的分值结果,用dp存储每个点的计算结果(选择四边的点作为计算的起点),然后直接暴力求解(过得很凶险,本来也想用排序后的写法做的但是没过)。
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
using namespace std;
int gra[305][305];
int dp[305][305][4];
int n,m,t;
int tp,tu,td; // 平 高 降
int work(int a,int b){
if(a==b) return tp;
if(a<b) return tu;
return td;
}
int abs(int a){
return a<0?-a:a;
}
int main()
{
while(~scanf("%d%d%d",&n,&m,&t)){
memset(dp,0,sizeof(dp));
scanf("%d%d%d",&tp,&tu,&td);
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){
for(int j=1;j<=m;j++){
scanf("%d",&gra[i][j]);
}
}
for(int j=2;j<=m;j++){
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){
dp[i][j][0]=dp[i][j-1][0]+work(gra[i][j-1],gra[i][j]);
}
}
for(int j=m-1;j>=1;j--){
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){
dp[i][j][2]=dp[i][j+1][2]+work(gra[i][j+1],gra[i][j]);
}
}
for(int i=2;i<=n;i++){
for(int j=1;j<=m;j++){
dp[i][j][1]=dp[i-1][j][1]+work(gra[i-1][j],gra[i][j]);
}
}
for(int i=n-1;i>=1;i--){
for(int j=1;j<=m;j++){
dp[i][j][3]=dp[i+1][j][3]+work(gra[i+1][j],gra[i][j]);
}
}
int dtime=0x3f3f3f3f;
int p1x=0,p1y=0,p2x=0,p2y=0;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){
for(int j=1;j<=m;j++){
for(int ii=i+2;ii<=n;ii++){
for(int jj=j+2;jj<=m;jj++){
int t0=dp[i][jj][0]-dp[i][j][0];
int t1=dp[ii][jj][1]-dp[i][jj][1];
int t2=dp[ii][j][2]-dp[ii][jj][2];
int t3=dp[i][j][3]-dp[ii][j][3];
int dt=t0+t1+t2+t3;
int r=abs(dt-t);
if(r<dtime){
dtime=r;
p1x=i;
p1y=j;
p2x=ii;
p2y=jj;
if(dtime==0){
goto tag;
}
}
}
}
}
}
tag:
printf("%d %d %d %d\n",p1x,p1y,p2x,p2y);
}
return 0;
}
Recently an official statement of the world Olympic Committee said that the Olympic Winter Games 2030 will be held in Tomsk. The city officials decided to prepare for the Olympics thoroughly and to build all the necessary Olympic facilities as early as possible.
First, a biathlon track will be built.
To construct a biathlon track a plot of land was allocated, which is a rectangle divided into
n × m identical squares. Each of the squares has two coordinates: the number of the row (from 1 to
n), where it is located, the number of the column (from 1 to
m), where it is located. Also each of the squares is characterized by its height. During the sports the biathletes will have to move from one square to another. If a biathlete moves from a higher square to a lower one,
he makes a descent. If a biathlete moves from a lower square to a higher one, he makes an ascent. If a biathlete moves between two squares with the same height, then he moves on flat ground.
The biathlon track should be a border of some rectangular area of the allocated land on which biathletes will move in the clockwise direction. It is known that on one move on flat ground an average biathlete spends
tp seconds, an ascent takes
tu seconds, a descent takes
td seconds. The Tomsk Administration wants to choose the route so that the average biathlete passes it in as close to
t seconds as possible. In other words, the difference between time
ts of passing the selected track and
t should be minimum.
For a better understanding you can look at the first sample of the input data. In this sample
n = 6, m = 7, and the administration wants the track covering time to be as close to
t = 48 seconds as possible, also,
tp = 3,
tu = 6 and
td = 2. If we consider the rectangle shown on the image by arrows, the average biathlete can move along the boundary in a clockwise direction in exactly
48 seconds. The upper left corner of this track is located in the square with the row number
4, column number 3 and the lower right corner is at square with row number
6, column number 7.

Among other things the administration wants all sides of the rectangle which boundaries will be the biathlon track to consist of no less than three squares and to be completely contained within the selected land.
You are given the description of the given plot of land and all necessary time values. You are to write the program to find the most suitable rectangle for a biathlon track. If there are several such rectangles, you are allowed to print any of them.
Input
The first line of the input contains three integers n,
m and t (3 ≤ n, m ≤ 300,
1 ≤ t ≤ 109) — the sizes of the land plot and the desired distance covering time.
The second line also contains three integers tp,
tu and
td (1 ≤ tp, tu, td ≤ 100)
— the time the average biathlete needs to cover a flat piece of the track, an ascent and a descent respectively.
Then n lines follow, each line contains
m integers that set the heights of each square of the given plot of land. Each of the height values is a positive integer, not exceeding
106.
Output
In a single line of the output print four positive integers — the number of the row and the number of the column of the upper left corner and the number of the row and the number of the column of the lower right corner of the rectangle that is chosen for
the track.
Sample test(s)
Input
6 7 48 3 6 2 5 4 8 3 3 7 9 4 1 6 8 7 1 1 1 6 4 6 4 8 6 7 2 6 1 6 9 4 1 9 8 6 3 9 2 4 5 6 8 4 3 7
Output
4 3 6 7
分析:

行走的四个方向有不同的分值结果,用dp存储每个点的计算结果(选择四边的点作为计算的起点),然后直接暴力求解(过得很凶险,本来也想用排序后的写法做的但是没过)。
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
using namespace std;
int gra[305][305];
int dp[305][305][4];
int n,m,t;
int tp,tu,td; // 平 高 降
int work(int a,int b){
if(a==b) return tp;
if(a<b) return tu;
return td;
}
int abs(int a){
return a<0?-a:a;
}
int main()
{
while(~scanf("%d%d%d",&n,&m,&t)){
memset(dp,0,sizeof(dp));
scanf("%d%d%d",&tp,&tu,&td);
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){
for(int j=1;j<=m;j++){
scanf("%d",&gra[i][j]);
}
}
for(int j=2;j<=m;j++){
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){
dp[i][j][0]=dp[i][j-1][0]+work(gra[i][j-1],gra[i][j]);
}
}
for(int j=m-1;j>=1;j--){
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){
dp[i][j][2]=dp[i][j+1][2]+work(gra[i][j+1],gra[i][j]);
}
}
for(int i=2;i<=n;i++){
for(int j=1;j<=m;j++){
dp[i][j][1]=dp[i-1][j][1]+work(gra[i-1][j],gra[i][j]);
}
}
for(int i=n-1;i>=1;i--){
for(int j=1;j<=m;j++){
dp[i][j][3]=dp[i+1][j][3]+work(gra[i+1][j],gra[i][j]);
}
}
int dtime=0x3f3f3f3f;
int p1x=0,p1y=0,p2x=0,p2y=0;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){
for(int j=1;j<=m;j++){
for(int ii=i+2;ii<=n;ii++){
for(int jj=j+2;jj<=m;jj++){
int t0=dp[i][jj][0]-dp[i][j][0];
int t1=dp[ii][jj][1]-dp[i][jj][1];
int t2=dp[ii][j][2]-dp[ii][jj][2];
int t3=dp[i][j][3]-dp[ii][j][3];
int dt=t0+t1+t2+t3;
int r=abs(dt-t);
if(r<dtime){
dtime=r;
p1x=i;
p1y=j;
p2x=ii;
p2y=jj;
if(dtime==0){
goto tag;
}
}
}
}
}
}
tag:
printf("%d %d %d %d\n",p1x,p1y,p2x,p2y);
}
return 0;
}
相关文章推荐
- android shape的使用(转载)
- Numpy基础解析(来自通联量化)
- 应用未打开时,静态广播的接受
- excel
- Android View嵌套和事件传递手稿
- 高通骁龙MSM8916核心板 ARM Cortex-A53 四核
- 跟我一起写 Makefile(五)
- Storyboard有用方法搜集
- using的用法
- Object_C 中的通知 iOS
- oracle中 判断是否 有记录 然后插入的sql语句
- Visual C++6.0 程序设计从入门到精通(四) - MFC类对象和资源之间的关系
- Devexpress 汉化
- Facebook 内部高效工作PPT
- 编程语言的基本组成
- 在pdf中绘制表格与插入图片
- Storm DRPC
- leetcode -- Substring with Concatenation of All Words -- 思路简单,再做一遍
- PHP学习练手(四)
- 卷积神经网络CNN理解
