最小生成树——Prim(普利姆)算法
2015-11-20 15:21
591 查看
【0】README
0.1) 本文总结于 数据结构与算法分析, 源代码均为原创, 旨在 理解Prim算法的idea 并用 源代码加以实现;0.2)最小生成树的基础知识,参见 http://blog.csdn.net/pacosonswjtu/article/details/49947085
【1】Prim算法相关
1.1)计算最小生成树的一种方法是使其连续地一步一步长成。在每一步, 都要吧一个节点当做根并往上加边,这样也就把相关联的顶点加到增长中的树上;1.2)在算法中的任一时刻, 我们都可以看到一个已经添加到树上的顶点集, 而其余顶点尚未加到这颗树中。此时, 算法在每一阶段都可以通过选择边(u, v),使得(u, v)的值是所有u 在树上但v不在树上的边的值中的最小者, 而找出一个新的顶点并吧它添加到这颗树中;
1.3)具体步骤概括为:
step1)给定一个顶点为根节点;
step2)每一步加一条边和一个顶点; (这也迎合了 顶点个数-边个数=1 );
1.4)看个荔枝:
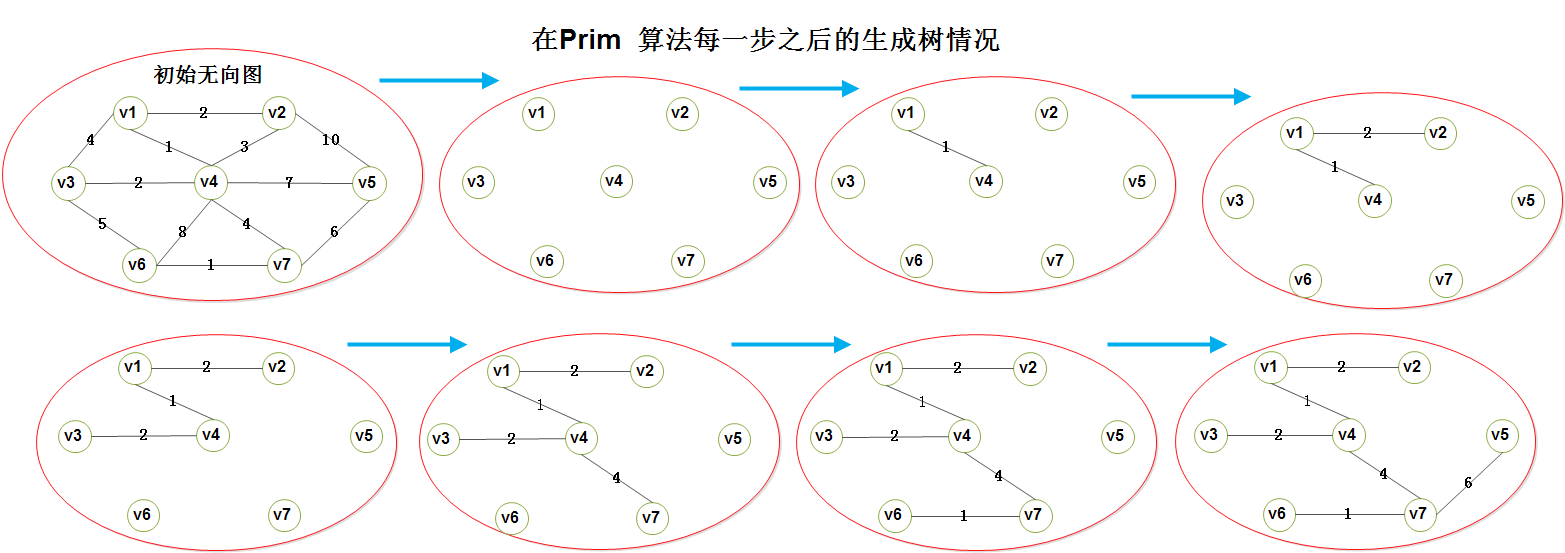
对上图的分析(Analysis):
A1)可以看到, 其实Prim算法基本上和求最短路径的 Dijkstra算法一样, 因此和前面一样,我们对每一个顶点保留值 Dv和Pv 以及一个指标,指示该顶点是已知的还是未知的。这里,Dv是连接v 到已知顶点的最短边的权, 而 Pv则是导致Dv改变的最后的顶点。
A2)算法的其余部分一样, 唯一不同的是: 由于Dv的定义不同, 因此它的更新法则不一样。事实上,Prim算法的更新法则比 Dijkstra算法简单:在每一个顶点v被选取后, 对于每一个与 v 邻接的未知的w, Dw=min(Dw, Cw,v);
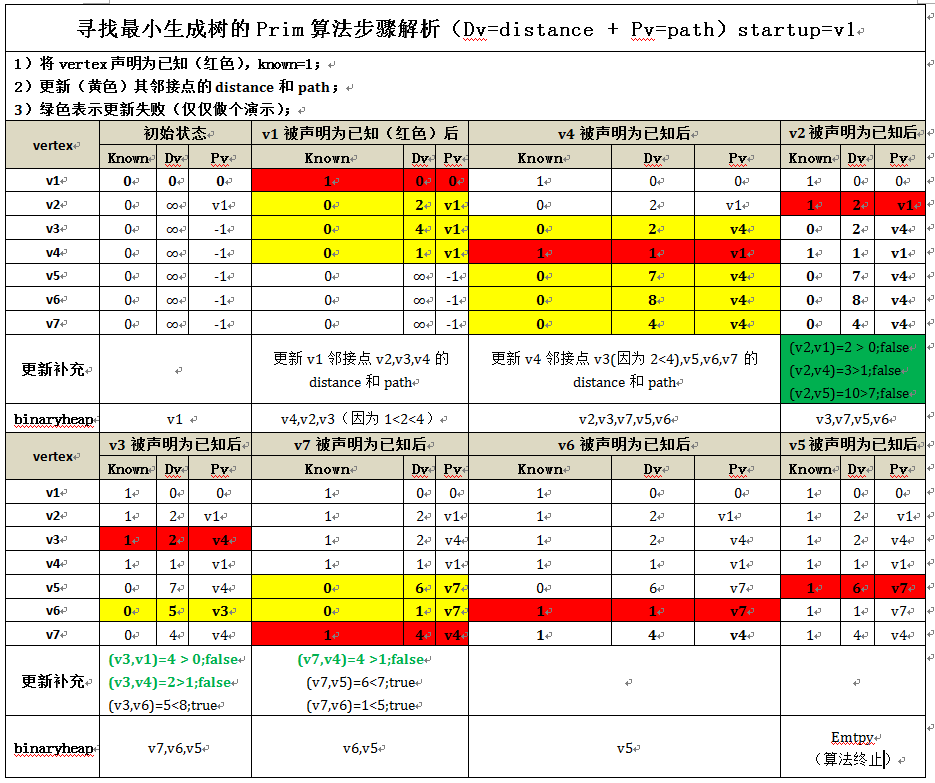
对上图的分析(Analysis):
A1)该算法整个的实现实际上和 Dijkstra算法的实现是一样的, 对于 Dijkstra算法分析所做的每一件事都可以用到这里。 不过要注意, Prim算法是在无向图上运行的, 因此当编写代码的时候要记住要吧每一条变都要放到两个邻接表中。
A2)不用堆时的运行时间为O(|V|^2), 它对于稠密图来说是最优的; 使用二叉堆的运行时间为 O(|E|log|V|), 它对于稀疏图是一个好的界限;
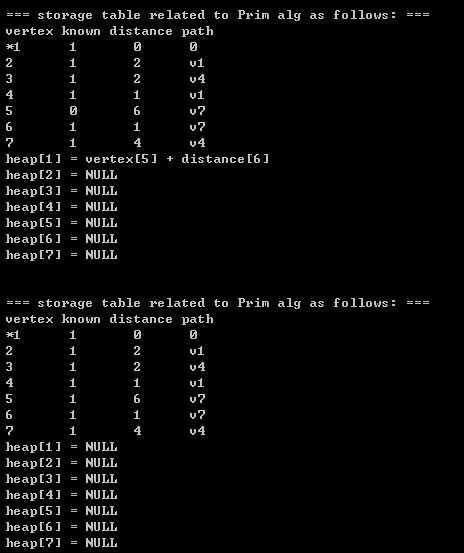
【2】source code + printing results(将我的代码打印结果 同 上图中的手动模拟的prim算法的结果进行比较,你会发现, 它们的结果完全相同,这也证实了我的代码的可行性)
2.1)download source code: https://github.com/pacosonTang/dataStructure-algorithmAnalysis/tree/master/chapter9/p237_prim2.2)source code at a glance(for complete code , please click the given link above):
#include "prim.h"
//allocate the memory for initializing unweighted table
WeightedTable *initWeightedTable(int size)
{
WeightedTable* table;
int i;
table = (WeightedTable*)malloc(sizeof(WeightedTable) * size);
if(!table)
{
Error("out of space ,from func initWeightedTable");
return NULL;
}
for(i = 0; i < size; i++)
{
table[i] = makeEmptyWeightedTable();
if(!table[i])
return NULL;
}
return table;
}
// allocate the memory for every element in unweighted table
WeightedTable makeEmptyWeightedTable()
{
WeightedTable element;
element = (WeightedTable)malloc(sizeof(struct WeightedTable));
if(!element)
{
Error("out of space ,from func makeEmptyWeightedTable");
return NULL;
}
element->known = 0; // 1 refers to accessed , also 0 refers to not accessed
element->distance = MaxInt;
element->path = -1; // index starts from 0 and -1 means the startup vertex unreaches other vertexs
return element;
}
// allocate the memory for storing index of vertex in heap and let every element -1
int *makeEmptyArray(int size)
{
int *array;
int i;
array = (int*)malloc(size * sizeof(int));
if(!array)
{
Error("out of space ,from func makeEmptyArray");
return NULL;
}
for(i=0; i<size; i++)
array[i] = -1;
return array;
}
//computing the unweighted shortest path between the vertex under initIndex and other vertexs
void prim(AdjTable* adj, int size, int startVertex, BinaryHeap bh)
{
int adjVertex;
int tempDistance;
WeightedTable* table;
int vertex;
AdjTable temp;
Distance tempDisStruct;
int *indexOfVertexInHeap;
int indexOfHeap;
table = initWeightedTable(size);
tempDisStruct = makeEmptyDistance();
indexOfVertexInHeap = makeEmptyArray(size);
tempDisStruct->distance = table[startVertex-1]->distance;
tempDisStruct->vertexIndex = startVertex-1;
insert(tempDisStruct, bh, indexOfVertexInHeap); // insert the (startVertex-1) into the binary heap
table[startVertex-1]->distance = 0;// update the distance
table[startVertex-1]->path = 0;// update the path of starting vertex
while(!isEmpty(bh))
{
vertex = deleteMin(bh, indexOfVertexInHeap).vertexIndex; // return the minimal element in binary heap
//printBinaryHeap(bh);
table[vertex]->known = 1; // update the vertex as accessed, also let responding known be 1
temp = adj[vertex]->next;
while(temp)
{
adjVertex = temp->index;
if(table[adjVertex]->known == 1) // judge whether table[adjVertex]->known is 1 or not
{
temp = temp->next;
continue;
}
//tempDistance = table[vertex]->distance + temp->weight; // update the distance
tempDistance = temp->weight;
if(tempDistance < table[adjVertex]->distance)
{
table[adjVertex]->distance = tempDistance;
table[adjVertex]->path = vertex; //update the path of adjVertex, also responding path evaluated as vertex
// key, we should judge whether adjVertex was added into the binary heap
//if true , obviously the element has been added into the binary heap(so we can't add the element into heap once again)
if(indexOfVertexInHeap[adjVertex] != -1)
{
indexOfHeap = indexOfVertexInHeap[adjVertex];
bh->elements[indexOfHeap]->distance = tempDistance; // update the distance of corresponding vertex in binary heap
}
else // if not ture
{
tempDisStruct->distance = table[adjVertex]->distance;
tempDisStruct->vertexIndex = adjVertex;
insert(tempDisStruct, bh, indexOfVertexInHeap); // insert the adjVertex into the binary heap
}
}
temp = temp->next;
}
printPrim(table, size, startVertex);
printBinaryHeap(bh);
printf("\n");
}
printf("\n");
}
//print unweighted table
void printPrim(WeightedTable* table, int size, int startVertex)
{
int i;
char *str[4] =
{
"vertex",
"known",
"distance",
"path"
};
printf("\n\t === storage table related to Prim alg as follows: === ");
printf("\n\t %6s%6s%9s%5s", str[0], str[1], str[2], str[3]);
for(i=0; i<size; i++)
{
if(i != startVertex-1 && table[i]->path!=-1)
printf("\n\t %-3d %3d %5d v%-3d ", i+1, table[i]->known, table[i]->distance, table[i]->path+1);
else if(table[i]->path == -1)
printf("\n\t %-3d %3d %5d %-3d ", i+1, table[i]->known, table[i]->distance, table[i]->path);
else
printf("\n\t *%-3d %3d %5d %-3d ", i+1, table[i]->known, table[i]->distance, 0);
}
}
int main()
{
AdjTable* adj;
BinaryHeap bh;
int size = 7;
int capacity;
int i;
int j;
int startVertex;
int adjTable[7][7] =
{
{0, 2, 4, 1, 0, 0, 0},
{2, 0, 0, 3, 10, 0, 0},
{4, 0, 0, 2, 0, 5, 0},
{1, 3, 2, 0, 7, 8, 4},
{0, 10, 0, 7, 0, 0, 6},
{0, 0, 5, 8, 0, 0, 1},
{0, 0, 0, 4, 6, 1, 0},
};
printf("\n\n\t ====== test for Prim alg finding weighted shortest path from adjoining table ======\n");
adj = initAdjTable(size);
printf("\n\n\t ====== the initial weighted adjoining table is as follows:======\n");
for(i = 0; i < size; i++)
for(j = 0; j < size; j++)
if(adjTable[i][j])
insertAdj(adj, j, i, adjTable[i][j]); // insertAdj the adjoining table over
printAdjTable(adj, size);
capacity = 7;
bh = initBinaryHeap(capacity+1);
//conducting prim alg to find minimum spanning tree(MST)
startVertex = 1; // you should know our index for storing vertex starts from 0
prim(adj, size, startVertex, bh);
return 0;
}2.3)printing results:
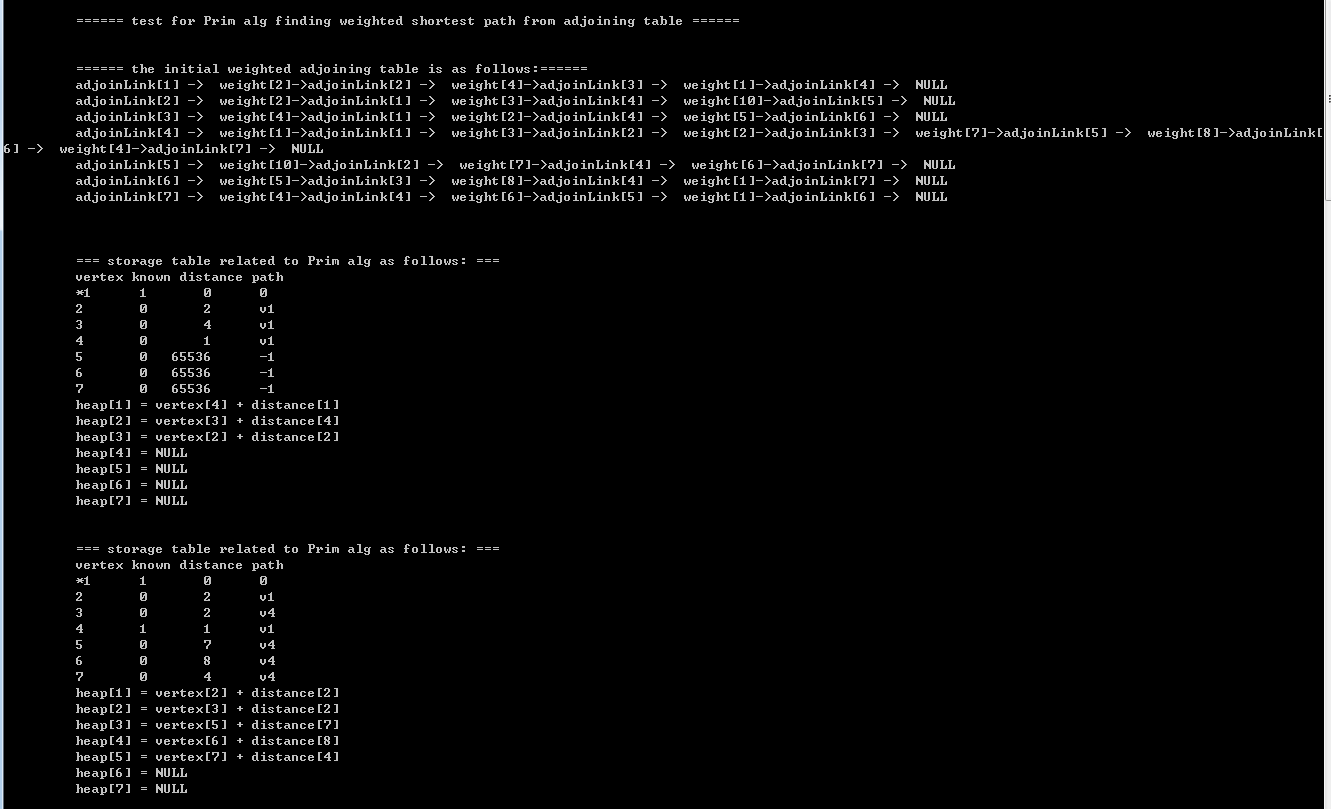
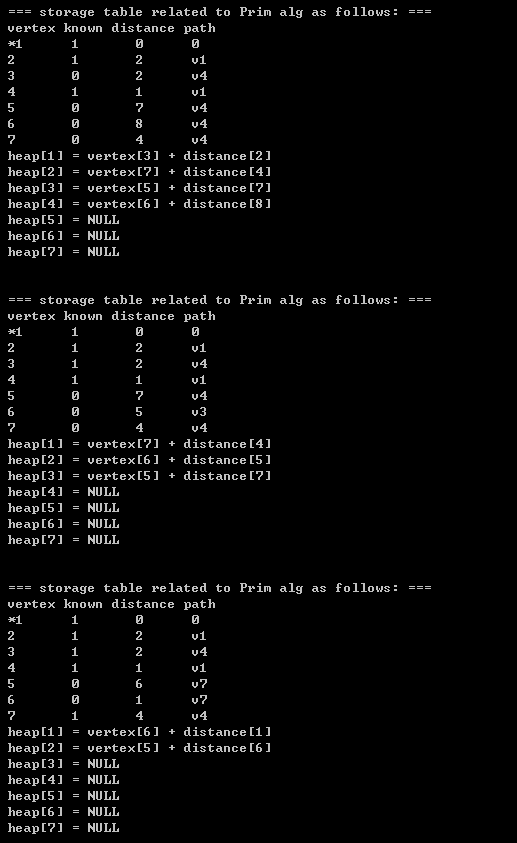
相关文章推荐
- Lua教程(七):数据结构详解
- 解析从源码分析常见的基于Array的数据结构动态扩容机制的详解
- C#数据结构揭秘一
- 数据结构之Treap详解
- JavaScript数据结构和算法之图和图算法
- Java数据结构及算法实例:冒泡排序 Bubble Sort
- Java数据结构及算法实例:插入排序 Insertion Sort
- Java数据结构及算法实例:考拉兹猜想 Collatz Conjecture
- java数据结构之java实现栈
- java数据结构之实现双向链表的示例
- Java数据结构及算法实例:选择排序 Selection Sort
- Java数据结构及算法实例:朴素字符匹配 Brute Force
- Java数据结构及算法实例:汉诺塔问题 Hanoi
- Java数据结构及算法实例:快速计算二进制数中1的个数(Fast Bit Counting)
- java数据结构和算法学习之汉诺塔示例
- Java数据结构及算法实例:三角数字
- Java数据结构之简单链表的定义与实现方法示例
- 数据结构之AVL树详解
- qqwry.dat的数据结构图文解释第1/2页
- JavaScript中数据结构与算法(五):经典KMP算法
