UVa1451 - Average
2015-09-17 17:59
411 查看
UVa1451 - Average
A DNA sequence consists of four letters, A, C, G, and T. The GC-ratio of a DNA sequence is thenumber of Cs and Gs of the sequence divided by the length of the sequence. GC-ratio is important in gene finding because DNA sequences with relatively high GC-ratios might be good candidates for the starting parts of genes. Given a very long DNA sequence, researchers are usually interested in locating a subsequence whose GC-ratio is maximum over all subsequences of the sequence. Since short subsequences with high GC-ratios are sometimes meaningless in gene finding, a length lower bound is given to ensure that a long subsequence with high GC-ratio could be found. If, in a DNA sequence, a 0 is assigned to every A and T and a 1 to every C and G, the DNA sequence is transformed into a binary sequence of the same length. GC-ratios in the DNA sequence are now equivalent to averages in the binary sequence.
Position 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1
Index 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7
Sequence 0 0 1 0 1 0 1 1 0 1 1 0 1 1 0 1 0
For the binary sequence above, if the length lower bound is 7, the maximum average is 6/8 which
happens in the subsequence [7,14]. Its length is 8, which is greater than the length lower bound 7. If the length lower bound is 5, then the subsequence [7,11] gives the maximum average 4/5. The length is 5 which is equal to the length lower bound. For the subsequence [7,11], 7 is its starting index and 11 is its ending index.
Given a binary sequence and a length lower bound L, write a program to find a subsequence of the binary sequence whose length is at least L and whose average is maximum over all subsequences of the binary sequence. If two or more subsequences have the maximum average, then find the shortest one; and if two or more shortest subsequences with the maximum average exist, then find the one with the smallest starting index.
Input
Your program is to read from standard input. The input consists of T test cases. The number of test cases T is given in the first line of the input. Each test case starts with a line containing two integers n(1≤n≤100,000) and L(1≤L≤1,000) which are the length of a binary sequence and a length lower bound, respectively. In the next line, a string, binary sequence, of length n is given.Output
Your program is to write to standard output. Print the starting and ending index of the subsequence.Sample Input
217 5
00101011011011010
20 4
11100111100111110000
Sample Output
7 116 9
题意
给出一个01串,要求找到一个长度最小为L且均值最大的子串。题解
首先预处理出前缀和s,令s[0]=0,以A为横坐标,s为纵坐标画图,i到j的平均值ave=s[j]−s[i−1]j−i+1,即点i−1与点j连线的斜率。枚举子串终点t,假设终点之前有三个候选起点i,j,k,如图,可知t点必然在B上方,当t处于A,B之间时,i点优于j,k点;当t点在A,C之间时,k点优于i,j点;当t点处于C上方时,k点优于i,j点;所以上凸点一定不是最优的,在扫描的过程中可以去掉上凸点。处理之后的图像是下凸的,斜率是逐渐上升的,所以在候选点中扫描到斜率变小后停止,枚举新的t点即可。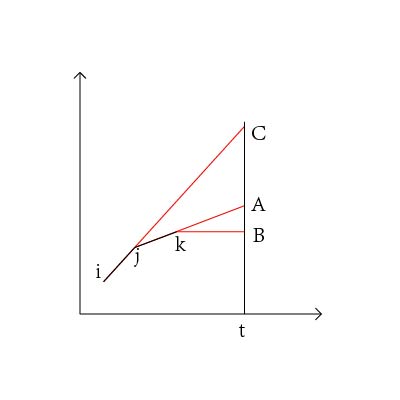
代码
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <algorithm>
#include <queue>
#include <vector>
#include <map>
#include <set>
#define fout freopen("out.txt","w",stdout)
#define fin freopen("in.txt","r",stdin)
using namespace std;
int T;
int n,L;
int a[100005],s[100005];
int P[100005];
int ansl,ansr;
int cmp(int x1,int x2,int x3,int x4)
{
return (s[x2]-s[x1])*(x4-x3)-(s[x4]-s[x3])*(x2-x1);
}
int main()
{
scanf("%d",&T);
while(T--)
{
scanf("%d%d",&n,&L);
s[0]=a[0]=0;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
{
scanf("%1d",&a[i]);
s[i]=s[i-1]+a[i];
}
ansl=0;
ansr=n;
int i=0,j=0;
for(int t=L;t<=n;t++)
{
while(j-i>1&&cmp(P[j-2],t-L,P[j-1],t-L)>=0)
j--;
P[j++]=t-L;
while(i<j-1&&cmp(P[i],t,P[i+1],t)<=0)
i++;
int c=cmp(P[i],t,ansl,ansr);
if(c>0||(c==0&&ansr-ansl>t-P[i]))
{
ansl=P[i];
ansr=t;
}
}
printf("%d %d\n",ansl+1,ansr);
}
return 0;
}
相关文章推荐
- 1.10055 - Hashmat the brave warrior
- 2.10071 - Back to High School Physics
- 3.458 - The Decoder
- 4.694 - The Collatz Sequence
- 6.494 - Kindergarten Counting Game
- 7.490 - Rotating Sentences
- 8.414 - Machined Surfaces
- 9.488 - Triangle Wave
- A.457 - Linear Cellular Automata
- B.489 - Hangman Judge
- C.445 - Marvelous Mazes
- 1.10494 - If We Were a Child Again
- 2.424 - Integer Inquiry
- 3.10250 - The Other Two Trees
- 5.465 - Overflow
- 6.113 - Power of Cryptography
- 7.10161 - Ant on a Chessboard
- 8.621 - Secret Research
- 9.401 - Palindromes
- A.537 - Artificial Intelligence?
