android 之 桌面的小控件AppWidget
2015-11-11 21:59
609 查看
AppWidget是创建的桌面窗口小控件,在这个小控件上允许我们进行一些操作(这个视自己的需要而定)。作为菜鸟,我在这里将介绍一下AppWeight的简单使用。
1.在介绍AppWidget之前,我们先来了解一下PendingIntent和RemoteViews;
PendingIntent:A description of an Intent and target action to perform with it. Instances of this class are created with
翻译:通过PendingIntent来描述一个Intent和target action,这个类的实例和getActivity,getActivites,getBroadCast,getService一起创建:返回的对象能够传给其他程序,以便它们能在后来执行你想让他们执行的动作。
结合Mars老师的讲解可以这样来理解:PendingIntent能够包含一个Intent对象,能够将这个Intent传递给其他的应用,当满足一定条件时,就会执行这个Intent中包含的动作。getActivity和getActivities是为了启动活动,getBroadcast是为了发送广播,getService是为了开启一个服务。(这个在下面有讲解)
RemoteViews:A class that describes a view hierarchy that can be displayed in another process. The hierarchy is inflated from a layout resource file, and this class provides some basic operations for modifying the content of the inflated hierarchy.
翻译:remoteviews:一个类描述了一个视图的层次结构,可以显示在另一个进程。该层次结构从布局资源文件中增长,该类提供一些基本操作来修改虚化层次结构的内容。
简言之就是RemoteView代表的是显示在桌面上的appwidget这整个布局,包括设置的按钮,图片什么的。。。
2.了解了上面的概念,就可以更好的理解AppWeight了。
实现AppWeige的步骤:
文件的结构:
1).在res下新建一个文件夹,里面新建一个类型为appwidget_provider的xml文件。这个是代表显示在桌面上的整个布局(只是布局的框架,不包含细节,至于显示的内容需要引用另一个布局文件),示例中我的xml文件名为example_appwidget_provider.xml:
2).在layout中新建一个xml文件来作为在appwidget中的布局显示,就是上面的@layout/example_appwidget中的example_appwidget。
3).新建一个Activity,这个Activity继承AppWidgetProvider,复写其中的方法。在这里注释的代码实现了点击AppWidget中的按钮就启动另一个Activity,未注释的代码实现了ImagView中的Image的替换:值得注意的是,AppWiget所进行的活动并不与当前Main_Activity所在的线程在同一个线程中,因此这里并不能像在主线程中那样操作布局内容,AppWiget的操作方法可以看下面代码。
4).在AndroidManifest.xml文件中的<application 中声明。
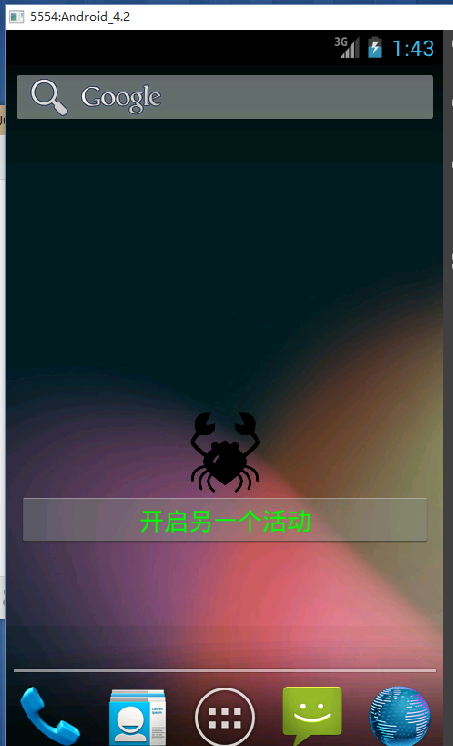
效果图:
1.在介绍AppWidget之前,我们先来了解一下PendingIntent和RemoteViews;
PendingIntent:A description of an Intent and target action to perform with it. Instances of this class are created with
getActivity,
getActivities,
getBroadcast, and
getService; the returned object can be handed to other applications so that they can perform the action you described on your behalf at a later time.
翻译:通过PendingIntent来描述一个Intent和target action,这个类的实例和getActivity,getActivites,getBroadCast,getService一起创建:返回的对象能够传给其他程序,以便它们能在后来执行你想让他们执行的动作。
结合Mars老师的讲解可以这样来理解:PendingIntent能够包含一个Intent对象,能够将这个Intent传递给其他的应用,当满足一定条件时,就会执行这个Intent中包含的动作。getActivity和getActivities是为了启动活动,getBroadcast是为了发送广播,getService是为了开启一个服务。(这个在下面有讲解)
RemoteViews:A class that describes a view hierarchy that can be displayed in another process. The hierarchy is inflated from a layout resource file, and this class provides some basic operations for modifying the content of the inflated hierarchy.
翻译:remoteviews:一个类描述了一个视图的层次结构,可以显示在另一个进程。该层次结构从布局资源文件中增长,该类提供一些基本操作来修改虚化层次结构的内容。
简言之就是RemoteView代表的是显示在桌面上的appwidget这整个布局,包括设置的按钮,图片什么的。。。
2.了解了上面的概念,就可以更好的理解AppWeight了。
实现AppWeige的步骤:
文件的结构:
1).在res下新建一个文件夹,里面新建一个类型为appwidget_provider的xml文件。这个是代表显示在桌面上的整个布局(只是布局的框架,不包含细节,至于显示的内容需要引用另一个布局文件),示例中我的xml文件名为example_appwidget_provider.xml:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <appwidget-provider xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" android:minWidth = "280dp" android:minHeight = "100dp" android:updatePeriodMillis = "864000000" android:initialLayout="@layout/example_appwidget"> </appwidget-provider> <!-- 上面设置了布局的宽、高、更新时间周期(毫秒)、包含的布局 -->
2).在layout中新建一个xml文件来作为在appwidget中的布局显示,就是上面的@layout/example_appwidget中的example_appwidget。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" android:orientation="vertical" > <!-- 这里是显示在桌面的appWidget的布局 --> <ImageView android:id="@+id/imageId" android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="60dp" android:src="@drawable/cancer"/> <Button android:id="@+id/changeButton" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="40dp" android:textColor="#00ff00" android:text="开启另一个活动"/> </LinearLayout>
3).新建一个Activity,这个Activity继承AppWidgetProvider,复写其中的方法。在这里注释的代码实现了点击AppWidget中的按钮就启动另一个Activity,未注释的代码实现了ImagView中的Image的替换:值得注意的是,AppWiget所进行的活动并不与当前Main_Activity所在的线程在同一个线程中,因此这里并不能像在主线程中那样操作布局内容,AppWiget的操作方法可以看下面代码。
package com.example.appwight;
import android.app.PendingIntent;
import android.appwidget.AppWidgetManager;
import android.appwidget.AppWidgetProvider;
import android.content.ComponentName;
import android.content.Context;
import android.content.Intent;
import android.widget.RemoteViews;
public class ExampleAppWidgetProvider extends AppWidgetProvider{
//广播名称,需要在AppWidget Manifest.xml文件中声明
private static final String UPDATE_INTENT = "com.example.appwidget";
@Override
public void onReceive(Context context, Intent intent) {
//接受广播的时候调用
//接受广播Action
String action = intent.getAction();
//当接受到指定的广播时,就执行下main代码
if (UPDATE_INTENT.equals(action)) {
System.out.println("action=======>"+UPDATE_INTENT);
RemoteViews remoteViews = new RemoteViews(context.getPackageName(), R.layout.example_appwidget);
//第一个参数:ImagView的Id,第二个参数:用来替换的图片
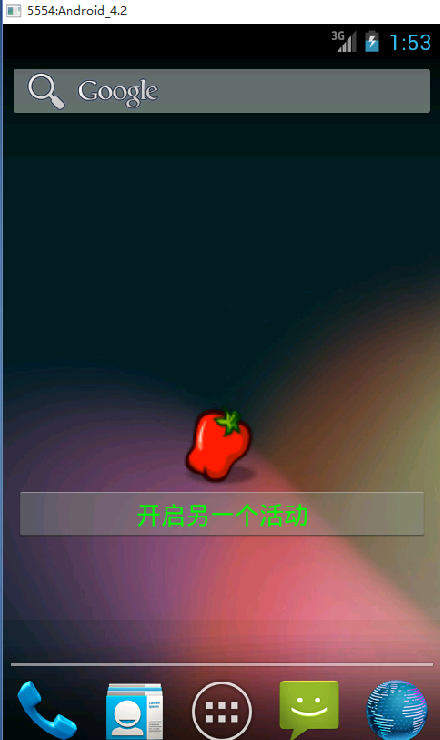
remoteViews.setImageViewResource(R.id.imageId, R.drawable.chilli);
AppWidgetManager appWidgetManager = AppWidgetManager.getInstance(context);
//ComponentName也代表AppWidget控件,与RemoteViews不同的是。前者只是代表着“整个”控件,后者包含Button,ImageView,,,等内容
ComponentName componentName = new ComponentName(context, ExampleAppWidgetProvider.class);
appWidgetManager.updateAppWidget(componentName, remoteViews);
}else {
//调用父类的onReceive方法
super.onReceive(context, intent);
}
}
@Override
public void onUpdate(Context context, AppWidgetManager appWidgetManager,
int[] appWidgetIds) {
super.onUpdate(context, appWidgetManager, appWidgetIds);
System.out.println("onUpdate");
for (int i = 0; i < appWidgetIds.length; i++) {
//Intent intent = new Intent(context, SecondActivity.class);
Intent intent = new Intent();
intent.setAction(UPDATE_INTENT);
/*
* pendingIntent可以包含一个intent
* 第一个参数是当前上下文,第二个参数是包含的intent
* getAcitivity表明这个PendingIntent的目的是为了启动一个activity,此外还有getService(),和getBroadcast()
*PendingIntent pendingIntent = PendingIntent.getActivity(context, 0, intent, 0);
*/
PendingIntent pendingIntent = PendingIntent.getBroadcast(context, 0, intent, 0);
//remoteView代表的是AppWidget的整个布局,第一个参数是包名,第二个参数是AppWidget的布局
RemoteViews remoteViews = new RemoteViews(context.getPackageName(), R.layout.example_appwidget);
//为remoteVIew中的按钮设置点击事件,第一个为按钮的id,第二个参数为要启动的PendingIntent。
remoteViews.setOnClickPendingIntent(R.id.changeButton, pendingIntent);
//更新AppWidget,第一个参数为表明是当前哪个AppWidget(因为可以在桌面上创建多个AppWidget)
//第二个参数为要更新的RemoteViews的对象
appWidgetManager.updateAppWidget(appWidgetIds[i], remoteViews);
}
}
@Override
public void onDeleted(Context context, int[] appWidgetIds) {
//删除AppWidget的时候调用
super.onDeleted(context, appWidgetIds);
System.out.println("onDeleted");
}
@Override
public void onEnabled(Context context) {
//当AppWidget被创建的时候调用
super.onEnabled(context);
System.out.println("onEnabled");
}
@Override
public void onDisabled(Context context) {
//当最后一个AppWidget被删除的时候调用
super.onDisabled(context);
System.out.println("onDisable");
}
}4).在AndroidManifest.xml文件中的<application 中声明。
<receiver android:name="com.example.appwight.ExampleAppWidgetProvider"> //过滤广播 <intent-filter > <action android:name="android.appwidget.action.APPWIDGET_UPDATE"/> <action android:name="com.example.appwidget"/> </intent-filter> //元数据,将布局与类绑定 <meta-data android:name="android.appwidget.provider" android:resource="@xml/example_appwidget_provider"/> </receiver>
效果图:


相关文章推荐
- Android WebRTC视频旋转问题
- java.lang.NoClassDefFoundError: android.support.v4.view.ViewConfigurationCompat
- android-csv-variants
- 在Unity中生成二维码
- Android之android.intent.category.LAUNCHER的用途和使用
- ios单例传值
- ios之手动内存管理
- 高效开发Android App的10个建
- 技巧-如何在android项目中将布局文件存放在不同目录中
- 【iOS】集成支付宝钱包支付iOS SDK的方法与经验
- OpenGL ES 3.0之Fragment buffer objects(FBO)详解(一)
- 转:Oculus Unity Development Guide开发指南(2015-7-21更新)
- git stash使用 笔记
- iOS.swift 如何设置tableview禁止上下滚动
- (NO.00003)iOS游戏简单的机器人投射游戏成形记(十九)
- GestureDetector类及其用法
- (NO.00003)iOS游戏简单的机器人投射游戏成形记(十九)
- (NO.00003)iOS游戏简单的机器人投射游戏成形记(十九)
- Android: 水平滑动线性布局的实现
- IOS: iPhone键盘通知与键盘定制
