IO的使用说明
2015-07-31 10:53
661 查看
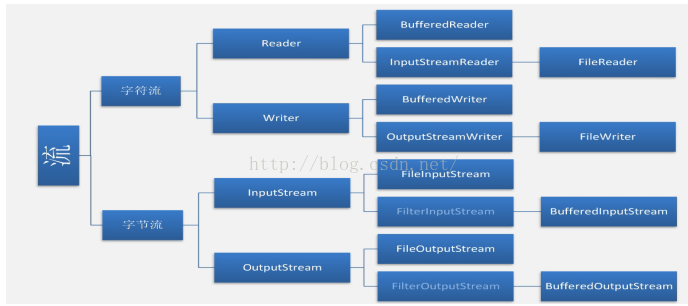
IO有字符流和字节流两种,字节流可以读取任何数据(图片、二进制、纯文本、properties...)字符流只能读纯文本。切记!!!!!
怎么看要用相对应的Io类
一、
源:InputStream,Reader
目的:OutputStream,Writer
二、
明确具体的设备。
是硬盘就加File;
是键盘用System.in(是一个InputStream对象);
是内存用数组;是网络用Socket流。
同样目的是哪个设备:
是硬盘就加File;
是键盘用System.out(是一个OutoutStream对象);
是内存用数组;是网络用Socket流。
三、
明确是否还需要其他额外功能呢,例如
①是否需要较高的效率,即是否需要使用缓冲区,是就加上Buffered;
②是否需要转换,是,就使用转换流,InputStreamReader
和OutputStreamWriter。
InputStream:
一般不用他,一般用FileInputStream
构造可以用File也可以直接写路径
读取方法:
while((i = input.read())!=-1){
System.out.println((char)i);
}
当read()返回-1的时候说明到尾了!
但是还有两个read()用法
如第二个用法:
例1:
byte[] buf = new byte[12];
int len = 0;
while((len =input.read(buf))!=-1){
System.out.print(new String(buf, 0, len));
}
例2:
byte[] buf = new byte[12];
int len = in.read(buf);
System.out.println(buf);
System.out.println(new String(buf, 0, len));
一般不用Reader,因为如果使用就要重写其中的两个方法,所以一般使用FileReader或者BufferReader
FileReader:
读取方法:
while((i=reader.read())!=-1){
System.out.println((char)i);
}这里和InputStream的一样,但是注意他没有
BufferReader:
他有readLin()方法!不过他的构造需要一个FileReader对象!!
读取方法:
BufferedReader
bReader = new BufferedReader(reader);
String line = null;
while((line=bReader.readLine())!=null){
System.out.println(line);
}
一行行读取!!
写文件:
FileOutputStream:
File
file = null;
FileOutputStream output = null;
try {
file = new File("src/info.properties");
output = new FileOutputStream(file,true);
byte[] data = "testtest".getBytes("GB2312");
output.write(data);
} catch (Exception e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}finally{
try {
if(output!=null)
output.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
在构造的时候回发现有多重构造方法:
FileWriter :
FileWriter wt = null;
try {
wt = new FileWriter ("E:/b.txt",true);
wt.write("oo=oo");
wt.write("\r\nxx=xx");
} catch (IOException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}finally{
try {
wt.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
回车是\t\n
byte和string相互转换
1、string 转 byte[]
2、byte[] 转 string
3、设定编码方式相互转换
其中有涉及带编码:UTF-8、gbk
怎么看要用相对应的Io类
一、
源:InputStream,Reader
目的:OutputStream,Writer
二、
明确具体的设备。
是硬盘就加File;
是键盘用System.in(是一个InputStream对象);
是内存用数组;是网络用Socket流。
同样目的是哪个设备:
是硬盘就加File;
是键盘用System.out(是一个OutoutStream对象);
是内存用数组;是网络用Socket流。
三、
明确是否还需要其他额外功能呢,例如
①是否需要较高的效率,即是否需要使用缓冲区,是就加上Buffered;
②是否需要转换,是,就使用转换流,InputStreamReader
和OutputStreamWriter。

InputStream:
一般不用他,一般用FileInputStream
构造可以用File也可以直接写路径
读取方法:
while((i = input.read())!=-1){
System.out.println((char)i);
}
当read()返回-1的时候说明到尾了!
但是还有两个read()用法
int | read() 从此输入流中读取一个数据字节。 |
int | read(byte[] b) 从此输入流中将最多 b.length个字节的数据读入一个 byte 数组中。 |
int | read(byte[] b, int off, int len) 从此输入流中将最多 len个字节的数据读入一个 byte 数组中。 |
例1:
byte[] buf = new byte[12];
int len = 0;
while((len =input.read(buf))!=-1){
System.out.print(new String(buf, 0, len));
}
例2:
byte[] buf = new byte[12];
int len = in.read(buf);
System.out.println(buf);
System.out.println(new String(buf, 0, len));
一般不用Reader,因为如果使用就要重写其中的两个方法,所以一般使用FileReader或者BufferReader
FileReader:
读取方法:
while((i=reader.read())!=-1){
System.out.println((char)i);
}这里和InputStream的一样,但是注意他没有
readLine()方法!!
BufferReader:
他有readLin()方法!不过他的构造需要一个FileReader对象!!
读取方法:
BufferedReader
bReader = new BufferedReader(reader);
String line = null;
while((line=bReader.readLine())!=null){
System.out.println(line);
}
一行行读取!!
写文件:
FileOutputStream:
File
file = null;
FileOutputStream output = null;
try {
file = new File("src/info.properties");
output = new FileOutputStream(file,true);
byte[] data = "testtest".getBytes("GB2312");
output.write(data);
} catch (Exception e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}finally{
try {
if(output!=null)
output.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
在构造的时候回发现有多重构造方法:
FileOutputStream(File file) 创建一个向指定 File对象表示的文件中写入数据的文件输出流。 |
FileOutputStream(File file, boolean append) 创建一个向指定 File对象表示的文件中写入数据的文件输出流。 |
FileOutputStream(FileDescriptor fdObj) 创建一个向指定文件描述符处写入数据的输出文件流,该文件描述符表示一个到文件系统中的某个实际文件的现有连接。 |
FileOutputStream(String name) 创建一个向具有指定名称的文件中写入数据的输出文件流。 |
FileOutputStream(String name, boolean append) 创建一个向具有指定 name的文件中写入数据的输出文件流。 |
FileOutputStream(File file, boolean append)append 如果为true则是在后面追加信息
FileWriter :
FileWriter wt = null;
try {
wt = new FileWriter ("E:/b.txt",true);
wt.write("oo=oo");
wt.write("\r\nxx=xx");
} catch (IOException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}finally{
try {
wt.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
回车是\t\n
byte和string相互转换
1、string 转 byte[]
String str = "Hello"; byte[] srtbyte = str.getBytes();
2、byte[] 转 string
byte[] srtbyte; String res = new String(srtbyte); System.out.println(res);
3、设定编码方式相互转换
String str = "hello";
byte[] srtbyte = null;
try {
srtbyte = str.getBytes("UTF-8");
String res = new String(srtbyte,"UTF-8");
System.out.println(res);
} catch (UnsupportedEncodingException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}其中有涉及带编码:UTF-8、gbk
相关文章推荐
- java对世界各个时区(TimeZone)的通用转换处理方法(转载)
- java-注解annotation
- java-模拟tomcat服务器
- java-用HttpURLConnection发送Http请求.
- java-WEB中的监听器Lisener
- Android IPC进程间通讯机制
- Android Native 绘图方法
- Android java 与 javascript互访(相互调用)的方法例子
- 介绍一款信息管理系统的开源框架---jeecg
- 聚类算法之kmeans算法java版本
- java实现 PageRank算法
- PropertyChangeListener简单理解
- 插入排序
- 冒泡排序
- 堆排序
- 快速排序
- 二叉查找树
- [原创]java局域网聊天系统
