第三周项目1—顺序表的基本运算
2015-09-19 13:17
295 查看
问题:
/*
*Copyright (c)2015,烟台大学计算机与控制工程学院
*All rights reserved.
*文件名称:顺序表的基本运算.cpp
*作 者:李艺
*完成日期:2015年9月19日
*版 本 号:v1.0
*
*问题描述:实现顺序表基本运算有算法,依据“最小化”的原则进行测试。所谓最小化
原则,指的是利用尽可能少的基本运算,组成一个程序,并设计main函数
完成测试。
*输入描述:无
*程序输出:依据各个函数而定
*/
代码:
#ifndef LIST_H_INCLUDED
#define LIST_H_INCLUDED
#include <stdio.h>
#include <malloc.h>
#define MaxSize 50
typedef int ElemType;
typedef struct
{
ElemType data[MaxSize];
int length;
} SqList;
void CreateList(SqList *&L, ElemType a[], int n);//用数组创建线性表
bool ListEmpty(SqList *L);//判定是否为空表ListEmpty(L)
void DispList(SqList *L);//输出线性表DispList(L)
#endif
//测试函数
int main()
{
SqList *sq;
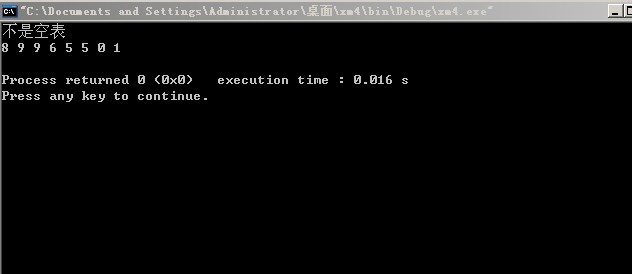
ElemType x[8]= {1,9,9,6,0,5,0,1};
CreateList(sq, x, 8);//最后为0则是空表
if((ListEmpty(sq))>0) //测试不能找到的情形
printf("是空表\n");
else
printf("不是空表\n");
DispList(sq);
return 0;
}
//定义各个自定义函数
//用数组创建线性表
void CreateList(SqList *&L, ElemType a[], int n)
{
int i;
L=(SqList *)malloc(sizeof(SqList));
for (i=0; i<n; i++)
L->data[i]=a[i];
L->length=n;
}
//判定是否为空表ListEmpty(L)
bool ListEmpty(SqList *L)
{
return(L->length==0);
}
//输出线性表DispList(L)
void DispList(SqList *L)
{
int i;
if (ListEmpty(L)) return;
for (i=0; i<L->length; i++)
printf("%d ",L->data[i]);
printf("\n");
}
运行结果:
增加求线性表的长度ListLength的函数并测试;
增加求线性表L中指定位置的某个数据元素GetElem的函数并测试;
增加查找元素LocateElem的函数并测试;
代码:
#ifndef LIST_H_INCLUDED
#define LIST_H_INCLUDED
#include <stdio.h>
#include <malloc.h>
#define MaxSize 50
typedef int ElemType;
typedef struct
{
ElemType data[MaxSize];
int length;
} SqList;
void CreateList(SqList *&L, ElemType a[], int n);//用数组创建线性表
bool ListEmpty(SqList *L);//判定是否为空表ListEmpty(L)
void DispList(SqList *L);//输出线性表DispList(L)
int ListLength(SqList *L);//求线性表的长度ListLength(L)
bool GetElem(SqList *L,int i,ElemType &e);//求某个数据元素值GetElem(L,i,e)
int LocateElem(SqList *L, ElemType e);//按元素值查找LocateElem(L,e)
#endif
//测试函数
int main()
{
SqList *sq;
int k;
ElemType E;
ElemType x[8]= {1,9,9,6,0,5,0,1};
CreateList(sq, x, 8);//最后为0则是空表
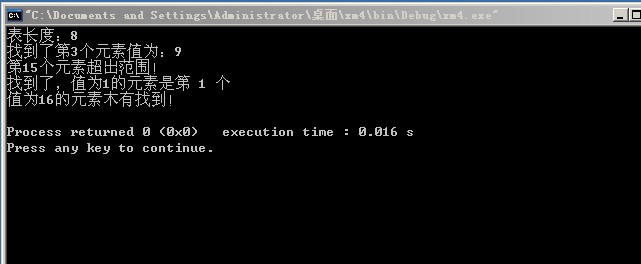
printf("表长度:%d\n", ListLength(sq)); //测试求长度
if(GetElem(sq, 3, E)) //测试在范围内的情形
printf("找到了第3个元素值为:%d\n", E);
else
printf("第3个元素超出范围!\n");
if(GetElem(sq, 15, E)) //测试不在范围内的情形
printf("找到了第15个元素值为:%d\n", E);
else
printf("第15个元素超出范围!\n");
if((k=LocateElem(sq, 1))>0) //测试能找到的情形
printf("找到了,值为1的元素是第 %d 个\n", k);
else
printf("值为1的元素木有找到!\n");
if((k=LocateElem(sq, 16))>0) //测试不能找到的情形
printf("找到了,值为16的元素是第 %d 个\n", k);
else
printf("值为16的元素木有找到!\n");
return 0;
}
//定义各个自定义函数
//用数组创建线性表
void CreateList(SqList *&L, ElemType a[], int n)
{
int i;
L=(SqList *)malloc(sizeof(SqList));
for (i=0; i<n; i++)
L->data[i]=a[i];
L->length=n;
}
//判定是否为空表ListEmpty(L)
bool ListEmpty(SqList *L)
{
return(L->length==0);
}
//求线性表的长度ListLength(L)
int ListLength(SqList *L)
{
return(L->length);
}
//输出线性表DispList(L)
void DispList(SqList *L)
{
int i;
if (ListEmpty(L)) return;
for (i=0; i<L->length; i++)
printf("%d ",L->data[i]);
printf("\n");
}
//求某个数据元素值GetElem(L,i,e)
bool GetElem(SqList *L,int i,ElemType &e)
{
if (i<1 || i>L->length) return false;
e=L->data[i-1];
return true;
}
//按元素值查找LocateElem(L,e)
int LocateElem(SqList *L, ElemType e)
{
int i=0;
while (i<L->length && L->data[i]!=e) i++;
if (i>=L->length) return 0;
else return i+1;
}
运行结果:
代码:
运行结果:
知识点总结:
让我们对线性表算法库有了一个系统的认识,算法库对于我们认识学习算法有非常大的帮助。
/*
*Copyright (c)2015,烟台大学计算机与控制工程学院
*All rights reserved.
*文件名称:顺序表的基本运算.cpp
*作 者:李艺
*完成日期:2015年9月19日
*版 本 号:v1.0
*
*问题描述:实现顺序表基本运算有算法,依据“最小化”的原则进行测试。所谓最小化
原则,指的是利用尽可能少的基本运算,组成一个程序,并设计main函数
完成测试。
*输入描述:无
*程序输出:依据各个函数而定
*/
(1)目的是要测试“建立线性表”的算法CreateList,为查看建表的结果,需要实现“输出线性表”的算法DispList。在研习DispList中发现,要输出线性表,还要判断表是否为空,这样,实现判断线性表是否为空的算法ListEmpty成为必要。这样,再加上main函数,这个程序由4个函数构成。main函数用于写测试相关的代码。
代码:
#ifndef LIST_H_INCLUDED
#define LIST_H_INCLUDED
#include <stdio.h>
#include <malloc.h>
#define MaxSize 50
typedef int ElemType;
typedef struct
{
ElemType data[MaxSize];
int length;
} SqList;
void CreateList(SqList *&L, ElemType a[], int n);//用数组创建线性表
bool ListEmpty(SqList *L);//判定是否为空表ListEmpty(L)
void DispList(SqList *L);//输出线性表DispList(L)
#endif
//测试函数
int main()
{
SqList *sq;
ElemType x[8]= {1,9,9,6,0,5,0,1};
CreateList(sq, x, 8);//最后为0则是空表
if((ListEmpty(sq))>0) //测试不能找到的情形
printf("是空表\n");
else
printf("不是空表\n");
DispList(sq);
return 0;
}
//定义各个自定义函数
//用数组创建线性表
void CreateList(SqList *&L, ElemType a[], int n)
{
int i;
L=(SqList *)malloc(sizeof(SqList));
for (i=0; i<n; i++)
L->data[i]=a[i];
L->length=n;
}
//判定是否为空表ListEmpty(L)
bool ListEmpty(SqList *L)
{
return(L->length==0);
}
//输出线性表DispList(L)
void DispList(SqList *L)
{
int i;
if (ListEmpty(L)) return;
for (i=0; i<L->length; i++)
printf("%d ",L->data[i]);
printf("\n");
}
运行结果:

(2)在已经创建线性表的基础上,求线性表的长度ListLength、求线性表L中指定位置的某个数据元素GetElem、查找元素LocateElem的算法都可以实现了。就在原程序的基础上增加:
增加求线性表的长度ListLength的函数并测试; 增加求线性表L中指定位置的某个数据元素GetElem的函数并测试;
增加查找元素LocateElem的函数并测试;
代码:
#ifndef LIST_H_INCLUDED
#define LIST_H_INCLUDED
#include <stdio.h>
#include <malloc.h>
#define MaxSize 50
typedef int ElemType;
typedef struct
{
ElemType data[MaxSize];
int length;
} SqList;
void CreateList(SqList *&L, ElemType a[], int n);//用数组创建线性表
bool ListEmpty(SqList *L);//判定是否为空表ListEmpty(L)
void DispList(SqList *L);//输出线性表DispList(L)
int ListLength(SqList *L);//求线性表的长度ListLength(L)
bool GetElem(SqList *L,int i,ElemType &e);//求某个数据元素值GetElem(L,i,e)
int LocateElem(SqList *L, ElemType e);//按元素值查找LocateElem(L,e)
#endif
//测试函数
int main()
{
SqList *sq;
int k;
ElemType E;
ElemType x[8]= {1,9,9,6,0,5,0,1};
CreateList(sq, x, 8);//最后为0则是空表
printf("表长度:%d\n", ListLength(sq)); //测试求长度
if(GetElem(sq, 3, E)) //测试在范围内的情形
printf("找到了第3个元素值为:%d\n", E);
else
printf("第3个元素超出范围!\n");
if(GetElem(sq, 15, E)) //测试不在范围内的情形
printf("找到了第15个元素值为:%d\n", E);
else
printf("第15个元素超出范围!\n");
if((k=LocateElem(sq, 1))>0) //测试能找到的情形
printf("找到了,值为1的元素是第 %d 个\n", k);
else
printf("值为1的元素木有找到!\n");
if((k=LocateElem(sq, 16))>0) //测试不能找到的情形
printf("找到了,值为16的元素是第 %d 个\n", k);
else
printf("值为16的元素木有找到!\n");
return 0;
}
//定义各个自定义函数
//用数组创建线性表
void CreateList(SqList *&L, ElemType a[], int n)
{
int i;
L=(SqList *)malloc(sizeof(SqList));
for (i=0; i<n; i++)
L->data[i]=a[i];
L->length=n;
}
//判定是否为空表ListEmpty(L)
bool ListEmpty(SqList *L)
{
return(L->length==0);
}
//求线性表的长度ListLength(L)
int ListLength(SqList *L)
{
return(L->length);
}
//输出线性表DispList(L)
void DispList(SqList *L)
{
int i;
if (ListEmpty(L)) return;
for (i=0; i<L->length; i++)
printf("%d ",L->data[i]);
printf("\n");
}
//求某个数据元素值GetElem(L,i,e)
bool GetElem(SqList *L,int i,ElemType &e)
{
if (i<1 || i>L->length) return false;
e=L->data[i-1];
return true;
}
//按元素值查找LocateElem(L,e)
int LocateElem(SqList *L, ElemType e)
{
int i=0;
while (i<L->length && L->data[i]!=e) i++;
if (i>=L->length) return 0;
else return i+1;
}
运行结果:

(3)其余的4个基本运算:插入数据元素ListInsert、删除数据元素ListDelete、初始化线性表InitList、销毁线性表DestroyList
代码:<span style="font-size:12px;">#ifndef LIST_H_INCLUDED
#define LIST_H_INCLUDED
#include <stdio.h>
#include <malloc.h>
#define MaxSize 50
typedef int ElemType;
typedef struct
{
ElemType data[MaxSize];
int length;
} SqList;
void DispList(SqList *L);
bool ListEmpty(SqList *L);
void InitList(SqList *&L); //引用型指针
void DestroyList(SqList *&L);
bool ListInsert(SqList *&L,int i,ElemType e);
bool ListDelete(SqList *&L,int i,ElemType &e);
#endif
//测试函数
int main()
{
SqList *sq;
ElemType E;
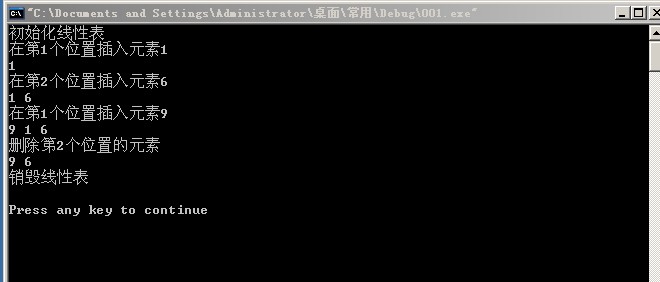
printf("初始化线性表\n");
InitList(sq);
printf("在第1个位置插入元素1\n");
ListInsert(sq, 1, 1);
DispList(sq);
printf("在第2个位置插入元素6\n");
ListInsert(sq, 2, 6);
DispList(sq);
printf("在第1个位置插入元素9\n");
ListInsert(sq, 1, 9);
DispList(sq);
printf("删除第2个位置的元素\n");
ListDelete(sq,2,E);
DispList(sq);
printf("销毁线性表\n");
DestroyList(sq);
DispList(sq);
return 0;
}
//定义各个自定义函数
//输出线性表DispList(L)
void DispList(SqList *L)
{
int i;
if (ListEmpty(L)) return;
for (i=0; i<L->length; i++)
printf("%d ",L->data[i]);
printf("\n");
}
//判定是否为空表ListEmpty(L)
bool ListEmpty(SqList *L)
{
return(L->length==0);
}
//初始化线性表InitList(L)
void InitList(SqList *&L) //引用型指针
{
L=(SqList *)malloc(sizeof(SqList));
//分配存放线性表的空间
L->length=0;
}
//销毁线性表DestroyList(L)
void DestroyList(SqList *&L)
{
free(L);
}
//插入数据元素ListInsert(L,i,e)
bool ListInsert(SqList *&L,int i,ElemType e)
{
int j;
if (i<1 || i>L->length+1)
return false; //参数错误时返回false
i--; //将顺序表逻辑序号转化为物理序号
for (j=L->length; j>i; j--) //将data[i..n]元素后移一个位置
L->data[j]=L->data[j-1];
L->data[i]=e; //插入元素e
L->length++; //顺序表长度增1
return true; //成功插入返回true
}
//删除数据元素ListDelete(L,i,e)
bool ListDelete(SqList *&L,int i,ElemType &e)
{
int j;
if (i<1 || i>L->length) //参数错误时返回false
return false;
i--; //将顺序表逻辑序号转化为物理序号
e=L->data[i];
for (j=i; j<L->length-1; j++) //将data[i..n-1]元素前移
L->data[j]=L->data[j+1];
L->length--; //顺序表长度减1
return true; //成功删除返回true
}运行结果:

知识点总结:
让我们对线性表算法库有了一个系统的认识,算法库对于我们认识学习算法有非常大的帮助。
相关文章推荐
- mac是否启动了ssh
- Scala深入浅出实战经典:21,Scala中的偏函数实战详解
- IO多路复用之select总结
- android 两个线程的交互
- 假设动态运行java文字,当在脚本式配置,这是非常方便的
- 递归求素数加强版
- 使用DataTable和hibernate加载数据的几个问题
- httpd服务配置(未完待续)
- 静态测试与动态测试
- php基础------SESSION
- Scala深入浅出实战经典:20,Scala中的本地函数与作为语言一等公民的函数详解
- Ubuntu14.04 工作区设置
- html框架
- react-redux(2)
- WPF 绘制图表
- POJ-1658
- android 数据库升级
- android事件传递机制的详细了解
- 腾讯面试经历2015
- Session
