Linux多线程基础学习(七)pthread一次性初始化
2015-10-20 19:31
796 查看
在多线程环境中,有些事仅需要执行一次。通常当初始化应用程序时,可以比较容易地将其放在main函数中。但当你写一个库时,就不能在main里面初始化了,你可以用静态初始化,但使用一次初始化(pthread_once)会比较容易些。
首先要定义一个pthread_once_t变量,这个变量要用宏PTHREAD_ONCE_INIT初始化。
pthread_once_t once_control =PTHREAD_ONCE_INIT;
然后创建一个与控制变量相关的初始化函数。
void init_routine()
{
//各种初始化操作
......
}
接下来就可以在任何时刻调用pthread_once函数。
int pthread_once(pthread_once_t *once_control,void (*init_routin)(void));
功能:本函数使用初值为PTHREAD_ONCE_INIT的once_control变量保证init_routine()函数在本进程执行序列中仅执行一次。
在多线程编程环境下,尽管pthread_once()调用会出现在多个线程中,init_routine()函数仅执行一次,究竟在哪个线程中执行是不定的,是由内核调度来决定。
如果once_control的初值不是PTHREAD_ONCE_INIT(Linux Threads定义为0),pthread_once() 的行为就会不正常。
在LinuxThreads中,实际"一次性函数"的执行状态有三种:
NEVER(0)、
IN_PROGRESS(1)、
DONE (2),
如果once_control初值为0,那么 pthread_once从未执行过,init_routine()函数会执行。
如果once初值设为1,则由于所有pthread_once()都必须等待其中一个激发"已执行一次"信号,因此所有pthread_once()都会陷入永久的等待中;
如果设为2,则表示该函数已执行过一次,从而所有pthread_once()都会立即返回0
当pthread_once函数成功返回,once_control就会被设置为2
首先要定义一个pthread_once_t变量,这个变量要用宏PTHREAD_ONCE_INIT初始化。
pthread_once_t once_control =PTHREAD_ONCE_INIT;
然后创建一个与控制变量相关的初始化函数。
void init_routine()
{
//各种初始化操作
......
}
接下来就可以在任何时刻调用pthread_once函数。
int pthread_once(pthread_once_t *once_control,void (*init_routin)(void));
功能:本函数使用初值为PTHREAD_ONCE_INIT的once_control变量保证init_routine()函数在本进程执行序列中仅执行一次。
在多线程编程环境下,尽管pthread_once()调用会出现在多个线程中,init_routine()函数仅执行一次,究竟在哪个线程中执行是不定的,是由内核调度来决定。
如果once_control的初值不是PTHREAD_ONCE_INIT(Linux Threads定义为0),pthread_once() 的行为就会不正常。
在LinuxThreads中,实际"一次性函数"的执行状态有三种:
NEVER(0)、
IN_PROGRESS(1)、
DONE (2),
如果once_control初值为0,那么 pthread_once从未执行过,init_routine()函数会执行。
如果once初值设为1,则由于所有pthread_once()都必须等待其中一个激发"已执行一次"信号,因此所有pthread_once()都会陷入永久的等待中;
如果设为2,则表示该函数已执行过一次,从而所有pthread_once()都会立即返回0
当pthread_once函数成功返回,once_control就会被设置为2
/*============================================================================
// Name : thread_initOnce.cpp
// Author : Ryan
// Version :
// Copyright : zjut
// Description : pthread_once_t的理解demo
//============================================================================*/
#include<iostream>
#include<pthread.h>
using namespace std;
pthread_once_t once = PTHREAD_ONCE_INIT;//变量初始化
void once_run(void)
{
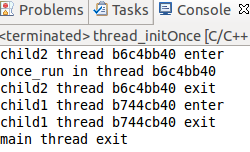
cout<<"once_run in thread "<<(unsigned int )pthread_self()<<endl;
}
void *child1(void * arg)
{
pthread_t tid =pthread_self();
cout<<"child1 thread "<<(unsigned int )tid<<" enter"<<endl;
pthread_once(&once,once_run);
cout<<"child1 thread "<<tid<<" exit"<<endl;
return 0;
}
void * child2(void * arg)
{
pthread_t tid =pthread_self();
cout<<"child2 thread "<<hex<<(unsigned int )tid<<" enter"<<endl;
pthread_once(&once,once_run);
cout<<"child2 thread "<<tid<<" exit"<<endl;
return 0;
}
int main(void)
{
pthread_t tid1,tid2;
if(pthread_create(&tid1,NULL,child1,NULL))
return 1;
if(pthread_create(&tid2,NULL,child2,NULL))
return 1;
pthread_join(tid1, NULL);
pthread_join(tid2, NULL);
cout<<"main thread exit"<<endl;
return 0;
}
相关文章推荐
- Linux socket 初步
- Python3写爬虫(四)多线程实现数据爬取
- linux lsof详解
- linux 文件权限
- Linux 执行数学运算
- 10 篇对初学者和专家都有用的 Linux 命令教程
- Linux 与 Windows 对UNICODE 的处理方式
- Ubuntu12.04下QQ完美走起啊!走起啊!有木有啊!
- 解決Linux下Android开发真机调试设备不被识别问题
- 运维入门
- 运维提升
- Linux 自检和 SystemTap
- Ubuntu Linux使用体验
- c语言实现hashmap(转载)
- Linux 信号signal处理机制
- linux下mysql添加用户
- Scientific Linux 5.5 图形安装教程
- 基于 Linux 集群环境上 GPFS 的问题诊断
- 谁是桌面王者?Win PK Linux三大镇山之宝
