看数据结构写代码(36) 图的邻接表表示与实现
2015-04-09 11:08
543 查看
图的邻接表表示法,是为每一个顶点建立一个链表,链表里存放着相同弧尾的 弧的信息,这些链表顺序存放在数组中。下面是无向图g2的邻接表
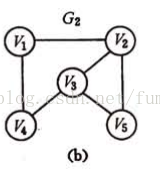
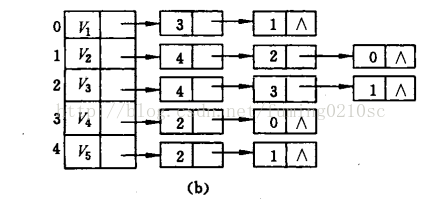
邻接表 比 邻接矩阵 节省空间,同时 也带来一些操作上的 不便,例如 看 两个顶点是否 相邻,需要 遍历 链表,在 求 无向图顶点的度时,只需 遍历 顶点的链表,而 求 有向图 顶点的度 需要 遍历 整个图 查找 弧头 为这个顶点的 个数。 如果 不想这样做,可以 建立 逆邻接表,即 链表里 存放着 相同 弧头的 弧 的信息。 下一节 要说的 十字链表 类似于这种结构。
下面 上代码:
源代码网盘地址:点击打开链接
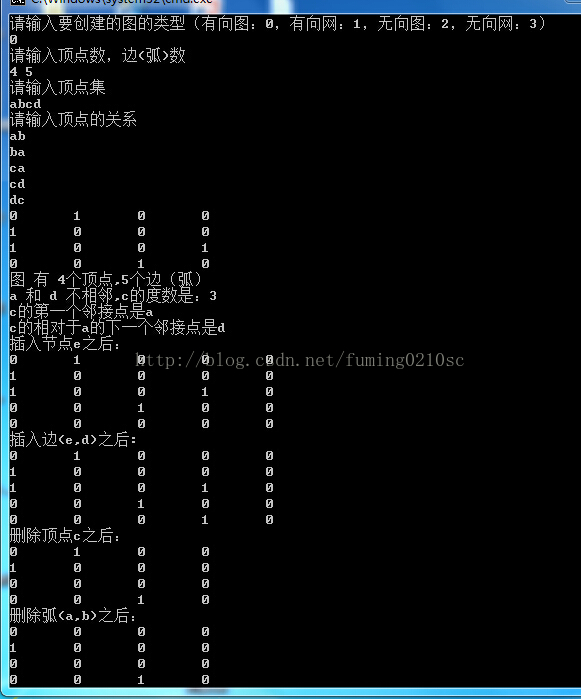
最后 图的 顶点树为 4, 边(弧) 数 为 1


邻接表 比 邻接矩阵 节省空间,同时 也带来一些操作上的 不便,例如 看 两个顶点是否 相邻,需要 遍历 链表,在 求 无向图顶点的度时,只需 遍历 顶点的链表,而 求 有向图 顶点的度 需要 遍历 整个图 查找 弧头 为这个顶点的 个数。 如果 不想这样做,可以 建立 逆邻接表,即 链表里 存放着 相同 弧头的 弧 的信息。 下一节 要说的 十字链表 类似于这种结构。
下面 上代码:
源代码网盘地址:点击打开链接
// Graph.cpp : 定义控制台应用程序的入口点。
//图的邻接表 表示法
#include "stdafx.h"
#include <cstdlib>
#include <climits>
#define MAX_VERTEX_NUM 20
#define INFINITY INT_MAX
enum E_Graph_Kind
{
DG = 0,//有向图
DN,//有向网
UDG,//无向图
UDN,//无向网
};
struct ArcNode//边(弧)
{
int adjVex;//顶点在数组中的位置
ArcNode * nextAdj;
int weight;//权值
};
typedef struct VNode//顶点
{
ArcNode * head;//头指针
char vexName;//顶点名称
}AdjList[MAX_VERTEX_NUM];
struct Graph//图
{
AdjList list;//邻接表
int arcNum,vexNum;
E_Graph_Kind kind;
};
//顶点在数组中的位置
int vexLocation(Graph g,char vex){
for (int i = 0; i < g.vexNum; i++){
if (g.list[i].vexName == vex){
return i;
}
}
return -1;
}
ArcNode * getHeadNode(){//获得头节点..
ArcNode * node = (ArcNode*)malloc(sizeof(ArcNode));
if (node != NULL){
node->adjVex = -1;
node->nextAdj = NULL;
node->weight = INFINITY;
}
return node;
}
ArcNode * getArcNode(Graph g,char vexName){
ArcNode * node = getHeadNode();
if (node != NULL){
int location = vexLocation(g,vexName);
node->adjVex = location;
}
return node;
}
void createDG(Graph * graph);
void createDN(Graph * graph);
void createUDG(Graph * graph);
void createUDN(Graph * graph);
void graphCreate(Graph * graph){
E_Graph_Kind kind;
printf("请输入要创建的图的类型(有向图:0,有向网:1,无向图:2,无向网:3)\n");
scanf("%d",&kind);
switch (kind){
case DG:
createDG(graph);
break;
case DN:
createDN(graph);
break;
case UDG:
createUDG(graph);
break;
case UDN:
createUDN(graph);
break;
default:
break;
}
}
//有向图
void createDG(Graph * g){
g->kind = DG;
printf("输入图的顶点树 和 边(弧)树\n");
scanf("%d%d%*c",&g->vexNum,&g->arcNum);
//构造顶点集
printf("请输入顶点集\n");
for (int i = 0; i < g->vexNum; i++){
char name;
scanf("%c",&name);
g->list[i].vexName = name;
g->list[i].head = getHeadNode();//头指针指向头节点.
}
//构造顶点关系
fflush(stdin);
printf("请输入顶点的关系\n");
for (int i = 0; i < g->arcNum; i++){
char vex1,vex2;
scanf("%c%c%*c",&vex1,&vex2);
int location1 = vexLocation(*g,vex1);
ArcNode * node = getArcNode(*g,vex2);
node->nextAdj = g->list[location1].head->nextAdj;
g->list[location1].head->nextAdj = node;
}
}
//有向网..
void createDN(Graph * g){
g->kind = DN;
printf("输入图的顶点树 和 边(弧)树\n");
scanf("%d%d%*c",&g->vexNum,&g->arcNum);
//构造顶点集
printf("请输入顶点集\n");
for (int i = 0; i < g->vexNum; i++){
char name;
scanf("%c",&name);
g->list[i].vexName = name;
g->list[i].head = getHeadNode();
}
//构造顶点关系
fflush(stdin);
printf("请输入顶点的关系\n");
for (int i = 0; i < g->arcNum; i++){
char vex1,vex2;
int weight;
scanf("%c%c%d%*c",&vex1,&vex2,&weight);
int location1 = vexLocation(*g,vex1);
ArcNode * node = getArcNode(*g,vex2);
node->weight = weight;
node->nextAdj = g->list[location1].head->nextAdj;
g->list[location1].head->nextAdj = node;
}
}
//无向图
void createUDG(Graph * g){
g->kind = UDG;
printf("输入图的顶点树 和 边(弧)树\n");
scanf("%d%d%*c",&g->vexNum,&g->arcNum);
//构造顶点集
printf("请输入顶点集\n");
for (int i = 0; i < g->vexNum; i++){
char name;
scanf("%c",&name);
g->list[i].vexName = name;
g->list[i].head = getHeadNode();
}
//构造顶点关系
fflush(stdin);
printf("请输入顶点的关系\n");
for (int i = 0; i < g->arcNum; i++){
char vex1,vex2;
scanf("%c%c%*c",&vex1,&vex2);
int location1 = vexLocation(*g,vex1);
ArcNode * node1 = getArcNode(*g,vex2);
node1->nextAdj = g->list[location1].head->nextAdj;
g->list[location1].head->nextAdj = node1;
int location2 = vexLocation(*g,vex2);
ArcNode * node2 = getArcNode(*g,vex1);
node2->nextAdj = g->list[location2].head->nextAdj;
g->list[location2].head->nextAdj = node2;
}
}
//无向网
void createUDN(Graph * g){
g->kind = UDN;
printf("输入图的顶点树 和 边(弧)树\n");
scanf("%d%d%*c",&g->vexNum,&g->arcNum);
//构造顶点集
printf("请输入顶点集\n");
for (int i = 0; i < g->vexNum; i++){
char name;
scanf("%c",&name);
g->list[i].vexName = name;
g->list[i].head = getHeadNode();
}
//构造顶点关系
fflush(stdin);
printf("请输入顶点的关系\n");
for (int i = 0; i < g->arcNum; i++){
char vex1,vex2;
int weight;
scanf("%c%c%d%*c",&vex1,&vex2,&weight);
int location1 = vexLocation(*g,vex1);
ArcNode * node1 = getArcNode(*g,vex2);
node1->weight = weight;
node1->nextAdj = g->list[location1].head->nextAdj;
g->list[location1].head->nextAdj = node1;
int location2 = vexLocation(*g,vex2);
ArcNode * node2 = getArcNode(*g,vex1);
node2->weight = weight;
node2->nextAdj = g->list[location2].head->nextAdj;
g->list[location2].head->nextAdj = node2;
}
}
void graphDestory(Graph * g){
for (int i = 0; i < g->vexNum; i++){
ArcNode * next = g->list[i].head;
while (next != NULL){
ArcNode * freeNode = next;
next = next->nextAdj;
free(freeNode);
}
g->list[i].head = NULL;
g->list[i].vexName = ' ';
}
g->vexNum = g->arcNum = 0;
}
//vex1 和 vex2是否相邻..
bool grphIsAdj(Graph g,char vex1,char vex2){
int location = vexLocation(g,vex1);
ArcNode * next = g.list[location].head->nextAdj;//第一个节点是头结点的后继
while (next != NULL){
if (g.list[next->adjVex].vexName == vex2){
return true;
}
next = next->nextAdj;
}
return false;
}
//顶点vex的度.
//有向 = 出度 + 入度
//无向 = 出度
int graphDegree(Graph g,char vex){
int degree = 0;
int location = vexLocation(g,vex);
ArcNode * next = g.list[location].head->nextAdj;
while (next != NULL){//出度
degree ++;
next = next->nextAdj;
}
if (g.kind == DG || g.kind == DN){
//有向图还需要遍历图,寻找入度.
for (int i = 0; i < g.vexNum; i++){
ArcNode * next = g.list[i].head->nextAdj;
while (next != NULL){
if (next->adjVex == location){
degree ++;
}
next = next->nextAdj;
}
}
}
return degree;
}
//vex 的第一个邻接点
char firstAdj(Graph g,char vex){
int location = vexLocation(g,vex);
ArcNode * next = g.list[location].head->nextAdj;
if (next != NULL){
return g.list[next->adjVex].vexName;
}
return ' ';
}
//vex1 相对于 vex2 的下一个邻接点。。。
char nextAdj(Graph g,char vex1,char vex2){
int location = vexLocation(g,vex1);
ArcNode * next = g.list[location].head->nextAdj;
while (next != NULL){//查找到 vex2
if (g.list[next->adjVex].vexName == vex2){
break;
}
next = next->nextAdj;
}
if (next != NULL){
ArcNode * nextNode = next->nextAdj;
if (nextNode != NULL){
return g.list[nextNode->adjVex].vexName;
}
}
return ' ';
}
//插入顶点
void insertVex(Graph * g,char vex){
if (g->vexNum < MAX_VERTEX_NUM){
g->list[g->vexNum].vexName = vex;
g->list[g->vexNum].head = getHeadNode();
g->vexNum++;
}
}
//删除顶点
void deleteVex(Graph * g,char vex){
int location = vexLocation(*g,vex);
//释放空间
ArcNode * next = g->list[location].head->nextAdj;
int delNum = 0;
while (next != NULL){
ArcNode * freeNode = next;
next = next->nextAdj;
free(freeNode);
delNum++;
}
//vex下面的 顶点上移
for (int i = location + 1; i < g->vexNum; i++){
g->list[i-1] = g->list[i];
}
g->vexNum --;
//删除与顶点vex 相关的边(弧)(以及更新 所有节点的 adjVex )要遍历图..
for (int i = 0; i < g->vexNum; i++){
ArcNode * next = g->list[i].head->nextAdj;
ArcNode * pre = g->list[i].head;
while (next != NULL){
if (next->adjVex == location){
ArcNode * freeNode = next;
next = next->nextAdj;
pre->nextAdj = next;
free(freeNode);
delNum++;
}
else {
if (next->adjVex > location){//在顶点下面的节点位置要减1
next->adjVex --;
}
pre = next;
next = next->nextAdj;
}
}
}
g->arcNum -= delNum;//有向
if (g->kind == UDG || g->kind == UDN){
g->arcNum += delNum/2;
}
}
//插入边(弧)
void insertArc(Graph * g,char vex1,char vex2){
int location1 = vexLocation(*g,vex1);
ArcNode * node1 = getArcNode(*g,vex2);
node1->nextAdj = g->list[location1].head->nextAdj;
g->list[location1].head->nextAdj = node1;
//无向图需要插入另外一边.
if (g->kind == UDG || g->kind == UDN){
int location2 = vexLocation(*g,vex2);
ArcNode * node2 = getArcNode(*g,vex1);
node2->nextAdj = g->list[location2].head->nextAdj;
g->list[location2].head->nextAdj = node2;
}
g->arcNum ++;
}
//删除边(弧)
void deleteArc(Graph * g,char vex1,char vex2){
g->arcNum--;
int location1 = vexLocation(*g,vex1);
int location2 = vexLocation(*g,vex2);
ArcNode * next = g->list[location1].head->nextAdj;
ArcNode * pre = g->list[location1].head;
while (next != NULL){
if (next->adjVex == location2){
pre->nextAdj = next->nextAdj;
free(next);
break;
}
pre = next;
next = next->nextAdj;
}
if (g->kind == UDG || g->kind == UDN ){//无向图还需要删除 另外一边
next = g->list[location2].head->nextAdj;
pre = g->list[location2].head;
while (next != NULL){
if (next->adjVex == location1){
pre->nextAdj = next->nextAdj;
free(next);
break;
}
pre = next;
next = next->nextAdj;
}
}
}
void printGrahp(Graph g){
for (int i = 0; i < g.vexNum; i++){
printf("%c的邻接点有:",g.list[i].vexName);
ArcNode * next = g.list[i].head->nextAdj;
while (next != NULL){
printf("%c",g.list[next->adjVex].vexName);
next = next->nextAdj;
}
printf("\n");
}
}
int _tmain(int argc, _TCHAR* argv[])
{
Graph g;
graphCreate(&g);
printGrahp(g);
printf("图的顶点数:%d,边(弧)树为:%d\n",g.vexNum,g.arcNum);
char first = firstAdj(g,'a');
char next = nextAdj(g,'a','c');
char * isAdj = grphIsAdj(g,'c','d')? "相邻" : "不相邻";
int degree = graphDegree(g,'d');
printf("a的第一个邻接点是%c,a的c邻接点的下一个邻接点是:%c\n",first,next);
printf("c 和 d %s,d的度为:%d\n",isAdj,degree);
insertVex(&g,'e');
printf("插入e顶点之后图结构如下:\n");
printGrahp(g);
insertArc(&g,'a','e');
printf("插入(a,e)边(弧)之后图结构如下:\n");
printGrahp(g);
deleteArc(&g,'d','c');
printf("删除(d,c)边(弧)之后图结构如下:\n");
printGrahp(g);
deleteVex(&g,'a');
printf("删除顶点a之后图结构如下:\n");
printGrahp(g);
printf("图的顶点数:%d,边(弧)树为:%d\n",g.vexNum,g.arcNum);
//及时销毁内存是个好习惯
graphDestory(&g);
return 0;
}运行截图:
最后 图的 顶点树为 4, 边(弧) 数 为 1
相关文章推荐
- 数据结构算法代码实现——线性表的链式表示与实现(单链表)(三 )
- 数据结构(C实现)------- 图的邻接表表示
- 看数据结构写代码(30) 树的双亲孩子表示法的实现
- 看数据结构写代码(37) 图的十字链表的表示与实现
- 数据结构(一) 抽象数据类型的表示与实现 代码示例
- 【数据结构】图的邻接表表示(GNU C++实现)
- 数据结构之---C语言实现图的邻接表存储表示
- 数据结构与算法——图的邻接表表示法类的C++实现
- 数据结构——图的链表实现(邻接表表示法)
- 看数据结构写代码(38) 图的邻接多重表表示法与实现
- 数据结构之---C语言实现图的邻接表存储表示
- 数据结构教程 第六课 线性表的顺序表示和实现
- 数据结构—线性表的链式表示和实现
- 单链表的表示和实现 - 数据结构
- 算法——数据结构图的最短路径实现JAVA代码
- 数据结构——图的邻接表表示法
- java数据结构之线性表代码实现
- 数据结构,图的邻接矩阵创建,邻接矩阵与邻接表的交换,两种表的输出,过程用C++实现
- 数据结构4:栈的表示和实现
- 图的C程序实现代码(邻接表表示)
