C程序设计语言(第2版)
2015-09-14 17:41
225 查看
C程序设计语言(第2版)
这儿有一篇写的很好的读后感:http://www.cnblogs.com/xkfz007/articles/2566424.html
第1章 导言
1. 单词计数
#include <stdio.h>
int main(){
int c,nl,nw,nc,flag;
flag=0;
nl=nw=nc=0;
while((c=getchar())!=EOF){
++nc;
if(c=='\n')
nl++;
if(c==' '||c=='\n'||c=='\t')
flag=0;
else if(!flag){
flag=1;
++nw;
}
}
printf("%3d %3d %3d\n",nl,nw,nc);
return 0;
}
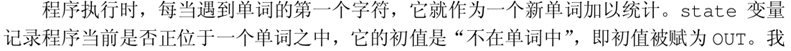
2. 函数参数——传值调用
在C语言中,所有函数参数都是通过"值"传递的。也就是说,传递给被调用函数的参数值存放在临时变量中,而不是存放在原来的变量中。这与其他某些语言是不同的。比如,Fortran等语言是通过"引用"调用,Pascal则采用var参数方式,在这些语言中,被调用的函数必须访问原始参数,而不是访问参数的本地副本。
最主要的区别在于,在C语言中,被调用函数不能直接修改主调函数中变量的值,而只能修改其私有临时副本的值。
传值调用的利大于弊。在被调用该函数中,参数可以看作是便于初始化的局部变量,因此额外使用的变量更少。这样程序可以更紧凑简洁。
3. 读入一组文本,打印出最长文本

#include <stdio.h>
int getline_(char s[],int lim){
int c,i;
i=0;
while(i<lim-1&&(c=getchar())!=EOF&&c!='\n'){
s[i++]=c;
}
if(c==EOF&&i==0)
return -1;
if(c=='\n')
s[i++]=c;
s[i++]='\0';
return i;
}
void copy(char str1[],char str2[]){
while((*str1++=*str2++)!='\0');
}
int main(){
char line[256];
char longest[256];
char shortest[256];
int len;
int max=0,min=256;
while((len=getline_(line,256))>-1){
if(len>=max)
{
max=len;
copy(longest,line);
}
else if(len<=min)
{
min=len;
copy(shortest,line);
}
}
if(max>0)
printf("%d:%s",max,longest);
if(min<256)
printf("%d:%s",min,shortest);
return 0;
}
下面是输出结果,输入是上面的源代码:

课后题程序:
习题1-8 编写一个统计空格、制表符和换行符个数的程序。

#include <stdio.h>
int main(){
int c,nb,nt,nl;
nb=0;
nt=0;
nl=0;
while((c=getchar())!=EOF){
if(c==' ')
nb++;
else if(c=='\t')
nt++;
else if(c=='\n')
nl++;
}
printf("%2d %2d %2d\n",nb,nt,nl);
}
习题1-9 编写一个将输入复制到输出的程序,并将其中连续的多个空格使用一个空格代替
#include <stdio.h>
int main(){
int c;
int nb;
int prec=-1;
while((c=getchar())!=EOF){
if(c==' '&&prec==' ')
continue;
else
{
putchar(c);
prec=c;
}
}
}
习题1-12 编写一个程序,以每行一个单词的形式打印其输入

int main(){
int c;
int flag;
flag=0;
while((c=getchar())!=EOF){
if(c==' '||c=='\n'||c=='\t'){
if(flag){
putchar('\n');
flag=0;
}
}
else if(!flag){
flag=1;
putchar(c);
}
else{
putchar(c);
}
}
}
习题1-13 编写一个程序,打印输入中单词长度的直方图。水平方向的直方图比较容易绘制,垂直方向的直方图则要困难写。

#include <stdio.h>
#define MAXHIST 15
#define MAXWORD 11
int word_stats(int wl[]){
int flag;
int c,nc,i,ovflow;
flag=0;
nc=0;
ovflow=0;
for(i=0;i<MAXWORD;i++)
wl[i]=0;
while((c=getchar())!=EOF){
if(c==' '||c=='\n'||c=='\t'){
if(flag){
flag=0;
// if(nc>0)
if(nc<MAXWORD)
wl[nc]++;
else
ovflow++;
nc=0;
}
}
else if(!flag){
flag=1;
nc=1;
}
else
nc++;
}
return ovflow;
}
void hist_h(int wl[]){
int i;
int maxvlaue=0;
int len;
for(i=1;i<MAXWORD;i++)
if(wl[i]>maxvlaue)
maxvlaue=wl[i];
for(i=1;i<MAXWORD;++i){
printf("%5d - %5d :",i,wl[i]);
if(wl[i]>0){
if((len=wl[i]*MAXHIST/maxvlaue)<=0)
len=1;
}
else
len=0;
while(len>0){
putchar('*');
len--;
}
putchar('\n');
}
}
void hist_v(int wl[]){
int i,j;
int maxvlaue=0;
int len;
for(i=1;i<MAXWORD;i++)
if(wl[i]>maxvlaue)
maxvlaue=wl[i];
for(i=MAXHIST;i>0;i--){
for(j=1;j<MAXWORD;j++)
if(wl[j]*MAXHIST/maxvlaue>=i)
printf(" * ");
else
printf(" ");
putchar('\n');
}
for(i=1;i<MAXWORD;i++)
printf("%4d ",i);
putchar('\n');
for(i=1;i<MAXWORD;i++)
printf("%4d ",wl[i]);
putchar('\n');
}
int main(){
int wl[MAXWORD];
int ovflow;
ovflow=word_stats(wl);
hist_h(wl);
hist_v(wl);
if(ovflow)
printf("Overflow: %d\n",ovflow);
}

下面是以上面的源文件为输入得到的运行结果:
习题1-18 编写一个程序,删除每个输入行末尾的空格及制表符,并删除完全是空格的行

#include <stdio.h>
int getline_(char s[],int lim){
int c;
int i;
i=0;
while(i<lim-1&&(c=getchar())!=EOF&&c!='\n'){
s[i++]=c;
}
if(c==EOF&&i==0)
return -1;
if(c=='\n')
s[i++]=c;
s[i++]='\0';
return i;
}
int remove_(char s[]){
int i;
i=0;
while(s[i]!='\n')
++i;
--i;
while(i>=0&&(s[i]==' '||s[i]=='\t'))
--i;
if(i>=0){
s[++i]='\n';
s[++i]='\0';
}
return i;
}
int main(){
char line[256];
while(getline_(line,256)>0){
if(remove_(line)>0)
printf("%s",line);
}
}
习题1-19 编写函数rverse(s)将字符串s中的字符顺序颠倒过来。使用该函数编写一个程序,每次颠倒一个输入行中的字符顺序。

#include <stdio.h>
int getline_(char s[],int lim){
int c;
int i;
i=0;
while(i<lim-1&&(c=getchar())!=EOF&&c!='\n'){
s[i++]=c;
}
if(c==EOF&&i==0)
return -1;
if(c=='\n')
s[i++]=c;
s[i++]='\0';
return i;
}
void reverse_(char s[]){
int i,j;
char c;
i=0;
while(s[i]!='\0')
i++;
i--;
if(s[i]=='\n')
i--;
j=0;
while(j<i){
c=s[i];
s[i]=s[j];
s[j]=c;
j++;
i--;
}
}
int main(){
char line[256];
while(getline_(line,256)>0){
reverse_(line);
printf("%s",line);
}
}
习题1-20
请编写程序detab,将输入中的制表符替换成适当数目的空格,使空格充满到下一个制表符终止的地方。假设制表符终止的位置是固定的,比如每隔n列就会出现一个制表符终止位。n应该作为变量还是常量呢?

#include <stdio.h>
#define TABINC 8
int main(){
int c,nb,pos;
nb=0;
pos=1;
while((c=getchar())!=EOF){
if(c=='\t'){
nb=TABINC-(pos-1)%TABINC;
while(nb>0){
putchar(' ');
pos++;
nb--;
}
}
else if(c=='\n'){
putchar(c);
pos=1;
}
else{
putchar(c);
pos++;
}
}
}

习题1-21 编写程序entab,将空格串替换为最少数量的制表符和空格,但要保持单词之间的间隔不变。假设制表符终止位的位置与练习1-20的detab程序的情况相同。当使用一个制表符或者一个空格都可以到达下一个制表符终止位时,选用那种替换字符比较好?

#include <stdio.h>
#define TABINC 8
int main(){
int c,nb,nt,pos;
nb=0;
nt=0;
pos=1;
while((c=getchar())!=EOF){
if(c==' '){
if(pos%TABINC!=0)
++nb;
else{
nb=0;
nt++;
}
}
else{
while(nt>0){
putchar('\t');
nt--;
}
if(c=='\t')
nb=0;
else
while(nb>0){
putchar(' ');
nb--;
}
putchar(c);
if(c=='\n')
pos=0;
else if(c=='\t')
pos=pos+(TABINC-(pos-1)%TABINC)-1;
}
pos++;
}
}

习题1-22


#include <stdio.h>
#define MAXCOL 10
#define TABINC 8
char line[MAXCOL];
int exptab(int pos);
int findblnk(int pos);
int newpos(int pos);
void printl(int pos);
int main(){
int c,pos;
pos=0;
while((c=getchar())!=EOF){
line[pos]=c;
if(c=='\t')
pos=exptab(pos);
else if(c=='\n') {
printl(pos);
pos=0;
}
else if(++pos>=MAXCOL){
pos=findblnk(pos);
printl(pos);
pos=newpos(pos);
}
}
}
void printl(int pos){
int i;
for(i=0;i<pos;i++)
putchar(line[i]);
if(pos>0)
putchar('\n');
}
int exptab(int pos){
line[pos]=' ';
for(++pos;pos<MAXCOL&&pos%TABINC!=0;++pos)
line[pos]=' ';
if(pos<MAXCOL)
return pos;
else{
printl(pos);
return 0;
}
}
int findblnk(int pos){
while(pos>0&&line[pos]!=' ')
pos--;
if(pos==0)
return MAXCOL;
else
return pos+1;
}
int newpos(int pos){
int i,j;
if(pos<=0||pos>=MAXCOL)
return 0;
else{
i=0;
for(j=pos;j<MAXCOL;++j){
line[i]=line[j];
++i;
}
return i;
}
}

习题1-23 编写一个删除C语言程序中所有的注释语句。要正确处理带银行的字符串与字符常量。在C语言中,注释不允许嵌套。

#include <stdio.h>
void rcomment(int c);
void in_comment(void);
void echo_quote(int c);
int main(){
int c;
while((c=getchar())!=EOF)
rcomment(c);
return 0;
}
void rcomment(int c){
int d;
if(c=='/')
if((d=getchar())=='*')
in_comment();
else if(d=='/'){
putchar(c);
rcomment(d);
}
else{
putchar(c);
putchar(d);
}
else if(c=='\''||c=='"')
echo_quote(c);
else
putchar(c);
}
void in_comment(void){
int c,d;
c=getchar();
d=getchar();
while(c!='*'||d!='/'){
c=d;
d=getchar();
}
}
void echo_quote(int c){
int d;
putchar(c);
while((d=getchar())!=c){
putchar(d);
if(d=='\\')
putchar(getchar());
}
putchar(d);
}

习题1-24 编写一个程序,检查C语言程序中的基本语法错误


#include <stdio.h>
int brace,brack,paren;
void in_quote(int c);
void in_comment(void);
void search(int c);
int main(){
int c;
while((c=getchar())!=EOF){
if(c=='/'){
if((c=getchar())=='*')
in_comment();
else
search(c);
}
else if(c=='\''||c=='"')
in_quote(c);
else
search(c);
if(brace<0){
printf("Unbalanced braces\n");
brace=0;
}
else if(brack<0){
printf("Unbalanced brackets\n");
brack=0;
}
else if(paren<0){
printf("Unbalanced parentheses\n");
paren=0;
}
}
if(brace>0)
printf("Unbalanced braces\n");
if(brack>0)
printf("Unbalanced brackets\n");
if(paren>0)
printf("Unbalanced parentheses\n");
}
void search(int c){
if(c=='{')
++brace;
else if(c=='}')
--brace;
else if(c=='[')
++brack;
else if(c==']')
--brack;
else if(c=='(')
++paren;
else if(c==')')
--paren;
}
void in_comment(void){
int c,d;
c=getchar();
d=getchar();
while(c!='*'||d!='/'){
c=d;
d=getchar();
}
}
void in_quote(int c){
int d;
while((d=getchar())!=c)
if(d=='\\')
getchar();
}

第2章 类型,运算符与表达式
1. const限定符
任何变量的声明都可以使用const限定符限定。该限定符指定变量的值不能被修改。对于数组而言,const限定符指定数组所有元素的值都不能被修改。
const char msg[]="warning:";
const限定符也可以配合数组参数使用,它表明函数不能修改该数组元素的值。
2. char类型
char类型是小整型

3. 算术中的隐式类型转换
一般情况下,如果不含有unsigned类型,可以采用下面的方式:

注意float类型的特殊性:

当表达式中含有unsigned类型时:

函数参数中的类型转换:

4. 标准库中的伪随机数发生器函数:rand和srand
标准库中包含一个可移植的实现伪随机数发生器的函数rand以及一个初始化种子数的函数srand。rand函数中使用了强制类型转换:
unsigned long int next=1;
/*rand:return pseudo-random integer on 0..32767*/
int rand(void)
{
next=next*1103515245+12345;
return (unsigned int)(next/65536)%32768;
}
/*srand:set seed for rand()*/
void srand(unsigned int seed){
next=seed;
}
习题2-3 编写函数htoi(s),把由十六进制数字组成的字符串(包含可选的前缀0x或0X)转换为与之等价的整型数。字符串中允许包含的数字包括:0~9,a~f以及A-F

#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#define YES 1
#define NO 0
int htoi(char s[]){
int hexd,i,inhex,n;
i=0;
if(s[i]=='0'){
++i;
if(s[i]=='x'||s[i]=='X')
++i;
}
n=0;
inhex=YES;
while(inhex){
if(s[i]>='0'&&s[i]<='9')
hexd=s[i]-'0';
else if(s[i]>='a'&&s[i]<='f')
hexd=s[i]-'a'+10;
else if(s[i]>='A'&&s[i]<='F')
hexd=s[i]-'A'+10;
else
inhex=NO;
if(inhex==YES)
n=16*n+hexd;
i++;
}
return n;
}
int main(){
int count=10;
int i;
char s[100];
for(i=0;i<10;i++){
int num=rand()%10000;
int n;
sprintf(s,"%#0x",num);
n=htoi(s);
printf("%#0x %s %d %d \n",num,s,num,n);
}
}
一个运行结果展示:

习题2-4 重写函数squeeze(s1,s2),将字符串s1中任何与字符串s2中字符匹配的字符都删除
void squeeze(char s1[],char s2[]){
int i,j,k;
for(i=k=0;s1[i]!='\0';i++){
for(j=0;s2[j]!='\0'&&s2[j]!=s1[i];j++);
if(s2[j]=='\0')
s1[k++]=s1[i];
}
s1[k]='\0';
}

习题2-5

void any(char s1[],char s2[]){
int i,j;
for(i=0;s1[i]!='\0';i++)
for(j=0;s2[j]!='\0';j++)
if(s1[i]==s2[j])
return i;
return -1;
}
5. C语言中的位操作
getbits函数:返回x中从右边数第p位开始向右数n位的字段。这里假定最右边的一位是第0位,n与p都是合理的正值。
unsigned getbits(unsigned x,int p,int n){
return (x>>(p+1-n))&~(~0<<n);
}

unsigned sebits(unsgined x,int p,int n,unsigned y){
unsigned x1=x&(~0<<(p+1));//获取x的高32-(p+1)位
unsigned x2=x&((1<<(p-n+1))-1);//获取x的低p-n+1位
unsigned y1=(y&~(~0<<n))<<(p+1-n);//获得y的最低n位,并且移动到合适的位置
return x1|x2|y1;
}
可以换一种方式写:
unsigned sebits(unsgined x,int p,int n,unsigned y){
unsigned m1= (~0<<(p+1))| ((1<<(p-n+1))-1);//得到屏蔽码
unsigned x1=x&m1;
unsigned y1=(y&~(~0<<n))<<(p+1-n);//获得y的最低n位,并且移动到合适的位置
return x1|y1;
}
下面是一个标准答案:

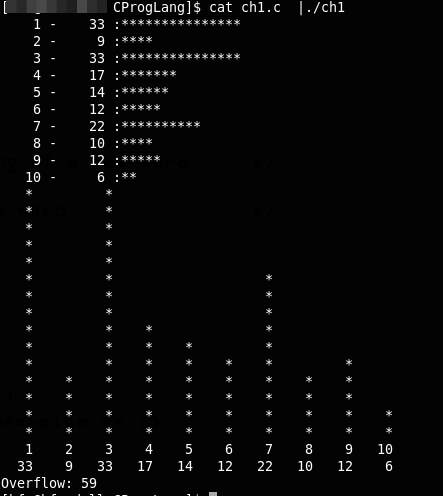
这儿比较难写是就是x的屏蔽码,下面的程序是对比两种方法产生的屏蔽码:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int main(){
int i;
for(i=0;i<10;i++){
int p=rand()%32;
int n=rand()%p+1;
unsigned m1=(~0<<(p+1))|((1<<(p-n+1))-1);
unsigned m2=~(~(~0<<n)<<(p+1-n));
printf("p=%d n=%d: %#0x %#0x ",p,n,m1,m2);
if(m1==m2)
printf("OK\n");
else
printf("NO\n");
}
}
一个输出结果如下:

unsigned invert(unsigned x,int p,int n){
unsigned x1=x&(~0<<(p+1));//获取x的高32-(p+1)位
unsigned x2=x&((1<<(p-n+1))-1);//获取x的低p-n+1位
unsigned x3=~x&(~(~0<<n)<<(p-n+1));//获取x的中间n位
return x1|x2|x3;
}
下面是一个标准答案

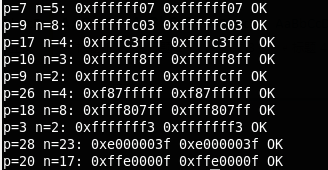
下面是一个测试:

#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
unsigned invert(unsigned x,int p,int n){
unsigned m1=(~0<<(p+1));//获取x的高32-(p+1)位
unsigned x1=x&m1;
unsigned m2=((1<<(p-n+1))-1);//获取x的低p-n+1位
unsigned x2=x&m2;
unsigned m3=(~(~0<<n)<<(p-n+1));//获取x的中间n位
unsigned x3=(~x)&m3;
printf("%#0x %#0x %#0x\n",m1,m2,m3);
return x1|x2|x3;
}
unsigned invert2(unsigned x,int p,int n){
return x^(~(~0<<n)<<(p+1-n));
}
int main(){
int i;
unsigned x=rand();
for(i=0;i<25;i++){
int p=rand()%32;
int n=rand()%p+1;
int y1=invert(x,p,n);
int y2=invert2(x,p,n);
printf("%#0x %2d %2d %#0x %#0x ",x,p,n,y1,y2);
if(y1==y2)
printf("OK\n");
else
printf("NO\n");
}
}
输出如下:
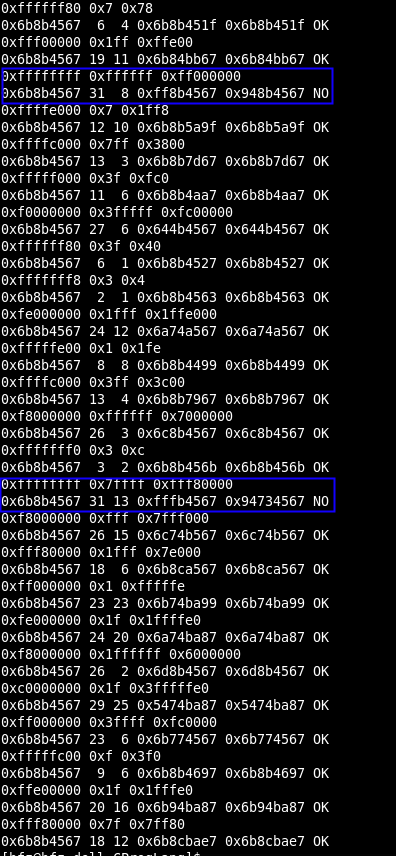
可以看到当p=31时,第一种方法就出错了。主要是将一个无符号数进行右移32位(移出所有位)时,编译器会给出一个【 warning: right shift count >= width of type】的警告。然后返回原始值,而不是0

unsigned rightrot(unsigned x,int n){
unsigned x1=x>>n;//左移得到高32-n位
unsigned x2=x<<(sizeof(x)*8-n);//右移得到低n位
return x1|x2;
}
下面标准答案给出的解释:

#include <stdio.h>
int wordlength()
{
int i;
unsigned v=(unsigned)~0;
for(i=1;(v=v>>1)>0;i++)
;
return 1;
}
unsigned rightrot(unsigned x,int n){
int rbit;
while(n-->0){
rbit=(x&1)<<(wordlength()-1);
x=x>>1;
x=x|rbit;
}
return x;
}

unsigned rightrot2(unsigned x,int n){
unsigned rbits;
if((n-n%wordlength())>0){
rbits=~(~0<<n)&x;
rbits=rbits<<(wordlength()-n);
x=x>>n;
x=x|rbits;
}
return x;
}

6. 统计整型数中二进制位1的个数:
int bitcount(unsigned x){
int n=0;
while(x!=0){
if(x&0x1)
n++;
x>>1;
}
return n;
}
习题 2-9 在求对二的补码时,表达式x&(x-1)可以删除x中最右边为1的一个二进制位。请解释这样做的道理。用这一方法重写bitcount函数, 以加快其执行速度。
重写的代码如下:
int bitcount(unsigned x){
int b;
b=0;
while(x!=0){
b++;
x&=x-1;
}
return b;
}


第3章 程序流控制
1. 折半查找

int bin_search(int x,int v[],int n){
int low,high,mid;
low=0;
high=n-1;
while(low<=high){
mid=(low+high)>>1;
if(x<v[mid])
high=mid-1;
else if(x>v[mid])
low=mid+1;
else
return mid;
}
return -1;
}
int bin_search(int x,int v[],int n){
int low,high,mid;
low=0;
high=n-1;
mid=(low+high)/2;
while(low<=high&&x!=v[mid]){
if(x<v[mid])
high=mid-1;
else
low=mid+1;
mid=(low+high)/2;
}
if(x==v[mid])
return mid;
else
return -1;
}

2. atoi函数
字符串转换为对应数值的函数atoi

View
Code
测试输出如下:
希尔排序shell
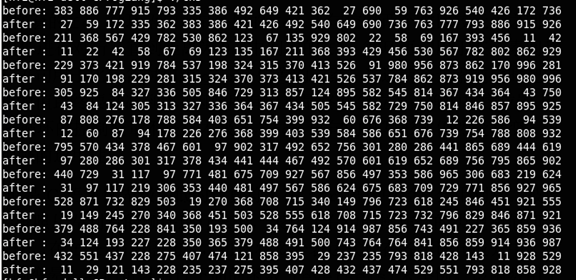
shell算法是D.L. Shell于1959年发明的,基本思想是:先比较近距离的元素,而不是像简单交换排序算法那样先比较相邻的元素。这样可以快速减少大量的无序情况,从而减轻后序的工作。被比较的元素之间的距离逐步减少,直到减少为1,这时编程了相邻元素的互换。

#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
void shellsort(int v[],int n){
int gap,i,j,temp;
for(gap=n/2;gap>0;gap/=2)
for(i=gap;i<n;i++)
for(j=i-gap;j>=0&&v[j]>v[j+gap];j-=gap){
temp=v[j];
v[j]=v[j+gap];
v[j+gap]=temp;
}
}
void print_arr(int v[],int n){
int i;
for(i=0;i<n;i++)
printf("%4d",v[i]);
printf("\n");
}
int main(){
int i;
for(i=0;i<10;i++){
int arr[20],j,b[20];
for(j=0;j<20;j++)
{
int val=rand()%1000;
arr[j]=val;
b[j]=val;
}
printf("before:");
print_arr(b,20);
shellsort(arr,20);
printf("after :");
print_arr(arr,20);
}
}
测试输出如下:
习题 3-3 讲些函数expand(s1,s2),将字符串s1中类似于a-z一类的速记符号在字符串s2中扩展为等价的完整列表abc...xyz。该函数可以处理大小写字母和数字,并且可以处理a-b-c,a-z0-9与a-z等类似的情况。作为前导和尾随的字符原样复制。

#include <stdio.h>
void expand(char s1[],char s2[]){
char c;
int i,j;
i=0;
j=0;
while((c=s1[i++])!='\0'){
if(s1[i]=='-'&&s1[i+1]>=c){
i++;
while(c<s1[i])
s2[j++]=c++;
}
else
s2[j++]=c;
}
s2[j]='\0';
}

函数itoa:将整型数转化为字符串

#include <stdio.h>
void itoa(int n,char s[]){
int i,sign;
int x,y;
if((sign=n)<0)
n=-n;
i=0;
do{
s[i++]=n%10+'0';
}
while((n/=10)>0);
if(sign<0)
s[i++]='-';
s[i]='\0';
for(x=0,y=i-1;x<y;x++,y--) {
char c=s[x];
s[x]=s[y];
s[y]=c;
}
}
int atoi_(char s[]){
int i,n,sign;
for(i=0;isspace(s[i]);i++);
sign=(s[i]=='-')?-1:1;
if(s[i]=='+'||s[i]=='-')
i++;
for(n=0;isdigit(s[i]);i++)
n=10*n+(s[i]-'0');
return sign*n;
}
int main(){
int i;
char s[20];
for(i=0;i<10;i++){
int val=rand();
int d;
itoa(val,s);
d=atoi_(s);
printf("%12d %12s %12d ",val,s,d);
if(val==d)
printf("OK\n");
else
printf("NO\n");
}
}
测试结果如下:

习题3-4


void itoa2(int n,char s[]){
int i,sign;
int x,y;
sign=n;
i=0;
do{
s[i++]= ABS(n%10)+'0';
}
while((n/=10)!=0);
if(sign<0)
s[i++]='-';
s[i]='\0';
for(x=0,y=i-1;x<y;x++,y--) {
char c=s[x];
s[x]=s[y];
s[y]=c;
}
}

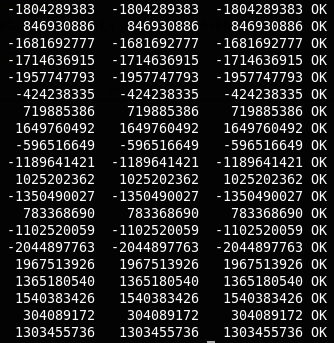
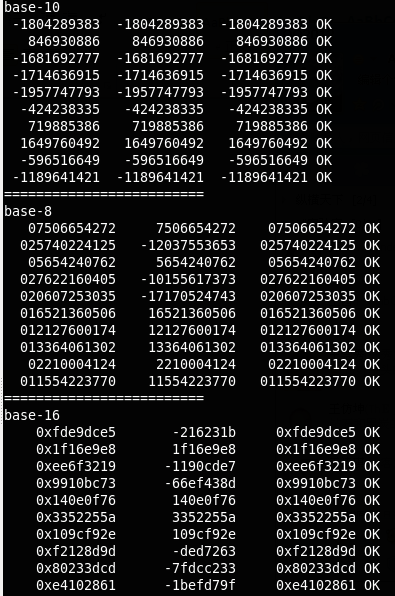
习题 3-5 编写函数itob(n,s,b),将整数n转换为以b为底的数,并将结果以字符的形式保存到字符串s中。例如,itob(n,s,16)把整数n格式化为十六进制整数保存在s中。

#include <stdio.h>
#define ABS(x) ((x)<0?-(x):(x))
void itob(int n,char s[],int b){
int i,j,sign;
int x,y;
sign=n;
i=0;
do{
j=ABS(n%b);
s[i++]=(j<10)?j+'0':j+'a'-10;
}
while((n/=b)!=0);
if(sign<0)
s[i++]='-';
s[i]='\0';
for(x=0,y=i-1;x<y;x++,y--) {
char c=s[x];
s[x]=s[y];
s[y]=c;
}
}
void test_10(){
int i;
char s[20];
for(i=0;i<10;i++){
int val=rand();
int d;
if(val&0x1)
val=-val;
itob(val,s,10);
sscanf(s,"%d",&d);
printf("%12d %12s %12d ",val,s,d);
if(val==d)
printf("OK\n");
else
printf("NO\n");
}
}
void test_8(){
int i;
char s[20];
for(i=0;i<10;i++){
int val=rand();
int d;
if(val&0x1)
val=-val;
itob(val,s,8);
// d=atoi_(s);
sscanf(s,"%o",&d);
printf("%#14o %14s %#14o ",val,s,d);
if(val==d)
printf("OK\n");
else
printf("NO\n");
}
}
void test_16(){
int i;
char s[40];
for(i=0;i<10;i++){
int val=rand();
int d;
if(val&0x1)
val=-val;
itob(val,s,16);
sscanf(s,"%x",&d);
printf("%#14x %14s %#14x ",val,s,d);
if(val==d)
printf("OK\n");
else
printf("NO\n");
}
}
int main(){
printf("base-10\n");
test_10();
printf("=========================\n");
printf("base-8\n");
test_8();
printf("=========================\n");
printf("base-16\n");
test_16();
}

我们在测试程序中进行8,10和16三种进制的测试。主要是C语言提供到这三种进制的转换,这样便于我们的测试。
测试结果如下:
函数trim:用于删除字符串尾部的空格、制表符与换行符。当发现最右边的字符为非空格符、非制表符、非换行符时,就使用break语句从循环中退出。
#include <stdio.h>
int trim(char s[]){
int i;
for(i=strlen(s)-1;i>=0;i--)
if(s[i]!=' '&&s[i]!='\t'&&s[i]!='\n')
break;
s[i+1]='\0';
return i;
}
第4章 函数与程序结构
1. 实现类似UNIX系统上的grep类似的功能:strindex


#include <stdio.h>
#define MAXLINE 1000
char pattern[]="line";
int getline_(char line[],int lim){
int i,c;
i=0;
while(i<lim-1&&((c=getchar())!=EOF)&&c!='\n')
line[i++]=c;
if(c==EOF&&i==0)
return -1;
if(c=='\n')
line[i++]=c;
line[i]='\0';
return i;
}
int strindex(char src[],char itm[]){
int i,j;
// int len1=strlen(src);
// int len2=strlen(itm);
for(i=0;src[i]!='\0';i++){
int k;
for(j=0,k=i;itm[j]!='\0'&&itm[j]==src[k];j++,k++);
if(itm[j]=='\0')
return i;
}
return -1;
}
int main(){
char line[MAXLINE];
int found=0;
while(getline_(line,MAXLINE)>0)
if(strindex(line,pattern)>=0){
printf("%s",line);
found++;
}
}
习题 4-1 编写函数strrindex(s,t),它返回字符串t在s中最右边出现的位置。如果s中不包含t,则返回-1

int strrindex(char s[],char t[]){
int i,j;
int pos=-1;
for(i=0;s[i]!='\0';i++){
int k;
for(j=0,k=i;t[j]!='\0'&&t[j]==s[k];j++,k++);
if(t[j]=='\0')
pos=i;
}
return pos;
}

int strrindex2(char s[],char t[]){
int i,j;
int ls=strlen(s);
int lt=strlen(t);
for(i=ls-lt;i>=0;i--){
int k;
for(j=0,k=i;t[j]!='\0'&&t[j]==s[k];j++,k++);
if(t[j]=='\0')
return i;
}
return -1;
}

函数atof:将字符串转换为浮点数

#include <stdio.h>
#include <ctype.h>
double atof_(char s[]){
double val,power;
int i,sign;
for(i=0;isspace(s[i]);i++);
sign=(s[i]=='-')?-1:1;
if(s[i]=='+'||s[i]=='-')
i++;
for(val=0.0;isdigit(s[i]);i++)
val=10.0*val+(s[i]-'0');
if(s[i]=='.')
i++;
for(power=1.0;isdigit(s[i]);i++){
val=10.0*val+(s[i]-'0');
power*=10;
}
return sign*val/power;
}
int main(){
int i;
for(i=0;i<25;i++){
double val=rand()%100000/100.0;
char s[20];
double val2;
sprintf(s,"%f",val);
val2=atof_(s);
printf("%10.5f %12s %10.5f\n",val,s,val2);
}
}

习题4-2 对atof函数进行扩充,使他可以处理形如:
123.45e-6
的科学表示法,其中浮点数后面可能会紧跟一个e或E以及一个指数(可能有正负号)。

double atof_(char s[]){
double val,power;
int i,sign;
for(i=0;isspace(s[i]);i++);
sign=(s[i]=='-')?-1:1;
if(s[i]=='+'||s[i]=='-')
i++;
for(val=0.0;isdigit(s[i]);i++)
val=10.0*val+(s[i]-'0');
if(s[i]=='.')
i++;
for(power=1.0;isdigit(s[i]);i++){
val=10.0*val+(s[i]-'0');
power*=10;
}
val= sign*val/power;
if(s[i]=='e'||s[i]=='E'){
int exp;
sign=(s[++i]=='-')?-1:1;
if(s[i]=='+'||s[i]=='-')
i++;
for(exp=0;isdigit(s[i]);i++)
exp=10*exp+(s[i]-'0');
if(sign)
while(exp-->0)
val*=10;
else
while(exp-->0)
val/=10;
}
return val;
}

4.3 外部变量

一个简单的计算器程序

#if 1
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <ctype.h>
#define ABS(x) ((x)<0?-(x):(x))
double atof_(char s[]){
double val,power;
int i,sign;
for(i=0;isspace(s[i]);i++);
sign=(s[i]=='-')?-1:1;
if(s[i]=='+'||s[i]=='-')
i++;
for(val=0.0;isdigit(s[i]);i++)
val=10.0*val+(s[i]-'0');
if(s[i]=='.')
i++;
for(power=1.0;isdigit(s[i]);i++){
val=10.0*val+(s[i]-'0');
power*=10;
}
val= sign*val/power;
if(s[i]=='e'||s[i]=='E'){
int exp;
sign=(s[++i]=='-')?-1:1;
if(s[i]=='+'||s[i]=='-')
i++;
for(exp=0;isdigit(s[i]);i++)
exp=10*exp+(s[i]-'0');
if(sign)
while(exp-->0)
val*=10;
else
while(exp-->0)
val/=10;
}
return val;
}
#define MAXVAL 1000
int sp=0;
double val[MAXVAL];
void push(double f){
if(sp<MAXVAL)
val[sp++]=f;
else
printf("error:stack full\n");
}
double pop(void){
if(sp>0)
return val[--sp];
else
printf("error:stack empty\n");
return 0.0;
}
#define BUFSIZE 100
char buf[BUFSIZE];
int bufp=0;
int getch(void){
return bufp>0?buf[--bufp]:getchar();
}
void ungetch(int c){
if(bufp>=BUFSIZE)
printf("ungetch: too many characters\n");
else
buf[bufp++]=c;
}
#define MAXOP 1000
#define NUMBER '0'
int getop(char s[]){
int i,c;
while((s[0]=c=getch())==' '||c=='\t')
;
s[1]='\0';
if(!isdigit(c)&&c!='.')
return c;
i=0;
if(isdigit(c))
while(isdigit(s[++i]=c=getch()))
;
if(c=='.')
while(isdigit(s[++i]=c=getch()))
;
s[i]='\0';
if(c!=EOF)
ungetch(c);
return NUMBER;
}
int main(){
int type;
double op2;
char s[MAXOP];
while((type=getop(s))!=EOF){
switch(type){
case NUMBER:
push(atof_(s));
break;
case '+':
push(pop()+pop());
break;
case '-':
op2=pop();
push(pop()-op2);
break;
case '*':
push(pop()*pop());
break;
case '/':
op2=pop();
if(ABS(op2)>1e-10)
push(pop()/op2);
else
printf("error:zero divisor\n");
break;
case '\n':
printf("\t%.8g\n",pop());
break;
default:
printf("error: unknown command %s\n",s);
break;
}
}
}



#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <ctype.h>
#include <math.h>
#define ABS(x) ((x)<0?-(x):(x))
double atof_(char s[]){
double val,power;
int i,sign;
for(i=0;isspace(s[i]);i++);
sign=(s[i]=='-')?-1:1;
if(s[i]=='+'||s[i]=='-')
i++;
for(val=0.0;isdigit(s[i]);i++)
val=10.0*val+(s[i]-'0');
if(s[i]=='.')
i++;
for(power=1.0;isdigit(s[i]);i++){
val=10.0*val+(s[i]-'0');
power*=10;
}
val= sign*val/power;
if(s[i]=='e'||s[i]=='E'){
int exp;
sign=(s[++i]=='-')?-1:1;
if(s[i]=='+'||s[i]=='-')
i++;
for(exp=0;isdigit(s[i]);i++)
exp=10*exp+(s[i]-'0');
if(sign)
while(exp-->0)
val*=10;
else
while(exp-->0)
val/=10;
}
return val;
}
#define MAXVAL 1000
int sp=0;
double val[MAXVAL];
void push(double f){
if(sp<MAXVAL)
val[sp++]=f;
else
printf("error:stack full\n");
}
double pop(void){
if(sp>0)
return val[--sp];
else
printf("error:stack empty\n");
return 0.0;
}
#define BUFSIZE 100
char buf[BUFSIZE];
int bufp=0;
int getch(void){
return bufp>0?buf[--bufp]:getchar();
}
void ungetch(int c){
if(bufp>=BUFSIZE)
printf("ungetch: too many characters\n");
else
buf[bufp++]=c;
}
#define MAXOP 1000
#define NUMBER '0'
int getop(char s[]){
int i,c;
while((s[0]=c=getch())==' '||c=='\t')
;
s[1]='\0';
if(!isdigit(c)&&c!='.'&&c!='-')
return c;
i=0;
if(c=='-')
if(isdigit(c=getch())||c=='.')
s[++i]=c;
else
{
if(c!=EOF)
ungetch(c);
return '-';
}
if(isdigit(c))
while(isdigit(s[++i]=c=getch()))
;
if(c=='.')
while(isdigit(s[++i]=c=getch()))
;
s[i]='\0';
if(c!=EOF)
ungetch(c);
return NUMBER;
}
int main(){
int type;
double op2;
char s[MAXOP];
while((type=getop(s))!=EOF){
switch(type){
case NUMBER:
push(atof_(s));
break;
case '+':
push(pop()+pop());
break;
case '-':
op2=pop();
push(pop()-op2);
break;
case '*':
push(pop()*pop());
break;
case '/':
op2=pop();
if(ABS(op2)>1e-10)
push(pop()/op2);
else
printf("error:zero divisor\n");
break;
case '%':
op2=pop();
if(ABS(op2)>1e-10)
push(fmod(pop(),op2));
else
printf("error:zero divisor\n");
break;
case '\n':
printf("\t%.8g\n",pop());
break;
default:
printf("error: unknown command %s\n",s);
break;
}
}
}



#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <ctype.h>
#include <math.h>
#define ABS(x) ((x)<0?-(x):(x))
double atof_(char s[]){
double val,power;
int i,sign;
for(i=0;isspace(s[i]);i++);
sign=(s[i]=='-')?-1:1;
if(s[i]=='+'||s[i]=='-')
i++;
for(val=0.0;isdigit(s[i]);i++)
val=10.0*val+(s[i]-'0');
if(s[i]=='.')
i++;
for(power=1.0;isdigit(s[i]);i++){
val=10.0*val+(s[i]-'0');
power*=10;
}
val= sign*val/power;
if(s[i]=='e'||s[i]=='E'){
int exp;
sign=(s[++i]=='-')?-1:1;
if(s[i]=='+'||s[i]=='-')
i++;
for(exp=0;isdigit(s[i]);i++)
exp=10*exp+(s[i]-'0');
if(sign)
while(exp-->0)
val*=10;
else
while(exp-->0)
val/=10;
}
return val;
}
#define MAXVAL 1000
int sp=0;
double val[MAXVAL];
void push(double f){
if(sp<MAXVAL)
val[sp++]=f;
else
printf("error:stack full\n");
}
double pop(void){
if(sp>0)
return val[--sp];
else
printf("error:stack empty\n");
return 0.0;
}
void clear(void){
sp=0;
}
#define BUFSIZE 100
char buf[BUFSIZE];
int bufp=0;
int getch(void){
return bufp>0?buf[--bufp]:getchar();
}
void ungetch(int c){
if(bufp>=BUFSIZE)
printf("ungetch: too many characters\n");
else
buf[bufp++]=c;
}
#define MAXOP 1000
#define NUMBER '0'
int getop(char s[]){
int i,c;
while((s[0]=c=getch())==' '||c=='\t')
;
s[1]='\0';
if(!isdigit(c)&&c!='.'&&c!='-')
return c;
i=0;
if(c=='-')
if(isdigit(c=getch())||c=='.')
s[++i]=c;
else
{
if(c!=EOF)
ungetch(c);
return '-';
}
if(isdigit(c))
while(isdigit(s[++i]=c=getch()))
;
if(c=='.')
while(isdigit(s[++i]=c=getch()))
;
s[i]='\0';
if(c!=EOF)
ungetch(c);
return NUMBER;
}
int main(){
int type;
double op1,op2;
char s[MAXOP];
while((type=getop(s))!=EOF){
switch(type){
case NUMBER:
push(atof_(s));
break;
case '+':
push(pop()+pop());
break;
case '-':
op2=pop();
push(pop()-op2);
break;
case '*':
push(pop()*pop());
break;
case '/':
op2=pop();
if(ABS(op2)>1e-10)
push(pop()/op2);
else
printf("error:zero divisor\n");
break;
case '%':
op2=pop();
if(ABS(op2)>1e-10)
push(fmod(pop(),op2));
else
printf("error:zero divisor\n");
break;
case '?':
op2=pop();
printf("\t%.8g\n",op2);
push(op2);
break;
case 'c':
clear();
break;
case 'd':
op2=pop();
push(op2);
push(op2);
break;
case 's':
op1=pop();
op2=pop();
push(op1);
push(op2);
case '\n':
printf("\t%.8g\n",pop());
break;
default:
printf("error: unknown command %s\n",s);
break;
}
}
}

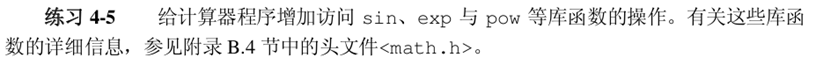

#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <ctype.h>
#include <math.h>
#include <string.h>
#define ABS(x) ((x)<0?-(x):(x))
double atof_(char s[]){
double val,power;
int i,sign;
for(i=0;isspace(s[i]);i++);
sign=(s[i]=='-')?-1:1;
if(s[i]=='+'||s[i]=='-')
i++;
for(val=0.0;isdigit(s[i]);i++)
val=10.0*val+(s[i]-'0');
if(s[i]=='.')
i++;
for(power=1.0;isdigit(s[i]);i++){
val=10.0*val+(s[i]-'0');
power*=10;
}
val= sign*val/power;
if(s[i]=='e'||s[i]=='E'){
int exp;
sign=(s[++i]=='-')?-1:1;
if(s[i]=='+'||s[i]=='-')
i++;
for(exp=0;isdigit(s[i]);i++)
exp=10*exp+(s[i]-'0');
if(sign)
while(exp-->0)
val*=10;
else
while(exp-->0)
val/=10;
}
return val;
}
#define MAXVAL 1000
int sp=0;
double val[MAXVAL];
void push(double f){
if(sp<MAXVAL)
val[sp++]=f;
else
printf("error:stack full\n");
}
double pop(void){
if(sp>0)
return val[--sp];
else
printf("error:stack empty\n");
return 0.0;
}
#define BUFSIZE 100
char buf[BUFSIZE];
int bufp=0;
int getch(void){
return bufp>0?buf[--bufp]:getchar();
}
void ungetch(int c){
if(bufp>=BUFSIZE)
printf("ungetch: too many characters\n");
else
buf[bufp++]=c;
}
void mathfnc(char s[]){
double op2;
if(strcmp(s,"sin")==0)
push(sin(pop()));
else if(strcmp(s,"cos")==0)
push(cos(pop()));
else if(strcmp(s,"exp")==0)
push(exp(pop()));
else if(strcmp(s,"pow")==0) {
op2=pop();
push(pow(pop(),op2));
}
else
printf("error: %s not supported\n",s);
}
#define MAXOP 1000
#define NUMBER '0'
#define NAME 'n'
int getop(char s[]){
int i,c;
while((s[0]=c=getch())==' '||c=='\t')
;
s[1]='\0';
i=0;
if(islower(c)){
while(islower(s[++i]=c=getch()))
;
s[i]='\0';
if(c!=EOF)
ungetch(c);
if(strlen(s)>1)
return NAME;
else
return c;
}
if(!isdigit(c)&&c!='.'&&c!='-')
return c;
if(c=='-')
if(isdigit(c=getch())||c=='.')
s[++i]=c;
else
{
if(c!=EOF)
ungetch(c);
return '-';
}
if(isdigit(c))
while(isdigit(s[++i]=c=getch()))
;
if(c=='.')
while(isdigit(s[++i]=c=getch()))
;
s[i]='\0';
if(c!=EOF)
ungetch(c);
return NUMBER;
}
int main(){
int type;
double op1,op2;
char s[MAXOP];
while((type=getop(s))!=EOF){
switch(type){
case NUMBER:
push(atof_(s));
break;
case NAME:
mathfnc(s);
break;
case '+':
push(pop()+pop());
break;
case '-':
op2=pop();
push(pop()-op2);
break;
case '*':
push(pop()*pop());
break;
case '/':
op2=pop();
if(ABS(op2)>1e-10)
push(pop()/op2);
else
printf("error:zero divisor\n");
break;
case '%':
op2=pop();
if(ABS(op2)>1e-10)
push(fmod(pop(),op2));
else
printf("error:zero divisor\n");
break;
case '\n':
printf("\t%.8g\n",pop());
break;
default:
printf("error: unknown command %s\n",s);
break;
}
}
}



#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <ctype.h>
#include <math.h>
#define ABS(x) ((x)<0?-(x):(x))
double atof_(char s[]){
double val,power;
int i,sign;
for(i=0;isspace(s[i]);i++);
sign=(s[i]=='-')?-1:1;
if(s[i]=='+'||s[i]=='-')
i++;
for(val=0.0;isdigit(s[i]);i++)
val=10.0*val+(s[i]-'0');
if(s[i]=='.')
i++;
for(power=1.0;isdigit(s[i]);i++){
val=10.0*val+(s[i]-'0');
power*=10;
}
val= sign*val/power;
if(s[i]=='e'||s[i]=='E'){
int exp;
sign=(s[++i]=='-')?-1:1;
if(s[i]=='+'||s[i]=='-')
i++;
for(exp=0;isdigit(s[i]);i++)
exp=10*exp+(s[i]-'0');
if(sign)
while(exp-->0)
val*=10;
else
while(exp-->0)
val/=10;
}
return val;
}
#define MAXVAL 1000
int sp=0;
double val[MAXVAL];
void push(double f){
if(sp<MAXVAL)
val[sp++]=f;
else
printf("error:stack full\n");
}
double pop(void){
if(sp>0)
return val[--sp];
else
printf("error:stack empty\n");
return 0.0;
}
#define BUFSIZE 100
char buf[BUFSIZE];
int bufp=0;
int getch(void){
return bufp>0?buf[--bufp]:getchar();
}
void ungetch(int c){
if(bufp>=BUFSIZE)
printf("ungetch: too many characters\n");
else
buf[bufp++]=c;
}
#define MAXOP 1000
#define NUMBER '0'
int getop(char s[]){
int i,c;
while((s[0]=c=getch())==' '||c=='\t')
;
s[1]='\0';
if(!isdigit(c)&&c!='.'&&c!='-')
return c;
i=0;
if(c=='-')
if(isdigit(c=getch())||c=='.')
s[++i]=c;
else
{
if(c!=EOF)
ungetch(c);
return '-';
}
if(isdigit(c))
while(isdigit(s[++i]=c=getch()))
;
if(c=='.')
while(isdigit(s[++i]=c=getch()))
;
s[i]='\0';
if(c!=EOF)
ungetch(c);
return NUMBER;
}
int main(){
int type,i,var=0;
double op2, v;
char s[MAXOP];
double variable[26];
for(i=0;i<26;i++)
variable[i]=0.0;
while((type=getop(s))!=EOF){
switch(type){
case NUMBER:
push(atof_(s));
break;
case '+':
push(pop()+pop());
break;
case '-':
op2=pop();
push(pop()-op2);
break;
case '*':
push(pop()*pop());
break;
case '/':
op2=pop();
if(ABS(op2)>1e-10)
push(pop()/op2);
else
printf("error:zero divisor\n");
break;
case '%':
op2=pop();
if(ABS(op2)>1e-10)
push(fmod(pop(),op2));
else
printf("error:zero divisor\n");
break;
case '\n':
v=pop();
printf("\t%.8g\n",v);
break;
case '=':
pop();
if(var>='A'&&var<='Z')
variable[var-'A']=pop();
else
printf("error: no variable name\n");
break;
default:
if(type>='A'&&type<='Z')
push(variable[type-'A']);
else if(type =='v')
push(v);
else
printf("error: unknown command %s\n",s);
break;
}
var=type;
}
}

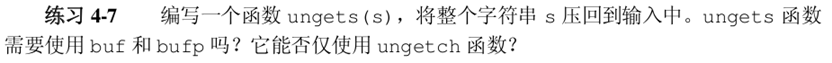
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#define BUFSIZE 100
char buf[BUFSIZE];
int bufp=0;
int getch(void){
return bufp>0?buf[--bufp]:getchar();
}
void ungetch(int c){
if(bufp>=BUFSIZE)
printf("ungetch: too many characters\n");
else
buf[bufp++]=c;
}
void ungets(char s[]){
int len=strlen(s);
while(len>0)
ungetch(s[--len]);
}

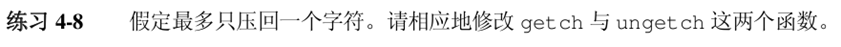

char buf=0;
int getch(void){
int c;
if(buf!=0)
c=buf;
else
c=getchar();
buf=0;
return c;
}
void ungetch(int c){
if(buf!=0)
printf("ungetch:too many characters\n");
else
buf=c;
}



#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <ctype.h>
#include <math.h>
#define ABS(x) ((x)<0?-(x):(x))
double atof_(char s[]){
double val,power;
int i,sign;
for(i=0;isspace(s[i]);i++);
sign=(s[i]=='-')?-1:1;
if(s[i]=='+'||s[i]=='-')
i++;
for(val=0.0;isdigit(s[i]);i++)
val=10.0*val+(s[i]-'0');
if(s[i]=='.')
i++;
for(power=1.0;isdigit(s[i]);i++){
val=10.0*val+(s[i]-'0');
power*=10;
}
val= sign*val/power;
if(s[i]=='e'||s[i]=='E'){
int exp;
sign=(s[++i]=='-')?-1:1;
if(s[i]=='+'||s[i]=='-')
i++;
for(exp=0;isdigit(s[i]);i++)
exp=10*exp+(s[i]-'0');
if(sign)
while(exp-->0)
val*=10;
else
while(exp-->0)
val/=10;
}
return val;
}
#define MAXVAL 1000
int sp=0;
double val[MAXVAL];
void push(double f){
if(sp<MAXVAL)
val[sp++]=f;
else
printf("error:stack full\n");
}
double pop(void){
if(sp>0)
return val[--sp];
else
printf("error:stack empty\n");
return 0.0;
}
//#define BUFSIZE 100
//char buf[BUFSIZE];
//int bufp=0;
//int getch(void){
// return bufp>0?buf[--bufp]:getchar();
//}
//void ungetch(int c){
// if(bufp>=BUFSIZE)
// printf("ungetch: too many characters\n");
// else
// buf[bufp++]=c;
//}
#define MAXLINE 100
char line[MAXLINE];
int li=0;
int getline_(char line[],int lim){
int i,c;
i=0;
while(i<lim-1&&((c=getchar())!=EOF)&&c!='\n')
line[i++]=c;
if(c==EOF&&i==0)
return -1;
if(c=='\n')
line[i++]=c;
line[i]='\0';
return i;
}
#define MAXOP 1000
#define NUMBER '0'
int getop(char s[]){
int i,c;
if(line[li]=='\0')
if(getline_(line,MAXLINE)==-1)
return EOF;
else
li=0;
while((s[0]=c=line[li++])==' '||c=='\t')
;
s[1]='\0';
if(!isdigit(c)&&c!='.'&&c!='-')
return c;
i=0;
if(c=='-')
if(isdigit(c=line[li++])||c=='.')
s[++i]=c;
else
{
if(c!=EOF)
li--;
return '-';
}
if(isdigit(c))
while(isdigit(s[++i]=c=line[li++]))
;
if(c=='.')
while(isdigit(s[++i]=c=line[li++]))
;
s[i]='\0';
li--;
return NUMBER;
}
int main(){
int type;
double op2;
char s[MAXOP];
while((type=getop(s))!=EOF){
switch(type){
case NUMBER:
push(atof_(s));
break;
case '+':
push(pop()+pop());
break;
case '-':
op2=pop();
push(pop()-op2);
break;
case '*':
push(pop()*pop());
break;
case '/':
op2=pop();
if(ABS(op2)>1e-10)
push(pop()/op2);
else
printf("error:zero divisor\n");
break;
case '%':
op2=pop();
if(ABS(op2)>1e-10)
push(fmod(pop(),op2));
else
printf("error:zero divisor\n");
break;
case '\n':
printf("\t%.8g\n",pop());
break;
default:
printf("error: unknown command %s\n",s);
break;
}
}
}

快速排序


#include <stdio.h>
//#include <stdlib.h>
void swap(int *x,int *y){
int temp=*x;
*x=*y;
*y=temp;
}
void qsort(int v[],int left,int right){
int i,last;
if(left>=right)
return;
swap(v+left,v+(left+right)/2);
last=left;
for(i=left+1;i<=right;i++)
if(v[i]<v[left]) {
last++;
swap(v+last,v+i);
}
swap(v+left,v+last);
qsort(v,left,last-1);
qsort(v,last+1,right);
}
void Qsort(int v[],int n){
qsort(v,0,n-1);
}
void print_arr(int v[],int n){
int i;
for(i=0;i<n;i++)
printf("%4d",v[i]);
printf("\n");
}
int main(){
int i;
for(i=0;i<10;i++){
int arr[20],j,b[20];
for(j=0;j<20;j++)
{
int val=rand()%1000;
arr[j]=val;
b[j]=val;
}
printf("before:");
print_arr(b,20);
Qsort(arr,20);
printf("after :");
print_arr(arr,20);
}
}
测试结果如下:
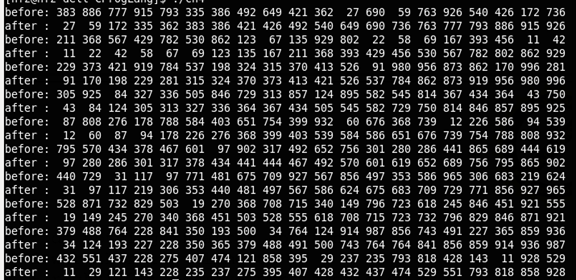
swap宏

第5章 指针与数组


int strend(char *s,char*t){
char *bs=s;
char *bt=t;
while(*s++);
while(*t++);
while(*--s==*--t){
if(t==bt||s==st)
break;
}
if(*s==*t&&t==bt&&*s!='\0')
return 1;
else
return 0;
}



void strncpy(char* s,char *t,int n){
while(*t&&n-->0)
*s++=*t++;
while(n-->0)
*s++='\0';
}
void strncat(char *s,char *t,int n){
strncpy(s+strlen(s),t,n);
}
int strncmp(char* s,char* t,int n){
for(;*s==*t;s++,t++)
if(*s=='\0'||--n<=0)
return 0;
return *s-*t;
}
UNIX系统中sort程序的一个简单版本,实现对输入文本的排序。


#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#define MAXLINES 5000
char *lineptr[MAXLINES];
#define MAXLEN 1000
int getline_(char line[],int lim){
int i,c;
i=0;
while(i<lim-1&&((c=getchar())!=EOF)&&c!='\n')
line[i++]=c;
if(c==EOF&&i==0)
return -1;
if(c=='\n')
line[i++]=c;
line[i]='\0';
return i;
}
char* alloc(int len){
char *p=(char*)malloc(len*sizeof(char));
return p;
}
int readlines(char* lineptr[],int maxlines){
int len,nlines;
char *p,line[MAXLEN];
nlines=0;
while((len=getline_(line,MAXLEN))>0)
if(nlines>=maxlines||(p=alloc(len))==NULL)
return -1;
else{
line[len-1]='\0';
strcpy(p,line);
lineptr[nlines++]=p;
}
return nlines;
}
void writelines(char *lineptr[],int nlines){
int i;
for(i=0;i<nlines;i++)
printf("%s\n",lineptr[i]);
}
void swap(char **x,char **y){
char*tmp;
tmp=*x;
*x=*y;
*y=tmp;
}
void qsort_(char *v[],int left,int right){
int i,last;
if(left>=right)
return ;
swap(v+left,v+(left+right)/2);
last=left;
for(i=left+1;i<=right;i++)
if(strcmp(v[i],v[left])<0)
{
last++;
swap(v+last,v+i);
}
swap(v+left,v+last);
qsort_(v,left,last-1);
qsort_(v,last+1,right);
}
int main(){
int nlines;
int i;
if((nlines=readlines(lineptr,MAXLINES))>0){
qsort_(lineptr,0,nlines-1);
writelines(lineptr,nlines);
for(i=0;i<nlines;i++)
free(lineptr[i]);
return 0;
}
else{
printf("error: input too big to sort\n");
return 1;
}
}
根据日期计算是一年的第几天:

static int daytab[][13]={{0,31,28,31,30,31,30,31,31,30,31,30,31}
,{0,31,29,31,30,31,30,31,31,30,31,30,31}};
int day_of_year(int year,int month,int day){
int i,leap;
leap=year%4==0&&year%100!=0||year%400==0;
if(month<1||month>12)
return -1;
if(day<1||day>daytab[leap][month])
return -1;
for(i=1;i<month;i++)
day+=daytab[leap][i];
return day;
}
void month_day(int year,int yearday,int *pmonth,int *pday){
int i,leap;
if(year<1){
*pmonth=-1;
*pday=-1;
return ;
}
leap=year%4==0&&year%100!=0||year%400==0;
for(i=1;i<=12&&yearday>daytab[leap][i];i++)
yearday-=daytab[leap][i];
if(i>12&&yearday>daytab[leap][12]){
*pmonth=-1;
*pday=-1;
}
else{
*pmonth=i;
*pday=yearday;
}
}
习题5-13


#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#define DEFLINES 10
#define MAXLINES 10
#define MAXLEN 100
int getline_(char line[],int lim){
int i,c;
i=0;
while(i<lim-1&&((c=getchar())!=EOF)&&c!='\n')
line[i++]=c;
if(c==EOF&&i==0)
return -1;
if(c=='\n')
line[i++]=c;
line[i]='\0';
return i;
}
void error(char *s){
printf("%s\n",s);
exit(1);
}
int main(int argc,char* argv[]){
char *p,*buf,*bufend;
char line[MAXLEN];
char *lineptr[MAXLINES];
int first,i,last,len,n,nlines;
if(argc==1)
n=DEFLINES;
else if(argc==2&&(*++argv)[0]=='-')
n=atoi(argv[0]+1);
if(n<1||n>MAXLINES)
n=MAXLINES;
for(i=0;i<MAXLINES;i++)
lineptr[i]=NULL;
if((p=buf=malloc(MAXLINES*MAXLEN))==NULL)
error("tail:cannot allocate buf");
bufend=buf+MAXLINES*MAXLEN;
last=0;
nlines=0;
while((len=getline_(line,MAXLEN))>0){
if(p+len+1>=bufend)
p=buf;
lineptr[last]=p;
strcpy(lineptr[last],line);
if(++last>=MAXLINES)
last=0;
p+=len+1;
nlines++;
}
if(n>nlines)
n=nlines;
first=last-n;
if(first<0)
first+=MAXLINES;
for(i=first;n-->0;i=(i+1)%MAXLINES)
printf("%s",lineptr[i]);
free(buf);
return 0;
}



#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <ctype.h>
#define NUMERIC 1
#define DECR 2
#define FOLD 4
#define DIR 8
//#define LINES 100
#define MAXLINES 100
#define MAXLEN 1000
char option=0;
int pos1=0;
int pos2=0;
int getline_(char line[],int lim){
int i,c;
i=0;
while(i<lim-1&&((c=getchar())!=EOF)&&c!='\n')
line[i++]=c;
if(c==EOF&&i==0)
return -1;
if(c=='\n')
line[i++]=c;
line[i]='\0';
return i;
}
void error(char *s){
printf("%s\n",s);
exit(1);
}
char* alloc(int len){
char *p=(char*)malloc(len*sizeof(char));
return p;
}
int readlines(char* lineptr[],int maxlines){
int len,nlines;
char *p,line[MAXLEN];
nlines=0;
while((len=getline_(line,MAXLEN))>0)
if(nlines>=maxlines||(p=alloc(len))==NULL)
return -1;
else{
line[len-1]='\0';
strcpy(p,line);
lineptr[nlines++]=p;
}
return nlines;
}
void writelines(char *lineptr[],int nlines,int decr){
int i;
if(decr)
for(i=nlines-1;i>=0;i--)
printf("%s\n",lineptr[i]);
else
for(i=0;i<nlines;i++)
printf("%s\n",lineptr[i]);
}
void swap(void**x,void**y){
void*tmp;
tmp=*x;
*x=*y;
*y=tmp;
}
void qsort_(void*v[],int left,int right,
int(*comp)(void*,void*)){
int i,last;
if(left>=right)
return ;
swap(v+left,v+(left+right)/2);
last=left;
for(i=left+1;i<=right;i++)
if(strcmp(v[i],v[left])<0)
{
last++;
swap(v+last,v+i);
}
swap(v+left,v+last);
qsort_(v,left,last-1,comp);
qsort_(v,last+1,right,comp);
}
void readargs(int argc,char*argv[]){
int c;
while(--argc>0&&(c=(*++argv)[0])=='-'||c=='+'){
if(c=='-'&&!isdigit(*(argv[0]+1)))
while(c=*++argv[0])
switch(c){
case 'd':
option|=DIR;
break;
case 'f':
option|=FOLD;
break;
case 'n':
option|=NUMERIC;
break;
case 'r':
option|=DECR;
break;
default:
printf("sort: illegal option %c\n",c);
error("usage: sort -dfnr [+pos1] [-pos2]");
break;
}
else if(c=='-')
pos2=atoi(argv[0]+1);
else if((pos1=atoi(argv[0]+1))<0)
error("usage: sort -dfnr [+pos1] [-pos2]");
}
if(argc||pos1>pos2)
error("usage: sort -dfnr [+pos1] [-pos2]");
}
#define MAXSTR 100
void substr(char *s,char *str){
int i,j,len;
len=strlen(s);
if(pos2>0&&len>pos2)
len=pos2;
else if(pos2>0&&len<pos2)
error("substr:string too short");
for(j=0,i=pos1;i<len;i++,j++)
str[j]=s[i];
str[j]='\0';
}
#define ABS(x) ((x)<0?-(x):(x))
double atof_(char s[]){
double val,power;
int i,sign;
for(i=0;isspace(s[i]);i++);
sign=(s[i]=='-')?-1:1;
if(s[i]=='+'||s[i]=='-')
i++;
for(val=0.0;isdigit(s[i]);i++)
val=10.0*val+(s[i]-'0');
if(s[i]=='.')
i++;
for(power=1.0;isdigit(s[i]);i++){
val=10.0*val+(s[i]-'0');
power*=10;
}
val= sign*val/power;
if(s[i]=='e'||s[i]=='E'){
int exp;
sign=(s[++i]=='-')?-1:1;
if(s[i]=='+'||s[i]=='-')
i++;
for(exp=0;isdigit(s[i]);i++)
exp=10*exp+(s[i]-'0');
if(sign)
while(exp-->0)
val*=10;
else
while(exp-->0)
val/=10;
}
return val;
}
int numcmp(char *s1,char *s2){
double v1,v2;
char str[MAXSTR];
substr(s1,str);
v1=atof_(str);
substr(s2,str);
v2=atof_(str);
if(v1<v2)
return -1;
else if(v1>v2)
return 1;
else
return 0;
}
//#define FOLD 4
//#define DIR 8
int charcmp(char *s,char *t){
char a,b;
int i,j,endpos;
int fold=(option&FOLD)?1:0;
int dir=(option&DIR)?1:0;
i=j=pos1;
if(pos2>0)
endpos=pos2;
else if((endpos-strlen(s))>strlen(t))
endpos=strlen(t);
do{
if(dir){
while(i<endpos&&!isalnum(s[i])&&
s[i]!=' '&&s[i]!='\0')
i++;
while(j<endpos&&!isalnum(t[j])&&
t[j]!=' '&&t[j]!='\0')
j++;
}
if(i<endpos&&j<endpos){
a=fold?tolower(s[i]):s[i];
i++;
b=fold?tolower(t[j]):t[j];
j++;
if(a==b&&a=='\0')
return 0;
}
}
while(a==b&&i<endpos&&j<endpos);
return a-b;
}
int main(int argc,char*argv[]){
char *lineptr[MAXLINES];
int nlines;
int i;
readargs(argc,argv);
if((nlines=readlines(lineptr,MAXLINES))>0){
if(option&NUMERIC)
qsort_((void**)lineptr,0,nlines-1,
(int(*)(void*,void*))numcmp);
else
qsort_((void**)lineptr,0,nlines-1,
(int(*)(void*,void*))charcmp);
writelines(lineptr,nlines,option&DECR);
for(i=0;i<nlines;i++)
free(lineptr[i]);
return 0;
}
else{
printf("error: input too big to sort\n");
return 1;
}
}

dcl一个比较不错的程序:将声明转化为文字描述或将文字描述转化为声明


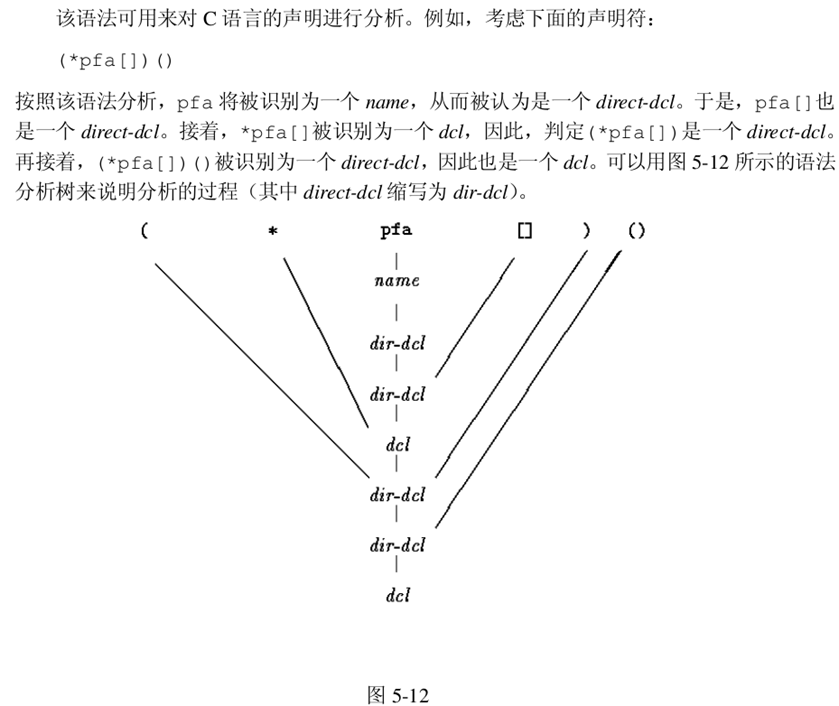


#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <ctype.h>
#define MAXTOKEN 100
enum{NAME,PARENS,BRACKETS};
int tokentype;
char token[MAXTOKEN];
char name[MAXTOKEN];
char datatype[MAXTOKEN];
char out[1000];
#define BUFSIZE 10
char buf[BUFSIZE];
int bufp=0;
int getch(void){
return bufp>0?buf[--bufp]:getchar();
}
void ungetch(int c){
if(bufp>=BUFSIZE)
printf("ungetch: too many characters\n");
else
buf[bufp++]=c;
}
int gettoken(){
char *p=token;
int c;
while((c=getch())==' '||c=='\t')
;
if(c=='('){
if((c=getch())==')'){
strcpy(token,"()");
return tokentype=PARENS;
}
else{
ungetch(c);
return tokentype='(';
}
}
else if(c=='['){
for(*p++=c;(*p++=getch())!=']';)
;
*p='\0';
return tokentype=BRACKETS;
}
else if(isalpha(c)){
for(*p++=c;isalnum(c=getch());)
*p++=c;
*p='\0';
ungetch(c);
return tokentype=NAME;
}
else
return tokentype=c;
}
void dcl(void);
void dirdcl(void){
int type;
if(tokentype=='('){
dcl();
if(tokentype!=')')
printf("error:missing )\n");
}
else if(tokentype==NAME)
strcpy(name,token);
else
printf("error:expected name or (dcl)\n");
while((type=gettoken())==PARENS||type==BRACKETS)
if(type==PARENS)
strcat(out," function returning");
else{
strcat(out, " array");
strcat(out,token);
strcat(out," of");
}
}
void dcl(void){
int ns;
for(ns=0;gettoken()=='*';)
ns++;
dirdcl();
while(ns-->0)
strcat(out," pointer to");
}
int main(){
while(gettoken()!=EOF){
strcpy(datatype,token);
out[0]='\0';
dcl();
if(tokentype!='\n')
printf("syntax error\n");
printf("%s: %s %s\n",name,out,datatype);
}
return 0;
}
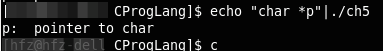


int main(){
int type;
char temp[MAXTOKEN];
while(gettoken()!=EOF){
strcpy(out,token);
while((type=gettoken())!='\n')
if(type==PARENS||type==BRACKETS)
strcat(out,token);
else if(type=='*'){
sprintf(temp,"(*%s)",out);
strcpy(out,temp);
}
else if(type==NAME){
sprintf(temp,"%s %s",token,out);
strcpy(out,temp);
}
else {
printf("invalid input at %s\n",token);
}
}
printf("%s\n",out);
return 0;
}
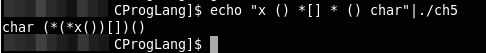


#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <ctype.h>
#define MAXTOKEN 100
enum{NAME,PARENS,BRACKETS};
enum{NO,YES};
int tokentype;
char token[MAXTOKEN];
char name[MAXTOKEN];
char datatype[MAXTOKEN];
char out[1000];
int prevtoken=NO;
#define BUFSIZE 10
char buf[BUFSIZE];
int bufp=0;
int getch(void){
return bufp>0?buf[--bufp]:getchar();
}
void ungetch(int c){
if(bufp>=BUFSIZE)
printf("ungetch: too many characters\n");
else
buf[bufp++]=c;
}
void errmsg(char *msg){
printf("%s",msg);
prevtoken=YES;
}
int gettoken(){
char *p=token;
int c;
if(prevtoken==YES){
prevtoken=NO;
return tokentype;
}
while((c=getch())==' '||c=='\t')
;
if(c=='('){
if((c=getch())==')'){
strcpy(token,"()");
return tokentype=PARENS;
}
else{
ungetch(c);
return tokentype='(';
}
}
else if(c=='['){
for(*p++=c;(*p++=getch())!=']';)
;
*p='\0';
return tokentype=BRACKETS;
}
else if(isalpha(c)){
for(*p++=c;isalnum(c=getch());)
*p++=c;
*p='\0';
ungetch(c);
return tokentype=NAME;
}
else
return tokentype=c;
}
void dcl(void);
void dirdcl(void){
int type;
if(tokentype=='('){
dcl();
if(tokentype!=')')
printf("error:missing )\n");
}
else if(tokentype==NAME)
strcpy(name,token);
else
errmsg("error:expected name or (dcl)\n");
while((type=gettoken())==PARENS||type==BRACKETS)
if(type==PARENS)
strcat(out," function returning");
else{
strcat(out, " array");
strcat(out,token);
strcat(out," of");
}
}
void dcl(void){
int ns;
for(ns=0;gettoken()=='*';)
ns++;
dirdcl();
while(ns-->0)
strcat(out," pointer to");
}
int main(){
while(gettoken()!=EOF){
strcpy(datatype,token);
out[0]='\0';
dcl();
if(tokentype!='\n')
printf("syntax error\n");
printf("%s: %s %s\n",name,out,datatype);
}
return 0;
}




int nexttoken(){
int type;
type=gettoken();
prevtoken=YES;
return type;
}
int main(){
int type;
char temp[MAXTOKEN];
while(gettoken()!=EOF){
strcpy(out,token);
while((type=gettoken())!='\n')
if(type==PARENS||type==BRACKETS)
strcat(out,token);
else if(type=='*'){
if((type=nexttoken())==PARENS||
type==BRACKETS)
sprintf(temp,"(*%s)",out);
else
sprintf(temp,"*%s",out);
strcpy(out,temp);
}
else if(type==NAME){
sprintf(temp,"%s %s",token,out);
strcpy(out,temp);
}
else {
printf("invalid input at %s\n",token);
}
}
printf("%s\n",out);
return 0;
}


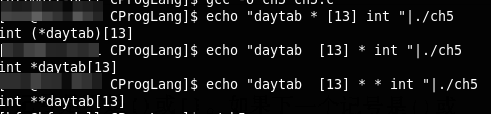



#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <ctype.h>
#define MAXTOKEN 100
enum{NAME,PARENS,BRACKETS};
enum{NO,YES};
int tokentype;
char token[MAXTOKEN];
char name[MAXTOKEN];
char datatype[MAXTOKEN];
char out[1000];
int prevtoken=NO;
#define BUFSIZE 10
char buf[BUFSIZE];
int bufp=0;
int getch(void){
return bufp>0?buf[--bufp]:getchar();
}
void ungetch(int c){
if(bufp>=BUFSIZE)
printf("ungetch: too many characters\n");
else
buf[bufp++]=c;
}
void errmsg(char *msg){
printf("%s",msg);
prevtoken=YES;
}
int gettoken(){
char *p=token;
int c;
if(prevtoken==YES){
prevtoken=NO;
return tokentype;
}
while((c=getch())==' '||c=='\t')
;
if(c=='('){
if((c=getch())==')'){
strcpy(token,"()");
return tokentype=PARENS;
}
else{
ungetch(c);
return tokentype='(';
}
}
else if(c=='['){
for(*p++=c;(*p++=getch())!=']';)
;
*p='\0';
return tokentype=BRACKETS;
}
else if(isalpha(c)){
for(*p++=c;isalnum(c=getch());)
*p++=c;
*p='\0';
ungetch(c);
return tokentype=NAME;
}
else
return tokentype=c;
}
int compare(char **s,char **t){
return strcmp(*s,*t);
}
int typespec(void){
static char *types[]={
"char","int","void"
};
char *pt=token;
if(bsearch(&pt,types,sizeof(types)/sizeof(char*),sizeof(char*),compare)==NULL)
return NO;
else
return YES;
}
int typequal(void){
static char *typeq[]={
"const","volatile"
};
char *pt=token;
if(bsearch(&pt,typeq,sizeof(typeq)/sizeof(char*),sizeof(char*),compare)==NULL)
return NO;
else
return YES;
}
void dcl(void);
void dclspec(void){
char temp[MAXTOKEN];
temp[0]='\0';
gettoken();
do{
if(tokentype!=NAME){
prevtoken=YES;
dcl();
}
else if(typespec()==YES){
strcat(temp," ");
strcat(temp,token);
gettoken();
}
else if(typequal()==YES){
strcat(temp," ");
strcat(temp,token);
gettoken();
}
else
errmsg("unknown type in parameter list\n");
}
while(tokentype!=','&&tokentype!=')');
strcat(out,temp);
if(tokentype==',')
strcat(out,",");
}
void parmdcl(void){
do{
dclspec();
}while(tokentype==',');
if(tokentype!=')')
errmsg("missing ) in parameter declaration\n");
}
void dirdcl(void){
int type;
if(tokentype=='('){
dcl();
if(tokentype!=')')
printf("error:missing )\n");
}
else if(tokentype==NAME) {
if(name[0]=='\0')
strcpy(name,token);
}
else
prevtoken=YES;
while((type=gettoken())==PARENS||type==BRACKETS||type=='(')
if(type==PARENS)
strcat(out," function returning");
else if(type=='('){
strcat(out," function expecting");
parmdcl();
strcat(out," and returning");
}
else{
strcat(out, " array");
strcat(out,token);
strcat(out," of");
}
}
void dcl(void){
int ns;
for(ns=0;gettoken()=='*';)
ns++;
dirdcl();
while(ns-->0)
strcat(out," pointer to");
}
int main(){
while(gettoken()!=EOF){
strcpy(datatype,token);
out[0]='\0';
dcl();
if(tokentype!='\n')
printf("syntax error\n");
printf("%s: %s %s\n",name,out,datatype);
}
return 0;
}
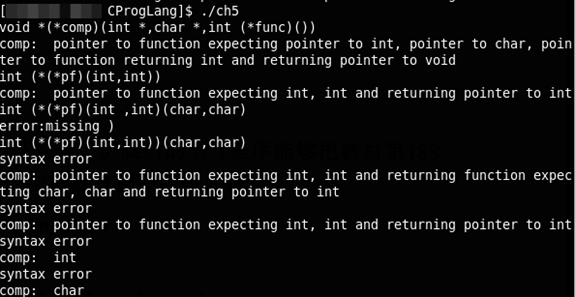
这个网站很不错的:http://cdecl.org/
第6章 结构体
统计关键字出现的次数

#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <ctype.h>
#include <string.h>
#define MAXWORD 1000
struct key {
char *word;
int count;
}
keytab[]={
"auto",0,
"break",0,
"case",0,
"char",0,
"const",0,
"continue",0,
"default",0,
"do",0,
"double",0,
"else",0,
"enum",0,
"extern",0,
"float",0,
"for",0,
"goto",0,
"if",0,
"int",0,
"long",0,
"register",0,
"return",0,
"short",0,
"signed",0,
"sizeof",0,
"static",0,
"struct",0,
"switch",0,
"typedef",0,
"union",0,
"unsigned",0,
"void",0,
"volatile",0,
"while",0,
};
#define NKEYS (sizeof keytab/sizeof(keytab[0]))
#define BUFSIZE 10
char buf[BUFSIZE];
int bufp=0;
int getch(void){
return bufp>0?buf[--bufp]:getchar();
}
void ungetch(int c){
if(bufp>=BUFSIZE)
printf("ungetch: too many characters\n");
else
buf[bufp++]=c;
}
int binsearch(char *word,struct key tab[],int n){
int cond;
int low,high,mid;
low=0;
high=n-1;
while(low<=high){
mid=(low+high)/2;
if((cond=strcmp(word,tab[mid].word))<0)
high=mid-1;
else if(cond>0)
low=mid+1;
else
return mid;
}
return -1;
}
int comment(void){
int c;
while((c=getch())!=EOF)
if(c=='*')
if((c=getch())=='/')
break;
else
ungetch(c);
return c;
}
int getword(char *word,int lim){
char *w=word;
int c,d;
while(isspace(c=getch()))
;
if(c!=EOF)
*w++=c;
if(isalpha(c)||c=='-'||c=='#'){
for(;--lim>0;w++)
if(!isalnum(*w=getch())&&*w!='-'){
ungetch(*w);
break;
}
}
else if(c=='\''||c=='"'){
for(;--lim>0;w++)
if((*w=getch())=='\\')
*++w=getch();
else if(*w==c){
w++;
break;
}
else if(*w==EOF)
break;
}
else if(c=='/')
if((d=getch())=='*')
c=comment();
else
ungetch(d);
*w='\0';
return c;
}
int main(){
int n;
char word[MAXWORD];
while(getword(word,MAXWORD)!=EOF)
if(isalpha(word[0]))
if((n=binsearch(word,keytab,NKEYS))>=0)
keytab
.count++;
for(n=0;n<NKEYS;n++)
if(keytab
.count>0)
printf("%4d %s\n",
keytab
.count,keytab
.word);
return 0;
}



#include <stdio.h>
#include <ctype.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#define BUFSIZE 10
char buf[BUFSIZE];
int bufp=0;
int getch(void){
return bufp>0?buf[--bufp]:getchar();
}
void ungetch(int c){
if(bufp>=BUFSIZE)
printf("ungetch: too many characters\n");
else
buf[bufp++]=c;
}
int comment(void){
int c;
while((c=getch())!=EOF)
if(c=='*')
if((c=getch())=='/')
break;
else
ungetch(c);
return c;
}
int getword(char *word,int lim){
char *w=word;
int c,d;
while(isspace(c=getch()))
;
if(c!=EOF)
*w++=c;
if(isalpha(c)||c=='-'||c=='#'){
for(;--lim>0;w++)
if(!isalnum(*w=getch())&&*w!='-'){
ungetch(*w);
break;
}
}
else if(c=='\''||c=='"'){
for(;--lim>0;w++)
if((*w=getch())=='\\')
*++w=getch();
else if(*w==c){
w++;
break;
}
else if(*w==EOF)
break;
}
else if(c=='/')
if((d=getch())=='*')
c=comment();
else
ungetch(d);
*w='\0';
return c;
}
struct tnode{
char *word;
int match;
struct tnode *left;
struct tnode *right;
};
#define MAXWORD 100
#define YES 1
#define NO 0
int compare(char *s,struct tnode *p,int num,int *found){
int i;
char *t=p->word;
for(i=0;*s==*t;i++,s++,t++)
if(*s=='\0')
return 0;
if(i>=num){
*found=YES;
p->match=YES;
}
return *s-*t;
}
struct tnode* talloc(void){
return (struct tnode*)malloc(sizeof(struct tnode));
}
char *strdup_(char *s){
char *p;
p=(char*)malloc(strlen(s)+1);
if(p!=NULL)
strcpy(p,s);
return p;
}
struct tnode* addtreex(struct tnode*p,char *w,int num,int *found){
int cond;
if(p==NULL){
p=talloc();
p->word=strdup_(w);
p->match=*found;
p->left=p->right=NULL;
}
else if((cond=compare(w,p,num,found))<0)
p->left=addtreex(p->left,w,num,found);
else if(cond>0)
p->right=addtreex(p->right,w,num,found);
return p;
}
void treeprint(struct tnode* p){
if(p!=NULL){
treeprint(p->left);
if(p->match)
printf("%s]n",p->word);
treeprint(p->right);
}
}
void freetree(struct tnode*p){
if(p!=NULL){
freetree(p->left);
freetree(p->right);
free(p->word);
}
}
int main(int argc,char *argv[]){
struct tnode *root;
char word[MAXWORD];
int found=NO;
int num;
num=(--argc&&(*++argv)[0]=='-')?atoi(argv[0]+1):6;
root=NULL;
while(getword(word,MAXWORD)!=EOF){
if(isalpha(word[0])&&strlen(word)>=num)
root=addtreex(root,word,num,&found);
found=NO;
}
treeprint(root);
freetree(root);
return 0;
}



#include <stdio.h>
#include <ctype.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#define BUFSIZE 10
char buf[BUFSIZE];
int bufp=0;
int getch(void){
return bufp>0?buf[--bufp]:getchar();
}
void ungetch(int c){
if(bufp>=BUFSIZE)
printf("ungetch: too many characters\n");
else
buf[bufp++]=c;
}
int comment(void){
int c;
while((c=getch())!=EOF)
if(c=='*')
if((c=getch())=='/')
break;
else
ungetch(c);
return c;
}
int getword(char *word,int lim){
char *w=word;
int c,d;
while(isspace(c=getch()))
;
if(c!=EOF)
*w++=c;
if(isalpha(c)||c=='-'||c=='#'){
for(;--lim>0;w++)
if(!isalnum(*w=getch())&&*w!='-'){
ungetch(*w);
break;
}
}
else if(c=='\''||c=='"'){
for(;--lim>0;w++)
if((*w=getch())=='\\')
*++w=getch();
else if(*w==c){
w++;
break;
}
else if(*w==EOF)
break;
}
else if(c=='/')
if((d=getch())=='*')
c=comment();
else
ungetch(d);
*w='\0';
return c;
}
struct linklist{
int lnum;
struct linklist *ptr;
};
struct tnode{
char *word;
struct linklist *lines;
struct tnode *left;
struct tnode *right;
};
#define MAXWORD 100
#define YES 1
#define NO 0
struct tnode* talloc(void){
return (struct tnode*)malloc(sizeof(struct tnode));
}
struct linklist *lalloc(void){
return (struct linklist*)malloc(sizeof(struct linklist));
}
char *strdup_(char *s){
char *p;
p=(char*)malloc(strlen(s)+1);
if(p!=NULL)
strcpy(p,s);
return p;
}
void addln(struct tnode *p,int linenum){
struct linklist *temp;
temp=p->lines;
while(temp->ptr!=NULL&&temp->lnum!=linenum)
temp=temp->ptr;
if(temp->lnum==linenum){
temp->ptr=lalloc();
temp->ptr->lnum=linenum;
temp->ptr->ptr=NULL;
}
}
struct tnode* addtreex(struct tnode*p,char *w,int linenum){
int cond;
if(p==NULL){
p=talloc();
p->word=strdup_(w);
p->lines=lalloc();
p->lines->lnum=linenum;
p->lines->ptr=NULL;
p->left=p->right=NULL;
}
else if((cond=strcmp(w,p->word))<0)
p->left=addtreex(p->left,w,linenum);
else if(cond>0)
p->right=addtreex(p->right,w,linenum);
else
addln(p,linenum);
return p;
}
void treeprint(struct tnode* p){
struct linklist *temp;
if(p!=NULL){
treeprint(p->left);
printf("%10s: ",p->word);
for(temp=p->lines;temp!=NULL;temp=temp->ptr)
printf("%4d ",temp->lnum);
printf("\n");
treeprint(p->right);
}
}
void freetree(struct tnode*p){
if(p!=NULL){
freetree(p->left);
freetree(p->right);
free(p->word);
free(p->lines);
}
}
int noiseword(char *w){
static char *nw[]={
"a","an","and","are","in","is","of","or","that","the","this","to"
};
int cond,mid;
int low=0;
int high=sizeof(nw)/sizeof(char*)-1;
while(low<=high){
mid=(low+high)/2;
if((cond=strcmp(w,nw[mid]))<0)
high=mid-1;
else if(cond>0)
low=mid+1;
else
return mid;
}
return -1;
}
int main(int argc,char *argv[]){
struct tnode *root;
char word[MAXWORD];
int linenum=1;
root=NULL;
while(getword(word,MAXWORD)!=EOF){
if(isalpha(word[0])&&noiseword(word)==-1)
root=addtreex(root,word,linenum);
else if(word[0]=='\n')
linenum++;
}
treeprint(root);
freetree(root);
return 0;
}

表查找程序核心代码:




#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
struct nlist{
struct nlist *next;
char *name;
char *defn;
};
#define HASHSIZE 101
static struct nlist *hashtab[HASHSIZE];
unsigned hash(char *s)
{
unsigned hashval;
for(hashval=0;*s!='\0';s++)
hashval=*s+32*hashval;
return hashval%HASHSIZE;
}
struct nlist *lookup(char *s){
struct nlist *np;
for(np=hashtab[hash(s)];np!=NULL;np=np->next)
if(strcmp(s,np->name)==0)
return np;
return NULL;
}
struct nlist *install(char *name,char*defn){
struct nlist *np;
unsigned hashval;
if((np=lookup(name))==NULL){
np=(struct nlist *)malloc(sizeof(struct nlist));
if(np==NULL||(np->name=strdup(name))==NULL)
return NULL;
hashval=hash(name);
np->next=hashtab[hashval];
hashtab[hashval]=np;
}
else
free((void*)np->defn);
if((np->defn=strdup(defn))==NULL)
return NULL;
return np;
}
void undef(char*s){
int h;
struct nlist *prev,*np;
prev=NULL;
h=hash(s);
for(np=hashtab[h];np!=NULL;np=np->next){
if(strcmp(s,np->name)==0)
break;
prev=np;
}
if(np!=NULL){
if(prev==NULL)
hashtab[h]=np->next;
else
prev->next=np->next;
free(np->name);
free(np->defn);
free(np);
}
}


#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <ctype.h>
#define BUFSIZE 10
char buf[BUFSIZE];
int bufp=0;
int getch(void){
return bufp>0?buf[--bufp]:getchar();
}
void ungetch(int c){
if(bufp>=BUFSIZE)
printf("ungetch: too many characters\n");
else
buf[bufp++]=c;
}
void ungets(char *s){
int len=strlen(s);
while(len>0)
ungetch(s[--len]);
}
char *strdup_(char *s){
char *p;
p=(char*)malloc(strlen(s)+1);
if(p!=NULL)
strcpy(p,s);
return p;
}
int comment(void){
int c;
while((c=getch())!=EOF)
if(c=='*')
if((c=getch())=='/')
break;
else
ungetch(c);
return c;
}
int getword(char *word,int lim){
char *w=word;
int c,d;
while(isspace(c=getch()))
;
if(c!=EOF)
*w++=c;
if(isalpha(c)||c=='-'||c=='#'){
for(;--lim>0;w++)
if(!isalnum(*w=getch())&&*w!='-'){
ungetch(*w);
break;
}
}
else if(c=='\''||c=='"'){
for(;--lim>0;w++)
if((*w=getch())=='\\')
*++w=getch();
else if(*w==c){
w++;
break;
}
else if(*w==EOF)
break;
}
else if(c=='/')
if((d=getch())=='*')
c=comment();
else
ungetch(d);
*w='\0';
return c;
}
struct nlist{
struct nlist *next;
char *name;
char *defn;
};
#define HASHSIZE 101
static struct nlist *hashtab[HASHSIZE];
unsigned hash(char *s)
{
unsigned hashval;
for(hashval=0;*s!='\0';s++)
hashval=*s+32*hashval;
return hashval%HASHSIZE;
}
struct nlist *lookup(char *s){
struct nlist *np;
for(np=hashtab[hash(s)];np!=NULL;np=np->next)
if(strcmp(s,np->name)==0)
return np;
return NULL;
}
struct nlist *install(char *name,char*defn){
struct nlist *np;
unsigned hashval;
if((np=lookup(name))==NULL){
np=(struct nlist *)malloc(sizeof(struct nlist));
if(np==NULL||(np->name=strdup_(name))==NULL)
return NULL;
hashval=hash(name);
np->next=hashtab[hashval];
hashtab[hashval]=np;
}
else
free((void*)np->defn);
if((np->defn=strdup_(defn))==NULL)
return NULL;
return np;
}
void undef(char*s){
int h;
struct nlist *prev,*np;
prev=NULL;
h=hash(s);
for(np=hashtab[h];np!=NULL;np=np->next){
if(strcmp(s,np->name)==0)
break;
prev=np;
}
if(np!=NULL){
if(prev==NULL)
hashtab[h]=np->next;
else
prev->next=np->next;
free(np->name);
free(np->defn);
free(np);
}
}
void error(int c,char *s){
printf("error:%s\n",s);
while(c!=EOF&&c!='\n')
c=getch();
}
void skipblanks(){
int c;
while((c=getch())==' '||c=='\t')
;
ungetch(c);
}
#define MAXWORD 100
void getdef(){
int c,i;
char def[MAXWORD],dir[MAXWORD],name[MAXWORD];
skipblanks();
if(!isalpha(getword(dir,MAXWORD)))
error(dir[0],"getdef:expecting a directive after #");
else if(strcmp(dir,"define")==0){
skipblanks();
if(!isalpha(getword(name,MAXWORD)))
error(name[0],"getdef:non-alpha -name expected");
else{
skipblanks();
for(i=0;i<MAXWORD-1;i++)
if((def[i]=getch())==EOF||
def[i]=='\n')
break;
def[i]='\0';
if(i<=0)
error('\n',"getdef:incomplete define");
else
install(name,def);
}
}
else if(strcmp(dir,"undef")==0){
skipblanks();
if(!isalpha(getword(name,MAXWORD)))
error(name[0],"getdef:non-alpha in undef");
else
undef(name);
}
else
error(dir[0],"getdef:expecting a directive after #");
}
int main(){
char w[MAXWORD];
struct nlist *p;
while(getword(w,MAXWORD)!=EOF){
if(strcmp(w,"#")==0)
getdef();
else if(!isalpha(w[0]))
printf("%s",w);
else if((p=lookup(w))==NULL)
printf("%s",w);
else
ungets(p->defn);
}
return 0;
}

第7章 输入与输出
变长参数列表


#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdarg.h>
void minprintf(char *fmt,...){
va_list ap;
char *p,*sval;
int ival;
double dval;
va_start(ap,fmt);
for(p=fmt;*p;p++){
if(*p!='%'){
putchar(*p);
continue;
}
switch(*++p){
case 'd':
ival=va_arg(ap,int);
printf("%d",ival);
break;
case 'f':
dval=va_arg(ap,double);
printf("%f",dval);
break;
case 's':
for(sval=va_arg(ap,char*);*sval;sval++)
putchar(*sval);
break;
default:
putchar(*p);
break;
}
}
va_end(ap);
}
int main(){
int a=3;
double d=8.7;
minprintf("%d %f\n",a,d);
}

#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdarg.h>
#include <ctype.h>
#define LOCALFMT 100
void minprintf(char *fmt,...){
va_list ap;
char *p,*sval;
char localfmt[LOCALFMT];
int ival,i;
unsigned uval;
double dval;
va_start(ap,fmt);
for(p=fmt;*p;p++){
if(*p!='%'){
putchar(*p);
continue;
}
i=0;
localfmt[i++]='%';
while(*(p+1)&&!isalpha(*(p+1)))
localfmt[i++]=*++p;
localfmt[i++]=*(p+1);
localfmt[i]='\0';
switch(*++p){
case 'd':
case 'i':
ival=va_arg(ap,int);
printf(localfmt,ival);
break;
case 'x':
case 'X':
case 'u':
case 'o':
uval=va_arg(ap,unsigned);
printf(localfmt,uval);
case 'f':
dval=va_arg(ap,double);
printf(localfmt,dval);
break;
case 's':
sval=va_arg(ap,char*);
printf(localfmt,sval);
break;
default:
putchar(*p);
break;
}
}
va_end(ap);
}
int main(){
int a=3;
double d=8.7;
minprintf("%d %f\n",a,d);
}



#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdarg.h>
#include <ctype.h>
#define LOCALFMT 100
void minscanf(char *fmt,...){
va_list ap;
char *p,*sval;
char localfmt[LOCALFMT];
int c,i,*ival;
unsigned *uval;
double *dval;
va_start(ap,fmt);
for(p=fmt;*p;p++){
if(*p!='%'){
localfmt[i++]=*p;
continue;
}
i=0;
localfmt[i++]='%';
while(*(p+1)&&!isalpha(*(p+1)))
localfmt[i++]=*++p;
localfmt[i++]=*(p+1);
localfmt[i]='\0';
switch(*++p){
case 'd':
case 'i':
ival=va_arg(ap,int*);
scanf(localfmt,ival);
break;
case 'x':
case 'X':
case 'u':
case 'o':
uval=va_arg(ap,unsigned*);
scanf(localfmt,uval);
break;
case 'f':
dval=va_arg(ap,double*);
scanf(localfmt,dval);
break;
case 's':
sval=va_arg(ap,char*);
scanf(localfmt,sval);
break;
default:
scanf(localfmt);
break;
}
}
}


下面是标准库中对fgets和fputs函数的实现:

char *fgets(char *s,int n,FILE*iop){
register int c;
register char *cs;
cs=s;
while(--n>0&&(c=getc(iop))!=EOF)
if((*cs++=c)=='\n')
break;
*cs='\0';
return (c==EOF&&cs==s)?NULL:s;
}
int fputs(char*s ,FILE*iop){
int c;
while(c=*s++)
putc(c,iop);
return ferror(ip)?EOF:0;
}


#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#define MAXLINE 100
void filecomp(FILE*fp1,FILE*fp2){
char line1[MAXLINE],line2[MAXLINE];
char*lp1,*lp2;
do{
lp1=fgets(line1,MAXLINE,fp1);
lp2=fgets(line2,MAXLINE,fp2);
if(lp1==line1&&lp2==line2){
if(strcmp(line1,line2)!=0){
printf("first difference in line\n %s\n",line1);
lp1=lp2=NULL;
}
}
else if(lp1!=line1&&lp2==line2)
printf("end of first at line\n%s\n",line2);
else if(lp1==line1&&lp2!=line2)
printf("end of first at line\n%s\n",line1);
}
while(lp1==line1&&lp2==line2);
}
int main(int argc,char *argv[]){
FILE *fp1,*fp2;
if(argc!=3){
fprintf(stderr,"comp:need two file names\n");
exit(1);
}
else{
if((fp1=fopen(*++argv,"r"))==NULL){
fprintf(stderr,"comp:can't open %s\n",*argv);
exit(1);
}
else if((fp2=fopen(*++argv,"r"))==NULL){
fprintf(stderr,"comp:can't open %s\n",*argv);
exit(1);
}
else{
filecomp(fp1,fp2);
fclose(fp1);
fclose(fp2);
exit(0);
}
}
}


#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#define MAXLINE 1000
void fpat(FILE *fp,char *fname,char *pattern,int except,int number);
int main(int argc,char*argv[]){
char pattern[MAXLINE];
int c,except=0,number=0;
FILE *fp;
while(--argc>0&&(*++argv)[0]=='-')
while(c=*++argv[0])
switch(c){
case 'x':
except=1;
break;
case 'n':
number=1;
break;
default:
printf("find:illegal option %c\n",c);
argc=0;
break;
}
if(argc>=1)
strcpy(pattern,*argv);
else{
printf("Usage:find [-x] [-n] pattern [file ..]\n");
exit(1);
}
if(argc==1)
fpat(stdin,"",pattern,except,number);
else
while(--argc>0)
if((fp=fopen(*++argv,"r"))==NULL){
fprintf(stderr,"find: can't open %s\n",*argv);
exit(1);
}else{
fpat(fp,*argv,pattern,except,number);
fclose(fp);
}
return 0;
}
void fpat(FILE *fp,char *fname,char *pattern,int except,int number){
char line[MAXLINE];
long lineno=0;
while(fgets(line,MAXLINE,fp)!=NULL){
++lineno;
if((strstr(line,pattern)!=NULL)!=except){
if(*fname)
printf("%s - ",fname);
if(number)
printf("%ld: ",lineno);
printf("%s",line);
}
}
}



#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#define MAXBOT 3
#define MAXHDR 5
#define MAXLINE 100
#define MAXPAGE 66
int heading(char *fname,int pageno){
int ln=3;
fprintf(stdout,"\n\n");
fprintf(stdout,"%s page %d\n",fname,pageno);
while(ln++<MAXHDR)
fprintf(stdout,"\n");
return ln;
}
void fileprint(FILE*fp,char *fname){
int lineno,pageno=1;
char line[MAXLINE];
lineno=heading(fname,pageno++);
while(fgets(line,MAXLINE,fp)!=NULL){
if(lineno==1){
fprintf(stdout,"\f");
lineno=heading(fname,pageno++);
}
fputs(line,stdout);
if(++lineno>MAXPAGE-MAXBOT)
lineno=1;
}
fprintf(stdout,"\f");
}
int main(int argc,char *argv[]){
FILE *fp;
if(argc==1)
fileprint(stdin," ");
else
while(--argc>0)
if((fp=fopen(*++argv,"r"))==NULL){
fprintf(stderr,"print:can't open %s\n",*argv);
exit(1);
}
else{
fileprint(fp,*argv);
fclose(fp);
}
return 0;
}

随机数发生器,生成浮点数的方法

第8章 UNIX系统接口

利用低级的read和write函数来构造高级函数getchar,putchar等。
int getchar_(void){
char c;
return (read(0,&c,1)==1)?(unsigned char)c:EOF;
}
int getchar__(void){
static char buf[BUFSIZ];
static char *bufp=buf;
static int n=0;
if(n==0){
n=read(0,buf,sizeof buf);
bufp=buf;
}
return (--n>0)?(unsigned char )*bufp++:EOF;
}


#include <unistd.h>
#define NULL 0
#define EOF (-1)
#define BUFSIZ 1024
#define OPEN_MAX 20
typedef struct _iobuf{
int cnt;
char *ptr;
char *base;
int flag;
int fd;
}FILE;
extern FILE _iob[OPEN_MAX];
#define stdin (&_iob[0])
#define stdout (&_iob[1])
#define stderr (&_iob[2])
enum _flags{
_READ =01,
_WRITE =02,
_UNBUF=04,
_EOF =010,
_ERR=020
};
int _fillbuf(FILE*);
int _flushbuf(int ,FILE *);
#define feof(p) (((p)->flag&_EOF)!=0)
#define ferror(p) (((p)->flag&_ERR)!=0)
#define fileno(p) ((p)->fd)
#define getc(p) (--(p)->cnt>=0\
?(unsigned char)*(p)->ptr++:_fillbuf(p))
#define putc(x,p) (--(p)->cnt>=0\
?*(p)->ptar++=(x):_flushbuf((x),p))
#define getchar() getc(stdin)
#define putchar(x) putc(x,stdout)
#include <fcntl.h>
#define PERMS 0666
FILE *fopen(char *name,char *mode)
{
int fd;
FILE *fp;
if(*mode!='r'&&*mode!='w'&&*mode!='a')
return NULL;
for(fp=_iob;fp<_iob+OPEN_MAX;fp++)
if((fp->flag&(_READ|_WRITE))==0)
break;
if(fp>=_iob+OPEN_MAX)
return NULL;
if(*mode=='w')
fd=creat(name,PERMS);
else if(*mode=='a'){
if((fd=open(name,O_WRONLY,0))==-1)
fd=creat(name,PERMS);
lseek(fd,0L,2);
}
else
fd=open(name,O_RDONLY,0);
if(fd==-1)
return NULL;
fp->fd=fd;
fp->cnt=0;
fp->base=NULL;
fp->flag=(*mode=='r')?_READ:_WRITE;
return fp;
}
int _fillbuf(FILE*fp){
int bufsize;
if((fp->flag&(_READ|_EOF|_ERR))!=_READ)
return EOF;
bufsize=(fp->flag&_UNBUF)?1:BUFSIZ;
if(fp->base==NULL)
if((fp->base=(char*)malloc(bufsize))==NULL)
return EOF;
fp->ptr=fp->base;
fp->cnt=read(fp->fd,fp->ptr,bufsize);
if(--fp->cnt<0){
if(fp->cnt==-1)
fp->flag|=_EOF;
else
fp->flag|=_ERR;
fp->cnt=0;
return EOF;
}
return (unsigned char)*fp->ptr++;
}
FILE _iob[OPEN_MAX]={
{0,(char*)0,(char*)0,_READ,0 },
{0,(char*)0,(char*)0,_WRITE,1 },
{0,(char*)0,(char*)0,_WRITE|_UNBUF,2 },
};
int _flushbuf(int x,FILE*fp){
unsigned nc;
int bufsize;
if(fp<_iob||fp>=_iob+OPEN_MAX)
return EOF;
if((fp->flag&(_WRITE|_ERR))!=_WRITE)
return EOF;
bufsize=(fp->flag&_UNBUF)?1:BUFSIZ;
if(fp->base==NULL){
if((fp->base=(char*)malloc(bufsize))==NULL){
fp->flag|=_ERR;
return EOF;
}
}
else{
nc=fp->ptr-fp->base;
if(write(fp->fd,fp->base,nc)!=nc){
fp->flag|=_ERR;
return EOF;
}
}
fp->ptr=fp->base;
*fp->ptr++=(char)x;
fp->cnt=bufsize-1;
return x;
}
int fclose(FILE *fp){
int rc;
if((rc=fflush(fp))!=EOF){
free(fp->base);
fp->ptr=NULL;
fp->cnt=0;
fp->base=NULL;
fp->flag&=(_READ|_WRITE);
}
return rc;
}
int fflush(FILE*fp){
int rc=0;
if(fp<_iob||fp>=_iob+OPEN_MAX)
return EOF;
if(fp->flag&_WRITE)
rc=_flushbuf(0,fp);
fp->ptr=fp->base;
fp->cnt=(fp->flag&_UNBUF)?1:BUFSIZ;
return rc;
}
int fseek(FILE *fp,long offset,int origin){
unsigned nc;
long rc=0;
if(fp->flag&_READ){
if(origin==1)
offset-=fp->cnt;
rc=lseek(fp->fd,offset,origin);
fp->cnt=0;
}
else if(fp->flag&_WRITE){
if((nc=fp->ptr-fp->base)>0)
if(write(fp->fd,fp->base,nc)!=nc)
rc=-1;
if(rc!=-1)
rc=lseek(fp->fd,offset,origin);
}
return (rc==-1)?-1:0;
}






#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <dirent.h>
//#define NAME_MAX 14
//typedef struct{
// long ino;
// char name[NAME_MAX+1];
//}Dirent;
//typedef struct{
// int fd;
// Dirent d;
//}DIR;
//DIR *opendir(char *dirname);
//Dirent* readdir(DIR*dfd);
//void closedir(DIR* dfd);
//char *name;
//struct stat stbuf;
//int stat(char *,struct stat*);
//#define S_IFMT 0160000
//#define S_IFDIR 0040000
//#define S_IFCHR 0020000
//#define S_IFBLK 0060000
//#define S_IFREG 001000
#define MAX_PATH 1024
void dirwalk(char *dir,void(*fcn)(char*)){
char name[MAX_PATH];
struct dirent *dp;
DIR *dfd;
if((dfd=opendir(dir))==NULL){
fprintf(stderr,"dirwalk:can't open %s\n",dir);
return;
}
while((dp=readdir(dfd))!=NULL){
if(strcmp(dp->d_name,".")==0||
strcmp(dp->d_name,"..")==0)
continue;
if(strlen(dir)+strlen(dp->d_name)+2>sizeof(name))
fprintf(stderr,"dirwalk:name %s %s too long\n",
dir,dp->d_name);
else{
sprintf(name,"%s/%s",dir,dp->d_name);
fcn(name);
}
}
closedir(dfd);
}
void fsize(char *name){
struct stat stbuf;
if(stat(name,&stbuf)==-1){
fprintf(stderr,"fsize:can't access %s\n",name);
return ;
}
if((stbuf.st_mode&S_IFMT)==S_IFDIR)
dirwalk(name,fsize);
printf("%5u %6o %3u %8ld %s\n",stbuf.st_ino,
stbuf.st_mode,stbuf.st_nlink,stbuf.st_size,name);
}
int main(int argc,char **argv){
if(argc==1)
fsize(".");
else
while(--argc>0)
fsize(*++argv);
return 0;
}
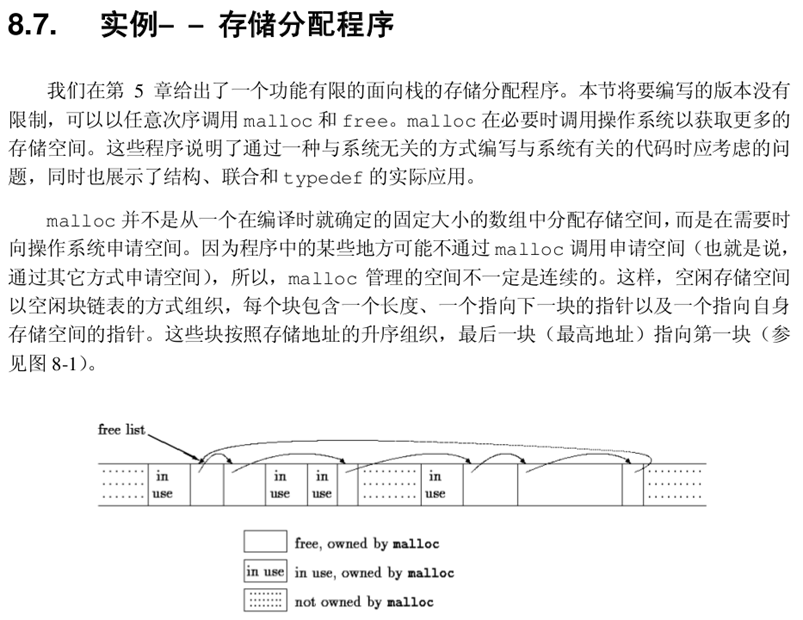








typedef long Align;
union header{
struct {
union header *ptr;
unsigned size;
}S;
Align x;
};
typedef union header Header;
static Header base;
static Header *freep=NULL;
void *malloc(unsigned nbytes){
Header *p,*prevp;
Header *moreroce(unsigned);
unsigned nuints;
nuints=(nbytes+sizeof(Header)-1)/sizeof(header)+1;
if((prevp=freep)==NULL){
base.s.ptr=freeptr=prevptr=&base;
base.s.size=0;
}
for(p=prevp->s.ptr;;prevp=p,p=p->s.ptr){
if(p->s.size>=nuints){
if(p->s.size==nuints)
prevp->s.ptr=p->s.ptr;
else{
p->s.size-=nuints;
p+=p->s.size;
p->s.size=nuints;
}
freep=prevp;
return (void*)(p+1);
}
if(p==freep)
if((p=moreroce(nuints))==NULL)
return NULL;
}
}
#define NALLOC 1024
static Header *moreroce(unsigned nu){
char *cp,*sbrk(int);
Header *up;
if(nu<NALLOC)
nu=NALLOC;
cp=sbrk(nu*sizeof(Header));
if(cp==(char*)-1)
return NULL;
up=(Header*)cp;
up->s.size=nu;
free((void*)(up+1));
return freep;
}
void free(void*ap){
Header *bp,*p;
bp=(Header*)ap-1;
for(p=freep;!(bp>p&&bp<p->s.ptr);p=p->s.ptr)
if(p>=p->s.ptr&&(bp>p||bp<p->s.ptr))
break;
if(bp+bp->size==p->s.ptr){
bp->s.size+=p->s.ptr->s.size;
bp->s.ptr=p->s.ptr->s.ptr;
}
else
bp->s.ptr=p->s.ptr;
if(p+p->size==bp){
p->s.size+=bp->s.size;
p->s.ptr=bp->s.ptr;
}
else
p->s.ptr=bp;
freep=p;
}
void *calloc(unsigned n,unsigned size){
unsigned i,nb;
char *p,*q;
nb=n*size;
if((p=q=malloc(nb))!=NULL)
for(i=0;i<nb;i++)
*p++=0;
return q;
}
这儿有一篇写的很好的读后感:http://www.cnblogs.com/xkfz007/articles/2566424.html
第1章 导言
1. 单词计数
#include <stdio.h>
int main(){
int c,nl,nw,nc,flag;
flag=0;
nl=nw=nc=0;
while((c=getchar())!=EOF){
++nc;
if(c=='\n')
nl++;
if(c==' '||c=='\n'||c=='\t')
flag=0;
else if(!flag){
flag=1;
++nw;
}
}
printf("%3d %3d %3d\n",nl,nw,nc);
return 0;
}
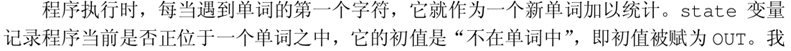
2. 函数参数——传值调用
在C语言中,所有函数参数都是通过"值"传递的。也就是说,传递给被调用函数的参数值存放在临时变量中,而不是存放在原来的变量中。这与其他某些语言是不同的。比如,Fortran等语言是通过"引用"调用,Pascal则采用var参数方式,在这些语言中,被调用的函数必须访问原始参数,而不是访问参数的本地副本。
最主要的区别在于,在C语言中,被调用函数不能直接修改主调函数中变量的值,而只能修改其私有临时副本的值。
传值调用的利大于弊。在被调用该函数中,参数可以看作是便于初始化的局部变量,因此额外使用的变量更少。这样程序可以更紧凑简洁。
3. 读入一组文本,打印出最长文本

#include <stdio.h>
int getline_(char s[],int lim){
int c,i;
i=0;
while(i<lim-1&&(c=getchar())!=EOF&&c!='\n'){
s[i++]=c;
}
if(c==EOF&&i==0)
return -1;
if(c=='\n')
s[i++]=c;
s[i++]='\0';
return i;
}
void copy(char str1[],char str2[]){
while((*str1++=*str2++)!='\0');
}
int main(){
char line[256];
char longest[256];
char shortest[256];
int len;
int max=0,min=256;
while((len=getline_(line,256))>-1){
if(len>=max)
{
max=len;
copy(longest,line);
}
else if(len<=min)
{
min=len;
copy(shortest,line);
}
}
if(max>0)
printf("%d:%s",max,longest);
if(min<256)
printf("%d:%s",min,shortest);
return 0;
}
下面是输出结果,输入是上面的源代码:

课后题程序:
习题1-8 编写一个统计空格、制表符和换行符个数的程序。

#include <stdio.h>
int main(){
int c,nb,nt,nl;
nb=0;
nt=0;
nl=0;
while((c=getchar())!=EOF){
if(c==' ')
nb++;
else if(c=='\t')
nt++;
else if(c=='\n')
nl++;
}
printf("%2d %2d %2d\n",nb,nt,nl);
}
习题1-9 编写一个将输入复制到输出的程序,并将其中连续的多个空格使用一个空格代替
#include <stdio.h>
int main(){
int c;
int nb;
int prec=-1;
while((c=getchar())!=EOF){
if(c==' '&&prec==' ')
continue;
else
{
putchar(c);
prec=c;
}
}
}
习题1-12 编写一个程序,以每行一个单词的形式打印其输入

int main(){
int c;
int flag;
flag=0;
while((c=getchar())!=EOF){
if(c==' '||c=='\n'||c=='\t'){
if(flag){
putchar('\n');
flag=0;
}
}
else if(!flag){
flag=1;
putchar(c);
}
else{
putchar(c);
}
}
}
习题1-13 编写一个程序,打印输入中单词长度的直方图。水平方向的直方图比较容易绘制,垂直方向的直方图则要困难写。

#include <stdio.h>
#define MAXHIST 15
#define MAXWORD 11
int word_stats(int wl[]){
int flag;
int c,nc,i,ovflow;
flag=0;
nc=0;
ovflow=0;
for(i=0;i<MAXWORD;i++)
wl[i]=0;
while((c=getchar())!=EOF){
if(c==' '||c=='\n'||c=='\t'){
if(flag){
flag=0;
// if(nc>0)
if(nc<MAXWORD)
wl[nc]++;
else
ovflow++;
nc=0;
}
}
else if(!flag){
flag=1;
nc=1;
}
else
nc++;
}
return ovflow;
}
void hist_h(int wl[]){
int i;
int maxvlaue=0;
int len;
for(i=1;i<MAXWORD;i++)
if(wl[i]>maxvlaue)
maxvlaue=wl[i];
for(i=1;i<MAXWORD;++i){
printf("%5d - %5d :",i,wl[i]);
if(wl[i]>0){
if((len=wl[i]*MAXHIST/maxvlaue)<=0)
len=1;
}
else
len=0;
while(len>0){
putchar('*');
len--;
}
putchar('\n');
}
}
void hist_v(int wl[]){
int i,j;
int maxvlaue=0;
int len;
for(i=1;i<MAXWORD;i++)
if(wl[i]>maxvlaue)
maxvlaue=wl[i];
for(i=MAXHIST;i>0;i--){
for(j=1;j<MAXWORD;j++)
if(wl[j]*MAXHIST/maxvlaue>=i)
printf(" * ");
else
printf(" ");
putchar('\n');
}
for(i=1;i<MAXWORD;i++)
printf("%4d ",i);
putchar('\n');
for(i=1;i<MAXWORD;i++)
printf("%4d ",wl[i]);
putchar('\n');
}
int main(){
int wl[MAXWORD];
int ovflow;
ovflow=word_stats(wl);
hist_h(wl);
hist_v(wl);
if(ovflow)
printf("Overflow: %d\n",ovflow);
}

下面是以上面的源文件为输入得到的运行结果:

习题1-18 编写一个程序,删除每个输入行末尾的空格及制表符,并删除完全是空格的行

#include <stdio.h>
int getline_(char s[],int lim){
int c;
int i;
i=0;
while(i<lim-1&&(c=getchar())!=EOF&&c!='\n'){
s[i++]=c;
}
if(c==EOF&&i==0)
return -1;
if(c=='\n')
s[i++]=c;
s[i++]='\0';
return i;
}
int remove_(char s[]){
int i;
i=0;
while(s[i]!='\n')
++i;
--i;
while(i>=0&&(s[i]==' '||s[i]=='\t'))
--i;
if(i>=0){
s[++i]='\n';
s[++i]='\0';
}
return i;
}
int main(){
char line[256];
while(getline_(line,256)>0){
if(remove_(line)>0)
printf("%s",line);
}
}
习题1-19 编写函数rverse(s)将字符串s中的字符顺序颠倒过来。使用该函数编写一个程序,每次颠倒一个输入行中的字符顺序。

#include <stdio.h>
int getline_(char s[],int lim){
int c;
int i;
i=0;
while(i<lim-1&&(c=getchar())!=EOF&&c!='\n'){
s[i++]=c;
}
if(c==EOF&&i==0)
return -1;
if(c=='\n')
s[i++]=c;
s[i++]='\0';
return i;
}
void reverse_(char s[]){
int i,j;
char c;
i=0;
while(s[i]!='\0')
i++;
i--;
if(s[i]=='\n')
i--;
j=0;
while(j<i){
c=s[i];
s[i]=s[j];
s[j]=c;
j++;
i--;
}
}
int main(){
char line[256];
while(getline_(line,256)>0){
reverse_(line);
printf("%s",line);
}
}
习题1-20
请编写程序detab,将输入中的制表符替换成适当数目的空格,使空格充满到下一个制表符终止的地方。假设制表符终止的位置是固定的,比如每隔n列就会出现一个制表符终止位。n应该作为变量还是常量呢?

#include <stdio.h>
#define TABINC 8
int main(){
int c,nb,pos;
nb=0;
pos=1;
while((c=getchar())!=EOF){
if(c=='\t'){
nb=TABINC-(pos-1)%TABINC;
while(nb>0){
putchar(' ');
pos++;
nb--;
}
}
else if(c=='\n'){
putchar(c);
pos=1;
}
else{
putchar(c);
pos++;
}
}
}

习题1-21 编写程序entab,将空格串替换为最少数量的制表符和空格,但要保持单词之间的间隔不变。假设制表符终止位的位置与练习1-20的detab程序的情况相同。当使用一个制表符或者一个空格都可以到达下一个制表符终止位时,选用那种替换字符比较好?

#include <stdio.h>
#define TABINC 8
int main(){
int c,nb,nt,pos;
nb=0;
nt=0;
pos=1;
while((c=getchar())!=EOF){
if(c==' '){
if(pos%TABINC!=0)
++nb;
else{
nb=0;
nt++;
}
}
else{
while(nt>0){
putchar('\t');
nt--;
}
if(c=='\t')
nb=0;
else
while(nb>0){
putchar(' ');
nb--;
}
putchar(c);
if(c=='\n')
pos=0;
else if(c=='\t')
pos=pos+(TABINC-(pos-1)%TABINC)-1;
}
pos++;
}
}

习题1-22


#include <stdio.h>
#define MAXCOL 10
#define TABINC 8
char line[MAXCOL];
int exptab(int pos);
int findblnk(int pos);
int newpos(int pos);
void printl(int pos);
int main(){
int c,pos;
pos=0;
while((c=getchar())!=EOF){
line[pos]=c;
if(c=='\t')
pos=exptab(pos);
else if(c=='\n') {
printl(pos);
pos=0;
}
else if(++pos>=MAXCOL){
pos=findblnk(pos);
printl(pos);
pos=newpos(pos);
}
}
}
void printl(int pos){
int i;
for(i=0;i<pos;i++)
putchar(line[i]);
if(pos>0)
putchar('\n');
}
int exptab(int pos){
line[pos]=' ';
for(++pos;pos<MAXCOL&&pos%TABINC!=0;++pos)
line[pos]=' ';
if(pos<MAXCOL)
return pos;
else{
printl(pos);
return 0;
}
}
int findblnk(int pos){
while(pos>0&&line[pos]!=' ')
pos--;
if(pos==0)
return MAXCOL;
else
return pos+1;
}
int newpos(int pos){
int i,j;
if(pos<=0||pos>=MAXCOL)
return 0;
else{
i=0;
for(j=pos;j<MAXCOL;++j){
line[i]=line[j];
++i;
}
return i;
}
}

习题1-23 编写一个删除C语言程序中所有的注释语句。要正确处理带银行的字符串与字符常量。在C语言中,注释不允许嵌套。

#include <stdio.h>
void rcomment(int c);
void in_comment(void);
void echo_quote(int c);
int main(){
int c;
while((c=getchar())!=EOF)
rcomment(c);
return 0;
}
void rcomment(int c){
int d;
if(c=='/')
if((d=getchar())=='*')
in_comment();
else if(d=='/'){
putchar(c);
rcomment(d);
}
else{
putchar(c);
putchar(d);
}
else if(c=='\''||c=='"')
echo_quote(c);
else
putchar(c);
}
void in_comment(void){
int c,d;
c=getchar();
d=getchar();
while(c!='*'||d!='/'){
c=d;
d=getchar();
}
}
void echo_quote(int c){
int d;
putchar(c);
while((d=getchar())!=c){
putchar(d);
if(d=='\\')
putchar(getchar());
}
putchar(d);
}

习题1-24 编写一个程序,检查C语言程序中的基本语法错误


#include <stdio.h>
int brace,brack,paren;
void in_quote(int c);
void in_comment(void);
void search(int c);
int main(){
int c;
while((c=getchar())!=EOF){
if(c=='/'){
if((c=getchar())=='*')
in_comment();
else
search(c);
}
else if(c=='\''||c=='"')
in_quote(c);
else
search(c);
if(brace<0){
printf("Unbalanced braces\n");
brace=0;
}
else if(brack<0){
printf("Unbalanced brackets\n");
brack=0;
}
else if(paren<0){
printf("Unbalanced parentheses\n");
paren=0;
}
}
if(brace>0)
printf("Unbalanced braces\n");
if(brack>0)
printf("Unbalanced brackets\n");
if(paren>0)
printf("Unbalanced parentheses\n");
}
void search(int c){
if(c=='{')
++brace;
else if(c=='}')
--brace;
else if(c=='[')
++brack;
else if(c==']')
--brack;
else if(c=='(')
++paren;
else if(c==')')
--paren;
}
void in_comment(void){
int c,d;
c=getchar();
d=getchar();
while(c!='*'||d!='/'){
c=d;
d=getchar();
}
}
void in_quote(int c){
int d;
while((d=getchar())!=c)
if(d=='\\')
getchar();
}

第2章 类型,运算符与表达式
1. const限定符
任何变量的声明都可以使用const限定符限定。该限定符指定变量的值不能被修改。对于数组而言,const限定符指定数组所有元素的值都不能被修改。
const char msg[]="warning:";
const限定符也可以配合数组参数使用,它表明函数不能修改该数组元素的值。
2. char类型
char类型是小整型

3. 算术中的隐式类型转换
一般情况下,如果不含有unsigned类型,可以采用下面的方式:

注意float类型的特殊性:

当表达式中含有unsigned类型时:

函数参数中的类型转换:

4. 标准库中的伪随机数发生器函数:rand和srand
标准库中包含一个可移植的实现伪随机数发生器的函数rand以及一个初始化种子数的函数srand。rand函数中使用了强制类型转换:
unsigned long int next=1;
/*rand:return pseudo-random integer on 0..32767*/
int rand(void)
{
next=next*1103515245+12345;
return (unsigned int)(next/65536)%32768;
}
/*srand:set seed for rand()*/
void srand(unsigned int seed){
next=seed;
}
习题2-3 编写函数htoi(s),把由十六进制数字组成的字符串(包含可选的前缀0x或0X)转换为与之等价的整型数。字符串中允许包含的数字包括:0~9,a~f以及A-F

#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#define YES 1
#define NO 0
int htoi(char s[]){
int hexd,i,inhex,n;
i=0;
if(s[i]=='0'){
++i;
if(s[i]=='x'||s[i]=='X')
++i;
}
n=0;
inhex=YES;
while(inhex){
if(s[i]>='0'&&s[i]<='9')
hexd=s[i]-'0';
else if(s[i]>='a'&&s[i]<='f')
hexd=s[i]-'a'+10;
else if(s[i]>='A'&&s[i]<='F')
hexd=s[i]-'A'+10;
else
inhex=NO;
if(inhex==YES)
n=16*n+hexd;
i++;
}
return n;
}
int main(){
int count=10;
int i;
char s[100];
for(i=0;i<10;i++){
int num=rand()%10000;
int n;
sprintf(s,"%#0x",num);
n=htoi(s);
printf("%#0x %s %d %d \n",num,s,num,n);
}
}
一个运行结果展示:

习题2-4 重写函数squeeze(s1,s2),将字符串s1中任何与字符串s2中字符匹配的字符都删除
void squeeze(char s1[],char s2[]){
int i,j,k;
for(i=k=0;s1[i]!='\0';i++){
for(j=0;s2[j]!='\0'&&s2[j]!=s1[i];j++);
if(s2[j]=='\0')
s1[k++]=s1[i];
}
s1[k]='\0';
}

习题2-5

void any(char s1[],char s2[]){
int i,j;
for(i=0;s1[i]!='\0';i++)
for(j=0;s2[j]!='\0';j++)
if(s1[i]==s2[j])
return i;
return -1;
}
5. C语言中的位操作
getbits函数:返回x中从右边数第p位开始向右数n位的字段。这里假定最右边的一位是第0位,n与p都是合理的正值。
unsigned getbits(unsigned x,int p,int n){
return (x>>(p+1-n))&~(~0<<n);
}

unsigned sebits(unsgined x,int p,int n,unsigned y){
unsigned x1=x&(~0<<(p+1));//获取x的高32-(p+1)位
unsigned x2=x&((1<<(p-n+1))-1);//获取x的低p-n+1位
unsigned y1=(y&~(~0<<n))<<(p+1-n);//获得y的最低n位,并且移动到合适的位置
return x1|x2|y1;
}
可以换一种方式写:
unsigned sebits(unsgined x,int p,int n,unsigned y){
unsigned m1= (~0<<(p+1))| ((1<<(p-n+1))-1);//得到屏蔽码
unsigned x1=x&m1;
unsigned y1=(y&~(~0<<n))<<(p+1-n);//获得y的最低n位,并且移动到合适的位置
return x1|y1;
}
下面是一个标准答案:

这儿比较难写是就是x的屏蔽码,下面的程序是对比两种方法产生的屏蔽码:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int main(){
int i;
for(i=0;i<10;i++){
int p=rand()%32;
int n=rand()%p+1;
unsigned m1=(~0<<(p+1))|((1<<(p-n+1))-1);
unsigned m2=~(~(~0<<n)<<(p+1-n));
printf("p=%d n=%d: %#0x %#0x ",p,n,m1,m2);
if(m1==m2)
printf("OK\n");
else
printf("NO\n");
}
}
一个输出结果如下:


unsigned invert(unsigned x,int p,int n){
unsigned x1=x&(~0<<(p+1));//获取x的高32-(p+1)位
unsigned x2=x&((1<<(p-n+1))-1);//获取x的低p-n+1位
unsigned x3=~x&(~(~0<<n)<<(p-n+1));//获取x的中间n位
return x1|x2|x3;
}
下面是一个标准答案

下面是一个测试:

#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
unsigned invert(unsigned x,int p,int n){
unsigned m1=(~0<<(p+1));//获取x的高32-(p+1)位
unsigned x1=x&m1;
unsigned m2=((1<<(p-n+1))-1);//获取x的低p-n+1位
unsigned x2=x&m2;
unsigned m3=(~(~0<<n)<<(p-n+1));//获取x的中间n位
unsigned x3=(~x)&m3;
printf("%#0x %#0x %#0x\n",m1,m2,m3);
return x1|x2|x3;
}
unsigned invert2(unsigned x,int p,int n){
return x^(~(~0<<n)<<(p+1-n));
}
int main(){
int i;
unsigned x=rand();
for(i=0;i<25;i++){
int p=rand()%32;
int n=rand()%p+1;
int y1=invert(x,p,n);
int y2=invert2(x,p,n);
printf("%#0x %2d %2d %#0x %#0x ",x,p,n,y1,y2);
if(y1==y2)
printf("OK\n");
else
printf("NO\n");
}
}
输出如下:

可以看到当p=31时,第一种方法就出错了。主要是将一个无符号数进行右移32位(移出所有位)时,编译器会给出一个【 warning: right shift count >= width of type】的警告。然后返回原始值,而不是0

unsigned rightrot(unsigned x,int n){
unsigned x1=x>>n;//左移得到高32-n位
unsigned x2=x<<(sizeof(x)*8-n);//右移得到低n位
return x1|x2;
}
下面标准答案给出的解释:

#include <stdio.h>
int wordlength()
{
int i;
unsigned v=(unsigned)~0;
for(i=1;(v=v>>1)>0;i++)
;
return 1;
}
unsigned rightrot(unsigned x,int n){
int rbit;
while(n-->0){
rbit=(x&1)<<(wordlength()-1);
x=x>>1;
x=x|rbit;
}
return x;
}

unsigned rightrot2(unsigned x,int n){
unsigned rbits;
if((n-n%wordlength())>0){
rbits=~(~0<<n)&x;
rbits=rbits<<(wordlength()-n);
x=x>>n;
x=x|rbits;
}
return x;
}

6. 统计整型数中二进制位1的个数:
int bitcount(unsigned x){
int n=0;
while(x!=0){
if(x&0x1)
n++;
x>>1;
}
return n;
}
习题 2-9 在求对二的补码时,表达式x&(x-1)可以删除x中最右边为1的一个二进制位。请解释这样做的道理。用这一方法重写bitcount函数, 以加快其执行速度。
重写的代码如下:
int bitcount(unsigned x){
int b;
b=0;
while(x!=0){
b++;
x&=x-1;
}
return b;
}


第3章 程序流控制
1. 折半查找

int bin_search(int x,int v[],int n){
int low,high,mid;
low=0;
high=n-1;
while(low<=high){
mid=(low+high)>>1;
if(x<v[mid])
high=mid-1;
else if(x>v[mid])
low=mid+1;
else
return mid;
}
return -1;
}
int bin_search(int x,int v[],int n){
int low,high,mid;
low=0;
high=n-1;
mid=(low+high)/2;
while(low<=high&&x!=v[mid]){
if(x<v[mid])
high=mid-1;
else
low=mid+1;
mid=(low+high)/2;
}
if(x==v[mid])
return mid;
else
return -1;
}

2. atoi函数
字符串转换为对应数值的函数atoi

View
Code
测试输出如下:

希尔排序shell
shell算法是D.L. Shell于1959年发明的,基本思想是:先比较近距离的元素,而不是像简单交换排序算法那样先比较相邻的元素。这样可以快速减少大量的无序情况,从而减轻后序的工作。被比较的元素之间的距离逐步减少,直到减少为1,这时编程了相邻元素的互换。

#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
void shellsort(int v[],int n){
int gap,i,j,temp;
for(gap=n/2;gap>0;gap/=2)
for(i=gap;i<n;i++)
for(j=i-gap;j>=0&&v[j]>v[j+gap];j-=gap){
temp=v[j];
v[j]=v[j+gap];
v[j+gap]=temp;
}
}
void print_arr(int v[],int n){
int i;
for(i=0;i<n;i++)
printf("%4d",v[i]);
printf("\n");
}
int main(){
int i;
for(i=0;i<10;i++){
int arr[20],j,b[20];
for(j=0;j<20;j++)
{
int val=rand()%1000;
arr[j]=val;
b[j]=val;
}
printf("before:");
print_arr(b,20);
shellsort(arr,20);
printf("after :");
print_arr(arr,20);
}
}
测试输出如下:

习题 3-3 讲些函数expand(s1,s2),将字符串s1中类似于a-z一类的速记符号在字符串s2中扩展为等价的完整列表abc...xyz。该函数可以处理大小写字母和数字,并且可以处理a-b-c,a-z0-9与a-z等类似的情况。作为前导和尾随的字符原样复制。

#include <stdio.h>
void expand(char s1[],char s2[]){
char c;
int i,j;
i=0;
j=0;
while((c=s1[i++])!='\0'){
if(s1[i]=='-'&&s1[i+1]>=c){
i++;
while(c<s1[i])
s2[j++]=c++;
}
else
s2[j++]=c;
}
s2[j]='\0';
}

函数itoa:将整型数转化为字符串

#include <stdio.h>
void itoa(int n,char s[]){
int i,sign;
int x,y;
if((sign=n)<0)
n=-n;
i=0;
do{
s[i++]=n%10+'0';
}
while((n/=10)>0);
if(sign<0)
s[i++]='-';
s[i]='\0';
for(x=0,y=i-1;x<y;x++,y--) {
char c=s[x];
s[x]=s[y];
s[y]=c;
}
}
int atoi_(char s[]){
int i,n,sign;
for(i=0;isspace(s[i]);i++);
sign=(s[i]=='-')?-1:1;
if(s[i]=='+'||s[i]=='-')
i++;
for(n=0;isdigit(s[i]);i++)
n=10*n+(s[i]-'0');
return sign*n;
}
int main(){
int i;
char s[20];
for(i=0;i<10;i++){
int val=rand();
int d;
itoa(val,s);
d=atoi_(s);
printf("%12d %12s %12d ",val,s,d);
if(val==d)
printf("OK\n");
else
printf("NO\n");
}
}
测试结果如下:

习题3-4


void itoa2(int n,char s[]){
int i,sign;
int x,y;
sign=n;
i=0;
do{
s[i++]= ABS(n%10)+'0';
}
while((n/=10)!=0);
if(sign<0)
s[i++]='-';
s[i]='\0';
for(x=0,y=i-1;x<y;x++,y--) {
char c=s[x];
s[x]=s[y];
s[y]=c;
}
}

习题 3-5 编写函数itob(n,s,b),将整数n转换为以b为底的数,并将结果以字符的形式保存到字符串s中。例如,itob(n,s,16)把整数n格式化为十六进制整数保存在s中。

#include <stdio.h>
#define ABS(x) ((x)<0?-(x):(x))
void itob(int n,char s[],int b){
int i,j,sign;
int x,y;
sign=n;
i=0;
do{
j=ABS(n%b);
s[i++]=(j<10)?j+'0':j+'a'-10;
}
while((n/=b)!=0);
if(sign<0)
s[i++]='-';
s[i]='\0';
for(x=0,y=i-1;x<y;x++,y--) {
char c=s[x];
s[x]=s[y];
s[y]=c;
}
}
void test_10(){
int i;
char s[20];
for(i=0;i<10;i++){
int val=rand();
int d;
if(val&0x1)
val=-val;
itob(val,s,10);
sscanf(s,"%d",&d);
printf("%12d %12s %12d ",val,s,d);
if(val==d)
printf("OK\n");
else
printf("NO\n");
}
}
void test_8(){
int i;
char s[20];
for(i=0;i<10;i++){
int val=rand();
int d;
if(val&0x1)
val=-val;
itob(val,s,8);
// d=atoi_(s);
sscanf(s,"%o",&d);
printf("%#14o %14s %#14o ",val,s,d);
if(val==d)
printf("OK\n");
else
printf("NO\n");
}
}
void test_16(){
int i;
char s[40];
for(i=0;i<10;i++){
int val=rand();
int d;
if(val&0x1)
val=-val;
itob(val,s,16);
sscanf(s,"%x",&d);
printf("%#14x %14s %#14x ",val,s,d);
if(val==d)
printf("OK\n");
else
printf("NO\n");
}
}
int main(){
printf("base-10\n");
test_10();
printf("=========================\n");
printf("base-8\n");
test_8();
printf("=========================\n");
printf("base-16\n");
test_16();
}

我们在测试程序中进行8,10和16三种进制的测试。主要是C语言提供到这三种进制的转换,这样便于我们的测试。
测试结果如下:

函数trim:用于删除字符串尾部的空格、制表符与换行符。当发现最右边的字符为非空格符、非制表符、非换行符时,就使用break语句从循环中退出。
#include <stdio.h>
int trim(char s[]){
int i;
for(i=strlen(s)-1;i>=0;i--)
if(s[i]!=' '&&s[i]!='\t'&&s[i]!='\n')
break;
s[i+1]='\0';
return i;
}
第4章 函数与程序结构
1. 实现类似UNIX系统上的grep类似的功能:strindex


#include <stdio.h>
#define MAXLINE 1000
char pattern[]="line";
int getline_(char line[],int lim){
int i,c;
i=0;
while(i<lim-1&&((c=getchar())!=EOF)&&c!='\n')
line[i++]=c;
if(c==EOF&&i==0)
return -1;
if(c=='\n')
line[i++]=c;
line[i]='\0';
return i;
}
int strindex(char src[],char itm[]){
int i,j;
// int len1=strlen(src);
// int len2=strlen(itm);
for(i=0;src[i]!='\0';i++){
int k;
for(j=0,k=i;itm[j]!='\0'&&itm[j]==src[k];j++,k++);
if(itm[j]=='\0')
return i;
}
return -1;
}
int main(){
char line[MAXLINE];
int found=0;
while(getline_(line,MAXLINE)>0)
if(strindex(line,pattern)>=0){
printf("%s",line);
found++;
}
}
习题 4-1 编写函数strrindex(s,t),它返回字符串t在s中最右边出现的位置。如果s中不包含t,则返回-1

int strrindex(char s[],char t[]){
int i,j;
int pos=-1;
for(i=0;s[i]!='\0';i++){
int k;
for(j=0,k=i;t[j]!='\0'&&t[j]==s[k];j++,k++);
if(t[j]=='\0')
pos=i;
}
return pos;
}

int strrindex2(char s[],char t[]){
int i,j;
int ls=strlen(s);
int lt=strlen(t);
for(i=ls-lt;i>=0;i--){
int k;
for(j=0,k=i;t[j]!='\0'&&t[j]==s[k];j++,k++);
if(t[j]=='\0')
return i;
}
return -1;
}

函数atof:将字符串转换为浮点数

#include <stdio.h>
#include <ctype.h>
double atof_(char s[]){
double val,power;
int i,sign;
for(i=0;isspace(s[i]);i++);
sign=(s[i]=='-')?-1:1;
if(s[i]=='+'||s[i]=='-')
i++;
for(val=0.0;isdigit(s[i]);i++)
val=10.0*val+(s[i]-'0');
if(s[i]=='.')
i++;
for(power=1.0;isdigit(s[i]);i++){
val=10.0*val+(s[i]-'0');
power*=10;
}
return sign*val/power;
}
int main(){
int i;
for(i=0;i<25;i++){
double val=rand()%100000/100.0;
char s[20];
double val2;
sprintf(s,"%f",val);
val2=atof_(s);
printf("%10.5f %12s %10.5f\n",val,s,val2);
}
}

习题4-2 对atof函数进行扩充,使他可以处理形如:
123.45e-6
的科学表示法,其中浮点数后面可能会紧跟一个e或E以及一个指数(可能有正负号)。

double atof_(char s[]){
double val,power;
int i,sign;
for(i=0;isspace(s[i]);i++);
sign=(s[i]=='-')?-1:1;
if(s[i]=='+'||s[i]=='-')
i++;
for(val=0.0;isdigit(s[i]);i++)
val=10.0*val+(s[i]-'0');
if(s[i]=='.')
i++;
for(power=1.0;isdigit(s[i]);i++){
val=10.0*val+(s[i]-'0');
power*=10;
}
val= sign*val/power;
if(s[i]=='e'||s[i]=='E'){
int exp;
sign=(s[++i]=='-')?-1:1;
if(s[i]=='+'||s[i]=='-')
i++;
for(exp=0;isdigit(s[i]);i++)
exp=10*exp+(s[i]-'0');
if(sign)
while(exp-->0)
val*=10;
else
while(exp-->0)
val/=10;
}
return val;
}

4.3 外部变量

一个简单的计算器程序

#if 1
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <ctype.h>
#define ABS(x) ((x)<0?-(x):(x))
double atof_(char s[]){
double val,power;
int i,sign;
for(i=0;isspace(s[i]);i++);
sign=(s[i]=='-')?-1:1;
if(s[i]=='+'||s[i]=='-')
i++;
for(val=0.0;isdigit(s[i]);i++)
val=10.0*val+(s[i]-'0');
if(s[i]=='.')
i++;
for(power=1.0;isdigit(s[i]);i++){
val=10.0*val+(s[i]-'0');
power*=10;
}
val= sign*val/power;
if(s[i]=='e'||s[i]=='E'){
int exp;
sign=(s[++i]=='-')?-1:1;
if(s[i]=='+'||s[i]=='-')
i++;
for(exp=0;isdigit(s[i]);i++)
exp=10*exp+(s[i]-'0');
if(sign)
while(exp-->0)
val*=10;
else
while(exp-->0)
val/=10;
}
return val;
}
#define MAXVAL 1000
int sp=0;
double val[MAXVAL];
void push(double f){
if(sp<MAXVAL)
val[sp++]=f;
else
printf("error:stack full\n");
}
double pop(void){
if(sp>0)
return val[--sp];
else
printf("error:stack empty\n");
return 0.0;
}
#define BUFSIZE 100
char buf[BUFSIZE];
int bufp=0;
int getch(void){
return bufp>0?buf[--bufp]:getchar();
}
void ungetch(int c){
if(bufp>=BUFSIZE)
printf("ungetch: too many characters\n");
else
buf[bufp++]=c;
}
#define MAXOP 1000
#define NUMBER '0'
int getop(char s[]){
int i,c;
while((s[0]=c=getch())==' '||c=='\t')
;
s[1]='\0';
if(!isdigit(c)&&c!='.')
return c;
i=0;
if(isdigit(c))
while(isdigit(s[++i]=c=getch()))
;
if(c=='.')
while(isdigit(s[++i]=c=getch()))
;
s[i]='\0';
if(c!=EOF)
ungetch(c);
return NUMBER;
}
int main(){
int type;
double op2;
char s[MAXOP];
while((type=getop(s))!=EOF){
switch(type){
case NUMBER:
push(atof_(s));
break;
case '+':
push(pop()+pop());
break;
case '-':
op2=pop();
push(pop()-op2);
break;
case '*':
push(pop()*pop());
break;
case '/':
op2=pop();
if(ABS(op2)>1e-10)
push(pop()/op2);
else
printf("error:zero divisor\n");
break;
case '\n':
printf("\t%.8g\n",pop());
break;
default:
printf("error: unknown command %s\n",s);
break;
}
}
}



#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <ctype.h>
#include <math.h>
#define ABS(x) ((x)<0?-(x):(x))
double atof_(char s[]){
double val,power;
int i,sign;
for(i=0;isspace(s[i]);i++);
sign=(s[i]=='-')?-1:1;
if(s[i]=='+'||s[i]=='-')
i++;
for(val=0.0;isdigit(s[i]);i++)
val=10.0*val+(s[i]-'0');
if(s[i]=='.')
i++;
for(power=1.0;isdigit(s[i]);i++){
val=10.0*val+(s[i]-'0');
power*=10;
}
val= sign*val/power;
if(s[i]=='e'||s[i]=='E'){
int exp;
sign=(s[++i]=='-')?-1:1;
if(s[i]=='+'||s[i]=='-')
i++;
for(exp=0;isdigit(s[i]);i++)
exp=10*exp+(s[i]-'0');
if(sign)
while(exp-->0)
val*=10;
else
while(exp-->0)
val/=10;
}
return val;
}
#define MAXVAL 1000
int sp=0;
double val[MAXVAL];
void push(double f){
if(sp<MAXVAL)
val[sp++]=f;
else
printf("error:stack full\n");
}
double pop(void){
if(sp>0)
return val[--sp];
else
printf("error:stack empty\n");
return 0.0;
}
#define BUFSIZE 100
char buf[BUFSIZE];
int bufp=0;
int getch(void){
return bufp>0?buf[--bufp]:getchar();
}
void ungetch(int c){
if(bufp>=BUFSIZE)
printf("ungetch: too many characters\n");
else
buf[bufp++]=c;
}
#define MAXOP 1000
#define NUMBER '0'
int getop(char s[]){
int i,c;
while((s[0]=c=getch())==' '||c=='\t')
;
s[1]='\0';
if(!isdigit(c)&&c!='.'&&c!='-')
return c;
i=0;
if(c=='-')
if(isdigit(c=getch())||c=='.')
s[++i]=c;
else
{
if(c!=EOF)
ungetch(c);
return '-';
}
if(isdigit(c))
while(isdigit(s[++i]=c=getch()))
;
if(c=='.')
while(isdigit(s[++i]=c=getch()))
;
s[i]='\0';
if(c!=EOF)
ungetch(c);
return NUMBER;
}
int main(){
int type;
double op2;
char s[MAXOP];
while((type=getop(s))!=EOF){
switch(type){
case NUMBER:
push(atof_(s));
break;
case '+':
push(pop()+pop());
break;
case '-':
op2=pop();
push(pop()-op2);
break;
case '*':
push(pop()*pop());
break;
case '/':
op2=pop();
if(ABS(op2)>1e-10)
push(pop()/op2);
else
printf("error:zero divisor\n");
break;
case '%':
op2=pop();
if(ABS(op2)>1e-10)
push(fmod(pop(),op2));
else
printf("error:zero divisor\n");
break;
case '\n':
printf("\t%.8g\n",pop());
break;
default:
printf("error: unknown command %s\n",s);
break;
}
}
}



#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <ctype.h>
#include <math.h>
#define ABS(x) ((x)<0?-(x):(x))
double atof_(char s[]){
double val,power;
int i,sign;
for(i=0;isspace(s[i]);i++);
sign=(s[i]=='-')?-1:1;
if(s[i]=='+'||s[i]=='-')
i++;
for(val=0.0;isdigit(s[i]);i++)
val=10.0*val+(s[i]-'0');
if(s[i]=='.')
i++;
for(power=1.0;isdigit(s[i]);i++){
val=10.0*val+(s[i]-'0');
power*=10;
}
val= sign*val/power;
if(s[i]=='e'||s[i]=='E'){
int exp;
sign=(s[++i]=='-')?-1:1;
if(s[i]=='+'||s[i]=='-')
i++;
for(exp=0;isdigit(s[i]);i++)
exp=10*exp+(s[i]-'0');
if(sign)
while(exp-->0)
val*=10;
else
while(exp-->0)
val/=10;
}
return val;
}
#define MAXVAL 1000
int sp=0;
double val[MAXVAL];
void push(double f){
if(sp<MAXVAL)
val[sp++]=f;
else
printf("error:stack full\n");
}
double pop(void){
if(sp>0)
return val[--sp];
else
printf("error:stack empty\n");
return 0.0;
}
void clear(void){
sp=0;
}
#define BUFSIZE 100
char buf[BUFSIZE];
int bufp=0;
int getch(void){
return bufp>0?buf[--bufp]:getchar();
}
void ungetch(int c){
if(bufp>=BUFSIZE)
printf("ungetch: too many characters\n");
else
buf[bufp++]=c;
}
#define MAXOP 1000
#define NUMBER '0'
int getop(char s[]){
int i,c;
while((s[0]=c=getch())==' '||c=='\t')
;
s[1]='\0';
if(!isdigit(c)&&c!='.'&&c!='-')
return c;
i=0;
if(c=='-')
if(isdigit(c=getch())||c=='.')
s[++i]=c;
else
{
if(c!=EOF)
ungetch(c);
return '-';
}
if(isdigit(c))
while(isdigit(s[++i]=c=getch()))
;
if(c=='.')
while(isdigit(s[++i]=c=getch()))
;
s[i]='\0';
if(c!=EOF)
ungetch(c);
return NUMBER;
}
int main(){
int type;
double op1,op2;
char s[MAXOP];
while((type=getop(s))!=EOF){
switch(type){
case NUMBER:
push(atof_(s));
break;
case '+':
push(pop()+pop());
break;
case '-':
op2=pop();
push(pop()-op2);
break;
case '*':
push(pop()*pop());
break;
case '/':
op2=pop();
if(ABS(op2)>1e-10)
push(pop()/op2);
else
printf("error:zero divisor\n");
break;
case '%':
op2=pop();
if(ABS(op2)>1e-10)
push(fmod(pop(),op2));
else
printf("error:zero divisor\n");
break;
case '?':
op2=pop();
printf("\t%.8g\n",op2);
push(op2);
break;
case 'c':
clear();
break;
case 'd':
op2=pop();
push(op2);
push(op2);
break;
case 's':
op1=pop();
op2=pop();
push(op1);
push(op2);
case '\n':
printf("\t%.8g\n",pop());
break;
default:
printf("error: unknown command %s\n",s);
break;
}
}
}


#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <ctype.h>
#include <math.h>
#include <string.h>
#define ABS(x) ((x)<0?-(x):(x))
double atof_(char s[]){
double val,power;
int i,sign;
for(i=0;isspace(s[i]);i++);
sign=(s[i]=='-')?-1:1;
if(s[i]=='+'||s[i]=='-')
i++;
for(val=0.0;isdigit(s[i]);i++)
val=10.0*val+(s[i]-'0');
if(s[i]=='.')
i++;
for(power=1.0;isdigit(s[i]);i++){
val=10.0*val+(s[i]-'0');
power*=10;
}
val= sign*val/power;
if(s[i]=='e'||s[i]=='E'){
int exp;
sign=(s[++i]=='-')?-1:1;
if(s[i]=='+'||s[i]=='-')
i++;
for(exp=0;isdigit(s[i]);i++)
exp=10*exp+(s[i]-'0');
if(sign)
while(exp-->0)
val*=10;
else
while(exp-->0)
val/=10;
}
return val;
}
#define MAXVAL 1000
int sp=0;
double val[MAXVAL];
void push(double f){
if(sp<MAXVAL)
val[sp++]=f;
else
printf("error:stack full\n");
}
double pop(void){
if(sp>0)
return val[--sp];
else
printf("error:stack empty\n");
return 0.0;
}
#define BUFSIZE 100
char buf[BUFSIZE];
int bufp=0;
int getch(void){
return bufp>0?buf[--bufp]:getchar();
}
void ungetch(int c){
if(bufp>=BUFSIZE)
printf("ungetch: too many characters\n");
else
buf[bufp++]=c;
}
void mathfnc(char s[]){
double op2;
if(strcmp(s,"sin")==0)
push(sin(pop()));
else if(strcmp(s,"cos")==0)
push(cos(pop()));
else if(strcmp(s,"exp")==0)
push(exp(pop()));
else if(strcmp(s,"pow")==0) {
op2=pop();
push(pow(pop(),op2));
}
else
printf("error: %s not supported\n",s);
}
#define MAXOP 1000
#define NUMBER '0'
#define NAME 'n'
int getop(char s[]){
int i,c;
while((s[0]=c=getch())==' '||c=='\t')
;
s[1]='\0';
i=0;
if(islower(c)){
while(islower(s[++i]=c=getch()))
;
s[i]='\0';
if(c!=EOF)
ungetch(c);
if(strlen(s)>1)
return NAME;
else
return c;
}
if(!isdigit(c)&&c!='.'&&c!='-')
return c;
if(c=='-')
if(isdigit(c=getch())||c=='.')
s[++i]=c;
else
{
if(c!=EOF)
ungetch(c);
return '-';
}
if(isdigit(c))
while(isdigit(s[++i]=c=getch()))
;
if(c=='.')
while(isdigit(s[++i]=c=getch()))
;
s[i]='\0';
if(c!=EOF)
ungetch(c);
return NUMBER;
}
int main(){
int type;
double op1,op2;
char s[MAXOP];
while((type=getop(s))!=EOF){
switch(type){
case NUMBER:
push(atof_(s));
break;
case NAME:
mathfnc(s);
break;
case '+':
push(pop()+pop());
break;
case '-':
op2=pop();
push(pop()-op2);
break;
case '*':
push(pop()*pop());
break;
case '/':
op2=pop();
if(ABS(op2)>1e-10)
push(pop()/op2);
else
printf("error:zero divisor\n");
break;
case '%':
op2=pop();
if(ABS(op2)>1e-10)
push(fmod(pop(),op2));
else
printf("error:zero divisor\n");
break;
case '\n':
printf("\t%.8g\n",pop());
break;
default:
printf("error: unknown command %s\n",s);
break;
}
}
}



#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <ctype.h>
#include <math.h>
#define ABS(x) ((x)<0?-(x):(x))
double atof_(char s[]){
double val,power;
int i,sign;
for(i=0;isspace(s[i]);i++);
sign=(s[i]=='-')?-1:1;
if(s[i]=='+'||s[i]=='-')
i++;
for(val=0.0;isdigit(s[i]);i++)
val=10.0*val+(s[i]-'0');
if(s[i]=='.')
i++;
for(power=1.0;isdigit(s[i]);i++){
val=10.0*val+(s[i]-'0');
power*=10;
}
val= sign*val/power;
if(s[i]=='e'||s[i]=='E'){
int exp;
sign=(s[++i]=='-')?-1:1;
if(s[i]=='+'||s[i]=='-')
i++;
for(exp=0;isdigit(s[i]);i++)
exp=10*exp+(s[i]-'0');
if(sign)
while(exp-->0)
val*=10;
else
while(exp-->0)
val/=10;
}
return val;
}
#define MAXVAL 1000
int sp=0;
double val[MAXVAL];
void push(double f){
if(sp<MAXVAL)
val[sp++]=f;
else
printf("error:stack full\n");
}
double pop(void){
if(sp>0)
return val[--sp];
else
printf("error:stack empty\n");
return 0.0;
}
#define BUFSIZE 100
char buf[BUFSIZE];
int bufp=0;
int getch(void){
return bufp>0?buf[--bufp]:getchar();
}
void ungetch(int c){
if(bufp>=BUFSIZE)
printf("ungetch: too many characters\n");
else
buf[bufp++]=c;
}
#define MAXOP 1000
#define NUMBER '0'
int getop(char s[]){
int i,c;
while((s[0]=c=getch())==' '||c=='\t')
;
s[1]='\0';
if(!isdigit(c)&&c!='.'&&c!='-')
return c;
i=0;
if(c=='-')
if(isdigit(c=getch())||c=='.')
s[++i]=c;
else
{
if(c!=EOF)
ungetch(c);
return '-';
}
if(isdigit(c))
while(isdigit(s[++i]=c=getch()))
;
if(c=='.')
while(isdigit(s[++i]=c=getch()))
;
s[i]='\0';
if(c!=EOF)
ungetch(c);
return NUMBER;
}
int main(){
int type,i,var=0;
double op2, v;
char s[MAXOP];
double variable[26];
for(i=0;i<26;i++)
variable[i]=0.0;
while((type=getop(s))!=EOF){
switch(type){
case NUMBER:
push(atof_(s));
break;
case '+':
push(pop()+pop());
break;
case '-':
op2=pop();
push(pop()-op2);
break;
case '*':
push(pop()*pop());
break;
case '/':
op2=pop();
if(ABS(op2)>1e-10)
push(pop()/op2);
else
printf("error:zero divisor\n");
break;
case '%':
op2=pop();
if(ABS(op2)>1e-10)
push(fmod(pop(),op2));
else
printf("error:zero divisor\n");
break;
case '\n':
v=pop();
printf("\t%.8g\n",v);
break;
case '=':
pop();
if(var>='A'&&var<='Z')
variable[var-'A']=pop();
else
printf("error: no variable name\n");
break;
default:
if(type>='A'&&type<='Z')
push(variable[type-'A']);
else if(type =='v')
push(v);
else
printf("error: unknown command %s\n",s);
break;
}
var=type;
}
}

#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#define BUFSIZE 100
char buf[BUFSIZE];
int bufp=0;
int getch(void){
return bufp>0?buf[--bufp]:getchar();
}
void ungetch(int c){
if(bufp>=BUFSIZE)
printf("ungetch: too many characters\n");
else
buf[bufp++]=c;
}
void ungets(char s[]){
int len=strlen(s);
while(len>0)
ungetch(s[--len]);
}


char buf=0;
int getch(void){
int c;
if(buf!=0)
c=buf;
else
c=getchar();
buf=0;
return c;
}
void ungetch(int c){
if(buf!=0)
printf("ungetch:too many characters\n");
else
buf=c;
}



#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <ctype.h>
#include <math.h>
#define ABS(x) ((x)<0?-(x):(x))
double atof_(char s[]){
double val,power;
int i,sign;
for(i=0;isspace(s[i]);i++);
sign=(s[i]=='-')?-1:1;
if(s[i]=='+'||s[i]=='-')
i++;
for(val=0.0;isdigit(s[i]);i++)
val=10.0*val+(s[i]-'0');
if(s[i]=='.')
i++;
for(power=1.0;isdigit(s[i]);i++){
val=10.0*val+(s[i]-'0');
power*=10;
}
val= sign*val/power;
if(s[i]=='e'||s[i]=='E'){
int exp;
sign=(s[++i]=='-')?-1:1;
if(s[i]=='+'||s[i]=='-')
i++;
for(exp=0;isdigit(s[i]);i++)
exp=10*exp+(s[i]-'0');
if(sign)
while(exp-->0)
val*=10;
else
while(exp-->0)
val/=10;
}
return val;
}
#define MAXVAL 1000
int sp=0;
double val[MAXVAL];
void push(double f){
if(sp<MAXVAL)
val[sp++]=f;
else
printf("error:stack full\n");
}
double pop(void){
if(sp>0)
return val[--sp];
else
printf("error:stack empty\n");
return 0.0;
}
//#define BUFSIZE 100
//char buf[BUFSIZE];
//int bufp=0;
//int getch(void){
// return bufp>0?buf[--bufp]:getchar();
//}
//void ungetch(int c){
// if(bufp>=BUFSIZE)
// printf("ungetch: too many characters\n");
// else
// buf[bufp++]=c;
//}
#define MAXLINE 100
char line[MAXLINE];
int li=0;
int getline_(char line[],int lim){
int i,c;
i=0;
while(i<lim-1&&((c=getchar())!=EOF)&&c!='\n')
line[i++]=c;
if(c==EOF&&i==0)
return -1;
if(c=='\n')
line[i++]=c;
line[i]='\0';
return i;
}
#define MAXOP 1000
#define NUMBER '0'
int getop(char s[]){
int i,c;
if(line[li]=='\0')
if(getline_(line,MAXLINE)==-1)
return EOF;
else
li=0;
while((s[0]=c=line[li++])==' '||c=='\t')
;
s[1]='\0';
if(!isdigit(c)&&c!='.'&&c!='-')
return c;
i=0;
if(c=='-')
if(isdigit(c=line[li++])||c=='.')
s[++i]=c;
else
{
if(c!=EOF)
li--;
return '-';
}
if(isdigit(c))
while(isdigit(s[++i]=c=line[li++]))
;
if(c=='.')
while(isdigit(s[++i]=c=line[li++]))
;
s[i]='\0';
li--;
return NUMBER;
}
int main(){
int type;
double op2;
char s[MAXOP];
while((type=getop(s))!=EOF){
switch(type){
case NUMBER:
push(atof_(s));
break;
case '+':
push(pop()+pop());
break;
case '-':
op2=pop();
push(pop()-op2);
break;
case '*':
push(pop()*pop());
break;
case '/':
op2=pop();
if(ABS(op2)>1e-10)
push(pop()/op2);
else
printf("error:zero divisor\n");
break;
case '%':
op2=pop();
if(ABS(op2)>1e-10)
push(fmod(pop(),op2));
else
printf("error:zero divisor\n");
break;
case '\n':
printf("\t%.8g\n",pop());
break;
default:
printf("error: unknown command %s\n",s);
break;
}
}
}

快速排序


#include <stdio.h>
//#include <stdlib.h>
void swap(int *x,int *y){
int temp=*x;
*x=*y;
*y=temp;
}
void qsort(int v[],int left,int right){
int i,last;
if(left>=right)
return;
swap(v+left,v+(left+right)/2);
last=left;
for(i=left+1;i<=right;i++)
if(v[i]<v[left]) {
last++;
swap(v+last,v+i);
}
swap(v+left,v+last);
qsort(v,left,last-1);
qsort(v,last+1,right);
}
void Qsort(int v[],int n){
qsort(v,0,n-1);
}
void print_arr(int v[],int n){
int i;
for(i=0;i<n;i++)
printf("%4d",v[i]);
printf("\n");
}
int main(){
int i;
for(i=0;i<10;i++){
int arr[20],j,b[20];
for(j=0;j<20;j++)
{
int val=rand()%1000;
arr[j]=val;
b[j]=val;
}
printf("before:");
print_arr(b,20);
Qsort(arr,20);
printf("after :");
print_arr(arr,20);
}
}
测试结果如下:

swap宏

第5章 指针与数组


int strend(char *s,char*t){
char *bs=s;
char *bt=t;
while(*s++);
while(*t++);
while(*--s==*--t){
if(t==bt||s==st)
break;
}
if(*s==*t&&t==bt&&*s!='\0')
return 1;
else
return 0;
}



void strncpy(char* s,char *t,int n){
while(*t&&n-->0)
*s++=*t++;
while(n-->0)
*s++='\0';
}
void strncat(char *s,char *t,int n){
strncpy(s+strlen(s),t,n);
}
int strncmp(char* s,char* t,int n){
for(;*s==*t;s++,t++)
if(*s=='\0'||--n<=0)
return 0;
return *s-*t;
}
UNIX系统中sort程序的一个简单版本,实现对输入文本的排序。


#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#define MAXLINES 5000
char *lineptr[MAXLINES];
#define MAXLEN 1000
int getline_(char line[],int lim){
int i,c;
i=0;
while(i<lim-1&&((c=getchar())!=EOF)&&c!='\n')
line[i++]=c;
if(c==EOF&&i==0)
return -1;
if(c=='\n')
line[i++]=c;
line[i]='\0';
return i;
}
char* alloc(int len){
char *p=(char*)malloc(len*sizeof(char));
return p;
}
int readlines(char* lineptr[],int maxlines){
int len,nlines;
char *p,line[MAXLEN];
nlines=0;
while((len=getline_(line,MAXLEN))>0)
if(nlines>=maxlines||(p=alloc(len))==NULL)
return -1;
else{
line[len-1]='\0';
strcpy(p,line);
lineptr[nlines++]=p;
}
return nlines;
}
void writelines(char *lineptr[],int nlines){
int i;
for(i=0;i<nlines;i++)
printf("%s\n",lineptr[i]);
}
void swap(char **x,char **y){
char*tmp;
tmp=*x;
*x=*y;
*y=tmp;
}
void qsort_(char *v[],int left,int right){
int i,last;
if(left>=right)
return ;
swap(v+left,v+(left+right)/2);
last=left;
for(i=left+1;i<=right;i++)
if(strcmp(v[i],v[left])<0)
{
last++;
swap(v+last,v+i);
}
swap(v+left,v+last);
qsort_(v,left,last-1);
qsort_(v,last+1,right);
}
int main(){
int nlines;
int i;
if((nlines=readlines(lineptr,MAXLINES))>0){
qsort_(lineptr,0,nlines-1);
writelines(lineptr,nlines);
for(i=0;i<nlines;i++)
free(lineptr[i]);
return 0;
}
else{
printf("error: input too big to sort\n");
return 1;
}
}
根据日期计算是一年的第几天:

static int daytab[][13]={{0,31,28,31,30,31,30,31,31,30,31,30,31}
,{0,31,29,31,30,31,30,31,31,30,31,30,31}};
int day_of_year(int year,int month,int day){
int i,leap;
leap=year%4==0&&year%100!=0||year%400==0;
if(month<1||month>12)
return -1;
if(day<1||day>daytab[leap][month])
return -1;
for(i=1;i<month;i++)
day+=daytab[leap][i];
return day;
}
void month_day(int year,int yearday,int *pmonth,int *pday){
int i,leap;
if(year<1){
*pmonth=-1;
*pday=-1;
return ;
}
leap=year%4==0&&year%100!=0||year%400==0;
for(i=1;i<=12&&yearday>daytab[leap][i];i++)
yearday-=daytab[leap][i];
if(i>12&&yearday>daytab[leap][12]){
*pmonth=-1;
*pday=-1;
}
else{
*pmonth=i;
*pday=yearday;
}
}
习题5-13


#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#define DEFLINES 10
#define MAXLINES 10
#define MAXLEN 100
int getline_(char line[],int lim){
int i,c;
i=0;
while(i<lim-1&&((c=getchar())!=EOF)&&c!='\n')
line[i++]=c;
if(c==EOF&&i==0)
return -1;
if(c=='\n')
line[i++]=c;
line[i]='\0';
return i;
}
void error(char *s){
printf("%s\n",s);
exit(1);
}
int main(int argc,char* argv[]){
char *p,*buf,*bufend;
char line[MAXLEN];
char *lineptr[MAXLINES];
int first,i,last,len,n,nlines;
if(argc==1)
n=DEFLINES;
else if(argc==2&&(*++argv)[0]=='-')
n=atoi(argv[0]+1);
if(n<1||n>MAXLINES)
n=MAXLINES;
for(i=0;i<MAXLINES;i++)
lineptr[i]=NULL;
if((p=buf=malloc(MAXLINES*MAXLEN))==NULL)
error("tail:cannot allocate buf");
bufend=buf+MAXLINES*MAXLEN;
last=0;
nlines=0;
while((len=getline_(line,MAXLEN))>0){
if(p+len+1>=bufend)
p=buf;
lineptr[last]=p;
strcpy(lineptr[last],line);
if(++last>=MAXLINES)
last=0;
p+=len+1;
nlines++;
}
if(n>nlines)
n=nlines;
first=last-n;
if(first<0)
first+=MAXLINES;
for(i=first;n-->0;i=(i+1)%MAXLINES)
printf("%s",lineptr[i]);
free(buf);
return 0;
}



#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <ctype.h>
#define NUMERIC 1
#define DECR 2
#define FOLD 4
#define DIR 8
//#define LINES 100
#define MAXLINES 100
#define MAXLEN 1000
char option=0;
int pos1=0;
int pos2=0;
int getline_(char line[],int lim){
int i,c;
i=0;
while(i<lim-1&&((c=getchar())!=EOF)&&c!='\n')
line[i++]=c;
if(c==EOF&&i==0)
return -1;
if(c=='\n')
line[i++]=c;
line[i]='\0';
return i;
}
void error(char *s){
printf("%s\n",s);
exit(1);
}
char* alloc(int len){
char *p=(char*)malloc(len*sizeof(char));
return p;
}
int readlines(char* lineptr[],int maxlines){
int len,nlines;
char *p,line[MAXLEN];
nlines=0;
while((len=getline_(line,MAXLEN))>0)
if(nlines>=maxlines||(p=alloc(len))==NULL)
return -1;
else{
line[len-1]='\0';
strcpy(p,line);
lineptr[nlines++]=p;
}
return nlines;
}
void writelines(char *lineptr[],int nlines,int decr){
int i;
if(decr)
for(i=nlines-1;i>=0;i--)
printf("%s\n",lineptr[i]);
else
for(i=0;i<nlines;i++)
printf("%s\n",lineptr[i]);
}
void swap(void**x,void**y){
void*tmp;
tmp=*x;
*x=*y;
*y=tmp;
}
void qsort_(void*v[],int left,int right,
int(*comp)(void*,void*)){
int i,last;
if(left>=right)
return ;
swap(v+left,v+(left+right)/2);
last=left;
for(i=left+1;i<=right;i++)
if(strcmp(v[i],v[left])<0)
{
last++;
swap(v+last,v+i);
}
swap(v+left,v+last);
qsort_(v,left,last-1,comp);
qsort_(v,last+1,right,comp);
}
void readargs(int argc,char*argv[]){
int c;
while(--argc>0&&(c=(*++argv)[0])=='-'||c=='+'){
if(c=='-'&&!isdigit(*(argv[0]+1)))
while(c=*++argv[0])
switch(c){
case 'd':
option|=DIR;
break;
case 'f':
option|=FOLD;
break;
case 'n':
option|=NUMERIC;
break;
case 'r':
option|=DECR;
break;
default:
printf("sort: illegal option %c\n",c);
error("usage: sort -dfnr [+pos1] [-pos2]");
break;
}
else if(c=='-')
pos2=atoi(argv[0]+1);
else if((pos1=atoi(argv[0]+1))<0)
error("usage: sort -dfnr [+pos1] [-pos2]");
}
if(argc||pos1>pos2)
error("usage: sort -dfnr [+pos1] [-pos2]");
}
#define MAXSTR 100
void substr(char *s,char *str){
int i,j,len;
len=strlen(s);
if(pos2>0&&len>pos2)
len=pos2;
else if(pos2>0&&len<pos2)
error("substr:string too short");
for(j=0,i=pos1;i<len;i++,j++)
str[j]=s[i];
str[j]='\0';
}
#define ABS(x) ((x)<0?-(x):(x))
double atof_(char s[]){
double val,power;
int i,sign;
for(i=0;isspace(s[i]);i++);
sign=(s[i]=='-')?-1:1;
if(s[i]=='+'||s[i]=='-')
i++;
for(val=0.0;isdigit(s[i]);i++)
val=10.0*val+(s[i]-'0');
if(s[i]=='.')
i++;
for(power=1.0;isdigit(s[i]);i++){
val=10.0*val+(s[i]-'0');
power*=10;
}
val= sign*val/power;
if(s[i]=='e'||s[i]=='E'){
int exp;
sign=(s[++i]=='-')?-1:1;
if(s[i]=='+'||s[i]=='-')
i++;
for(exp=0;isdigit(s[i]);i++)
exp=10*exp+(s[i]-'0');
if(sign)
while(exp-->0)
val*=10;
else
while(exp-->0)
val/=10;
}
return val;
}
int numcmp(char *s1,char *s2){
double v1,v2;
char str[MAXSTR];
substr(s1,str);
v1=atof_(str);
substr(s2,str);
v2=atof_(str);
if(v1<v2)
return -1;
else if(v1>v2)
return 1;
else
return 0;
}
//#define FOLD 4
//#define DIR 8
int charcmp(char *s,char *t){
char a,b;
int i,j,endpos;
int fold=(option&FOLD)?1:0;
int dir=(option&DIR)?1:0;
i=j=pos1;
if(pos2>0)
endpos=pos2;
else if((endpos-strlen(s))>strlen(t))
endpos=strlen(t);
do{
if(dir){
while(i<endpos&&!isalnum(s[i])&&
s[i]!=' '&&s[i]!='\0')
i++;
while(j<endpos&&!isalnum(t[j])&&
t[j]!=' '&&t[j]!='\0')
j++;
}
if(i<endpos&&j<endpos){
a=fold?tolower(s[i]):s[i];
i++;
b=fold?tolower(t[j]):t[j];
j++;
if(a==b&&a=='\0')
return 0;
}
}
while(a==b&&i<endpos&&j<endpos);
return a-b;
}
int main(int argc,char*argv[]){
char *lineptr[MAXLINES];
int nlines;
int i;
readargs(argc,argv);
if((nlines=readlines(lineptr,MAXLINES))>0){
if(option&NUMERIC)
qsort_((void**)lineptr,0,nlines-1,
(int(*)(void*,void*))numcmp);
else
qsort_((void**)lineptr,0,nlines-1,
(int(*)(void*,void*))charcmp);
writelines(lineptr,nlines,option&DECR);
for(i=0;i<nlines;i++)
free(lineptr[i]);
return 0;
}
else{
printf("error: input too big to sort\n");
return 1;
}
}

dcl一个比较不错的程序:将声明转化为文字描述或将文字描述转化为声明





#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <ctype.h>
#define MAXTOKEN 100
enum{NAME,PARENS,BRACKETS};
int tokentype;
char token[MAXTOKEN];
char name[MAXTOKEN];
char datatype[MAXTOKEN];
char out[1000];
#define BUFSIZE 10
char buf[BUFSIZE];
int bufp=0;
int getch(void){
return bufp>0?buf[--bufp]:getchar();
}
void ungetch(int c){
if(bufp>=BUFSIZE)
printf("ungetch: too many characters\n");
else
buf[bufp++]=c;
}
int gettoken(){
char *p=token;
int c;
while((c=getch())==' '||c=='\t')
;
if(c=='('){
if((c=getch())==')'){
strcpy(token,"()");
return tokentype=PARENS;
}
else{
ungetch(c);
return tokentype='(';
}
}
else if(c=='['){
for(*p++=c;(*p++=getch())!=']';)
;
*p='\0';
return tokentype=BRACKETS;
}
else if(isalpha(c)){
for(*p++=c;isalnum(c=getch());)
*p++=c;
*p='\0';
ungetch(c);
return tokentype=NAME;
}
else
return tokentype=c;
}
void dcl(void);
void dirdcl(void){
int type;
if(tokentype=='('){
dcl();
if(tokentype!=')')
printf("error:missing )\n");
}
else if(tokentype==NAME)
strcpy(name,token);
else
printf("error:expected name or (dcl)\n");
while((type=gettoken())==PARENS||type==BRACKETS)
if(type==PARENS)
strcat(out," function returning");
else{
strcat(out, " array");
strcat(out,token);
strcat(out," of");
}
}
void dcl(void){
int ns;
for(ns=0;gettoken()=='*';)
ns++;
dirdcl();
while(ns-->0)
strcat(out," pointer to");
}
int main(){
while(gettoken()!=EOF){
strcpy(datatype,token);
out[0]='\0';
dcl();
if(tokentype!='\n')
printf("syntax error\n");
printf("%s: %s %s\n",name,out,datatype);
}
return 0;
}



int main(){
int type;
char temp[MAXTOKEN];
while(gettoken()!=EOF){
strcpy(out,token);
while((type=gettoken())!='\n')
if(type==PARENS||type==BRACKETS)
strcat(out,token);
else if(type=='*'){
sprintf(temp,"(*%s)",out);
strcpy(out,temp);
}
else if(type==NAME){
sprintf(temp,"%s %s",token,out);
strcpy(out,temp);
}
else {
printf("invalid input at %s\n",token);
}
}
printf("%s\n",out);
return 0;
}



#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <ctype.h>
#define MAXTOKEN 100
enum{NAME,PARENS,BRACKETS};
enum{NO,YES};
int tokentype;
char token[MAXTOKEN];
char name[MAXTOKEN];
char datatype[MAXTOKEN];
char out[1000];
int prevtoken=NO;
#define BUFSIZE 10
char buf[BUFSIZE];
int bufp=0;
int getch(void){
return bufp>0?buf[--bufp]:getchar();
}
void ungetch(int c){
if(bufp>=BUFSIZE)
printf("ungetch: too many characters\n");
else
buf[bufp++]=c;
}
void errmsg(char *msg){
printf("%s",msg);
prevtoken=YES;
}
int gettoken(){
char *p=token;
int c;
if(prevtoken==YES){
prevtoken=NO;
return tokentype;
}
while((c=getch())==' '||c=='\t')
;
if(c=='('){
if((c=getch())==')'){
strcpy(token,"()");
return tokentype=PARENS;
}
else{
ungetch(c);
return tokentype='(';
}
}
else if(c=='['){
for(*p++=c;(*p++=getch())!=']';)
;
*p='\0';
return tokentype=BRACKETS;
}
else if(isalpha(c)){
for(*p++=c;isalnum(c=getch());)
*p++=c;
*p='\0';
ungetch(c);
return tokentype=NAME;
}
else
return tokentype=c;
}
void dcl(void);
void dirdcl(void){
int type;
if(tokentype=='('){
dcl();
if(tokentype!=')')
printf("error:missing )\n");
}
else if(tokentype==NAME)
strcpy(name,token);
else
errmsg("error:expected name or (dcl)\n");
while((type=gettoken())==PARENS||type==BRACKETS)
if(type==PARENS)
strcat(out," function returning");
else{
strcat(out, " array");
strcat(out,token);
strcat(out," of");
}
}
void dcl(void){
int ns;
for(ns=0;gettoken()=='*';)
ns++;
dirdcl();
while(ns-->0)
strcat(out," pointer to");
}
int main(){
while(gettoken()!=EOF){
strcpy(datatype,token);
out[0]='\0';
dcl();
if(tokentype!='\n')
printf("syntax error\n");
printf("%s: %s %s\n",name,out,datatype);
}
return 0;
}




int nexttoken(){
int type;
type=gettoken();
prevtoken=YES;
return type;
}
int main(){
int type;
char temp[MAXTOKEN];
while(gettoken()!=EOF){
strcpy(out,token);
while((type=gettoken())!='\n')
if(type==PARENS||type==BRACKETS)
strcat(out,token);
else if(type=='*'){
if((type=nexttoken())==PARENS||
type==BRACKETS)
sprintf(temp,"(*%s)",out);
else
sprintf(temp,"*%s",out);
strcpy(out,temp);
}
else if(type==NAME){
sprintf(temp,"%s %s",token,out);
strcpy(out,temp);
}
else {
printf("invalid input at %s\n",token);
}
}
printf("%s\n",out);
return 0;
}






#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <ctype.h>
#define MAXTOKEN 100
enum{NAME,PARENS,BRACKETS};
enum{NO,YES};
int tokentype;
char token[MAXTOKEN];
char name[MAXTOKEN];
char datatype[MAXTOKEN];
char out[1000];
int prevtoken=NO;
#define BUFSIZE 10
char buf[BUFSIZE];
int bufp=0;
int getch(void){
return bufp>0?buf[--bufp]:getchar();
}
void ungetch(int c){
if(bufp>=BUFSIZE)
printf("ungetch: too many characters\n");
else
buf[bufp++]=c;
}
void errmsg(char *msg){
printf("%s",msg);
prevtoken=YES;
}
int gettoken(){
char *p=token;
int c;
if(prevtoken==YES){
prevtoken=NO;
return tokentype;
}
while((c=getch())==' '||c=='\t')
;
if(c=='('){
if((c=getch())==')'){
strcpy(token,"()");
return tokentype=PARENS;
}
else{
ungetch(c);
return tokentype='(';
}
}
else if(c=='['){
for(*p++=c;(*p++=getch())!=']';)
;
*p='\0';
return tokentype=BRACKETS;
}
else if(isalpha(c)){
for(*p++=c;isalnum(c=getch());)
*p++=c;
*p='\0';
ungetch(c);
return tokentype=NAME;
}
else
return tokentype=c;
}
int compare(char **s,char **t){
return strcmp(*s,*t);
}
int typespec(void){
static char *types[]={
"char","int","void"
};
char *pt=token;
if(bsearch(&pt,types,sizeof(types)/sizeof(char*),sizeof(char*),compare)==NULL)
return NO;
else
return YES;
}
int typequal(void){
static char *typeq[]={
"const","volatile"
};
char *pt=token;
if(bsearch(&pt,typeq,sizeof(typeq)/sizeof(char*),sizeof(char*),compare)==NULL)
return NO;
else
return YES;
}
void dcl(void);
void dclspec(void){
char temp[MAXTOKEN];
temp[0]='\0';
gettoken();
do{
if(tokentype!=NAME){
prevtoken=YES;
dcl();
}
else if(typespec()==YES){
strcat(temp," ");
strcat(temp,token);
gettoken();
}
else if(typequal()==YES){
strcat(temp," ");
strcat(temp,token);
gettoken();
}
else
errmsg("unknown type in parameter list\n");
}
while(tokentype!=','&&tokentype!=')');
strcat(out,temp);
if(tokentype==',')
strcat(out,",");
}
void parmdcl(void){
do{
dclspec();
}while(tokentype==',');
if(tokentype!=')')
errmsg("missing ) in parameter declaration\n");
}
void dirdcl(void){
int type;
if(tokentype=='('){
dcl();
if(tokentype!=')')
printf("error:missing )\n");
}
else if(tokentype==NAME) {
if(name[0]=='\0')
strcpy(name,token);
}
else
prevtoken=YES;
while((type=gettoken())==PARENS||type==BRACKETS||type=='(')
if(type==PARENS)
strcat(out," function returning");
else if(type=='('){
strcat(out," function expecting");
parmdcl();
strcat(out," and returning");
}
else{
strcat(out, " array");
strcat(out,token);
strcat(out," of");
}
}
void dcl(void){
int ns;
for(ns=0;gettoken()=='*';)
ns++;
dirdcl();
while(ns-->0)
strcat(out," pointer to");
}
int main(){
while(gettoken()!=EOF){
strcpy(datatype,token);
out[0]='\0';
dcl();
if(tokentype!='\n')
printf("syntax error\n");
printf("%s: %s %s\n",name,out,datatype);
}
return 0;
}

这个网站很不错的:http://cdecl.org/
第6章 结构体
统计关键字出现的次数

#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <ctype.h>
#include <string.h>
#define MAXWORD 1000
struct key {
char *word;
int count;
}
keytab[]={
"auto",0,
"break",0,
"case",0,
"char",0,
"const",0,
"continue",0,
"default",0,
"do",0,
"double",0,
"else",0,
"enum",0,
"extern",0,
"float",0,
"for",0,
"goto",0,
"if",0,
"int",0,
"long",0,
"register",0,
"return",0,
"short",0,
"signed",0,
"sizeof",0,
"static",0,
"struct",0,
"switch",0,
"typedef",0,
"union",0,
"unsigned",0,
"void",0,
"volatile",0,
"while",0,
};
#define NKEYS (sizeof keytab/sizeof(keytab[0]))
#define BUFSIZE 10
char buf[BUFSIZE];
int bufp=0;
int getch(void){
return bufp>0?buf[--bufp]:getchar();
}
void ungetch(int c){
if(bufp>=BUFSIZE)
printf("ungetch: too many characters\n");
else
buf[bufp++]=c;
}
int binsearch(char *word,struct key tab[],int n){
int cond;
int low,high,mid;
low=0;
high=n-1;
while(low<=high){
mid=(low+high)/2;
if((cond=strcmp(word,tab[mid].word))<0)
high=mid-1;
else if(cond>0)
low=mid+1;
else
return mid;
}
return -1;
}
int comment(void){
int c;
while((c=getch())!=EOF)
if(c=='*')
if((c=getch())=='/')
break;
else
ungetch(c);
return c;
}
int getword(char *word,int lim){
char *w=word;
int c,d;
while(isspace(c=getch()))
;
if(c!=EOF)
*w++=c;
if(isalpha(c)||c=='-'||c=='#'){
for(;--lim>0;w++)
if(!isalnum(*w=getch())&&*w!='-'){
ungetch(*w);
break;
}
}
else if(c=='\''||c=='"'){
for(;--lim>0;w++)
if((*w=getch())=='\\')
*++w=getch();
else if(*w==c){
w++;
break;
}
else if(*w==EOF)
break;
}
else if(c=='/')
if((d=getch())=='*')
c=comment();
else
ungetch(d);
*w='\0';
return c;
}
int main(){
int n;
char word[MAXWORD];
while(getword(word,MAXWORD)!=EOF)
if(isalpha(word[0]))
if((n=binsearch(word,keytab,NKEYS))>=0)
keytab
.count++;
for(n=0;n<NKEYS;n++)
if(keytab
.count>0)
printf("%4d %s\n",
keytab
.count,keytab
.word);
return 0;
}




#include <stdio.h>
#include <ctype.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#define BUFSIZE 10
char buf[BUFSIZE];
int bufp=0;
int getch(void){
return bufp>0?buf[--bufp]:getchar();
}
void ungetch(int c){
if(bufp>=BUFSIZE)
printf("ungetch: too many characters\n");
else
buf[bufp++]=c;
}
int comment(void){
int c;
while((c=getch())!=EOF)
if(c=='*')
if((c=getch())=='/')
break;
else
ungetch(c);
return c;
}
int getword(char *word,int lim){
char *w=word;
int c,d;
while(isspace(c=getch()))
;
if(c!=EOF)
*w++=c;
if(isalpha(c)||c=='-'||c=='#'){
for(;--lim>0;w++)
if(!isalnum(*w=getch())&&*w!='-'){
ungetch(*w);
break;
}
}
else if(c=='\''||c=='"'){
for(;--lim>0;w++)
if((*w=getch())=='\\')
*++w=getch();
else if(*w==c){
w++;
break;
}
else if(*w==EOF)
break;
}
else if(c=='/')
if((d=getch())=='*')
c=comment();
else
ungetch(d);
*w='\0';
return c;
}
struct tnode{
char *word;
int match;
struct tnode *left;
struct tnode *right;
};
#define MAXWORD 100
#define YES 1
#define NO 0
int compare(char *s,struct tnode *p,int num,int *found){
int i;
char *t=p->word;
for(i=0;*s==*t;i++,s++,t++)
if(*s=='\0')
return 0;
if(i>=num){
*found=YES;
p->match=YES;
}
return *s-*t;
}
struct tnode* talloc(void){
return (struct tnode*)malloc(sizeof(struct tnode));
}
char *strdup_(char *s){
char *p;
p=(char*)malloc(strlen(s)+1);
if(p!=NULL)
strcpy(p,s);
return p;
}
struct tnode* addtreex(struct tnode*p,char *w,int num,int *found){
int cond;
if(p==NULL){
p=talloc();
p->word=strdup_(w);
p->match=*found;
p->left=p->right=NULL;
}
else if((cond=compare(w,p,num,found))<0)
p->left=addtreex(p->left,w,num,found);
else if(cond>0)
p->right=addtreex(p->right,w,num,found);
return p;
}
void treeprint(struct tnode* p){
if(p!=NULL){
treeprint(p->left);
if(p->match)
printf("%s]n",p->word);
treeprint(p->right);
}
}
void freetree(struct tnode*p){
if(p!=NULL){
freetree(p->left);
freetree(p->right);
free(p->word);
}
}
int main(int argc,char *argv[]){
struct tnode *root;
char word[MAXWORD];
int found=NO;
int num;
num=(--argc&&(*++argv)[0]=='-')?atoi(argv[0]+1):6;
root=NULL;
while(getword(word,MAXWORD)!=EOF){
if(isalpha(word[0])&&strlen(word)>=num)
root=addtreex(root,word,num,&found);
found=NO;
}
treeprint(root);
freetree(root);
return 0;
}



#include <stdio.h>
#include <ctype.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#define BUFSIZE 10
char buf[BUFSIZE];
int bufp=0;
int getch(void){
return bufp>0?buf[--bufp]:getchar();
}
void ungetch(int c){
if(bufp>=BUFSIZE)
printf("ungetch: too many characters\n");
else
buf[bufp++]=c;
}
int comment(void){
int c;
while((c=getch())!=EOF)
if(c=='*')
if((c=getch())=='/')
break;
else
ungetch(c);
return c;
}
int getword(char *word,int lim){
char *w=word;
int c,d;
while(isspace(c=getch()))
;
if(c!=EOF)
*w++=c;
if(isalpha(c)||c=='-'||c=='#'){
for(;--lim>0;w++)
if(!isalnum(*w=getch())&&*w!='-'){
ungetch(*w);
break;
}
}
else if(c=='\''||c=='"'){
for(;--lim>0;w++)
if((*w=getch())=='\\')
*++w=getch();
else if(*w==c){
w++;
break;
}
else if(*w==EOF)
break;
}
else if(c=='/')
if((d=getch())=='*')
c=comment();
else
ungetch(d);
*w='\0';
return c;
}
struct linklist{
int lnum;
struct linklist *ptr;
};
struct tnode{
char *word;
struct linklist *lines;
struct tnode *left;
struct tnode *right;
};
#define MAXWORD 100
#define YES 1
#define NO 0
struct tnode* talloc(void){
return (struct tnode*)malloc(sizeof(struct tnode));
}
struct linklist *lalloc(void){
return (struct linklist*)malloc(sizeof(struct linklist));
}
char *strdup_(char *s){
char *p;
p=(char*)malloc(strlen(s)+1);
if(p!=NULL)
strcpy(p,s);
return p;
}
void addln(struct tnode *p,int linenum){
struct linklist *temp;
temp=p->lines;
while(temp->ptr!=NULL&&temp->lnum!=linenum)
temp=temp->ptr;
if(temp->lnum==linenum){
temp->ptr=lalloc();
temp->ptr->lnum=linenum;
temp->ptr->ptr=NULL;
}
}
struct tnode* addtreex(struct tnode*p,char *w,int linenum){
int cond;
if(p==NULL){
p=talloc();
p->word=strdup_(w);
p->lines=lalloc();
p->lines->lnum=linenum;
p->lines->ptr=NULL;
p->left=p->right=NULL;
}
else if((cond=strcmp(w,p->word))<0)
p->left=addtreex(p->left,w,linenum);
else if(cond>0)
p->right=addtreex(p->right,w,linenum);
else
addln(p,linenum);
return p;
}
void treeprint(struct tnode* p){
struct linklist *temp;
if(p!=NULL){
treeprint(p->left);
printf("%10s: ",p->word);
for(temp=p->lines;temp!=NULL;temp=temp->ptr)
printf("%4d ",temp->lnum);
printf("\n");
treeprint(p->right);
}
}
void freetree(struct tnode*p){
if(p!=NULL){
freetree(p->left);
freetree(p->right);
free(p->word);
free(p->lines);
}
}
int noiseword(char *w){
static char *nw[]={
"a","an","and","are","in","is","of","or","that","the","this","to"
};
int cond,mid;
int low=0;
int high=sizeof(nw)/sizeof(char*)-1;
while(low<=high){
mid=(low+high)/2;
if((cond=strcmp(w,nw[mid]))<0)
high=mid-1;
else if(cond>0)
low=mid+1;
else
return mid;
}
return -1;
}
int main(int argc,char *argv[]){
struct tnode *root;
char word[MAXWORD];
int linenum=1;
root=NULL;
while(getword(word,MAXWORD)!=EOF){
if(isalpha(word[0])&&noiseword(word)==-1)
root=addtreex(root,word,linenum);
else if(word[0]=='\n')
linenum++;
}
treeprint(root);
freetree(root);
return 0;
}

表查找程序核心代码:




#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
struct nlist{
struct nlist *next;
char *name;
char *defn;
};
#define HASHSIZE 101
static struct nlist *hashtab[HASHSIZE];
unsigned hash(char *s)
{
unsigned hashval;
for(hashval=0;*s!='\0';s++)
hashval=*s+32*hashval;
return hashval%HASHSIZE;
}
struct nlist *lookup(char *s){
struct nlist *np;
for(np=hashtab[hash(s)];np!=NULL;np=np->next)
if(strcmp(s,np->name)==0)
return np;
return NULL;
}
struct nlist *install(char *name,char*defn){
struct nlist *np;
unsigned hashval;
if((np=lookup(name))==NULL){
np=(struct nlist *)malloc(sizeof(struct nlist));
if(np==NULL||(np->name=strdup(name))==NULL)
return NULL;
hashval=hash(name);
np->next=hashtab[hashval];
hashtab[hashval]=np;
}
else
free((void*)np->defn);
if((np->defn=strdup(defn))==NULL)
return NULL;
return np;
}
void undef(char*s){
int h;
struct nlist *prev,*np;
prev=NULL;
h=hash(s);
for(np=hashtab[h];np!=NULL;np=np->next){
if(strcmp(s,np->name)==0)
break;
prev=np;
}
if(np!=NULL){
if(prev==NULL)
hashtab[h]=np->next;
else
prev->next=np->next;
free(np->name);
free(np->defn);
free(np);
}
}


#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <ctype.h>
#define BUFSIZE 10
char buf[BUFSIZE];
int bufp=0;
int getch(void){
return bufp>0?buf[--bufp]:getchar();
}
void ungetch(int c){
if(bufp>=BUFSIZE)
printf("ungetch: too many characters\n");
else
buf[bufp++]=c;
}
void ungets(char *s){
int len=strlen(s);
while(len>0)
ungetch(s[--len]);
}
char *strdup_(char *s){
char *p;
p=(char*)malloc(strlen(s)+1);
if(p!=NULL)
strcpy(p,s);
return p;
}
int comment(void){
int c;
while((c=getch())!=EOF)
if(c=='*')
if((c=getch())=='/')
break;
else
ungetch(c);
return c;
}
int getword(char *word,int lim){
char *w=word;
int c,d;
while(isspace(c=getch()))
;
if(c!=EOF)
*w++=c;
if(isalpha(c)||c=='-'||c=='#'){
for(;--lim>0;w++)
if(!isalnum(*w=getch())&&*w!='-'){
ungetch(*w);
break;
}
}
else if(c=='\''||c=='"'){
for(;--lim>0;w++)
if((*w=getch())=='\\')
*++w=getch();
else if(*w==c){
w++;
break;
}
else if(*w==EOF)
break;
}
else if(c=='/')
if((d=getch())=='*')
c=comment();
else
ungetch(d);
*w='\0';
return c;
}
struct nlist{
struct nlist *next;
char *name;
char *defn;
};
#define HASHSIZE 101
static struct nlist *hashtab[HASHSIZE];
unsigned hash(char *s)
{
unsigned hashval;
for(hashval=0;*s!='\0';s++)
hashval=*s+32*hashval;
return hashval%HASHSIZE;
}
struct nlist *lookup(char *s){
struct nlist *np;
for(np=hashtab[hash(s)];np!=NULL;np=np->next)
if(strcmp(s,np->name)==0)
return np;
return NULL;
}
struct nlist *install(char *name,char*defn){
struct nlist *np;
unsigned hashval;
if((np=lookup(name))==NULL){
np=(struct nlist *)malloc(sizeof(struct nlist));
if(np==NULL||(np->name=strdup_(name))==NULL)
return NULL;
hashval=hash(name);
np->next=hashtab[hashval];
hashtab[hashval]=np;
}
else
free((void*)np->defn);
if((np->defn=strdup_(defn))==NULL)
return NULL;
return np;
}
void undef(char*s){
int h;
struct nlist *prev,*np;
prev=NULL;
h=hash(s);
for(np=hashtab[h];np!=NULL;np=np->next){
if(strcmp(s,np->name)==0)
break;
prev=np;
}
if(np!=NULL){
if(prev==NULL)
hashtab[h]=np->next;
else
prev->next=np->next;
free(np->name);
free(np->defn);
free(np);
}
}
void error(int c,char *s){
printf("error:%s\n",s);
while(c!=EOF&&c!='\n')
c=getch();
}
void skipblanks(){
int c;
while((c=getch())==' '||c=='\t')
;
ungetch(c);
}
#define MAXWORD 100
void getdef(){
int c,i;
char def[MAXWORD],dir[MAXWORD],name[MAXWORD];
skipblanks();
if(!isalpha(getword(dir,MAXWORD)))
error(dir[0],"getdef:expecting a directive after #");
else if(strcmp(dir,"define")==0){
skipblanks();
if(!isalpha(getword(name,MAXWORD)))
error(name[0],"getdef:non-alpha -name expected");
else{
skipblanks();
for(i=0;i<MAXWORD-1;i++)
if((def[i]=getch())==EOF||
def[i]=='\n')
break;
def[i]='\0';
if(i<=0)
error('\n',"getdef:incomplete define");
else
install(name,def);
}
}
else if(strcmp(dir,"undef")==0){
skipblanks();
if(!isalpha(getword(name,MAXWORD)))
error(name[0],"getdef:non-alpha in undef");
else
undef(name);
}
else
error(dir[0],"getdef:expecting a directive after #");
}
int main(){
char w[MAXWORD];
struct nlist *p;
while(getword(w,MAXWORD)!=EOF){
if(strcmp(w,"#")==0)
getdef();
else if(!isalpha(w[0]))
printf("%s",w);
else if((p=lookup(w))==NULL)
printf("%s",w);
else
ungets(p->defn);
}
return 0;
}

第7章 输入与输出
变长参数列表


#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdarg.h>
void minprintf(char *fmt,...){
va_list ap;
char *p,*sval;
int ival;
double dval;
va_start(ap,fmt);
for(p=fmt;*p;p++){
if(*p!='%'){
putchar(*p);
continue;
}
switch(*++p){
case 'd':
ival=va_arg(ap,int);
printf("%d",ival);
break;
case 'f':
dval=va_arg(ap,double);
printf("%f",dval);
break;
case 's':
for(sval=va_arg(ap,char*);*sval;sval++)
putchar(*sval);
break;
default:
putchar(*p);
break;
}
}
va_end(ap);
}
int main(){
int a=3;
double d=8.7;
minprintf("%d %f\n",a,d);
}

#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdarg.h>
#include <ctype.h>
#define LOCALFMT 100
void minprintf(char *fmt,...){
va_list ap;
char *p,*sval;
char localfmt[LOCALFMT];
int ival,i;
unsigned uval;
double dval;
va_start(ap,fmt);
for(p=fmt;*p;p++){
if(*p!='%'){
putchar(*p);
continue;
}
i=0;
localfmt[i++]='%';
while(*(p+1)&&!isalpha(*(p+1)))
localfmt[i++]=*++p;
localfmt[i++]=*(p+1);
localfmt[i]='\0';
switch(*++p){
case 'd':
case 'i':
ival=va_arg(ap,int);
printf(localfmt,ival);
break;
case 'x':
case 'X':
case 'u':
case 'o':
uval=va_arg(ap,unsigned);
printf(localfmt,uval);
case 'f':
dval=va_arg(ap,double);
printf(localfmt,dval);
break;
case 's':
sval=va_arg(ap,char*);
printf(localfmt,sval);
break;
default:
putchar(*p);
break;
}
}
va_end(ap);
}
int main(){
int a=3;
double d=8.7;
minprintf("%d %f\n",a,d);
}



#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdarg.h>
#include <ctype.h>
#define LOCALFMT 100
void minscanf(char *fmt,...){
va_list ap;
char *p,*sval;
char localfmt[LOCALFMT];
int c,i,*ival;
unsigned *uval;
double *dval;
va_start(ap,fmt);
for(p=fmt;*p;p++){
if(*p!='%'){
localfmt[i++]=*p;
continue;
}
i=0;
localfmt[i++]='%';
while(*(p+1)&&!isalpha(*(p+1)))
localfmt[i++]=*++p;
localfmt[i++]=*(p+1);
localfmt[i]='\0';
switch(*++p){
case 'd':
case 'i':
ival=va_arg(ap,int*);
scanf(localfmt,ival);
break;
case 'x':
case 'X':
case 'u':
case 'o':
uval=va_arg(ap,unsigned*);
scanf(localfmt,uval);
break;
case 'f':
dval=va_arg(ap,double*);
scanf(localfmt,dval);
break;
case 's':
sval=va_arg(ap,char*);
scanf(localfmt,sval);
break;
default:
scanf(localfmt);
break;
}
}
}


下面是标准库中对fgets和fputs函数的实现:

char *fgets(char *s,int n,FILE*iop){
register int c;
register char *cs;
cs=s;
while(--n>0&&(c=getc(iop))!=EOF)
if((*cs++=c)=='\n')
break;
*cs='\0';
return (c==EOF&&cs==s)?NULL:s;
}
int fputs(char*s ,FILE*iop){
int c;
while(c=*s++)
putc(c,iop);
return ferror(ip)?EOF:0;
}


#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#define MAXLINE 100
void filecomp(FILE*fp1,FILE*fp2){
char line1[MAXLINE],line2[MAXLINE];
char*lp1,*lp2;
do{
lp1=fgets(line1,MAXLINE,fp1);
lp2=fgets(line2,MAXLINE,fp2);
if(lp1==line1&&lp2==line2){
if(strcmp(line1,line2)!=0){
printf("first difference in line\n %s\n",line1);
lp1=lp2=NULL;
}
}
else if(lp1!=line1&&lp2==line2)
printf("end of first at line\n%s\n",line2);
else if(lp1==line1&&lp2!=line2)
printf("end of first at line\n%s\n",line1);
}
while(lp1==line1&&lp2==line2);
}
int main(int argc,char *argv[]){
FILE *fp1,*fp2;
if(argc!=3){
fprintf(stderr,"comp:need two file names\n");
exit(1);
}
else{
if((fp1=fopen(*++argv,"r"))==NULL){
fprintf(stderr,"comp:can't open %s\n",*argv);
exit(1);
}
else if((fp2=fopen(*++argv,"r"))==NULL){
fprintf(stderr,"comp:can't open %s\n",*argv);
exit(1);
}
else{
filecomp(fp1,fp2);
fclose(fp1);
fclose(fp2);
exit(0);
}
}
}


#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#define MAXLINE 1000
void fpat(FILE *fp,char *fname,char *pattern,int except,int number);
int main(int argc,char*argv[]){
char pattern[MAXLINE];
int c,except=0,number=0;
FILE *fp;
while(--argc>0&&(*++argv)[0]=='-')
while(c=*++argv[0])
switch(c){
case 'x':
except=1;
break;
case 'n':
number=1;
break;
default:
printf("find:illegal option %c\n",c);
argc=0;
break;
}
if(argc>=1)
strcpy(pattern,*argv);
else{
printf("Usage:find [-x] [-n] pattern [file ..]\n");
exit(1);
}
if(argc==1)
fpat(stdin,"",pattern,except,number);
else
while(--argc>0)
if((fp=fopen(*++argv,"r"))==NULL){
fprintf(stderr,"find: can't open %s\n",*argv);
exit(1);
}else{
fpat(fp,*argv,pattern,except,number);
fclose(fp);
}
return 0;
}
void fpat(FILE *fp,char *fname,char *pattern,int except,int number){
char line[MAXLINE];
long lineno=0;
while(fgets(line,MAXLINE,fp)!=NULL){
++lineno;
if((strstr(line,pattern)!=NULL)!=except){
if(*fname)
printf("%s - ",fname);
if(number)
printf("%ld: ",lineno);
printf("%s",line);
}
}
}



#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#define MAXBOT 3
#define MAXHDR 5
#define MAXLINE 100
#define MAXPAGE 66
int heading(char *fname,int pageno){
int ln=3;
fprintf(stdout,"\n\n");
fprintf(stdout,"%s page %d\n",fname,pageno);
while(ln++<MAXHDR)
fprintf(stdout,"\n");
return ln;
}
void fileprint(FILE*fp,char *fname){
int lineno,pageno=1;
char line[MAXLINE];
lineno=heading(fname,pageno++);
while(fgets(line,MAXLINE,fp)!=NULL){
if(lineno==1){
fprintf(stdout,"\f");
lineno=heading(fname,pageno++);
}
fputs(line,stdout);
if(++lineno>MAXPAGE-MAXBOT)
lineno=1;
}
fprintf(stdout,"\f");
}
int main(int argc,char *argv[]){
FILE *fp;
if(argc==1)
fileprint(stdin," ");
else
while(--argc>0)
if((fp=fopen(*++argv,"r"))==NULL){
fprintf(stderr,"print:can't open %s\n",*argv);
exit(1);
}
else{
fileprint(fp,*argv);
fclose(fp);
}
return 0;
}

随机数发生器,生成浮点数的方法

第8章 UNIX系统接口

利用低级的read和write函数来构造高级函数getchar,putchar等。
int getchar_(void){
char c;
return (read(0,&c,1)==1)?(unsigned char)c:EOF;
}
int getchar__(void){
static char buf[BUFSIZ];
static char *bufp=buf;
static int n=0;
if(n==0){
n=read(0,buf,sizeof buf);
bufp=buf;
}
return (--n>0)?(unsigned char )*bufp++:EOF;
}


#include <unistd.h>
#define NULL 0
#define EOF (-1)
#define BUFSIZ 1024
#define OPEN_MAX 20
typedef struct _iobuf{
int cnt;
char *ptr;
char *base;
int flag;
int fd;
}FILE;
extern FILE _iob[OPEN_MAX];
#define stdin (&_iob[0])
#define stdout (&_iob[1])
#define stderr (&_iob[2])
enum _flags{
_READ =01,
_WRITE =02,
_UNBUF=04,
_EOF =010,
_ERR=020
};
int _fillbuf(FILE*);
int _flushbuf(int ,FILE *);
#define feof(p) (((p)->flag&_EOF)!=0)
#define ferror(p) (((p)->flag&_ERR)!=0)
#define fileno(p) ((p)->fd)
#define getc(p) (--(p)->cnt>=0\
?(unsigned char)*(p)->ptr++:_fillbuf(p))
#define putc(x,p) (--(p)->cnt>=0\
?*(p)->ptar++=(x):_flushbuf((x),p))
#define getchar() getc(stdin)
#define putchar(x) putc(x,stdout)
#include <fcntl.h>
#define PERMS 0666
FILE *fopen(char *name,char *mode)
{
int fd;
FILE *fp;
if(*mode!='r'&&*mode!='w'&&*mode!='a')
return NULL;
for(fp=_iob;fp<_iob+OPEN_MAX;fp++)
if((fp->flag&(_READ|_WRITE))==0)
break;
if(fp>=_iob+OPEN_MAX)
return NULL;
if(*mode=='w')
fd=creat(name,PERMS);
else if(*mode=='a'){
if((fd=open(name,O_WRONLY,0))==-1)
fd=creat(name,PERMS);
lseek(fd,0L,2);
}
else
fd=open(name,O_RDONLY,0);
if(fd==-1)
return NULL;
fp->fd=fd;
fp->cnt=0;
fp->base=NULL;
fp->flag=(*mode=='r')?_READ:_WRITE;
return fp;
}
int _fillbuf(FILE*fp){
int bufsize;
if((fp->flag&(_READ|_EOF|_ERR))!=_READ)
return EOF;
bufsize=(fp->flag&_UNBUF)?1:BUFSIZ;
if(fp->base==NULL)
if((fp->base=(char*)malloc(bufsize))==NULL)
return EOF;
fp->ptr=fp->base;
fp->cnt=read(fp->fd,fp->ptr,bufsize);
if(--fp->cnt<0){
if(fp->cnt==-1)
fp->flag|=_EOF;
else
fp->flag|=_ERR;
fp->cnt=0;
return EOF;
}
return (unsigned char)*fp->ptr++;
}
FILE _iob[OPEN_MAX]={
{0,(char*)0,(char*)0,_READ,0 },
{0,(char*)0,(char*)0,_WRITE,1 },
{0,(char*)0,(char*)0,_WRITE|_UNBUF,2 },
};
int _flushbuf(int x,FILE*fp){
unsigned nc;
int bufsize;
if(fp<_iob||fp>=_iob+OPEN_MAX)
return EOF;
if((fp->flag&(_WRITE|_ERR))!=_WRITE)
return EOF;
bufsize=(fp->flag&_UNBUF)?1:BUFSIZ;
if(fp->base==NULL){
if((fp->base=(char*)malloc(bufsize))==NULL){
fp->flag|=_ERR;
return EOF;
}
}
else{
nc=fp->ptr-fp->base;
if(write(fp->fd,fp->base,nc)!=nc){
fp->flag|=_ERR;
return EOF;
}
}
fp->ptr=fp->base;
*fp->ptr++=(char)x;
fp->cnt=bufsize-1;
return x;
}
int fclose(FILE *fp){
int rc;
if((rc=fflush(fp))!=EOF){
free(fp->base);
fp->ptr=NULL;
fp->cnt=0;
fp->base=NULL;
fp->flag&=(_READ|_WRITE);
}
return rc;
}
int fflush(FILE*fp){
int rc=0;
if(fp<_iob||fp>=_iob+OPEN_MAX)
return EOF;
if(fp->flag&_WRITE)
rc=_flushbuf(0,fp);
fp->ptr=fp->base;
fp->cnt=(fp->flag&_UNBUF)?1:BUFSIZ;
return rc;
}
int fseek(FILE *fp,long offset,int origin){
unsigned nc;
long rc=0;
if(fp->flag&_READ){
if(origin==1)
offset-=fp->cnt;
rc=lseek(fp->fd,offset,origin);
fp->cnt=0;
}
else if(fp->flag&_WRITE){
if((nc=fp->ptr-fp->base)>0)
if(write(fp->fd,fp->base,nc)!=nc)
rc=-1;
if(rc!=-1)
rc=lseek(fp->fd,offset,origin);
}
return (rc==-1)?-1:0;
}






#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <dirent.h>
//#define NAME_MAX 14
//typedef struct{
// long ino;
// char name[NAME_MAX+1];
//}Dirent;
//typedef struct{
// int fd;
// Dirent d;
//}DIR;
//DIR *opendir(char *dirname);
//Dirent* readdir(DIR*dfd);
//void closedir(DIR* dfd);
//char *name;
//struct stat stbuf;
//int stat(char *,struct stat*);
//#define S_IFMT 0160000
//#define S_IFDIR 0040000
//#define S_IFCHR 0020000
//#define S_IFBLK 0060000
//#define S_IFREG 001000
#define MAX_PATH 1024
void dirwalk(char *dir,void(*fcn)(char*)){
char name[MAX_PATH];
struct dirent *dp;
DIR *dfd;
if((dfd=opendir(dir))==NULL){
fprintf(stderr,"dirwalk:can't open %s\n",dir);
return;
}
while((dp=readdir(dfd))!=NULL){
if(strcmp(dp->d_name,".")==0||
strcmp(dp->d_name,"..")==0)
continue;
if(strlen(dir)+strlen(dp->d_name)+2>sizeof(name))
fprintf(stderr,"dirwalk:name %s %s too long\n",
dir,dp->d_name);
else{
sprintf(name,"%s/%s",dir,dp->d_name);
fcn(name);
}
}
closedir(dfd);
}
void fsize(char *name){
struct stat stbuf;
if(stat(name,&stbuf)==-1){
fprintf(stderr,"fsize:can't access %s\n",name);
return ;
}
if((stbuf.st_mode&S_IFMT)==S_IFDIR)
dirwalk(name,fsize);
printf("%5u %6o %3u %8ld %s\n",stbuf.st_ino,
stbuf.st_mode,stbuf.st_nlink,stbuf.st_size,name);
}
int main(int argc,char **argv){
if(argc==1)
fsize(".");
else
while(--argc>0)
fsize(*++argv);
return 0;
}









typedef long Align;
union header{
struct {
union header *ptr;
unsigned size;
}S;
Align x;
};
typedef union header Header;
static Header base;
static Header *freep=NULL;
void *malloc(unsigned nbytes){
Header *p,*prevp;
Header *moreroce(unsigned);
unsigned nuints;
nuints=(nbytes+sizeof(Header)-1)/sizeof(header)+1;
if((prevp=freep)==NULL){
base.s.ptr=freeptr=prevptr=&base;
base.s.size=0;
}
for(p=prevp->s.ptr;;prevp=p,p=p->s.ptr){
if(p->s.size>=nuints){
if(p->s.size==nuints)
prevp->s.ptr=p->s.ptr;
else{
p->s.size-=nuints;
p+=p->s.size;
p->s.size=nuints;
}
freep=prevp;
return (void*)(p+1);
}
if(p==freep)
if((p=moreroce(nuints))==NULL)
return NULL;
}
}
#define NALLOC 1024
static Header *moreroce(unsigned nu){
char *cp,*sbrk(int);
Header *up;
if(nu<NALLOC)
nu=NALLOC;
cp=sbrk(nu*sizeof(Header));
if(cp==(char*)-1)
return NULL;
up=(Header*)cp;
up->s.size=nu;
free((void*)(up+1));
return freep;
}
void free(void*ap){
Header *bp,*p;
bp=(Header*)ap-1;
for(p=freep;!(bp>p&&bp<p->s.ptr);p=p->s.ptr)
if(p>=p->s.ptr&&(bp>p||bp<p->s.ptr))
break;
if(bp+bp->size==p->s.ptr){
bp->s.size+=p->s.ptr->s.size;
bp->s.ptr=p->s.ptr->s.ptr;
}
else
bp->s.ptr=p->s.ptr;
if(p+p->size==bp){
p->s.size+=bp->s.size;
p->s.ptr=bp->s.ptr;
}
else
p->s.ptr=bp;
freep=p;
}
void *calloc(unsigned n,unsigned size){
unsigned i,nb;
char *p,*q;
nb=n*size;
if((p=q=malloc(nb))!=NULL)
for(i=0;i<nb;i++)
*p++=0;
return q;
}
相关文章推荐
- C文件读取
- PHP_Get与Post提交后台取值
- val() 和attr() 取值的问题
- MyEclipse快捷键使用方法(很实用)
- Android EditText与第三方输入法删除键(退格键)冲突问题解决方案
- Linux文件管理系统
- Android 使用动态加载框架DL进行插件化开发
- iOS开发:一个瀑布流的设计与实现(已实现缓存池功能,该功能使得瀑布流cell可以循环利用)
- 基于C++ 苹果apns消息推送实现(2)
- Asp.Net_from标签中的Enctype=multipart/form-data作用
- IIS Express 的 applicationhost.config配置文件
- 第三周--顺序表的基本运算2
- ViewPager的使用(三)-viewPager与Fragment配合使用
- quick-3.5 绑定自定义C++类到Lua并使用cocos code ide 调式
- Linux学习笔记之CentOS网络设置
- 如何实现简单的位数组(bit array)(转)
- xml通配符
- lower_bound与upper_bound
- Android studio如何使用SVN进行版本控制?
- 转载:天涯——散文天下——《朋友》——作者:南方孤驴
