hdu 5375 多校
2015-08-12 20:51
302 查看
Gray code
Time Limit: 2000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 65536/65536 K (Java/Others)Total Submission(s): 604 Accepted Submission(s): 357
Problem Description
The reflected binary code, also known as Gray code after Frank Gray, is a binary numeral system where two successive values differ in only onebit (binary digit). The reflected binary code was originally designed to prevent spurious output from electromechanical
switches. Today, Gray codes are widely used to facilitate error correction in digital communications such as digital terrestrial television and some cable TV systems.
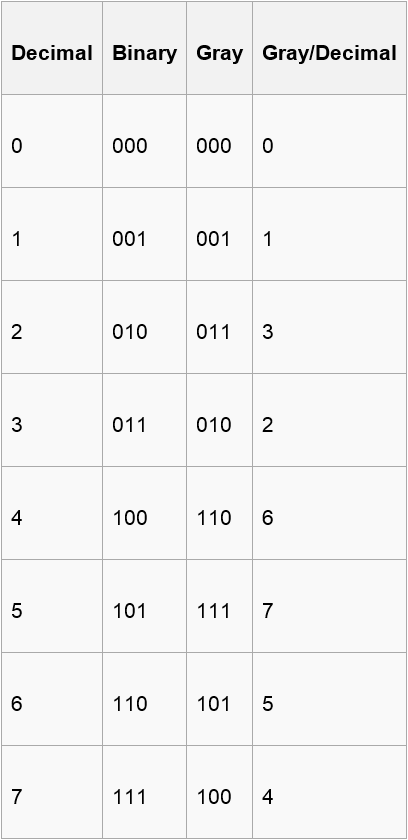
Now , you are given a binary number of length n including ‘0’ , ’1’ and ‘?’(? means that you can use either 0 or 1 to fill this position) and n integers(a1,a2,….,an) . A certain binary number corresponds to a gray code only. If the ith bit of this gray code
is 1,you can get the point ai.
Can you tell me how many points you can get at most?
For instance, the binary number “00?0” may be “0000” or “0010”,and the corresponding gray code are “0000” or “0011”.You can choose “0000” getting nothing or “0011” getting the point a3 and a4.
Input
The first line of the input contains the number of test cases T.
Each test case begins with string with ‘0’,’1’ and ‘?’.
The next line contains n (1<=n<=200000) integers (n is the length of the string).
a1 a2 a3 … an (1<=ai<=1000)
Output
For each test case, output “Case #x: ans”, in which x is the case number counted from one,’ans’ is the points you can get at most
Sample Input
2 00?0 1 2 4 8 ???? 1 2 4 8
Sample Output
Case #1: 12 Case #2: 15 Hint https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Gray_code http://baike.baidu.com/view/358724.htm
Source
2015 Multi-University Training Contest 7
Recommend
wange2014 | We have carefully selected several similar problems for you: 5379 5378 5377 5376 5375
//#pragma comment(linker, "/STACK:1024000000,1024000000")
#include<cstdio>
#include<cmath>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<map>
#include<set>
#include<time.h>
#include<vector>
#include<queue>
#include<string>
#include<string.h>
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
#define eps 1e-8
#define PI acos(-1.0)
#define INF 0x3f3f3f3f
#define LL long long
#define max(a,b) ((a)>(b)?(a):(b))
#define min(a,b) ((a)<(b)?(a):(b))
typedef pair<int , int> pii;
#define maxn 200000
int a[maxn];
char s[maxn];
int d[maxn][2];
int n;
int ans;
int main()
{
int T;
int kase = 0;
scanf("%d", &T);
while(T--)
{
scanf("%s", s + 1);
n = strlen(s + 1);
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
scanf("%d", a + i);
for(int i = 0; i <= n; i++)
d[i][0] = d[i][1] = -INF;
d[0][0] = 0;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
if(s[i] == '?')
{
d[i][0] = max(d[i-1][0], d[i-1][1] + a[i]);
d[i][1] = max(d[i-1][1], d[i-1][0] + a[i]);
}
else
{
int t = s[i] - '0';
d[i][t] = max(d[i-1][t], d[i-1][t^1] + a[i]);
}
}
// for(int i = 0; i <= n; i++)
// {
// printf("(%d---%d)\n", d[i][0], d[i][1]);
// }
ans = -INF;
ans = max(d
[0], d
[1]);
printf("Case #%d: %d\n", ++kase, ans);
}
return 0;
}
相关文章推荐
- _EX_PUSH_LOCK 结构
- 百度UEditor的介绍和图片上传的使用(java)
- .Net C# Winform 中判断本地系统的网络连接状态的方法
- java.lang.OutOfMemoryError: PermGen space(Myeclipse)
- Java——基本数据类型对象包装类
- HDU 1097.A hard puzzle【快速幂或规律】【8月12】
- Machine Learning “for Dummies” (Part 1)
- HTTPdoGet与HTTPdoPost
- Java final关键字用来修饰类、方法、属性
- 一个程序员如何做到结构上胸有成竹
- COGS 1441 NOIP 2013 花匠
- HDU 1087 Super Jumping! Jumping! Jumping!(动态规划)
- PHP生成HTML页面顶部出现空白部分(#65279字符)的解决办法
- setObjectForKey: object cannot be nil (key: av)'
- UI05_ 制造一个毛玻璃效果
- 【java】 内部类
- JavaScript基础学习之-JavaScript权威指南-第三章类型、值和变量(2)
- python的nltk中文使用和学习资料汇总帮你入门提高
- STM32F4 External event -- WFE 待机模式
- 转载【趣味算术】能被2、3、5、7、9、11、13整除的数的特点
