Android 初始化之Zygote
2015-07-02 18:06
656 查看
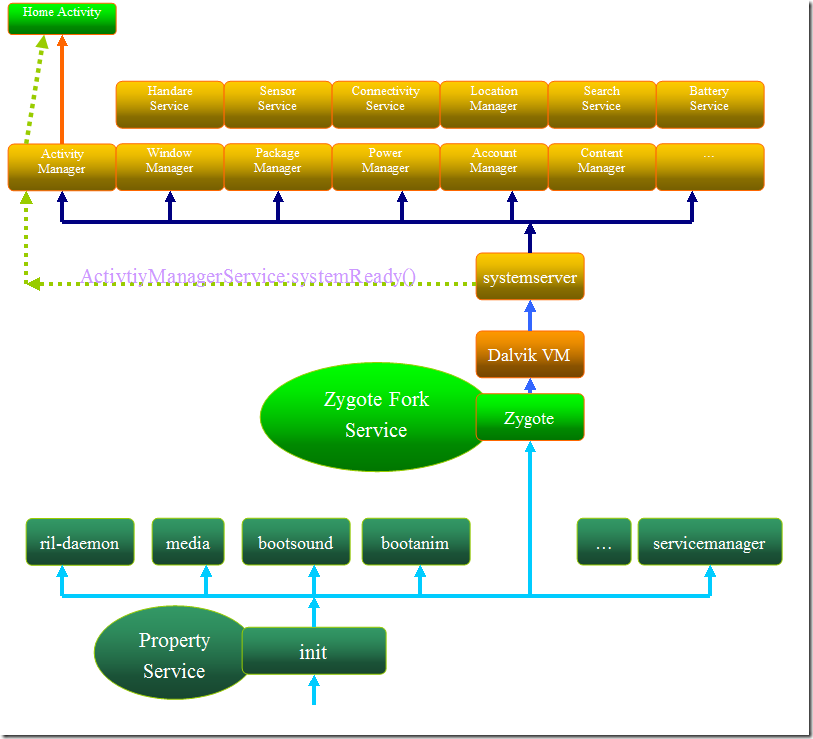
系统整体框架
了解android初始化之前,有必要了解一下系统的整体框架,下图是网上流传比较经典的架构图:
android的启动主要是linux内核启动之后,init进程来接手Android的初始化,完成后续一些服务和应用的启动,所有上层的应用和服务都依赖Dalvik VM,所以
该虚拟机应用该在所有应用启动之前完成初始化。
Zygote初始化
zygote进程实际上就是app_process进程,在init 进程的启动脚本中声明service zygote /system/bin/app_process -Xzygote /system/bin --zygote --start-system-server class main socket zygote stream 660 root system onrestart write /sys/android_power/request_state wake onrestart write /sys/power/state on另外zygote进程启动之后,会创建一个名为zygote的socket 来进程间通信,zygote 启动之后作为后台的守护进程一直等待其它应用或者服务的启动请求。
下图就是zygote启动大致流程,启动之后就创建dalvik vm ,接着systemserver 被启动,后面所有的系统服务进程都被systemserver启动,其实systemserver也是
一个比较重要的服务(SystemServer.java) ,添加一些平台级服务一般在此处添加,随着AMS的启动,launcher也被启动了。
Zygote的工作流程
ZygoteInit的启动
app_process(app_main.cpp)会创建AppRuntime,接着启动,zygoteInitif (zygote) {
runtime.start("com.android.internal.os.ZygoteInit", args);
} else if (className) {
runtime.start("com.android.internal.os.RuntimeInit", args);
} else {
fprintf(stderr, "Error: no class name or --zygote supplied.\n");
app_usage();
LOG_ALWAYS_FATAL("app_process: no class name or --zygote supplied.");
return 10;
} 通过runtime.start("com.android.internal.os.ZygoteInit", args)启动zygoteInitzygoteInit主逻辑
public static void main(String argv[]) {
try {
// Start profiling the zygote initialization.
SamplingProfilerIntegration.start();
boolean startSystemServer = false;
String socketName = "zygote";
String abiList = null;
for (int i = 1; i < argv.length; i++) {
if ("start-system-server".equals(argv[i])) {
startSystemServer = true;
} else if (argv[i].startsWith(ABI_LIST_ARG)) {
abiList = argv[i].substring(ABI_LIST_ARG.length());
} else if (argv[i].startsWith(SOCKET_NAME_ARG)) {
socketName = argv[i].substring(SOCKET_NAME_ARG.length());
} else {
throw new RuntimeException("Unknown command line argument: " + argv[i]);
}
}
if (abiList == null) {
throw new RuntimeException("No ABI list supplied.");
}
registerZygoteSocket(socketName);
EventLog.writeEvent(LOG_BOOT_PROGRESS_PRELOAD_START,
SystemClock.uptimeMillis());
preload();
EventLog.writeEvent(LOG_BOOT_PROGRESS_PRELOAD_END,
SystemClock.uptimeMillis());
// Finish profiling the zygote initialization.
SamplingProfilerIntegration.writeZygoteSnapshot();
// Do an initial gc to clean up after startup
gc();
// Disable tracing so that forked processes do not inherit stale tracing tags from
// Zygote.
Trace.setTracingEnabled(false);
if (startSystemServer) {
startSystemServer(abiList, socketName);
}
Log.i(TAG, "Accepting command socket connections");
runSelectLoop(abiList);
closeServerSocket();
} catch (MethodAndArgsCaller caller) {
caller.run();
} catch (RuntimeException ex) {
Log.e(TAG, "Zygote died with exception", ex);
closeServerSocket();
throw ex;
}
}从中我们可以发现,在registerZygoteSocket中创建一个“zygote” 的LocalServerSocket 给ZygoteConnection等待用户请求,而runSelectLoop就是等待应用层发来的启动请求事件
private static void runSelectLoop(String abiList) throws MethodAndArgsCaller {
ArrayList<FileDescriptor> fds = new ArrayList<FileDescriptor>();
ArrayList<ZygoteConnection> peers = new ArrayList<ZygoteConnection>();
FileDescriptor[] fdArray = new FileDescriptor[4];
fds.add(sServerSocket.getFileDescriptor());
peers.add(null);
int loopCount = GC_LOOP_COUNT;
while (true) {
int index;
/*
* Call gc() before we block in select().
* It's work that has to be done anyway, and it's better
* to avoid making every child do it. It will also
* madvise() any free memory as a side-effect.
*
* Don't call it every time, because walking the entire
* heap is a lot of overhead to free a few hundred bytes.
*/
if (loopCount <= 0) {
gc();
loopCount = GC_LOOP_COUNT;
} else {
loopCount--;
}
try {
fdArray = fds.toArray(fdArray);
index = selectReadable(fdArray);
} catch (IOException ex) {
throw new RuntimeException("Error in select()", ex);
}
if (index < 0) {
throw new RuntimeException("Error in select()");
} else if (index == 0) {
ZygoteConnection newPeer = acceptCommandPeer(abiList);
peers.add(newPeer);
fds.add(newPeer.getFileDescriptor());
} else {
boolean done;
done = peers.get(index).runOnce();
if (done) {
peers.remove(index);
fds.remove(index);
}
}
}
} 其中selectReadable(com_android_internal_os_ZygoteInit.cpp)是一个native函数,调用select等待客户端连接,一旦连接上就会返回,<0 内部连接错误,= 0 第一次连
接成功,> 0 表示已经建立连接,可以直接发送数据。第一连接成功之后,就会创建客户端连接对象ZygoteConnection,并添加至peers列表中。
接收到请求之后,就要为这些请求创建子进程, peers.get(index).runOnce(),也即子进程的孵化。
进程的孵化
peers.get(index).runOnce()来开启子进程的孵化,ZygoteConnection.runOnceboolean runOnce() throws ZygoteInit.MethodAndArgsCaller {
String args[];
Arguments parsedArgs = null;
FileDescriptor[] descriptors;
long startTime = SystemClock.elapsedRealtime();
......
try {
if (pid == 0) {
// in child
IoUtils.closeQuietly(serverPipeFd);
serverPipeFd = null;
handleChildProc(parsedArgs, descriptors, childPipeFd, newStderr);
// should never get here, the child is expected to either
// throw ZygoteInit.MethodAndArgsCaller or exec().
return true;
} else {
// in parent...pid of < 0 means failure
IoUtils.closeQuietly(childPipeFd);
childPipeFd = null;
return handleParentProc(pid, descriptors, serverPipeFd, parsedArgs);
}
} finally {
IoUtils.closeQuietly(childPipeFd);
IoUtils.closeQuietly(serverPipeFd);
}
} Zygote.forkAndSpecialize会调用native方法nativeForkAndSpecialize通过linux fork 来创建进程,handleChildProc和handleParentProc分别处理子进程,父进程。// Handles post-fork setup of child proc
private void handleChildProc(Arguments parsedArgs,...){
……
if (parsedArgs.runtimeInit) {
if (parsedArgs.invokeWith != null) {
//通过系统调用执行进程
WrapperInit.execApplication(parsedArgs.invokeWith,
parsedArgs.niceName, parsedArgs.targetSdkVersion,
pipeFd, parsedArgs.remainingArgs);
} else {
//通过寻找到相应目标类的main()函数并执行
RuntimeInit.zygoteInit(parsedArgs.targetSdkVersion,
parsedArgs.remainingArgs);
}
}
……
} 而执行子进程又分两种方式WrapperInit.execApplication,RuntimeInit.zygoteInit, 其中execApplicationpublic static void execApplication(String invokeWith, String niceName,
int targetSdkVersion, FileDescriptor pipeFd, String[] args) {
StringBuilder command = new StringBuilder(invokeWith);
command.append(" /system/bin/app_process /system/bin --application");
if (niceName != null) {
command.append(" '--nice-name=").append(niceName).append("'");
}
command.append(" com.android.internal.os.WrapperInit ");
command.append(pipeFd != null ? pipeFd.getInt$() : 0);
command.append(' ');
command.append(targetSdkVersion);
Zygote.appendQuotedShellArgs(command, args);
Zygote.execShell(command.toString());
} 接着zygote.execShell 通过shell来执行启动指令public static void execShell(String command) {
String[] args = { "/system/bin/sh", "-c", command };
try {
Os.execv(args[0], args);
} catch (ErrnoException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
} 而zygoteInit则又是另一条路public static final void zygoteInit(int targetSdkVersion, String[] argv, ClassLoader classLoader)
throws ZygoteInit.MethodAndArgsCaller {
if (DEBUG) Slog.d(TAG, "RuntimeInit: Starting application from zygote");
redirectLogStreams();
commonInit();
nativeZygoteInit();
applicationInit(targetSdkVersion, argv, classLoader);
} RuntimeInit.java中zygoteInit会继续向下call applicationInitprivate static void applicationInit(int targetSdkVersion, String[] argv, ClassLoader classLoader)
throws ZygoteInit.MethodAndArgsCaller {
// If the application calls System.exit(), terminate the process
// immediately without running any shutdown hooks. It is not possible to
// shutdown an Android application gracefully. Among other things, the
// Android runtime shutdown hooks close the Binder driver, which can cause
// leftover running threads to crash before the process actually exits.
nativeSetExitWithoutCleanup(true);
// We want to be fairly aggressive about heap utilization, to avoid
// holding on to a lot of memory that isn't needed.
VMRuntime.getRuntime().setTargetHeapUtilization(0.75f);
VMRuntime.getRuntime().setTargetSdkVersion(targetSdkVersion);
final Arguments args;
try {
args = new Arguments(argv);
} catch (IllegalArgumentException ex) {
Slog.e(TAG, ex.getMessage());
// let the process exit
return;
}
// Remaining arguments are passed to the start class's static main
invokeStaticMain(args.startClass, args.startArgs, classLoader);
} invokeStaticMain 就会最终call 到应用或者服务的main函数,这样就完成了整个创建的流程,后面分析应用的请求流程。应用请求流程
应用一般都是以startActivity方式来启动
最后执行到ActivityManagerService.startProcessLocked
private final void startProcessLocked(ProcessRecord app,
String hostingType, String hostingNameStr)
{
......
// Start the process. It will either succeed and return a result containing
// the PID of the new process, or else throw a RuntimeException.
Process.ProcessStartResult startResult =
Process.start("android.app.ActivityThread",
app.processName, uid, uid, gids, debugFlags,
app.info.targetSdkVersion, zygoteArgs);
......
}process.start函数
public static final ProcessStartResult start(final String processClass,
final String niceName,
int uid, int gid, int[] gids,
int debugFlags, int mountExternal,
int targetSdkVersion,
String seInfo,
String abi,
String instructionSet,
String appDataDir,
String[] zygoteArgs) {
try {
return startViaZygote(processClass, niceName, uid, gid, gids,
debugFlags, mountExternal, targetSdkVersion, seInfo,
abi, instructionSet, appDataDir, zygoteArgs);
} catch (ZygoteStartFailedEx ex) {
Log.e(LOG_TAG,
"Starting VM process through Zygote failed");
throw new RuntimeException(
"Starting VM process through Zygote failed", ex);
}
} startViaZygote中Process 会通过内部类ZygoteState 与 Zygote守护进程通信,通过“Zygote” socket 将启动应用的参数传给 服务端,在runSelectLoopMode ( select loop)收到请求就开始启动应用进程
private static ProcessStartResult startViaZygote(final String processClass,
final String niceName,
final int uid, final int gid,
final int[] gids,
int debugFlags, int mountExternal,
int targetSdkVersion,
String seInfo,
String abi,
String instructionSet,
String appDataDir,
String[] extraArgs)
throws ZygoteStartFailedEx {
synchronized(Process.class) {
ArrayList<String> argsForZygote = new ArrayList<String>();
// --runtime-init, --setuid=, --setgid=,
// and --setgroups= must go first
argsForZygote.add("--runtime-init");
argsForZygote.add("--setuid=" + uid);
argsForZygote.add("--setgid=" + gid);
......
argsForZygote.add(processClass);
if (extraArgs != null) {
for (String arg : extraArgs) {
argsForZygote.add(arg);
}
}
return zygoteSendArgsAndGetResult(openZygoteSocketIfNeeded(abi), argsForZygote);
}
} openZygoteSocketIfNeeded会判断是否与 服务端进程通过 “zygote” socket 进行连接通信private static ZygoteState openZygoteSocketIfNeeded(String abi) throws ZygoteStartFailedEx {
if (primaryZygoteState == null || primaryZygoteState.isClosed()) {
try {
primaryZygoteState = ZygoteState.connect(ZYGOTE_SOCKET);
} catch (IOException ioe) {
throw new ZygoteStartFailedEx("Error connecting to primary zygote", ioe);
}
}
......
} zygoteSendArgsAndGetResult完成启动参数消息的发送,并获取最终结果private static ProcessStartResult zygoteSendArgsAndGetResult(
ZygoteState zygoteState, ArrayList<String> args)
throws ZygoteStartFailedEx {
try {
/**
* See com.android.internal.os.ZygoteInit.readArgumentList()
* Presently the wire format to the zygote process is:
* a) a count of arguments (argc, in essence)
* b) a number of newline-separated argument strings equal to count
*
* After the zygote process reads these it will write the pid of
* the child or -1 on failure, followed by boolean to
* indicate whether a wrapper process was used.
*/
final BufferedWriter writer = zygoteState.writer;
final DataInputStream inputStream = zygoteState.inputStream;
writer.write(Integer.toString(args.size()));
writer.newLine();
int sz = args.size();
for (int i = 0; i < sz; i++) {
String arg = args.get(i);
if (arg.indexOf('\n') >= 0) {
throw new ZygoteStartFailedEx(
"embedded newlines not allowed");
}
writer.write(arg);
writer.newLine();
}
writer.flush();
// Should there be a timeout on this?
ProcessStartResult result = new ProcessStartResult();
result.pid = inputStream.readInt();
if (result.pid < 0) {
throw new ZygoteStartFailedEx("fork() failed");
}
result.usingWrapper = inputStream.readBoolean();
return result;
} catch (IOException ex) {
zygoteState.close();
throw new ZygoteStartFailedEx(ex);
}
}zygote相关链接文档: http://www.cnblogs.com/bastard/archive/2012/09/03/2668579.html /article/1807034.html
http://www.cnblogs.com/bastard/archive/2012/08/28/2660389.html http://blog.csdn.net/luoshengyang/article/details/6768304 /article/1361716.html
应用相关初始化流程: http://www.cloudchou.com/android/post-788.html http://www.cloudchou.com/android/post-793.html http://www.cloudchou.com/android/post-815.html http://www.cloudchou.com/android/post-805.html http://www.cloudchou.com/android/post-858.html
相关文章推荐
- Demo---分享45个android实例源码
- Android自动化测试-自动获取cpu和内存信息
- Android获取所有存储卡挂载路径
- View onRestoreInstanceState ClassCastException
- activity背景透明的2种方法
- android开发教程21篇(强烈推荐,几乎每一篇都是精华教程)
- Android Studio 简介及导入jar包和第三方开源库的方法
- android4.0以上,利用耳机接听键实现自动接听,部分手机失败原因+解决方法(比如华为P7)
- android 学习笔记 fill_parent、wrap_content和match_parent的区别
- android之EditText输入错误时该怎样提示用户
- Android unit test中通过颜色比对替代肉眼检查
- Android5.0编译问题:No rule to make target 'external/chromium_org/third_party/angle/.git/index',
- Android特效 五种Toast详解
- Android 编程下 Touch 事件的分发和响应机制
- Android 编程下 Touch 事件的分发和响应机制 分类: Android 2015-07-02 17:35 12人阅读 评论(0) 收藏
- Android TabHost布局
- HashMap类的理解
- Android 与 IIS服务器身份验证
- android Toast显示消息的几种方法
- Android 使用自定义字体
