用无向带权图实现校园导航系统
2015-04-16 22:42
260 查看
学校数据结构的课程实验之一。
用到的数据结构:无向带权图
用到的算法:Floyd最短路径算法,深度优先搜索(递归实现)
需求分析:
设计一个校园导航程序,为访客提供各种信息查询服务:
1. 以图中各顶点表示校内各单位地点,存放单位名称,代号,简介等信息;以边表示路径,存放路径长度等相关信息。
2. 图中任意单位地点相关信息的查询。
3. 图中任意单位的问路查询,即查询任意两个单位之间的一条最短的路径。
4. 从图中任意单位地点出发的一条深度优先遍历路径。
主函数:
学校类:
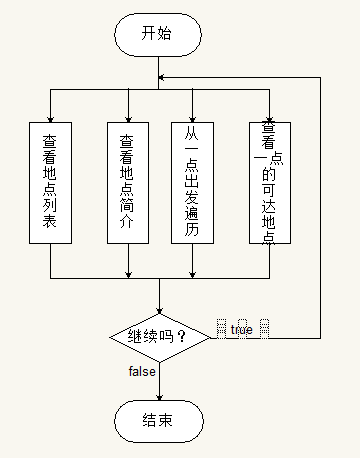
主程序流程图:
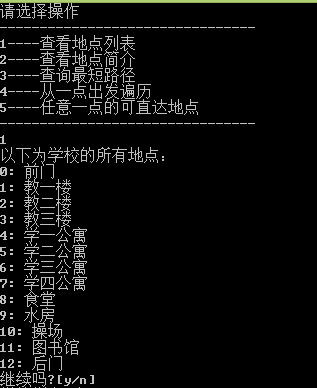
运行截图:


图类(邻接矩阵存储,因有向图是无向图的超集,所以可以定义为有向图,邻接矩阵为对称阵)
附:测试用的文件School.txt内容
用到的数据结构:无向带权图
用到的算法:Floyd最短路径算法,深度优先搜索(递归实现)
需求分析:
设计一个校园导航程序,为访客提供各种信息查询服务:
1. 以图中各顶点表示校内各单位地点,存放单位名称,代号,简介等信息;以边表示路径,存放路径长度等相关信息。
2. 图中任意单位地点相关信息的查询。
3. 图中任意单位的问路查询,即查询任意两个单位之间的一条最短的路径。
4. 从图中任意单位地点出发的一条深度优先遍历路径。
主函数:
#include <iostream>
#include "School.h"
using namespace std;
int main()
{
School mySchool=School("School.txt");
char choice='y';
while(choice=='y')
{
cout << "请选择操作"<<endl;
cout << "--------------------------------" << endl;
cout << "1----查看地点列表" << endl;
cout << "2----查看地点简介" << endl;
cout << "3----查询最短路径" << endl;
cout << "4----从一点出发遍历" << endl;
cout << "5----任意一点的可直达地点" << endl;
cout << "--------------------------------" << endl;
int option;
cin >> option;
switch (option)
{
case 1: mySchool.display(); break;
case 2: mySchool.search(); break;
case 3: mySchool.path(); break;
case 4: mySchool.traverse(); break;
case 5: mySchool.reachable(); break;
}
cout << "继续吗?[y/n]";
cin >> choice;
}
return 0;
}学校类:
#include <fstream>
#include <string>
#include "Digraph.h"
using namespace std;
struct Place//地点定义
{
int number;
string name;
string introduction;
Place(){}
Place(int num,string nam,string intro):number(num),name(nam),introduction(intro){}
void print()//显示此地点的信息
{
cout<<"---------------------------"<<endl;
cout<<"编号:"<<number<<endl;
cout<<"地点名:"<<name<<endl;
cout<<"简介:"<<introduction<<endl;
cout<<"---------------------------"<<endl;
}
};
ostream& operator<<(ostream &os, Place &aPlace)//重载输出运算符
{
os << aPlace.number << ":" << aPlace.name;
return os;
}
ofstream outFile;//输出流
class School
{
private:
int total;//总的地点数
Digraph<Place,13> places_graph;
void readFile(const char filename[20])//读文件
{
total = 0;
ifstream inFile;
inFile.open(filename);
char trying;
while(inFile.is_open() && !inFile.eof())
{
//先试探是否为结束符
inFile >> trying;
if (trying == '#') break;
else
{
inFile.putback(trying);
int number;
inFile>>number;
string name;
inFile>>name;
string introduction;
inFile>>introduction;
Place aPlace=Place(number,name,introduction);
//aPlace.print();//显示这个地点的信息
places_graph.insert(aPlace);
total++;
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < 13; i++)//读入距离内容
for (int j = 0; j < 13; j++)
{
int dis;
inFile >> dis;
places_graph.distance_set(i, j, dis);
}
inFile.close();
places_graph.calculate_path();//计算所有最短路径并存入数组
cout << "学校共有" << total << "个地方"<<endl;
}
static void readPlace(Place &aPlace)
{
outFile<<aPlace.number<<endl;
outFile<<aPlace.name<<endl;
outFile<<aPlace.introduction<<endl;
}
static void print(Place &aPlace)//显示此地点的信息编号、名称
{
cout<<aPlace.number<<": "<<aPlace.name<<endl;
}
static void visit(Place &aPlace)
{
cout << "->" << aPlace.number << ":" << aPlace.name << endl;
}
public:
School(const char filename[20])
{
readFile(filename);
}
void display()
{
cout<<"以下为学校的所有地点:"<<endl;
places_graph.traverse(print);
}
void search()
{
cout<<"请输入要查询的地点编号:";
int num;
cin>>num;
Place aPlace;
places_graph.search_vertex(num,aPlace);//查到要查的地点
cout<<"以下是这一地点的信息:"<<endl;
aPlace.print();
}
void path()
{
cout << "请输入想查询最短路径的两个地点的编号(如:5 7):";
int i, j;
cin >> i >> j;
places_graph.shortest_path(i, j);
}
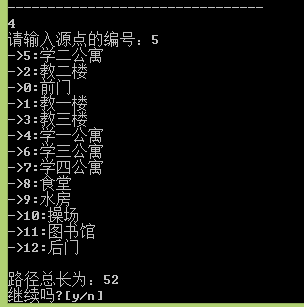
void traverse()//深度优先遍历,输出路线
{
cout << "请输入源点的编号:";
int v;
cin >> v;
int distance;
distance = places_graph.BFS(v, visit);
cout << endl << "路径总长为:" << distance<<endl;
}
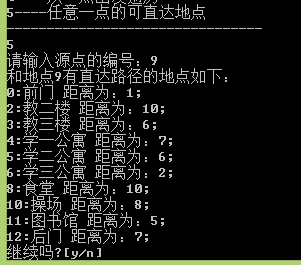
void reachable()
{
cout << "请输入源点的编号:";
int v;
cin >> v;
cout << "和地点" << v << "有直达路径的地点如下:" << endl;
places_graph.connected(v);
}
};主程序流程图:

运行截图:





图类(邻接矩阵存储,因有向图是无向图的超集,所以可以定义为有向图,邻接矩阵为对称阵)
#include <fstream>
#include <string>
template <class Vertex,int graph_size>
class Digraph
{
public:
Digraph()
{
count=0;
for (int i = 0; i < graph_size; i++)
adjacency[i][i] = 0;
}
void insert(Vertex &new_entry)
{
nodes[count++]=new_entry;
}
void distance_set(int i, int j, int dis)
{
adjacency[i][j] = adjacency[j][i] = dis;
}
void traverse(void (*visit)(Vertex &))//遍历整个图(逐个访问各结点)
{
for(int i=0;i<graph_size;i++)
(*visit)(nodes[i]);
}
void search_vertex(int num,Vertex &target)
{
target=nodes[num];
}
void calculate_path()//计算最短路径并将结果更新到以上两个二维数组里
{
for (int i = 0; i < graph_size; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < graph_size; j++)
{//初始化路径长度数组,结点跟踪数组
shortest_dis[i][j] = adjacency[i][j];
trace_node[i][j] = j;
}
}
cout << "这是邻接矩阵:" << endl;
for (int i = 0; i < graph_size; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < graph_size; j++)
cout << adjacency[i][j] << " ";
cout << endl;
}
//Floyd算法计算任意两点之间的最短路径
for (int k = 0; k < graph_size; k++)
for (int v = 0; v < graph_size; v++)
for (int w = 0; w < graph_size; w++)
if (shortest_dis[v][k] + shortest_dis[k][w] < shortest_dis[v][w])
{
shortest_dis[v][w] = shortest_dis[v][k] + shortest_dis[k][w];
trace_node[v][w] = trace_node[v][k];
}
cout << "这是最短路径数组:" << endl;
for (int i = 0; i < graph_size; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < graph_size; j++)
cout << shortest_dis[i][j] << " ";
cout << endl;
}
cout << "这是结点跟踪数组:" << endl;
for (int i = 0; i < graph_size; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < graph_size; j++)
cout << trace_node[i][j] << " ";
cout << endl;
}
}
void shortest_path(int i, int j)
{
cout << "从" << i << "到" << j << "的最短路径长度为" << shortest_dis[i][j] << endl;
cout << "路径为:" << endl;
int k = trace_node[i][j];
cout << i ;
while (k != j)
{
cout << "->" << k;
k = trace_node[k][j];//从起点出发,找到途经结点
}
cout << "->" << j << endl;
}
void connected(int v)//输出所有和v直达的结点
{
for (int i = 0; i < graph_size; i++)
{
if (adjacency[v][i] != 100 && adjacency[v][i] != 0)
cout << nodes[i] << " 距离为:" << adjacency[v][i] << ";" << endl;
}
}
int BFS(int v,void (*visit)(Vertex &))
{
distance = 0;
bool visited[graph_size] = { false };
Vertex src = nodes[v];//找到选定的源点
visited[v] = true;
(*visit)(src);
for (int i = 0; i < graph_size; i++)
{
if (adjacency[v][i] != 100 && adjacency[v][i] != 0)//对相邻点进行深度优先遍历
traverse(i, visited, visit);
}
return distance;
}
private:
int count;//结点数
int distance;//一条遍历路径总长
int adjacency[graph_size][graph_size];//存储权的邻接矩阵
Vertex nodes[graph_size];//存储结点内容的一维数组
int shortest_dis[graph_size][graph_size];//保存最短路径长度
int trace_node[graph_size][graph_size];//保存结点跟踪路径
void traverse(int v, bool visited[], void (*visit)(Vertex &))//辅助遍历函数
{
if (visited[v] == false)
{
(*visit)(nodes[v]);
visited[v] = true;
for (int i = 0; i < graph_size; i++)
if (adjacency[v][i] != 100 && adjacency[v][i] != 0 && visited[i] == false)
{
traverse(i, visited, visit);//递归地进行深度优先遍历
distance += adjacency[v][i];
}
}
}
};附:测试用的文件School.txt内容
前门 南门;车辆进出 教一楼 阶梯教室;英语教室 教二楼 普通教室 教三楼 实验室;办公室;阶梯教室 学一公寓 男生宿舍 学二公寓 男生宿舍 学三公寓 女生宿舍 学四公寓 男生宿舍 食堂 一层;二层;清真 水房 在食堂旁边 操场 300米一圈的跑道 图书馆 借阅部;自习室 后门 北门;取快递 # 1 4 8 6 100 100 10 100 1 100 10 100 0 3 4 5 100 10 100 1 100 1 100 100 3 0 10 1 7 100 6 100 10 100 100 8 4 10 0 2 100 3 100 100 6 5 9 7 5 1 2 0 3 6 9 100 7 9 8 5 100 7 100 3 0 100 5 100 6 7 8 4 10 100 3 6 100 0 2 7 2 9 10 2 100 6 100 9 5 2 0 4 100 2 3 7 1 100 100 100 100 7 4 0 10 4 5 1 100 10 6 7 6 2 100 10 0 8 5 7 1 100 5 9 7 9 2 4 8 0 2 9 100 100 9 8 8 10 3 5 5 2 0 100 100 8 7 5 4 2 7 1 7 9 100 0 School.txt
相关文章推荐
- 用无向带权图实现校园导航系统
- 滨州学院信息工程学院2015级数据结构 校园导航系统的设计与实现
- 基于Hadoop的校园云存储系统的实现研究
- Android系统联系人全特效实现(上),分组导航和挤压动画
- Android系统联系人全特效实现(上)分组导航和挤压动画(附源码)
- 利用系统APP实现导航---By张秀清
- 基于Web Service技术的校园数字化办公系统的设计与实现二(页1) - 信息 ...
- 基于node+koa2+mongodb实现简单的导航管理系统
- 模块管理常规功能自定义系统的设计与实现(13--Grid导航设计初步[3])
- 校园视频管理系统----EF+WCF+MVC实现SOA架构
- Android系统联系人全特效实现(上),分组导航和挤压动画
- 校园微博系统的设计与实现
- 校园导航系统,生成图,图之间最短路径问题(温习迪杰斯特拉算法,普利姆算法)
- Android系统联系人全特效实现(上),分组导航和挤压动画
- unity5之导航网格寻路系统-2使用NavMeshAgent实现类型英雄联盟右键行走功能
- Android实现系统联系人字符分组以及字母表导航效果 .
- 校园导航系统,生成图,图之间最短路径问题(温习迪杰斯特拉算法,普利姆算法)
- Android系统联系人全特效实现(上),分组导航和挤压动画
- 在iPhone中直接调用系统自带的地图程序实现导航
- Android系统联系人全特效实现(上),分组导航和挤压动画
