K-means clustering and K-nearest neighbourhood classifier
2015-12-06 20:54
453 查看
K-means clustering 是一个十分简单而又实用的聚类算法,其是一种无监督聚类学习,只需告诉分类器一共有几类,即可实现分类。K-nearest neighbourhood是一个有监督分类算法。
K-means clustering 算法思想:
随机给定k个观测作为初始种子点,m(1)1,m(1)2,...,m(1)km_1^{(1)}, m_2^{(1)},...,m_k^{(1)},
分配步:
for i = 1:K
S(t)i={xp:||xp−m(t)i||2≤||xp−m(t)j||2,∀j,1≤j≤k}S_i^{(t)} = \{{x_p:||x_p-m_i^{(t)}||^{2}}\le ||x_p -m_j^{(t)}||^2, \forall j,1\le j \le k\},
其中xpx_p 是第p个要聚类的点,将其分给2范数最小的i类。
更新步:
for i = 1 : K
m(t+1)i=1|S(t)i|∑xj∈S(t)ixjm_i^{(t +1)} = \frac{1}{|S_i^{(t)}|} \sum_{x_j \in S_i^{(t)} }x_j
m(t+1)im_i^{(t + 1)} 是第t次聚类后,i类用于计算t+1次聚类的中心。
举个例子:

图一:选择初始点
\space
\space

图二:根据初始点产生一组聚类
\space
\space

图三 重新计算聚类后的中心,作为种子点。
\space
\space

迭代2和3,产生最终的聚类
\space
\space
K-means 算法的K需要事先确定,而且初始的种子点随机选择。初始种子点的选择可采用K++算法改善。
1、从输入的数据点集合中随机选择一个点作为第一个聚类中心
2、对于数据集中的每一个点x,计算它与最近聚类中心(指已选择的聚类中心)的距离D(x)
3、选择一个新的数据点作为新的聚类中心,选择的原则是:D(x)较大的点,被选取作为聚类中心的概率较大
4、重复2和3直到k个聚类中心被选出来
5、利用这k个初始的聚类中心来运行标准的k-means算法
\space
\space
\space
\space
\space
\space
K-nearest neighbourhood classifier
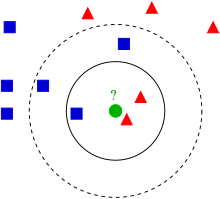
K近邻分类,指的是对于某个点,找出其最近的k个点,这k个点进行投票,选取相同点数最多的类别作为该点的label。
如果K=3,那么离绿色点最近的有2个红色三角形和1个蓝色的正方形,这3个点投票,于是绿色的这个待分类点属于红色的三角形
如果K=5,那么离绿色点最近的有2个红色三角形和3个蓝色的正方形,这5个点投票,于是绿色的这个待分类点属于蓝色的正方形
另一种变形:本人想的。对于某个点,找出其最近的k个相同的点,这k个相同的点属于哪一类,就将其作为该类的label。
如果K=1,则绿色的点属于红色。
如果K=2,则绿色的点属于红色。
如果K=3,则绿色的点属于蓝色。
这两种方法应用上有什么区别呢?待思考。
K-means 和 KNN的区别:
K-means
1、聚类算法
2、非监督
3、K是人为定的,需要一定先验知识
KNN
1、分类
2、监督
3、K个最近的点
K-means matlab 代码
K-means C++代码,转自wiki
KNN 代码
转自(http://www.cppblog.com/unixfy/archive/2012/02/14/165537.aspx)
train.txt:
a 1 2 3 4 5
b 5 4 3 2 1
c 3 3 3 3 3
d -3 -3 -3 -3 -3
a 1 2 3 4 4
b 4 4 3 2 1
c 3 3 3 2 4
d 0 0 1 1 -2
test.txt:
1 2 3 2 4
2 3 4 2 1
8 7 2 3 5
-3 -2 2 4 0
-4 -4 -4 -4 -4
1 2 3 4 4
4 4 3 2 1
3 3 3 2 4
0 0 1 1 -2
result.txt:
a 1 2 3 2 4
b 2 3 4 2 1
b 8 7 2 3 5
a -3 -2 2 4 0
d -4 -4 -4 -4 -4
a 1 2 3 4 4
b 4 4 3 2 1
c 3 3 3 2 4
d 0 0 1 1 -2
K-means clustering 算法思想:
随机给定k个观测作为初始种子点,m(1)1,m(1)2,...,m(1)km_1^{(1)}, m_2^{(1)},...,m_k^{(1)},
分配步:
for i = 1:K
S(t)i={xp:||xp−m(t)i||2≤||xp−m(t)j||2,∀j,1≤j≤k}S_i^{(t)} = \{{x_p:||x_p-m_i^{(t)}||^{2}}\le ||x_p -m_j^{(t)}||^2, \forall j,1\le j \le k\},
其中xpx_p 是第p个要聚类的点,将其分给2范数最小的i类。
更新步:
for i = 1 : K
m(t+1)i=1|S(t)i|∑xj∈S(t)ixjm_i^{(t +1)} = \frac{1}{|S_i^{(t)}|} \sum_{x_j \in S_i^{(t)} }x_j
m(t+1)im_i^{(t + 1)} 是第t次聚类后,i类用于计算t+1次聚类的中心。
举个例子:

图一:选择初始点
\space
\space

图二:根据初始点产生一组聚类
\space
\space

图三 重新计算聚类后的中心,作为种子点。
\space
\space

迭代2和3,产生最终的聚类
\space
\space
K-means 算法的K需要事先确定,而且初始的种子点随机选择。初始种子点的选择可采用K++算法改善。
1、从输入的数据点集合中随机选择一个点作为第一个聚类中心
2、对于数据集中的每一个点x,计算它与最近聚类中心(指已选择的聚类中心)的距离D(x)
3、选择一个新的数据点作为新的聚类中心,选择的原则是:D(x)较大的点,被选取作为聚类中心的概率较大
4、重复2和3直到k个聚类中心被选出来
5、利用这k个初始的聚类中心来运行标准的k-means算法
\space
\space
\space
\space
\space
\space
K-nearest neighbourhood classifier
K近邻分类,指的是对于某个点,找出其最近的k个点,这k个点进行投票,选取相同点数最多的类别作为该点的label。
如果K=3,那么离绿色点最近的有2个红色三角形和1个蓝色的正方形,这3个点投票,于是绿色的这个待分类点属于红色的三角形
如果K=5,那么离绿色点最近的有2个红色三角形和3个蓝色的正方形,这5个点投票,于是绿色的这个待分类点属于蓝色的正方形
另一种变形:本人想的。对于某个点,找出其最近的k个相同的点,这k个相同的点属于哪一类,就将其作为该类的label。
如果K=1,则绿色的点属于红色。
如果K=2,则绿色的点属于红色。
如果K=3,则绿色的点属于蓝色。
这两种方法应用上有什么区别呢?待思考。
K-means 和 KNN的区别:
K-means
1、聚类算法
2、非监督
3、K是人为定的,需要一定先验知识
KNN
1、分类
2、监督
3、K个最近的点

K-means matlab 代码
RGB= imread ('test.jpg'); %读入
img=rgb2gray(RGB);
[m,n]=size(img);
subplot(2,2,1),imshow(img);title(' 图一 原图像')
subplot(2,2,2),imhist(img);title(' 图二 原图像的灰度直方图')
hold off;
img=double(img);
c1(1)=25;
c2(1)=125;
c3(1)=200;%选择三个初始聚类中心
for i=1:200
r=abs(img-c1(i));
g=abs(img-c2(i));
b=abs(img-c3(i));%计算各像素灰度与聚类中心的距离
r_g=r-g;
g_b=g-b;
r_b=r-b;
n_r=find(r_g<=0&r_b<=0);%寻找最小的聚类中心
n_g=find(r_g>0&g_b<=0);%寻找中间的一个聚类中心
n_b=find(g_b>0&r_b>0);%寻找最大的聚类中心
i=i+1;
c1(i)=sum(img(n_r))/length(n_r);%将所有低灰度求和取平均,作为下一个低灰度中心
c2(i)=sum(img(n_g))/length(n_g);%将所有低灰度求和取平均,作为下一个中间灰度中心
c3(i)=sum(img(n_b))/length(n_b);%将所有低灰度求和取平均,作为下一个高灰度中心
d1(i)=abs(c1(i)-c1(i-1));
d2(i)=abs(c2(i)-c2(i-1));
d3(i)=abs(c3(i)-c3(i-1));
if d1(i)<=0.001&&d2(i)<=0.001&&d3(i)<=0.001
R=c1(i);
G=c2(i);
B=c3(i);
k=i;
break;
end
end
R
G
B
img=uint8(img);
img(find(img<R))=0;
img(find(img>R&img<G))=128;
img(find(img>G))=255;
subplot(2,2,3),imshow(img);title(' 图三 聚类后的图像')
subplot(2,2,4),imhist(img);title(' 图四 聚类后的图像直方图'K-means C++代码,转自wiki
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <math.h>
typedef struct { double x, y; int group; } point_t, *point;
double randf(double m)
{
return m * rand() / (RAND_MAX - 1.);
}
point gen_xy(int count, double radius)
{
double ang, r;
point p, pt = malloc(sizeof(point_t) * count);
/* note: this is not a uniform 2-d distribution */
for (p = pt + count; p-- > pt;) {
ang = randf(2 * M_PI);
r = randf(radius);
p->x = r * cos(ang);
p->y = r * sin(ang);
}
return pt;
}
inline double dist2(point a, point b)
{
double x = a->x - b->x, y = a->y - b->y;
return x*x + y*y;
}
inline int
nearest(point pt, point cent, int n_cluster, double *d2)
{
int i, min_i;
point c;
double d, min_d;
# define for_n for (c = cent, i = 0; i < n_cluster; i++, c++)
for_n {
min_d = HUGE_VAL;
min_i = pt->group;
for_n {
if (min_d > (d = dist2(c, pt))) {
min_d = d; min_i = i;
}
}
}
if (d2) *d2 = min_d;
return min_i;
}
void kpp(point pts, int len, point cent, int n_cent)
{
# define for_len for (j = 0, p = pts; j < len; j++, p++)
int i, j;
int n_cluster;
double sum, *d = malloc(sizeof(double) * len);
point p, c;
cent[0] = pts[ rand() % len ];
for (n_cluster = 1; n_cluster < n_cent; n_cluster++) {
sum = 0;
for_len {
nearest(p, cent, n_cluster, d + j);
sum += d[j];
}
sum = randf(sum);
for_len {
if ((sum -= d[j]) > 0) continue;
cent[n_cluster] = pts[j];
break;
}
}
for_len p->group = nearest(p, cent, n_cluster, 0);
free(d);
}
point lloyd(point pts, int len, int n_cluster)
{
int i, j, min_i;
int changed;
point cent = malloc(sizeof(point_t) * n_cluster), p, c;
/* assign init grouping randomly */
//for_len p->group = j % n_cluster;
/* or call k++ init */
kpp(pts, len, cent, n_cluster);
do {
/* group element for centroids are used as counters */
for_n { c->group = 0; c->x = c->y = 0; }
for_len {
c = cent + p->group;
c->group++;
c->x += p->x; c->y += p->y;
}
for_n { c->x /= c->group; c->y /= c->group; }
changed = 0;
/* find closest centroid of each point */
for_len {
min_i = nearest(p, cent, n_cluster, 0);
if (min_i != p->group) {
changed++;
p->group = min_i;
}
}
} while (changed > (len >> 10)); /* stop when 99.9% of points are good */
for_n { c->group = i; }
return cent;
}
void print_eps(point pts, int len, point cent, int n_cluster)
{
# define W 400
# define H 400
int i, j;
point p, c;
double min_x, max_x, min_y, max_y, scale, cx, cy;
double *colors = malloc(sizeof(double) * n_cluster * 3);
for_n {
colors[3*i + 0] = (3 * (i + 1) % 11)/11.;
colors[3*i + 1] = (7 * i % 11)/11.;
colors[3*i + 2] = (9 * i % 11)/11.;
}
max_x = max_y = -(min_x = min_y = HUGE_VAL);
for_len {
if (max_x < p->x) max_x = p->x;
if (min_x > p->x) min_x = p->x;
if (max_y < p->y) max_y = p->y;
if (min_y > p->y) min_y = p->y;
}
scale = W / (max_x - min_x);
if (scale > H / (max_y - min_y)) scale = H / (max_y - min_y);
cx = (max_x + min_x) / 2;
cy = (max_y + min_y) / 2;
printf("%%!PS-Adobe-3.0\n%%%%BoundingBox: -5 -5 %d %d\n", W + 10, H + 10);
printf( "/l {rlineto} def /m {rmoveto} def\n"
"/c { .25 sub exch .25 sub exch .5 0 360 arc fill } def\n"
"/s { moveto -2 0 m 2 2 l 2 -2 l -2 -2 l closepath "
" gsave 1 setgray fill grestore gsave 3 setlinewidth"
" 1 setgray stroke grestore 0 setgray stroke }def\n"
);
for_n {
printf("%g %g %g setrgbcolor\n",
colors[3*i], colors[3*i + 1], colors[3*i + 2]);
for_len {
if (p->group != i) continue;
printf("%.3f %.3f c\n",
(p->x - cx) * scale + W / 2,
(p->y - cy) * scale + H / 2);
}
printf("\n0 setgray %g %g s\n",
(c->x - cx) * scale + W / 2,
(c->y - cy) * scale + H / 2);
}
printf("\n%%%%EOF");
free(colors);
# undef for_n
# undef for_len
}
#define PTS 100000
#define K 11
int main()
{
int i;
point v = gen_xy(PTS, 10);
point c = lloyd(v, PTS, K);
print_eps(v, PTS, c, K);
// free(v); free(c);
return 0;
}KNN 代码
转自(http://www.cppblog.com/unixfy/archive/2012/02/14/165537.aspx)
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <vector>
#include <set>
#include <map>
#include <fstream>
#include <sstream>
#include <cassert>
#include <cmath>
using namespace std;
//样例结构体,所属类型和特征向量
struct sample
{
string type;
vector<double> features;
};
// 类型和距离结构体,未用到
struct typeDistance
{
string type;
double distance;
};
bool operator < (const typeDistance& lhs, const typeDistance& rhs)
{
return lhs.distance < rhs.distance;
}
// 读取训练样本
// 训练样本的格式是:每行代表一个样例
// 每行的第一个元素是类型名,后面的是样例的特征向量
// 例如:
/*
a 1 2 3 4 5
b 5 4 3 2 1
c 3 3 3 3 3
d -3 -3 -3 -3 -3
a 1 2 3 4 4
b 4 4 3 2 1
c 3 3 3 2 4
d 0 0 1 1 -2
*/
void readTrain(vector<sample>& train, const string& file)
{
ifstream fin(file.c_str());
if (!fin)
{
cerr << "File error!" << endl;
exit(1);
}
string line;
double d = 0.0;
while (getline(fin, line))
{
istringstream sin(line);
sample ts;
sin >> ts.type;
while (sin >> d)
{
ts.features.push_back(d);
}
train.push_back(ts);
}
fin.close();
}
// 读取测试样本
// 每行代表一个样例
// 每一行是一个样例的特征向量
// 例如:
/*
1 2 3 2 4
2 3 4 2 1
8 7 2 3 5
-3 -2 2 4 0
-4 -4 -4 -4 -4
1 2 3 4 4
4 4 3 2 1
3 3 3 2 4
0 0 1 1 -2
*/
void readTest(vector<sample>& test, const string& file)
{
ifstream fin(file.c_str());
if (!fin)
{
cerr << "File error!" << endl;
exit(1);
}
double d = 0.0;
string line;
while (getline(fin, line))
{
istringstream sin(line);
sample ts;
while (sin >> d)
{
ts.features.push_back(d);
}
test.push_back(ts);
}
fin.close();
}
// 计算欧氏距离
double euclideanDistance(const vector<double>& v1, const vector<double>& v2)
{
assert(v1.size() == v2.size());
double ret = 0.0;
/*
size_type由string类类型和vector类类型定义的类型,用以保存任意string对象或vector对象的长度,标准库类型将size_type定义为unsigned类型
*/
for (vector<double>::size_type i = 0; i != v1.size(); ++i)
{
ret += (v1[i] - v2[i]) * (v1[i] - v2[i]);
}
return sqrt(ret);
}
// 初始化距离矩阵
// 该矩阵是根据训练样本和测试样本而得
// 矩阵的行数为测试样本的数目,列数为训练样本的数目
// 每一行为一个测试样本到各个训练样本之间的欧式距离组成的数组
void initDistanceMatrix(vector<vector<double> >& dm, const vector<sample>& train, const vector<sample>& test)
{
for (vector<sample>::size_type i = 0; i != test.size(); ++i)
{
vector<double> vd;
for (vector<sample>::size_type j = 0; j != train.size(); ++j)
{
vd.push_back(euclideanDistance(test[i].features, train[j].features));
}
dm.push_back(vd);
}
}
// K-近邻法的实现
// 设定不同的 k 值,给每个测试样例予以一个类型
// 距离和权重成反比
void knnProcess(vector<sample>& test, const vector<sample>& train, const vector<vector<double> >& dm, unsigned int k)
{
for (vector<sample>::size_type i = 0; i != test.size(); ++i)
{
multimap<double, string> dts; //保存与测试样本i距离最近的k个点
for (vector<double>::size_type j = 0; j != dm[i].size(); ++j)
{
if (dts.size() < k) //把前面k个插入dts中
{
dts.insert(make_pair(dm[i][j], train[j].type)); //插入时会自动排序,按dts中的double排序,最小的排在最后
}
else
{
multimap<double, string>::iterator it = dts.end();
--it;
if (dm[i][j] < it->first) //把当前测试样本i到当前训练样本之间的欧氏距离与dts中最小距离比较,若更小就更新dts
{
dts.erase(it);
dts.insert(make_pair(dm[i][j], train[j].type));
}
}
}
map<string, double> tds;
string type = "";
double weight = 0.0;
//下面for循环主要是求出与测试样本i最邻近的k个样本点中大多数属于的类别,即将其作为测试样本点i的类别
for (multimap<double, string>::const_iterator cit = dts.begin(); cit != dts.end(); ++cit)
{
// 不考虑权重的情况,在 k 个样例中只要出现就加 1
// ++tds[cit->second];
// 这里是考虑距离与权重的关系,距离越大权重越小
tds[cit->second] += 1.0 / cit->first;
if (tds[cit->second] > weight)
{
weight = tds[cit->second];
type = cit->second; //保存一下类别
}
}
test[i].type = type;
}
}
// 输出结果
// 输出的格式和训练样本的格式一样
// 每行表示一个样例,第一个元素是该样例的类型,后面是该样例的特征向量
// 例如:
/*
a 1 2 3 2 4
b 2 3 4 2 1
b 8 7 2 3 5
a -3 -2 2 4 0
d -4 -4 -4 -4 -4
a 1 2 3 4 4
b 4 4 3 2 1
c 3 3 3 2 4
d 0 0 1 1 -2
*/
void writeTest(const vector<sample>& test, const string& file)
{
ofstream fout(file.c_str());
if (!fout)
{
cerr << "File error!" << endl;
exit(1);
}
for (vector<sample>::size_type i = 0; i != test.size(); ++i)
{
fout << test[i].type << '\t';
for (vector<double>::size_type j = 0; j != test[i].features.size(); ++j)
{
fout << test[i].features[j] << ' ';
}
fout << endl;
}
}
// 封装
void knn(const string& file1, const string& file2, const string& file3, int k)
{
vector<sample> train, test;
readTrain(train, file1.c_str());
readTest(test, file2.c_str());
vector<vector<double> > dm;
initDistanceMatrix(dm, train, test);
knnProcess(test, train, dm, k);
writeTest(test, file3.c_str());
}
// 测试
int main()
{
knn("train.txt", "test.txt", "result.txt", 5);
return 0;
}train.txt:
a 1 2 3 4 5
b 5 4 3 2 1
c 3 3 3 3 3
d -3 -3 -3 -3 -3
a 1 2 3 4 4
b 4 4 3 2 1
c 3 3 3 2 4
d 0 0 1 1 -2
test.txt:
1 2 3 2 4
2 3 4 2 1
8 7 2 3 5
-3 -2 2 4 0
-4 -4 -4 -4 -4
1 2 3 4 4
4 4 3 2 1
3 3 3 2 4
0 0 1 1 -2
result.txt:
a 1 2 3 2 4
b 2 3 4 2 1
b 8 7 2 3 5
a -3 -2 2 4 0
d -4 -4 -4 -4 -4
a 1 2 3 4 4
b 4 4 3 2 1
c 3 3 3 2 4
d 0 0 1 1 -2
相关文章推荐
- .Net 程序集按需加载机制
- 【算法设计与数据结构】为何程序员喜欢将INF设置为0x3f3f3f3f?
- equal() 和 == 的区别
- 完全二叉树的深度优先搜素
- 利用switch解决问题 课后题目
- CodeForces 603C/604E Lieges of Legendre SG函数
- @autowired详解
- 黑马程序员——Java重点基础之集合框架(四)
- Java-对象排序
- servlet (1) 基础
- 集合---1
- HDU 1175 连连看 (DFS + 剪枝)
- comparator接口与Comparable接口的区别
- Android - Buttons
- JavaScript 数组乱序方法
- 【转载】COM 组件设计与应用(八)——实现多接口
- 如何利用MVC+EF实现前台传值
- iOS 轮播图 KDCycleBannerView
- LeetCode Longest Valid Parentheses 括号匹配
- 基于TestNG 与Selenium 的自动化测试设计与实施
