图像处理------光束效果
2015-07-24 09:34
363 查看
原理:
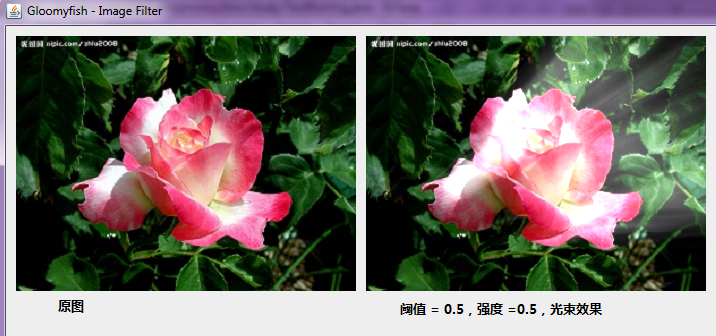
光束滤镜,对一幅图像完成光束效果,好似有一束光从图像本身激发出来,按照一定的角度
散发开来,光束滤镜是一种图像叠加效果,首先要借助于之前的完成的移动模糊滤镜,将一
幅图像按照一定的阈值二值化以后,加以移动模糊滤镜,将移动模糊之后的图像和原图像叠
加就产生了光束滤镜效果。
对光束滤镜而言,其最终效果除了移动模糊的三个参数以外,还取决于以下两个参数:
a. 图像RGB阈值的选取,建议可以直方图以后选取,程序以threshold表示
b. 光强度大小的值的选取,程序中以strength表示
程序运行效果如下:
关键代码解析:
计算RGB阈值代码如下– 输入的阈值范围为[0,1]
intthreshold3 = (int)(threshold*3*255);
求取二值像素的代码如下:
int l = r + g + b;
if (l < threshold3)
[x] =0xff000000;
else {
l /= 3;
pixels[x] = a | (l << 16) | (l << 8) | l;
}
像素叠加乘以强度系数的代码如下(其中r,g,b分别代表RGB的三个颜色分量值):
r = PixelUtils.clamp((int)(r * strength) + r2);
g = PixelUtils.clamp((int)(g * strength) + g2);
b = PixelUtils.clamp((int)(b * strength) + b2);
光束滤镜的完全源代码如下:
[java] view plaincopy<span style="font-weight: normal;">/*
** Copyright 2012 @gloomyfish. All rights reserved.
*/
package com.process.blur.study;
import java.awt.image.BufferedImage;
public class LaserFilter extends MotionFilter {
private float threshold = 0.5f;
private float strength = 0.8f;
public LaserFilter() {
}
public void setThreshold( float threshold ) {
this.threshold = threshold;
}
public float getThreshold() {
return threshold;
}
public void setStrength( float strength ) {
this.strength = strength;
}
public float getStrength() {
return strength;
}
public BufferedImage filter( BufferedImage src, BufferedImage dst ) {
int width = src.getWidth();
int height = src.getHeight();
int[] pixels = new int[width];
int[] srcPixels = new int[width];
BufferedImage laserImg = new BufferedImage(width, height, BufferedImage.TYPE_INT_ARGB);
int threshold3 = (int)(threshold*3*255);
for ( int y = 0; y < height; y++ ) {
getRGB( src, 0, y, width, 1, pixels );
for ( int x = 0; x < width; x++ ) {
int rgb = pixels[x];
int a = rgb & 0xff000000;
int r = (rgb >> 16) & 0xff;
int g = (rgb >> 8) & 0xff;
int b = rgb & 0xff;
int l = r + g + b;
if (l < threshold3)
pixels[x] = 0xff000000;
else {
l /= 3;
pixels[x] = a | (l << 16) | (l << 8) | l;
}
}
setRGB( laserImg, 0, y, width, 1, pixels );
}
laserImg = super.filter(laserImg, null );
for ( int y = 0; y < height; y++ ) {
getRGB( laserImg, 0, y, width, 1, pixels );
getRGB( src, 0, y, width, 1, srcPixels );
for ( int x = 0; x < width; x++ ) {
int rgb = pixels[x];
int a = rgb & 0xff000000;
int r = (rgb >> 16) & 0xff;
int g = (rgb >> 8) & 0xff;
int b = rgb & 0xff;
int rgb2 = srcPixels[x];
// int a2 = rgb2 & 0xff000000;
int r2 = (rgb2 >> 16) & 0xff;
int g2 = (rgb2 >> 8) & 0xff;
int b2 = rgb2 & 0xff;
if ( r > 0 ) {
r = clamp((int)(r * strength) + r2);
g = clamp((int)(g * strength) + g2);
b = clamp((int)(b * strength) + b2);
} else {
r = r2;
g = g2;
b = b2;
}
rgb = a | (r << 16) | (g << 8) | b;
pixels[x] = rgb;
}
setRGB( laserImg, 0, y, width, 1, pixels );
}
return laserImg;
}
public String toString() {
return "Light/Laser...";
}
}
</span>
光束滤镜,对一幅图像完成光束效果,好似有一束光从图像本身激发出来,按照一定的角度
散发开来,光束滤镜是一种图像叠加效果,首先要借助于之前的完成的移动模糊滤镜,将一
幅图像按照一定的阈值二值化以后,加以移动模糊滤镜,将移动模糊之后的图像和原图像叠
加就产生了光束滤镜效果。
对光束滤镜而言,其最终效果除了移动模糊的三个参数以外,还取决于以下两个参数:
a. 图像RGB阈值的选取,建议可以直方图以后选取,程序以threshold表示
b. 光强度大小的值的选取,程序中以strength表示
程序运行效果如下:

关键代码解析:
计算RGB阈值代码如下– 输入的阈值范围为[0,1]
intthreshold3 = (int)(threshold*3*255);
求取二值像素的代码如下:
int l = r + g + b;
if (l < threshold3)
[x] =0xff000000;
else {
l /= 3;
pixels[x] = a | (l << 16) | (l << 8) | l;
}
像素叠加乘以强度系数的代码如下(其中r,g,b分别代表RGB的三个颜色分量值):
r = PixelUtils.clamp((int)(r * strength) + r2);
g = PixelUtils.clamp((int)(g * strength) + g2);
b = PixelUtils.clamp((int)(b * strength) + b2);
光束滤镜的完全源代码如下:
[java] view plaincopy<span style="font-weight: normal;">/*
** Copyright 2012 @gloomyfish. All rights reserved.
*/
package com.process.blur.study;
import java.awt.image.BufferedImage;
public class LaserFilter extends MotionFilter {
private float threshold = 0.5f;
private float strength = 0.8f;
public LaserFilter() {
}
public void setThreshold( float threshold ) {
this.threshold = threshold;
}
public float getThreshold() {
return threshold;
}
public void setStrength( float strength ) {
this.strength = strength;
}
public float getStrength() {
return strength;
}
public BufferedImage filter( BufferedImage src, BufferedImage dst ) {
int width = src.getWidth();
int height = src.getHeight();
int[] pixels = new int[width];
int[] srcPixels = new int[width];
BufferedImage laserImg = new BufferedImage(width, height, BufferedImage.TYPE_INT_ARGB);
int threshold3 = (int)(threshold*3*255);
for ( int y = 0; y < height; y++ ) {
getRGB( src, 0, y, width, 1, pixels );
for ( int x = 0; x < width; x++ ) {
int rgb = pixels[x];
int a = rgb & 0xff000000;
int r = (rgb >> 16) & 0xff;
int g = (rgb >> 8) & 0xff;
int b = rgb & 0xff;
int l = r + g + b;
if (l < threshold3)
pixels[x] = 0xff000000;
else {
l /= 3;
pixels[x] = a | (l << 16) | (l << 8) | l;
}
}
setRGB( laserImg, 0, y, width, 1, pixels );
}
laserImg = super.filter(laserImg, null );
for ( int y = 0; y < height; y++ ) {
getRGB( laserImg, 0, y, width, 1, pixels );
getRGB( src, 0, y, width, 1, srcPixels );
for ( int x = 0; x < width; x++ ) {
int rgb = pixels[x];
int a = rgb & 0xff000000;
int r = (rgb >> 16) & 0xff;
int g = (rgb >> 8) & 0xff;
int b = rgb & 0xff;
int rgb2 = srcPixels[x];
// int a2 = rgb2 & 0xff000000;
int r2 = (rgb2 >> 16) & 0xff;
int g2 = (rgb2 >> 8) & 0xff;
int b2 = rgb2 & 0xff;
if ( r > 0 ) {
r = clamp((int)(r * strength) + r2);
g = clamp((int)(g * strength) + g2);
b = clamp((int)(b * strength) + b2);
} else {
r = r2;
g = g2;
b = b2;
}
rgb = a | (r << 16) | (g << 8) | b;
pixels[x] = rgb;
}
setRGB( laserImg, 0, y, width, 1, pixels );
}
return laserImg;
}
public String toString() {
return "Light/Laser...";
}
}
</span>
相关文章推荐
- 通过配置Windows 防火墙允许使用TCP/IP协议远程访问数据库
- openstack 与 ceph (架构)
- hdu 1251 统计难题
- Git .gitignore使用
- 【解决方法】Unexpected namespace prefix “xmlns” found for tag Layout
- git 上传文件到仓库
- 浏览器 仿新浪头像裁剪 有图有真相!!!
- android4.4 wifi 扫描流程分析
- 图像处理------光束效果
- android 自适应 多屏幕支持 --Android多分辨率适配
- 响应式设计的现状与趋势
- QQ 互联认证 回调地址提示说要http :// 但是事实不用
- 图像处理------光束效果 分类: 视频图像处理 2015-07-24 09:34 30人阅读 评论(0) 收藏
- UIActivityViewController
- 图像处理------移动模糊
- 图像处理------移动模糊
- Editplus 当前行高亮技巧
- Android之发送短信和接收验证码
- 图像处理------移动模糊
- 巧用dimens适配多个分辨率2
