HDU 3220 Alice’s Cube
2015-11-07 22:04
375 查看
[align=left]Problem Description[/align]
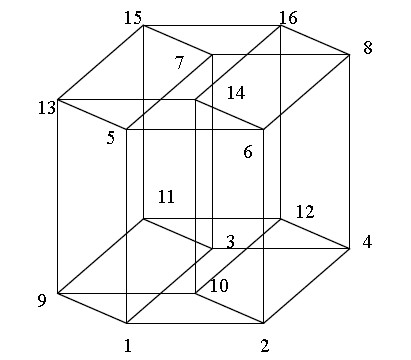
Alice has received a hypercube toy as her birthday present. This hypercube has 16 vertices, numbered from 1 to 16, as illustrated below. On every vertex, there is a light bulb that can be turned on or off. Initially, eight of the light bulbs are turned on and
the other eight are turned off. You are allowed to switch the states of two adjacent light bulbs with different states (“on” to “off”, and “off” to “on”; specifically, swap their states) in one operation.
Given the initial state of the lights, your task is to calculate the minimum number of steps needed to achieve the target state, in which the light bulbs on the sub cube (1,2,3,4)-(5,6,7,8) are turned off, and the rest of them are turned on.
[align=left]Input[/align]
There are multiple test cases. The first line of the input contains an integer T, meaning the number of the test cases. There are about 13000 test cases in total.
For each test case there are 16 numbers in a single line, the i-th number is 1 meaning the light of the i-th vertex on the picture is on, and otherwise it’s off.
[align=left]Output[/align]
For every test cases output a number with case number meaning the minimum steps needed to achieve the goal. If the number is larger than 3, you should output “more”.
[align=left]Sample Input[/align]
3
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1
0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 1 1 1 1 1 1
0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 1 0 1 1 1 1 1 1
[align=left]Sample Output[/align]
Case #1: 0
Case #2: 1
Case #3: more
[align=left]Source[/align]
2009 Asia Shanghai Regional Contest Host by DHU
[align=left]Recommend[/align]
zhuweicong | We have carefully selected several similar problems for you: 3221 3225 3222 3229 3228
打表+模拟
#include<cstdio>
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cstring>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
#include <cmath>
int vis[17];
int a11[20][8]= {1,2,2,3,2,3,3,4,
2,1,3,2,3,2,4,3,
2,3,1,2,3,4,2,3,
3,2,2,1,4,3,3,2,
2,3,3,4,1,2,2,3,
3,2,4,3,2,1,3,2,
3,4,2,3,2,3,1,2,
4,3,3,2,3,2,2,1
};
int main()
{
int t;
scanf("%d",&t);
int icase=0;
while(t--)
{
int x,j,i;
int sum=0;
int sum1=0;
int a[100];
int len=0;
// for(i=0;i<8;i++)
// {
// for(j=0;j<8;j++)
// {
// if(j==0)
// cout<<a11[i][j];
// else
// cout<<" "<<a11[i][j];
// }
// cout<<endl;
// }
memset(vis,0,sizeof(vis));
for(i=1; i<=16; i++)
{
scanf("%d",&x);
if(x==1)
{
vis[i]++;
sum1++;
}
else if(x==0)
sum++;
}
int ans=0;
for(i=9; i<=16; i++)
if(vis[i])
ans++;
if(ans==8)
{
printf("Case #%d: 0\n",++icase);
continue;
}
if(ans<5 || sum1!=8 &&sum!=8)
{
printf("Case #%d: more\n",++icase);
continue;
}
int res=0;
printf("Case #%d: ",++icase);
if(ans==7)
{
for(i=1; i<=8; i++)
{
if(vis[i])
for(j=9; j<=16; j++)
{
if(!vis[j])
{
res+=a11[i-1][j-9];
}
}
}
if(res<=3)
{
printf("%d\n",res);
}
else
printf("more\n");
}
if(ans==6)
{
res=99;
for(i=1; i<=8; i++)
{
if(vis[i])
for(j=9; j<=16; j++)
{
if(!vis[j])
{
a[len++]=a11[i-1][j-9];
}
}
}
// cout<<len<<endl;
res=min(res,a[0]+a[3]);
res=min(res,a[1]+a[2]);
if(res<=3)
{
printf("%d\n",res);
}
else
printf("more\n");
}
if(ans==5)
{
res=99;
for(i=1; i<=8; i++)
{
if(vis[i])
for(j=9; j<=16; j++)
{
if(!vis[j])
{
a[len++]=a11[i-1][j-9];
}
}
}
// cout<<len<<endl;
res=min(res,a[0]+a[4]+a[8]);
res=min(res,a[0]+a[5]+a[7]);
res=min(res,a[1]+a[3]+a[8]);
res=min(res,a[1]+a[5]+a[6]);
res=min(res,a[2]+a[3]+a[7]);
res=min(res,a[2]+a[4]+a[6]);
if(res<=3)
{
printf("%d\n",res);
}
else
printf("more\n");
}
}
return 0;
}

Alice has received a hypercube toy as her birthday present. This hypercube has 16 vertices, numbered from 1 to 16, as illustrated below. On every vertex, there is a light bulb that can be turned on or off. Initially, eight of the light bulbs are turned on and
the other eight are turned off. You are allowed to switch the states of two adjacent light bulbs with different states (“on” to “off”, and “off” to “on”; specifically, swap their states) in one operation.
Given the initial state of the lights, your task is to calculate the minimum number of steps needed to achieve the target state, in which the light bulbs on the sub cube (1,2,3,4)-(5,6,7,8) are turned off, and the rest of them are turned on.
[align=left]Input[/align]
There are multiple test cases. The first line of the input contains an integer T, meaning the number of the test cases. There are about 13000 test cases in total.
For each test case there are 16 numbers in a single line, the i-th number is 1 meaning the light of the i-th vertex on the picture is on, and otherwise it’s off.
[align=left]Output[/align]
For every test cases output a number with case number meaning the minimum steps needed to achieve the goal. If the number is larger than 3, you should output “more”.
[align=left]Sample Input[/align]
3
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1
0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 1 1 1 1 1 1
0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 1 0 1 1 1 1 1 1
[align=left]Sample Output[/align]
Case #1: 0
Case #2: 1
Case #3: more
[align=left]Source[/align]
2009 Asia Shanghai Regional Contest Host by DHU
[align=left]Recommend[/align]
zhuweicong | We have carefully selected several similar problems for you: 3221 3225 3222 3229 3228
打表+模拟
#include<cstdio>
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cstring>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
#include <cmath>
int vis[17];
int a11[20][8]= {1,2,2,3,2,3,3,4,
2,1,3,2,3,2,4,3,
2,3,1,2,3,4,2,3,
3,2,2,1,4,3,3,2,
2,3,3,4,1,2,2,3,
3,2,4,3,2,1,3,2,
3,4,2,3,2,3,1,2,
4,3,3,2,3,2,2,1
};
int main()
{
int t;
scanf("%d",&t);
int icase=0;
while(t--)
{
int x,j,i;
int sum=0;
int sum1=0;
int a[100];
int len=0;
// for(i=0;i<8;i++)
// {
// for(j=0;j<8;j++)
// {
// if(j==0)
// cout<<a11[i][j];
// else
// cout<<" "<<a11[i][j];
// }
// cout<<endl;
// }
memset(vis,0,sizeof(vis));
for(i=1; i<=16; i++)
{
scanf("%d",&x);
if(x==1)
{
vis[i]++;
sum1++;
}
else if(x==0)
sum++;
}
int ans=0;
for(i=9; i<=16; i++)
if(vis[i])
ans++;
if(ans==8)
{
printf("Case #%d: 0\n",++icase);
continue;
}
if(ans<5 || sum1!=8 &&sum!=8)
{
printf("Case #%d: more\n",++icase);
continue;
}
int res=0;
printf("Case #%d: ",++icase);
if(ans==7)
{
for(i=1; i<=8; i++)
{
if(vis[i])
for(j=9; j<=16; j++)
{
if(!vis[j])
{
res+=a11[i-1][j-9];
}
}
}
if(res<=3)
{
printf("%d\n",res);
}
else
printf("more\n");
}
if(ans==6)
{
res=99;
for(i=1; i<=8; i++)
{
if(vis[i])
for(j=9; j<=16; j++)
{
if(!vis[j])
{
a[len++]=a11[i-1][j-9];
}
}
}
// cout<<len<<endl;
res=min(res,a[0]+a[3]);
res=min(res,a[1]+a[2]);
if(res<=3)
{
printf("%d\n",res);
}
else
printf("more\n");
}
if(ans==5)
{
res=99;
for(i=1; i<=8; i++)
{
if(vis[i])
for(j=9; j<=16; j++)
{
if(!vis[j])
{
a[len++]=a11[i-1][j-9];
}
}
}
// cout<<len<<endl;
res=min(res,a[0]+a[4]+a[8]);
res=min(res,a[0]+a[5]+a[7]);
res=min(res,a[1]+a[3]+a[8]);
res=min(res,a[1]+a[5]+a[6]);
res=min(res,a[2]+a[3]+a[7]);
res=min(res,a[2]+a[4]+a[6]);
if(res<=3)
{
printf("%d\n",res);
}
else
printf("more\n");
}
}
return 0;
}
