codeforces 551 D. GukiZ and Binary Operations
2015-10-23 11:10
501 查看
D. GukiZ and Binary Operations
time limit per test
1 second
memory limit per test
256 megabytes
input
standard input
output
standard output
We all know that GukiZ often plays with arrays.
Now he is thinking about this problem: how many arrays a, of length n,
with non-negative elements strictly less then 2l meet
the following condition:
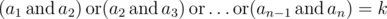
?
Here operation
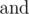
means
bitwise AND (in Pascalit is equivalent to and, in C/C++/Java/Python it
is equivalent to &), operation

means
bitwise OR (in Pascal it is equivalent to

,
in C/C++/Java/Python it is equivalent to |).
Because the answer can be quite large, calculate it modulo m. This time GukiZ hasn't come up with solution, and needs you to help him!
Input
First and the only line of input contains four integers n, k, l, m (2 ≤ n ≤ 1018, 0 ≤ k ≤ 1018, 0 ≤ l ≤ 64, 1 ≤ m ≤ 109 + 7).
Output
In the single line print the number of arrays satisfying the condition above modulo m.
Sample test(s)
input
output
input
output
input
output
Note
In the first sample, satisfying arrays are {1, 1}, {3, 1}, {1, 3}.
In the second sample, only satisfying array is {1, 1}.
In the third sample, satisfying arrays are {0, 3, 3}, {1, 3, 2}, {1, 3, 3}, {2, 3, 1}, {2, 3, 3}, {3, 3, 0}, {3, 3, 1}, {3, 3, 2}, {3, 3, 3}.
这道题只要想通在长度为n的0/1串中,相邻两个数不为1的情况的个数为斐波那契数就可以做了。
time limit per test
1 second
memory limit per test
256 megabytes
input
standard input
output
standard output
We all know that GukiZ often plays with arrays.
Now he is thinking about this problem: how many arrays a, of length n,
with non-negative elements strictly less then 2l meet
the following condition:
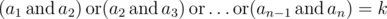
?
Here operation
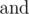
means
bitwise AND (in Pascalit is equivalent to and, in C/C++/Java/Python it
is equivalent to &), operation

means
bitwise OR (in Pascal it is equivalent to

,
in C/C++/Java/Python it is equivalent to |).
Because the answer can be quite large, calculate it modulo m. This time GukiZ hasn't come up with solution, and needs you to help him!
Input
First and the only line of input contains four integers n, k, l, m (2 ≤ n ≤ 1018, 0 ≤ k ≤ 1018, 0 ≤ l ≤ 64, 1 ≤ m ≤ 109 + 7).
Output
In the single line print the number of arrays satisfying the condition above modulo m.
Sample test(s)
input
2 1 2 10
output
3
input
2 1 1 3
output
1
input
3 3 2 10
output
9
Note
In the first sample, satisfying arrays are {1, 1}, {3, 1}, {1, 3}.
In the second sample, only satisfying array is {1, 1}.
In the third sample, satisfying arrays are {0, 3, 3}, {1, 3, 2}, {1, 3, 3}, {2, 3, 1}, {2, 3, 3}, {3, 3, 0}, {3, 3, 1}, {3, 3, 2}, {3, 3, 3}.
这道题只要想通在长度为n的0/1串中,相邻两个数不为1的情况的个数为斐波那契数就可以做了。
/*======================================================
# Author: whai
# Last modified: 2015-10-21 09:19# Filename: d.cpp
======================================================*/
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cstring>
#include <string>
#include <cmath>
#include <set>
#include <map>
using namespace std;
#define LL __int64
#define PB push_back
#define P pair<int, int>
#define X first
#define Y second
LL a_b_MOD_c(LL a, LL b, LL mod) {
LL ret = 1;
a %= mod;
while(b) {
if(b & 1) ret = ret * a % mod;
a = a * a % mod;
b >>= 1;
}
return ret;
}
LL MOD;
struct Matrix {
LL a[5][5];
int n, m;
Matrix(int _n = 0, int _m = 0, LL val = 0) {
n = _n;
m = _m;
for(int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
for(int j = 0; j < m; ++j) {
a[i][j] = (i == j ? val : 0);
}
}
}
Matrix operator * (Matrix tmp) {
Matrix ret(n, tmp.m);
for(int i = 0; i < n; ++i)
for(int j = 0; j < tmp.m; ++j)
for(int k = 0; k < m; ++k)
ret.a[i][j] = (ret.a[i][j] + a[i][k] * tmp.a[k][j]) % MOD;
return ret;
}
Matrix operator ^ (LL b) {
Matrix ret(n, m, 1), base = (*this);
while(b) {
if(b & 1) ret = ret * base;
base = base * base;
b >>= 1;
}
return ret;
}
};
bool ok(LL k, LL l) {
if(l >= 62) return true;
return k < (1LL << l);
}
LL get_fib(LL n, LL m) {
MOD = m;
if(n == 2) return 3;
Matrix a0(1, 2);
a0.a[0][0] = 2;
a0.a[0][1] = 3;
Matrix m0(2, 2);
m0.a[0][0] = 0;
m0.a[0][1] = m0.a[1][0] = m0.a[1][1] = 1;
m0 = m0 ^ (n - 2);
a0 = a0 * m0;
return a0.a[0][1];
}
int main() {
LL n, k, l, m;
cin>>n>>k>>l>>m;
if(!ok(k, l)) {
puts("0");
return 0;
}
LL fib = get_fib(n, m);
LL ans = 1;
for(int i = 0; i < l; ++i) {
if(i >= 62 || (k & (1LL << i)) == 0) {
ans = (ans * fib) % m;
} else {
ans = (ans * (a_b_MOD_c(2, n, m) - fib) % m) % m;
}
}
ans = (ans + m) % m;
cout<<ans<<endl;
return 0;
}
相关文章推荐
- 关于NopCommerce3.6版用户登录详解
- 看CSDN博客,用电脑访问其手机版网站——更清爽!
- CentOS学习笔记1:< yum提示another app is currently holding the yum lock;waiting for it to exit >
- zabbix 监控windows的网卡流量
- shell常用命令和方法总结记录
- Install vsftpd on centos
- intellij+maven 非插件形式使用tomcat
- Linux 获得机器的IP和网卡信息
- NSOperation之依赖关系和GCD之间的对比
- Show slave status 详解
- opencv2-第五章-图像处理2
- Flash中启动Linux的方法
- Linux 精萃
- linux 常用命令
- Tomcat启动报Error listenerStart错误
- Install nginx on centos
- 8.2.1.17 DISTINCT Optimization
- redhat6.4日常操作规范
- 解决linux buffer/cache 消耗内存过高引发的问题 推荐
- hadoop2.6.1源码编译
