cf 323 A. GCD Table (还原gcd_暴力)
2015-10-04 14:45
253 查看
The GCD table G of size n × n for
an array of positive integers a of length n is
defined by formula
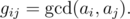
Let us remind you that the greatest common divisor (GCD) of two positive integers x and y is
the greatest integer that is divisor of both x and y,
it is denoted as
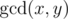
.
For example, for array a = {4, 3, 6, 2} of length 4 the GCD table will look as follows:
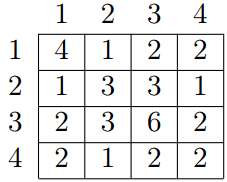
Given all the numbers of the GCD table G, restore array a.
Input
The first line contains number n (1 ≤ n ≤ 500)
— the length of array a. The second line contains n2 space-separated
numbers — the elements of the GCD table of G for array a.
All the numbers in the table are positive integers, not exceeding 109.
Note that the elements are given in an arbitrary order. It is guaranteed that the set of the input data corresponds to some array a.
Output
In the single line print n positive integers — the elements of array a.
If there are multiple possible solutions, you are allowed to print any of them.
Sample test(s)
input
output
input
output
input
output
an array of positive integers a of length n is
defined by formula
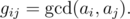
Let us remind you that the greatest common divisor (GCD) of two positive integers x and y is
the greatest integer that is divisor of both x and y,
it is denoted as
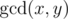
.
For example, for array a = {4, 3, 6, 2} of length 4 the GCD table will look as follows:

Given all the numbers of the GCD table G, restore array a.
Input
The first line contains number n (1 ≤ n ≤ 500)
— the length of array a. The second line contains n2 space-separated
numbers — the elements of the GCD table of G for array a.
All the numbers in the table are positive integers, not exceeding 109.
Note that the elements are given in an arbitrary order. It is guaranteed that the set of the input data corresponds to some array a.
Output
In the single line print n positive integers — the elements of array a.
If there are multiple possible solutions, you are allowed to print any of them.
Sample test(s)
input
4 2 1 2 3 4 3 2 6 1 12 2 1 2 3 2
output
4 3 6 2
input
1 42
output
42
input
2 1 11 1
output
1 1
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdio>
#include<algorithm>
#include<map>
#include<vector>
using namespace std;
map<int,int>mm;
vector<int>ans;
int a[600*600];
int main()
{
int n,i,j;cin>>n;
for(i=1;i<=n*n;i++) {
cin>>a[i];
mm[a[i]]++;
}
sort(a+1,a+1+n*n);
for(i=n*n;i>=1;i--) {
if(mm[a[i]]==0) continue;
mm[a[i]]--;
for(j=0;j<ans.size();j++) {
int t=__gcd(a[i],ans[j]);
mm[t]-=2;
}
ans.push_back(a[i]);
}
for(i=0;i<n;i++) cout<<ans[i]<<" ";
cout<<endl;
}#include <iostream>
#include <fstream>
#include <set>
#include <map>
#include <string>
#include <vector>
#include <bitset>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cstring>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <cmath>
#include <cassert>
#include <queue>
typedef long long ll;
typedef long double ld;
using namespace std;
vector<int> vv;
multiset<int> ss;
int main() {
int n;
scanf("%d", &n);
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i)
for (int j = 0; j < n; ++j) {
int a;
scanf("%d", &a);
ss.insert(a);
}
while (!ss.empty()) {
int x = *ss.rbegin();
printf("%d ", x);
for (int i = 0; i < (int)vv.size(); ++i)
ss.erase(ss.find(__gcd(x, vv[i]))), ss.erase(ss.find(__gcd(x, vv[i])));
vv.push_back(x);
ss.erase(ss.find(x));
}
return 0;
}#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
#include <algorithm>
#include <map>
#include <vector>
const int N = 2005;
typedef long long LL;
using namespace std;
int n , res
;
void work() {
scanf("%d" , &n);
map<int , int> Hash;
for (int i = 0 ; i < n * n ; ++ i) {
int x ;
scanf("%d" , &x);
++ Hash[x];
}
for (int i = 0 ; i < n ; ++ i) {
res[i] = (-- Hash.end()) -> first;
if (!-- Hash[res[i]])
Hash.erase(res[i]);
for (int j = 0 ; j < i ; ++ j) {
int x = __gcd(res[i] , res[j]);
if (!-- Hash[x])
Hash.erase(x);
if (!-- Hash[x])
Hash.erase(x);
}
printf("%d\n" , res[i]);
}
}
int main() {
work();
return 0;
}
相关文章推荐
- 第三方库AF之Post
- VS2010+PCL1.6.0+1.7.2(Win7 64位)安装教程
- 空类内存sizeof
- 检测网络状态代码
- Hadoop集群搭建
- *客户端禁用Cookie后的会话数据保存
- Java-二分查找算法
- 单例代码
- Web APi之过滤器创建过程原理解析【一】(十)
- POJ 1733 Parity game
- Haploview做单倍型分析
- [BZOJ1441] Min
- MyISAM vs InnoDB 分析之二
- RHCSA 系列(十四): 在 RHEL 7 中设置基于 LDAP 的认证
- 【WZOI第二次NOIP模拟赛Day1T2】世界末日 解题报告
- ISLR_StatisticalLearning
- CF 55D Beautiful numbers (数位DP)
- js基础学习笔记
- nginx for windows中的一项缺陷
- 大概是打招呼~
