树---求二叉搜索树中两节点的最低公共祖先(LCA)
2015-11-02 20:44
489 查看
一、问题描述
给定二叉搜索树(BST)中两节点,找出他们的最低公共祖先。
例如对于下图:
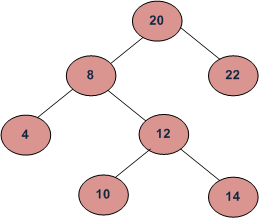
LCA(4, 14)=8; LCA(8, 10)=8.
二、问题求解
利用BST的性质,从根节点从上自下递归遍历BST。假设n1,n2都在BST中,并且n1 < n2。
(1)在遍历过程中,遇到的第一个值介于n1和n2之间的节点n,也即n1 =< n <= n2, 就是n1和n2的LCA。
(2)在遍历过程中,如果节点的值比n1和n2都大,那么LCA在节点的左子树。
(3)在遍历过程中,如果节点的值比n1和n2都小,那么LCA在节点的右子树。
三、代码
结果:
以上LCA函数的时间复杂度为O(h),h为二叉搜索树的高度,并且还会在函数调用栈中需要O(h)的额外空间,用以递归函数调用。我们可以改成迭代方法来做。并且在此提供生成二叉搜索树的另一种实现方式,也就是根据树的结构来插入。
迭代版本如下:
结果:
给定二叉搜索树(BST)中两节点,找出他们的最低公共祖先。
例如对于下图:

LCA(4, 14)=8; LCA(8, 10)=8.
二、问题求解
利用BST的性质,从根节点从上自下递归遍历BST。假设n1,n2都在BST中,并且n1 < n2。
(1)在遍历过程中,遇到的第一个值介于n1和n2之间的节点n,也即n1 =< n <= n2, 就是n1和n2的LCA。
(2)在遍历过程中,如果节点的值比n1和n2都大,那么LCA在节点的左子树。
(3)在遍历过程中,如果节点的值比n1和n2都小,那么LCA在节点的右子树。
三、代码
#include<iostream>
#include<stdlib.h>
using namespace std;
typedef int KeyType;
typedef struct BSTNode
{
KeyType key;
struct BSTNode *left;
struct BSTNode *right;
}BSTNode, *BSTree;
//插入元素。返回指向新树根的指针
BSTree Insert(BSTree T, KeyType x)
{//该插入过程,保证了是建立的二叉搜索树!!!
if(T == NULL)
{//T为空时,就建立新节点
T = (BSTNode*)malloc(sizeof(BSTNode));
T->key = x;
T->left = T->right = NULL;
}
else if(x < T->key)
{//将x递归插入到左子树
T->left = Insert(T->left, x);
}
else if(x > T->key)
{//将x递归插入到右子树
T->right = Insert(T->right, x);
}
//当x = T->key的情况就不用插入
return T;
}
//对于给定的树中两节点n1和n2,返回两者LCA的指针
//时间复杂度为O(h),h为树的高度!!!
BSTree LCA(BSTree T, int n1, int n2)
{
if (T == NULL) return NULL;
// 如果节点的值比n1和n2都大,那么LCA在节点的左子树
if (T->key > n1 && T->key > n2)
return LCA(T->left, n1, n2);
// 如果节点的值比n1和n2都小,那么LCA在节点的右子树
if (T->key < n1 && T->key < n2)
return LCA(T->right, n1, n2);
return T;
}
//打印排序后的二叉搜索树。中序遍历即可。
void PrintInOrderBST(BSTree T)
{//中序遍历后的二叉搜索树是有序序列!!!
if(T == NULL) return;
PrintInOrderBST(T->left);
cout<<T->key<<endl;
PrintInOrderBST(T->right);
}
int main()
{
BSTree bst = NULL;
//生成如图所示二叉搜索树。按先序插入。
bst = Insert(bst, 20);
bst = Insert(bst, 8);
bst = Insert(bst, 4);
bst = Insert(bst, 12);
bst = Insert(bst, 10);
bst = Insert(bst, 14);
bst = Insert(bst, 22);
cout<<"中序遍历BST : "<<endl;
PrintInOrderBST(bst);
cout<<"BST中两节点最小公共祖先:"<<endl;
BSTree lca1 = LCA(bst, 10, 14);
cout<<"LCA(10, 14) = "<<lca1->key<<endl;
BSTree lca2 = LCA(bst, 14, 8);
cout<<"LCA(14, 8) = "<<lca2->key<<endl;
BSTree lca3 = LCA(bst, 10, 22);
cout<<"LCA(10, 22) = "<<lca3->key<<endl;
return 0;
}结果:
中序遍历BST : 4 8 10 12 14 20 22 BST中两节点最小公共祖先: LCA(10, 14) = 12 LCA(14, 8) = 8 LCA(10, 22) = 20 Process returned 0 (0x0) execution time : 0.204 s Press any key to continue.
以上LCA函数的时间复杂度为O(h),h为二叉搜索树的高度,并且还会在函数调用栈中需要O(h)的额外空间,用以递归函数调用。我们可以改成迭代方法来做。并且在此提供生成二叉搜索树的另一种实现方式,也就是根据树的结构来插入。
迭代版本如下:
#include<iostream>
#include<stdlib.h>
using namespace std;
typedef int KeyType;
typedef struct BSTNode
{
KeyType key;
struct BSTNode *left;
struct BSTNode *right;
}BSTNode, *BSTree;
//创建二叉搜索树节点
BSTNode *CreateBSTNode(KeyType key)
{
BSTNode *node = new BSTNode;
node->key = key;
node->left = node->right = NULL;
return node;
}
//迭代方式实现LCA!!!
BSTree LCA(BSTree T, int n1, int n2)
{
while(T != NULL)
{
// 如果节点的值比n1和n2都大,那么LCA在节点的左子树
if (T->key > n1 && T->key > n2)
T = T->left;
// 如果节点的值比n1和n2都小,那么LCA在节点的右子树
else if (T->key < n1 && T->key < n2)
T = T->right;
else break;
}
return T;
}
//打印排序后的二叉搜索树。中序遍历即可。
void PrintInOrderBST(BSTree T)
{//中序遍历后的二叉搜索树是有序序列!!!
if(T == NULL) return;
PrintInOrderBST(T->left);
cout<<T->key<<endl;
PrintInOrderBST(T->right);
}
int main()
{
BSTree bst = CreateBSTNode(20);
//生成如图所示二叉搜索树。
bst->left = CreateBSTNode(8);
bst->right = CreateBSTNode(22);
bst->left->left = CreateBSTNode(4);
bst->left->right = CreateBSTNode(12);
bst->left->right->left = CreateBSTNode(10);
bst->left->right->right = CreateBSTNode(14);
cout<<"中序遍历BST : "<<endl;
PrintInOrderBST(bst);
cout<<"BST中两节点最小公共祖先(迭代版本):"<<endl;
BSTree lca1 = LCA(bst, 10, 14);
cout<<"LCA(10, 14) = "<<lca1->key<<endl;
BSTree lca2 = LCA(bst, 14, 8);
cout<<"LCA(14, 8) = "<<lca2->key<<endl;
BSTree lca3 = LCA(bst, 10, 22);
cout<<"LCA(10, 22) = "<<lca3->key<<endl;
return 0;
}结果:
中序遍历BST : 4 8 10 12 14 20 22 BST中两节点最小公共祖先(迭代版本): LCA(10, 14) = 12 LCA(14, 8) = 8 LCA(10, 22) = 20 Process returned 0 (0x0) execution time : 0.210 s Press any key to continue.
相关文章推荐
- LCA模板
- Binary Search Tree Iterator,Reverse Nodes in k-Group
- 【LCA】SPOJ QTREE2
- [LeetCode] Convert Sorted List to Binary Search Tree
- [LeetCode] Convert Sorted Array to Binary Search Tree
- [LeetCode] Recover Binary Search Tree
- [LeetCode] Validate Binary Search Tree
- [LeetCode] Unique Binary Search Tree
- Convert Sorted Array to Binary Search Tree
- poj3728
- hihocoder #1067 LCA
- hihocoder #1069 线段树
- LeetCode:Binary Search Tree相关题目合集
- LeetCode-Convert Sorted Array to Binary Search Tree
- POJ1330 Nearest Common Ancestors 非lca pascal 解题报告
- POJ1986 Distance Queries LCA pascal 解题报告
- Convert Sorted Array(List) to Binary Search Tree
- Validate Binary Search Tree
- LCA
- convert sorted array to binary search tree
