Codeforces 582A GCD Table
2015-10-06 12:05
447 查看
The GCD table G of size n × n for
an array of positive integers a of length n is
defined by formula
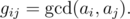
Let us remind you that the greatest common divisor (GCD) of two positive integers x and y is
the greatest integer that is divisor of both xand y,
it is denoted as
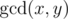
.
For example, for array a = {4, 3, 6, 2} of length 4 the GCD table will look as follows:
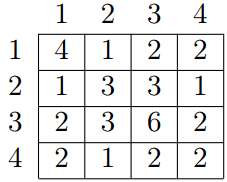
Given all the numbers of the GCD table G, restore array a.
Input
The first line contains number n (1 ≤ n ≤ 500)
— the length of array a. The second line contains n2 space-separated
numbers — the elements of the GCD table of G for array a.
All the numbers in the table are positive integers, not exceeding 109.
Note that the elements are given in an arbitrary order. It is guaranteed that the set of the input data corresponds to some array a.
Output
In the single line print n positive integers — the elements of array a.
If there are multiple possible solutions, you are allowed to print any of them.
Sample test(s)
input
output
input
output
input
output
an array of positive integers a of length n is
defined by formula
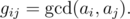
Let us remind you that the greatest common divisor (GCD) of two positive integers x and y is
the greatest integer that is divisor of both xand y,
it is denoted as
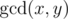
.
For example, for array a = {4, 3, 6, 2} of length 4 the GCD table will look as follows:

Given all the numbers of the GCD table G, restore array a.
Input
The first line contains number n (1 ≤ n ≤ 500)
— the length of array a. The second line contains n2 space-separated
numbers — the elements of the GCD table of G for array a.
All the numbers in the table are positive integers, not exceeding 109.
Note that the elements are given in an arbitrary order. It is guaranteed that the set of the input data corresponds to some array a.
Output
In the single line print n positive integers — the elements of array a.
If there are multiple possible solutions, you are allowed to print any of them.
Sample test(s)
input
4 2 1 2 3 4 3 2 6 1 12 2 1 2 3 2
output
4 3 6 2
input
1 42
output
42
input
2 1 11 1
output
1 1
解题思路:从大到小依次求解
#include <ctime>
#include <cmath>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <cstring>
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <vector>
#include <map>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
int ans[1010];
map<int, int> m;
int gcd(int x, int y) {
return y == 0 ? x : gcd(y, x % y);
}
int main() {
//freopen("aa.in", "r", stdin);
int n, x;
m.clear();
scanf("%d", &n);
for(int i = 1; i <= n*n; ++i) {
scanf("%d", &x);
m[x]++;
}
int cnt = 0;
for(map<int, int>::reverse_iterator it = m.rbegin(); it != m.rend(); ++it) {
if(it->second == 0) continue;
while(it->second > 0) {
ans[cnt] = it->first;
it->second--;
for(int j = 0; j < cnt; ++j) {
int d = gcd(ans[j], it->first);
m[d] -= 2;
}
cnt++;
}
}
printf("%d", ans[0]);
for(int i = 1; i < cnt; ++i) {
printf(" %d", ans[i]);
}
printf("\n");
return 0;
}
相关文章推荐
- Foundation框架之NSArray
- C#中Console.ReadLine()和Console.Read()有何区别?
- Readonly
- poj_1464 动态规划
- Jsp+Servlet实现文件上传下载——前台页面开发
- PHOTOSHOP常用快捷键大全
- JQuery.lazyload的使用.
- Packing Information into Names 2
- 面试题126-150
- 最长公共子序列
- UIPopoverController的简单使用
- iOS:多线程的详细介绍
- SpringMVC+Hibernate4+Bootstrap3
- Java最最常用的100个类排序(非官方)
- Java最最常用的100个类排序(非官方)
- json 拼装空list、object
- 字符串及串的模式匹配
- 悟透JavaScript
- C++ 编译出现字符串常量转化问题
- EasyUI-EasyUI框架入门学习
