验证
2015-11-09 21:18
309 查看
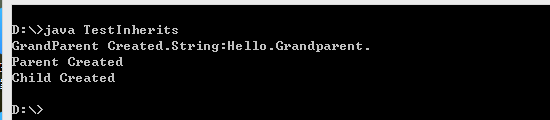
1.通过super()调用父类的有参构造方法,super语句必须是子类构造函数的第一句。
父类中使用了默认的构造方法或者有无参的构造方法,子类的构造函数会自动调用。
class Grandparent
{
public Grandparent()
{ System.out.println("GrandParent Created.");}
public Grandparent(String string)
{System.out.println("GrandParent Created.String:" + string);}
}
class Parent extends Grandparent
{
public Parent()
{
super("Hello.Grandparent.");
System.out.println("Parent Created");
}
}
class Child extends Parent
{ public Child()
{System.out.println("Child Created");}
}
public class TestInherits
{public static void main(String args[])
{Child c = new Child();}
}
class Grandparent
{
public Grandparent()
{ System.out.println("GrandParent Created.");}
public Grandparent(String string)
{System.out.println("GrandParent Created.String:" + string);}
}
class Parent extends Grandparent
{
public Parent()
{
// super("Hello.Grandparent.");
System.out.println("Parent Created");
}
}
class Child extends Parent
{ public Child()
{System.out.println("Child Created");}
}
public class TestInherits
{public static void main(String args[])
{Child c = new Child();}
}

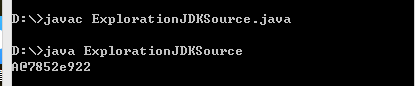
public class ExplorationJDKSource {
/**
* @param args
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println(new A());
}
}
class A{}
在java中,有时会遇到子类中的成员变量或方法与父类中的成员变量或方法同名。因为子类的优先级高,所以子类中的同名的成员或方法就隐藏了父类中的成员变量或方法,但是如果我们想要使用父类中的成员变量或方法,就要用到super.
package com;
class Country
{
String name;
void value()
{
name="Chine";
}
}
class City extends Country
{
String name;
void value()
{
name="hebei";
super.value();
System.out.println(name);
System.out.println(super.name);
}
}
public class T {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
City c=new City();
c.value();
}
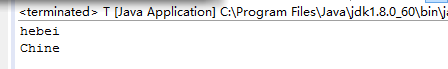
为了在子类中引用父类中的成员变量和方法value(),在代码中使用了super,super.name,super.value(),若不调用super.value()时,super.name返回的是父类成员的默认值null,调用方法时,super.value()方法先把成员变量name赋值为china,再用super.name调用父类成员变量的值。
继承与接口
package com;
interface Flyanimal
{void fly();}
class Insect
{
int legnum=6;
}
class Bird
{
int legnum=2;
void egg(){};
}
class Ant extends Insect implements Flyanimal
{
public void fly()
{System.out.println("Ant can fly");}
}
class Pigeon extends Bird implements Flyanimal
{
public void fly()
{System.out.println("Pigegon can fly");}
public void egg()
{System.out.println("Pigegon can lay eggs");}
}
public class T1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
Ant a=new Ant();
a.fly();
System.out.println("Ant's legnum is"+a.legnum);
Pigeon p=new Pigeon();
p.fly();
p.egg();
}
}

父类中使用了默认的构造方法或者有无参的构造方法,子类的构造函数会自动调用。
class Grandparent
{
public Grandparent()
{ System.out.println("GrandParent Created.");}
public Grandparent(String string)
{System.out.println("GrandParent Created.String:" + string);}
}
class Parent extends Grandparent
{
public Parent()
{
super("Hello.Grandparent.");
System.out.println("Parent Created");
}
}
class Child extends Parent
{ public Child()
{System.out.println("Child Created");}
}
public class TestInherits
{public static void main(String args[])
{Child c = new Child();}
}

class Grandparent
{
public Grandparent()
{ System.out.println("GrandParent Created.");}
public Grandparent(String string)
{System.out.println("GrandParent Created.String:" + string);}
}
class Parent extends Grandparent
{
public Parent()
{
// super("Hello.Grandparent.");
System.out.println("Parent Created");
}
}
class Child extends Parent
{ public Child()
{System.out.println("Child Created");}
}
public class TestInherits
{public static void main(String args[])
{Child c = new Child();}
}

public class ExplorationJDKSource {
/**
* @param args
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println(new A());
}
}
class A{}

在java中,有时会遇到子类中的成员变量或方法与父类中的成员变量或方法同名。因为子类的优先级高,所以子类中的同名的成员或方法就隐藏了父类中的成员变量或方法,但是如果我们想要使用父类中的成员变量或方法,就要用到super.
package com;
class Country
{
String name;
void value()
{
name="Chine";
}
}
class City extends Country
{
String name;
void value()
{
name="hebei";
super.value();
System.out.println(name);
System.out.println(super.name);
}
}
public class T {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
City c=new City();
c.value();
}

为了在子类中引用父类中的成员变量和方法value(),在代码中使用了super,super.name,super.value(),若不调用super.value()时,super.name返回的是父类成员的默认值null,调用方法时,super.value()方法先把成员变量name赋值为china,再用super.name调用父类成员变量的值。
继承与接口
package com;
interface Flyanimal
{void fly();}
class Insect
{
int legnum=6;
}
class Bird
{
int legnum=2;
void egg(){};
}
class Ant extends Insect implements Flyanimal
{
public void fly()
{System.out.println("Ant can fly");}
}
class Pigeon extends Bird implements Flyanimal
{
public void fly()
{System.out.println("Pigegon can fly");}
public void egg()
{System.out.println("Pigegon can lay eggs");}
}
public class T1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
Ant a=new Ant();
a.fly();
System.out.println("Ant's legnum is"+a.legnum);
Pigeon p=new Pigeon();
p.fly();
p.egg();
}
}

相关文章推荐
- mysql/mairadb双主复制
- [LeetCode] Search a 2D Matrix II
- Android apk反编译(附图+工具)
- TCP/IP详解学习笔记(1)-- 概述
- mysql半主从复制
- Python编写微信打飞机小游戏(三)
- AJAX 跨域请求 - JSONP获取JSON数据
- 初级案例
- JAVA反射系列之Method,java.lang.reflect.Method的使用
- Python/scikit-learn机器学习库(特征选取)
- Angular JS 学习 -- 服务Service
- 大道至简第六章读后感
- LightOJ 1294 - Positive Negative Sign (规律)
- SOJ 3300_Stockholm Coins
- SOJ 3300_Stockholm Coins
- JAVA中使用AES加密
- 搭建Erlang语言开发环境(文本编辑器+Erlang OTP,不是绑定IDE的环境)
- ionic tab选项卡置于顶部
- css布局 : 居中问题
- 课堂作业
