数据结构-栈
2015-12-15 11:23
489 查看
栈只允许访问一个数据项:即最后插入的数据。移除这个数据项后才能访问倒数第二个插入的数据项。它是一种“后进先出”的数据结构。栈最基本的操作是出栈(Pop)、入栈(Push),还有其他扩展操作,如查看栈顶元素,判断栈是否为空、是否已满,读取栈的大小等1,栈的ArrayList实现,底层是数组import java.util.ArrayList;public class MyArrayStack<E> {private ArrayList<E> list=new ArrayList<>();//栈的底层用数组实现//压入栈public void push(E e){list.add(e);}//弹出栈public E pop(){return list.remove(list.size()-1);}//获得大小public int getSize(){return list.size();}//清空栈public void clear(){list.clear();}public boolean isEmpty() {return list.isEmpty();}public String toString(){return list.toString();}}2,栈的LinkedList实现,底层是链表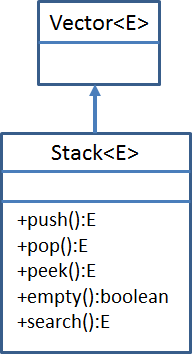 Stack本身通过扩展Vector而来,而Vector本身是一个可增长的对象数组
Stack本身通过扩展Vector而来,而Vector本身是一个可增长的对象数组
import java.util.LinkedList;public class MyLinkedStack<E> {private LinkedList<E> list=new LinkedList<E>();//栈的底层用链表实现//压入栈public void push(E e){list.add(e);}//弹出栈public E pop(){return list.remove(list.size()-1);}//获得大小public int getSize(){return list.size();}//清空栈public void clear(){list.clear();}public boolean isEmpty() {return list.isEmpty();}public String toString(){return list.toString();}}java提供的集合类java.util.Stack类简介Stack是一个后进先出(last in first out,LIFO)的堆栈,在Vector类的基础上扩展5个方法而来 Deque(双端队列)比起Stack具有更好的完整性和一致性,应该被优先使用  Stack本身通过扩展Vector而来,而Vector本身是一个可增长的对象数组
Stack本身通过扩展Vector而来,而Vector本身是一个可增长的对象数组E push(E item);//把项压入堆栈顶部。E pop();//移除堆栈顶部的对象,并作为此函数的值返回该对象。E peek();//查看堆栈顶部的对象,但不从堆栈中移除它。boolean empty();//测试堆栈是否为空。int search(Object o);//返回对象在堆栈中的位置,以 1 为基数。jdk1.6的源代码
public class Stack<E> extends Vector<E> {/*** Creates an empty Stack.*/public Stack() {}/*** Pushes an item onto the top of this stack. This has exactly* the same effect as:* <blockquote><pre>* addElement(item)</pre></blockquote>** @param item the item to be pushed onto this stack.* @return the <code>item</code> argument.* @see java.util.Vector#addElement*/public E push(E item) {addElement(item); //调用了父类数组Vector的方法return item;}/*** Removes the object at the top of this stack and returns that* object as the value of this function.** @return The object at the top of this stack (the last item* of the <tt>Vector</tt> object).* @exception EmptyStackException if this stack is empty.*/public synchronized E pop() { //同步方法E obj;int len = size();obj = peek();removeElementAt(len - 1); //<span style="font-family: Arial, Helvetica, sans-serif;">调用了父类数组Vector的方法</span>return obj;}/*** Looks at the object at the top of this stack without removing it* from the stack.** @return the object at the top of this stack (the last item* of the <tt>Vector</tt> object).* @exception EmptyStackException if this stack is empty.*/public synchronized E peek() { //同步方法,返回栈顶元素,但是不删除int len = size();if (len == 0)throw new EmptyStackException();return elementAt(len - 1);}/*** Tests if this stack is empty.** @return <code>true</code> if and only if this stack contains* no items; <code>false</code> otherwise.*/public boolean empty() {return size() == 0;}/*** Returns the 1-based position where an object is on this stack.* If the object <tt>o</tt> occurs as an item in this stack, this* method returns the distance from the top of the stack of the* occurrence nearest the top of the stack; the topmost item on the* stack is considered to be at distance <tt>1</tt>. The <tt>equals</tt>* method is used to compare <tt>o</tt> to the* items in this stack.** @param o the desired object.* @return the 1-based position from the top of the stack where* the object is located; the return value <code>-1</code>* indicates that the object is not on the stack.*/public synchronized int search(Object o) {int i = lastIndexOf(o);if (i >= 0) {return size() - i;}return -1;}/** use serialVersionUID from JDK 1.0.2 for interoperability */private static final long serialVersionUID = 1224463164541339165L;} Stack类为线程安全类测试java.util.Stack类import java.util.Stack;public class StackTest {public static void main(String[] args) {Stack<String> stack = new Stack<String>();stack.push("1");stack.push("2");stack.push("3");stack.push("4");stack.push("5");System.out.println("now the stack is " + isEmpty(stack));System.out.println("now the stack is " + stack.toString()); //toString()是Stack父类Vector的方法System.out.println("peek方法,返回但不删除栈顶:");System.out.println(stack.peek());System.out.println("peek之后的栈:" + stack.toString());System.out.println("pop方法,弹出栈顶:");System.out.println(stack.pop());System.out.println(stack.pop());System.out.println("pop之后的栈:" + stack.toString());System.out.println("search方法:");System.out.println(stack.search("2"));}public static String isEmpty(Stack<String> stack) {return stack.empty() ? "empty" : "not empty";}}now the stack is not emptynow the stack is [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]peek方法,返回但不删除栈顶:5peek之后的栈:[1, 2, 3, 4, 5]pop方法,弹出栈顶:54pop之后的栈:[1, 2, 3]search方法:2
相关文章推荐
- C#数据结构之顺序表(SeqList)实例详解
- Lua教程(七):数据结构详解
- 解析从源码分析常见的基于Array的数据结构动态扩容机制的详解
- C#数据结构之队列(Quene)实例详解
- C#数据结构揭秘一
- C#数据结构之单链表(LinkList)实例详解
- C++基于栈实现铁轨问题
- 数据结构之Treap详解
- C语言栈的表示与实现实例详解
- C语言实现颠倒栈的方法
- 算法系列15天速成 第十天 栈
- 一看就懂:图解C#中的值类型、引用类型、栈、堆、ref、out
- C#数据结构之堆栈(Stack)实例详解
- C#数据结构之双向链表(DbLinkList)实例详解
- JavaScript数据结构和算法之图和图算法
- Array栈方法和队列方法的特点说明
- Java数据结构及算法实例:冒泡排序 Bubble Sort
- Java数据结构及算法实例:插入排序 Insertion Sort
- Java数据结构及算法实例:考拉兹猜想 Collatz Conjecture
- java数据结构之java实现栈
