OpenCV3.0基本类型初探(一)
2015-09-24 18:34
330 查看
本篇主要讲述了CV中基本数据类型的定义以及一些模板的初步使用技巧,对于CV所支持数据类型的特性和操作讨论将放在下一章,如果对这些不感兴趣的同学可以跳过这章,不会影响阅读
CV的基本数据类型都在tyoes.hpp中进行声明
其和其他文件的结构关系大概是这样的(箭头指向表示包含关系)
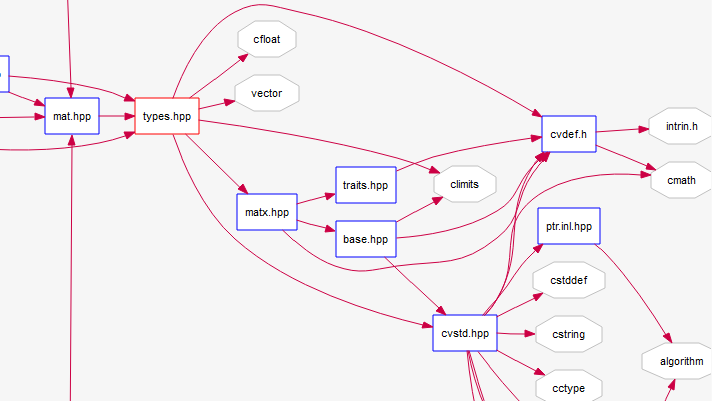
可以看到types文件是CV世界和C++其他文件在组织结构上的唯一桥梁
为什么这样设计呢
CV官方给出的解释是虽然泛型编程是一种非常exciting的特性,但是滥用泛型也会增长编译时间以及降低和其他语言的兼容性(每种接收不同类型的泛型模板都会被独立编译),所以CV只支持将以下类型加入到基本数据模板中
8-bit unsigned integer (uchar)
8-bit signed integer (schar)
16-bit unsigned integer (ushort)
16-bit signed integer (short)
32-bit signed integer (int)
32-bit floating-point number (float)
64-bit floating-point number (double)
a tuple of several elements where all elements have the same type (one of the above). An array whose elements are such tuples, are called multi-channel arrays, as opposite to the single-channel
arrays, whose elements are scalar values. The maximum possible number of channels is defined by the CV_CN_MAX constant,
which is currently set to 512.
这些都是在cvdef.h中定义的
为了保证在之后的工作中使用的是这些类型 还使用枚举出来限定类型范围
enum { CV_8U=0, CV_8S=1, CV_16U=2, CV_16S=3, CV_32S=4, CV_32F=5, CV_64F=6 }
当然,多通道图像的话可以使用这样的定义:
CV_8UC1 ... CV_64FC4 constants
(for a number of channels from 1 to 4)
就表示1到4通道的8-bit数据
参看如下例子可以知道大致的使用方法:
example:
Mat mtx(3, 3, CV_32F); //
make a 3x3 floating-point matrix
Mat cmtx(10, 1, CV_64FC2); //
make a 10x1 2-channel floating-point // matrix (10-element complex vector)
Mat img(Size(1920, 1080), CV_8UC3); //
make a 3-channel (color) image // of 1920 columns and 1080 rows.
Mat grayscale(image.size(), CV_MAKETYPE(image.depth(), 1)); //
make a 1-channel image of // the same size and same // channel type as img
而对于每一个type中定义的数据类型,都有名为DataType的模板与其对应,比如下面的Complex
template<typename _Tp> class Complex
{
public:
//! constructors
Complex();
Complex( _Tp _re, _Tp _im = 0 );
//! conversion to another data type
template<typename T2> operator Complex<T2>() const;
//! conjugation
Complex conj() const;
_Tp re, im; //< the real and the imaginary parts
};
typedef Complex<float> Complexf;
typedef Complex<double> Complexd;
其对应的特化模板如下,其主要设计意图在于 设计者希望不用添加其他的头文件等就能够描述对应数据结构所支持的数据类型
template<typename _Tp> class DataType< Complex<_Tp> >
{
public:
typedef Complex<_Tp> value_type;
typedef value_type work_type;
typedef _Tp channel_type;
enum { generic_type = 0,
depth = DataType<channel_type>::depth,
channels = 2,
fmt = DataType<channel_type>::fmt + ((channels - 1) << 8),
type = CV_MAKETYPE(depth, channels) };
typedef Vec<channel_type, channels> vec_type;
};
DataType可以这样使用
// allocates a 30x40 floating-point matrix
Mat A(30, 40, DataType<float>::type);
在这里 DataType作为提示float在cvdef.hpp中对应宏的数字编号,让我们做一个小实验来确定下:
std::cout<<"DataType<char> is:"<<DataType<char>::type<<std::endl;
std::cout<<"DataType<uchar> is:"<<DataType<uchar>::type<<std::endl;
std::cout<<"DataType<int> is:"<<DataType<int>::type<<std::endl;
std::cout<<"DataType<uint> is:"<<DataType<uint>::type<<std::endl;
std::cout<<"DataType<double> is:"<<DataType<double>::type<<std::endl;
输出为:
DataType<char> is:1
DataType<uchar> is:0
DataType<int> is:4
DataType<uint> is:7
DataType<double> is:6
回顾cvdef 中的宏:
#define CV_8U 0
#define CV_8S 1
#define CV_16U 2
#define CV_16S 3
#define CV_32S 4
#define CV_32F 5
#define CV_64F 6
#define CV_USRTYPE1 7
当然,其衍生数据类型依然可以用DataType运算
std::cout<<"DataType<Complex<int>> is:"<<DataType<Complex<int>>::type<<std::endl;
得到 DataType<Complex<int>> is:12
其具体计算公式可以参考CV_MAKETYPE对应的宏相关,在此不做过多讨论
我们只需要注意CV为了类型的安全做了如下工作,并且引入了DataType这样的机制来防范数据滥用就可以了
另外提一些CV在创建基本数据容器时候的小技巧:
还是以Complex为例子;
在types.hpp中还可以看到Complex的两种重载模板构造函数
template<typename _Tp> inline
Complex<_Tp>::Complex()
: re(0), im(0) {}
template<typename _Tp> inline
Complex<_Tp>::Complex( _Tp _re, _Tp _im )
: re(_re), im(_im) {}
分别提供默认(实部虚部都是0)以及 带参的初始化方式
也就是说模板也是可以进行重载的,但是如果模板的参数类型有多个,这时候需要十分小心,因为模板并不支持将各种参数隐式转换到模板需求的类型,这样的做法也是为了防止语言的二义性
为此,我们可以这样提供模板之间参数类型转换,在Complex中表现为这样
template<typename _Tp> template<typename T2> inline
Complex<_Tp>::operator Complex<T2>() const
{
return Complex<T2>(saturate_cast<T2>(re), saturate_cast<T2>(im));
}
用法大致是这样的
Complex<double> com1(2.2,2.3);
Complex<int> com2(com1);
通过()的重载,完成指定的参数转换
另外,CV的基本数据类型大部分都提供了==,!=,+,+=,-,-=,*,*=,/,/=的运算符重载
具体操作我们将在下一章讨论
CV的基本数据类型都在tyoes.hpp中进行声明
其和其他文件的结构关系大概是这样的(箭头指向表示包含关系)

可以看到types文件是CV世界和C++其他文件在组织结构上的唯一桥梁
为什么这样设计呢
CV官方给出的解释是虽然泛型编程是一种非常exciting的特性,但是滥用泛型也会增长编译时间以及降低和其他语言的兼容性(每种接收不同类型的泛型模板都会被独立编译),所以CV只支持将以下类型加入到基本数据模板中
8-bit unsigned integer (uchar)
8-bit signed integer (schar)
16-bit unsigned integer (ushort)
16-bit signed integer (short)
32-bit signed integer (int)
32-bit floating-point number (float)
64-bit floating-point number (double)
a tuple of several elements where all elements have the same type (one of the above). An array whose elements are such tuples, are called multi-channel arrays, as opposite to the single-channel
arrays, whose elements are scalar values. The maximum possible number of channels is defined by the CV_CN_MAX constant,
which is currently set to 512.
这些都是在cvdef.h中定义的
为了保证在之后的工作中使用的是这些类型 还使用枚举出来限定类型范围
enum { CV_8U=0, CV_8S=1, CV_16U=2, CV_16S=3, CV_32S=4, CV_32F=5, CV_64F=6 }
当然,多通道图像的话可以使用这样的定义:
CV_8UC1 ... CV_64FC4 constants
(for a number of channels from 1 to 4)
就表示1到4通道的8-bit数据
参看如下例子可以知道大致的使用方法:
example:
Mat mtx(3, 3, CV_32F); //
make a 3x3 floating-point matrix
Mat cmtx(10, 1, CV_64FC2); //
make a 10x1 2-channel floating-point // matrix (10-element complex vector)
Mat img(Size(1920, 1080), CV_8UC3); //
make a 3-channel (color) image // of 1920 columns and 1080 rows.
Mat grayscale(image.size(), CV_MAKETYPE(image.depth(), 1)); //
make a 1-channel image of // the same size and same // channel type as img
而对于每一个type中定义的数据类型,都有名为DataType的模板与其对应,比如下面的Complex
template<typename _Tp> class Complex
{
public:
//! constructors
Complex();
Complex( _Tp _re, _Tp _im = 0 );
//! conversion to another data type
template<typename T2> operator Complex<T2>() const;
//! conjugation
Complex conj() const;
_Tp re, im; //< the real and the imaginary parts
};
typedef Complex<float> Complexf;
typedef Complex<double> Complexd;
其对应的特化模板如下,其主要设计意图在于 设计者希望不用添加其他的头文件等就能够描述对应数据结构所支持的数据类型
template<typename _Tp> class DataType< Complex<_Tp> >
{
public:
typedef Complex<_Tp> value_type;
typedef value_type work_type;
typedef _Tp channel_type;
enum { generic_type = 0,
depth = DataType<channel_type>::depth,
channels = 2,
fmt = DataType<channel_type>::fmt + ((channels - 1) << 8),
type = CV_MAKETYPE(depth, channels) };
typedef Vec<channel_type, channels> vec_type;
};
DataType可以这样使用
// allocates a 30x40 floating-point matrix
Mat A(30, 40, DataType<float>::type);
在这里 DataType作为提示float在cvdef.hpp中对应宏的数字编号,让我们做一个小实验来确定下:
std::cout<<"DataType<char> is:"<<DataType<char>::type<<std::endl;
std::cout<<"DataType<uchar> is:"<<DataType<uchar>::type<<std::endl;
std::cout<<"DataType<int> is:"<<DataType<int>::type<<std::endl;
std::cout<<"DataType<uint> is:"<<DataType<uint>::type<<std::endl;
std::cout<<"DataType<double> is:"<<DataType<double>::type<<std::endl;
输出为:
DataType<char> is:1
DataType<uchar> is:0
DataType<int> is:4
DataType<uint> is:7
DataType<double> is:6
回顾cvdef 中的宏:
#define CV_8U 0
#define CV_8S 1
#define CV_16U 2
#define CV_16S 3
#define CV_32S 4
#define CV_32F 5
#define CV_64F 6
#define CV_USRTYPE1 7
当然,其衍生数据类型依然可以用DataType运算
std::cout<<"DataType<Complex<int>> is:"<<DataType<Complex<int>>::type<<std::endl;
得到 DataType<Complex<int>> is:12
其具体计算公式可以参考CV_MAKETYPE对应的宏相关,在此不做过多讨论
我们只需要注意CV为了类型的安全做了如下工作,并且引入了DataType这样的机制来防范数据滥用就可以了
另外提一些CV在创建基本数据容器时候的小技巧:
还是以Complex为例子;
在types.hpp中还可以看到Complex的两种重载模板构造函数
template<typename _Tp> inline
Complex<_Tp>::Complex()
: re(0), im(0) {}
template<typename _Tp> inline
Complex<_Tp>::Complex( _Tp _re, _Tp _im )
: re(_re), im(_im) {}
分别提供默认(实部虚部都是0)以及 带参的初始化方式
也就是说模板也是可以进行重载的,但是如果模板的参数类型有多个,这时候需要十分小心,因为模板并不支持将各种参数隐式转换到模板需求的类型,这样的做法也是为了防止语言的二义性
为此,我们可以这样提供模板之间参数类型转换,在Complex中表现为这样
template<typename _Tp> template<typename T2> inline
Complex<_Tp>::operator Complex<T2>() const
{
return Complex<T2>(saturate_cast<T2>(re), saturate_cast<T2>(im));
}
用法大致是这样的
Complex<double> com1(2.2,2.3);
Complex<int> com2(com1);
通过()的重载,完成指定的参数转换
另外,CV的基本数据类型大部分都提供了==,!=,+,+=,-,-=,*,*=,/,/=的运算符重载
具体操作我们将在下一章讨论
相关文章推荐
- shell split
- 【详解】回车 换行 0X0D 0X0A CR LF \R \N WIN LINUX MAC系统
- tomcat catalina.bat解读
- CentOS-6.5-x86_64 最小化安装,已安装包的总数,这些包?
- nginx 配置--限定用户访问,防止非80端口转80技巧
- CentOS7下Python开发环境搭建
- Openstack 快速入门(官方文档直译)
- Linux内核是如何启动android内核直到我们的helloword
- Linux下MySQL不能被远程访问
- LINUX信息安全系统设计基础第二周学习总结
- getPropertyDescriptors()获取类的属性
- 005 执行mapreduce加强,利用hive统计分析电商网站用户行为指标
- openfire整合现有系统用户
- Linux下安装使用NMON监控、分析系统性能
- OpenCV一些函数
- 】OPENGL加载BMP纹理图的方式 三种
- Linux select函数和poll函数
- arm-linux-gcc/ld/objcopy/objdump参数总结【转】
- 盘点 DevOps 世界的杰出女性(一)
- linux 查看网卡流量六种方法
