黑马程序员——基础知识总结_集合框架1
2015-06-21 07:07
851 查看
——Java培训、Android培训、iOS培训、.Net培训、期待与您交流! ——-
[b]Collection概述:[/b]
Collection 层次结构中的根接口。
[b]Collection常见方法:[/b]
[b]Iterator:[/b]
Iterator iterator() 返回在此 Collection 的元素上进行迭代的迭代器。 作为Collection的内部接口,使得其子类调用时不需要进行另外implements Iterator,也方便了对类中成员的访问。
[b]List概述:[/b]
有序的 collection(也称为序列)。此接口的用户可以对列表中每个元素的插入位置进行精确地控制。用户可以根据元素的整数索引(在列表中的位置)访问元素,并搜索列表中的元素。
[b]List特有方法:[/b]
凡是可以操作脚标的方法都是该体系特有的方法。
[b]IistIterator:[/b]
List集合特有的迭代器,继承了Iterator。在迭代过程中,不一定可以通过集合对象的方法操作集合中的元素,因为会发生ConcurrentModificationException异常。所以在迭代时,只能用迭代器的方法操作元素。可是Iterator方法是有限的,只能对元素进行判断,取出,删除的操作。如果想要其他的操作如添加,修改等就需要使用其子接口:ListIterator
[b]ArrayList:[/b]
AarrayList底层数据结构是数组结构。特点查询速度快,增,删慢。
[b]结果图:[/b]
[b]LinkdList:[/b]
LinkdList底层使用的链表数据结构。特点,增删速度快,查询速度慢。
LinkdList特有方法:
[b]Vector:[/b]
Vector底层是数组结构,与ArrayList的区别在于,Vector容器的增长可以控制,而ArrayList没有特定的增长方式。Vector是线性同步的,ArrayList线性不同步。
[b]Set概述:[/b]
一个不包含重复元素的collection。更确切地讲,set不包含满足 e1.equals(e2) 的元素对 e1 和 e2,并且最多包含一个 null 元素。正如其名称所暗示的,此接口模仿了数学上的 set 抽象。
[b]HashSet:[/b]
HashSet底层数据结构是哈希表。通过元素的两个方法hashCode()和equals()是否为true来判断值的唯一性,如果元素的hashCode()返回值为true则不会使用equals(),hashCode()返回值为false则根据equals()返回值来判断是否相等。
结果图:
分析:可以看到2个“hello”字符串对象的hash值是一样的,因此在没有重写equals()方法时,他们是无法同时存在同一个HashSet中的。同时也可以看出,HashSet默认排序方式不跟List一样,HashSet的默认排序是无序的。
[b]TreeSet:[/b]
TreeSet底层数据结构是二叉树。可以对Set集合中的元素进行排序。TreeSet排序方法有2种:
1.当元素自身具备比较性元素时实现comparable接口,覆盖comparaTo方法这种方法也成为元素的自然顺序或者默认顺序。
2.当元素自身不具备比较性元素或者不是所需要的比较性时,就需要让集合自身具备特有的比较性。可以构建一个比较器,简单的说就是实现comparator接口覆盖接口中compara方法和equals方法中构建要比较的方式。
[b]结果图:[/b]

第一话:Collection
[b]Collection概述:[/b]
Collection 层次结构中的根接口。

[b]Collection常见方法:[/b]
//确保此collection包含指定的元素 boolean add(E e) //将指定collection中的所有元素都添加到此collection中 boolean addAll(Collection<? extends E> c) //返回包含此 collection 中所有元素的数组 int size() // 从此 collection 中移除指定元素的单个实例,如果存在的话 boolean remove(Object o) //移除此 collection 中那些也包含在指定 collection 中的所有元素 boolean removeAll(Object o) //移除此 collection 中的所有元素 void clear() //如果此collection包含指定的元素,则返回 true boolean contains(Object o) //如果此 collection 不包含元素,则返回 true boolean isEmpety() //仅保留此 collection 中那些也包含在指定 collection 的元素 boolean retainAll(Collection<?> c)
[b]Iterator:[/b]
Iterator iterator() 返回在此 Collection 的元素上进行迭代的迭代器。 作为Collection的内部接口,使得其子类调用时不需要进行另外implements Iterator,也方便了对类中成员的访问。
第二话:List
[b]List概述:[/b]
有序的 collection(也称为序列)。此接口的用户可以对列表中每个元素的插入位置进行精确地控制。用户可以根据元素的整数索引(在列表中的位置)访问元素,并搜索列表中的元素。
[b]List特有方法:[/b]
凡是可以操作脚标的方法都是该体系特有的方法。
//在列表的指定位置插入指定元素 void add(int index, E element) //将指定 collection 中的所有元素都插入到列表中的指定位置 boolean addAll(int index, Collection<? extends E> c) //移除列表中指定位置的元素 E remove(int index) //返回列表中指定位置的元素 E get(int index) // 返回列表中指定的fromInde(包括)和toIndex(不包括)之间的部分视图 List<E> subList(int fromIndex, int toIndex) // 返回此列表元素的列表迭代器(按适当顺序) ListIterator<E> listIterator() //返回列表中元素的列表迭代器(按适当顺序),从列表的指定位置开始 ListIterator<E> listIterator(int index)
[b]IistIterator:[/b]
List集合特有的迭代器,继承了Iterator。在迭代过程中,不一定可以通过集合对象的方法操作集合中的元素,因为会发生ConcurrentModificationException异常。所以在迭代时,只能用迭代器的方法操作元素。可是Iterator方法是有限的,只能对元素进行判断,取出,删除的操作。如果想要其他的操作如添加,修改等就需要使用其子接口:ListIterator
[b]ArrayList:[/b]
AarrayList底层数据结构是数组结构。特点查询速度快,增,删慢。
/*
将容器内相同的对象删除
*/
import java.util.*;
class person
{
private String name;
private int age;
person(String name, int age)
{
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
//判断容器内的对象值是否相等要重写equals()方法,
//因为Object 对象的equals方法是比较2对象地址是否相等
public boolean equals(Object obj)
{
if(!(obj instanceof person))
return false;
person p = (person)obj;
return this.name.equals(p.name) && this.age == p.age;
}
public String getName()
{
return name;
}
public int getAge()
{
return age;
}
}
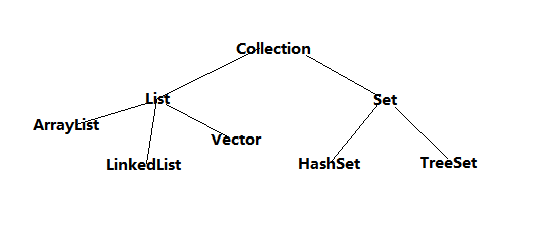
class ArrayListTest2
{
public static void sop(Object obj)
{
System.out.println(obj);
}
public static void main(String[] args)
{
ArrayList arrlist = new ArrayList();
arrlist.add(new person("person1",20));
arrlist.add(new person("person2",32));
arrlist.add(new person("person1",20));
arrlist.add(new person("person2",32));
arrlist.add(new person("person3",32));
//去重复
arrlist = singEmplement(arrlist);
Iterator ite = arrlist.iterator();
while(ite.hasNext())
{
person p = (person)ite.next();
sop(p.getName()+"::"+p.getAge())
bb0a
;
}
}
public static ArrayList singEmplement(ArrayList arrlist)
{
//定义一个临时容器
ArrayList newAl = new ArrayList();
for(Iterator it = arrlist.iterator(); it.hasNext(); )
{
Object obj = it.next();
if(!newAl.contains(obj))
newAl.add(obj);
}
return newAl;
}
}[b]结果图:[/b]

[b]LinkdList:[/b]
LinkdList底层使用的链表数据结构。特点,增删速度快,查询速度慢。
LinkdList特有方法:
//将指定元素添加到此列表的末尾 boolean offer(E e) //在此列表的开头插入指定的元素 boolean offerFirst(E e) //在此列表末尾插入指定的元素 boolean offerLast(E e) //获取并移除此列表的头 E poll() //获取并移除此列表的第一个元素;如果此列表为空,则返回 null E pollFirst() //获取并移除此列表的最后一个元素;如果此列表为空,则返回 null E pollLast() //获取但不移除此列表的头 E peek() //获取但不移除此列表的第一个元素;如果此列表为空,则返回 null E peekFirst() //获取但不移除此列表的最后一个元素;如果此列表为空,则返回 null E peekLast()
[b]Vector:[/b]
Vector底层是数组结构,与ArrayList的区别在于,Vector容器的增长可以控制,而ArrayList没有特定的增长方式。Vector是线性同步的,ArrayList线性不同步。
第三话:Set
[b]Set概述:[/b]
一个不包含重复元素的collection。更确切地讲,set不包含满足 e1.equals(e2) 的元素对 e1 和 e2,并且最多包含一个 null 元素。正如其名称所暗示的,此接口模仿了数学上的 set 抽象。
[b]HashSet:[/b]
HashSet底层数据结构是哈希表。通过元素的两个方法hashCode()和equals()是否为true来判断值的唯一性,如果元素的hashCode()返回值为true则不会使用equals(),hashCode()返回值为false则根据equals()返回值来判断是否相等。
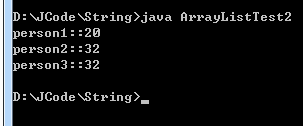
import java.util.*;
class hashSetDemo
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
HashSet hash = new HashSet();
// 返回字符串哈希码
System.out.println("hello".hashCode());
System.out.println("hello".hashCode());
//往hashSet添加元素,并打印出是否添加成功
System.out.println(hash.add("hello"));
System.out.println(hash.add("hello"));
System.out.println(hash.add("hello1"));
hash.add("hello2");
//遍历hashSet并打印
for(Iterator it = hash.iterator(); it.hasNext();)
{
System.out.println(it.next());
}
}结果图:

分析:可以看到2个“hello”字符串对象的hash值是一样的,因此在没有重写equals()方法时,他们是无法同时存在同一个HashSet中的。同时也可以看出,HashSet默认排序方式不跟List一样,HashSet的默认排序是无序的。
[b]TreeSet:[/b]
TreeSet底层数据结构是二叉树。可以对Set集合中的元素进行排序。TreeSet排序方法有2种:
1.当元素自身具备比较性元素时实现comparable接口,覆盖comparaTo方法这种方法也成为元素的自然顺序或者默认顺序。
2.当元素自身不具备比较性元素或者不是所需要的比较性时,就需要让集合自身具备特有的比较性。可以构建一个比较器,简单的说就是实现comparator接口覆盖接口中compara方法和equals方法中构建要比较的方式。
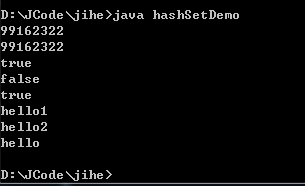
import java.util.*;
class TreeSetTest
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// 创建一个TreeSet集合并指定比较器
TreeSet ts = new TreeSet(new mycomparator());
ts.add("avads");
ts.add("fdsw");
ts.add("s");
ts.add("sq");
ts.add("dfq");
//使用迭代器遍历TreeSet集合
for( Iterator it = ts.iterator(); it.hasNext(); )
{
System.out.println(it.next());
}
}
} //自定义一个比较器让字符按长度排序
class mycomparator implements Comparator
{
public int compare(Object s1,Object s2)
{
String o1 = (String)s1;
String o2 = (String)s2;
int num = new Integer(o1.length())
.compareTo(new Integer(o2.length()));
if (num == 0)
return o1.compareTo(o2);
return num;
}
}[b]结果图:[/b]

相关文章推荐
- 开发人员、程序员与计算机科学家三者之间的区别
- 程序员必备,程序员四大忌
- 程序员们,做好你手里的俩份试卷
- 程序员必备的10大健康装备! 我们要工作更要健康!
- AVG 7.5.1.43 版本 序列号 集合
- 一篇关于程序员性格的文章第1/3页
- SQL Server游标的使用/关闭/释放/优化小结
- 8种类型极品程序员,不知你属于哪一种?
- C#检查指定对象是否存在于ArrayList集合中的方法
- 程序员编程从初级到中级的10个秘诀
- 做一个优秀程序员应该知道的15件事
- 程序员开发项目是选择效率还是质量呢?
- 程序员的八种境界,你在哪一境?
- 五个PHP程序员工具
- PHP 程序员应该使用的10个组件
- C#中的集合用法分析
- JavaScript Archive Network 集合
- Backbone.js中的集合详解
- jQuery学习7 操作JavaScript对象和集合的函数
- 网页代码常用小技巧总结第1/3页
