数据结构的JAVA实现
2015-03-29 22:01
267 查看
一.数组与Arrays
(1)Arrays的使用
The output is
44 77 55 22 99 88 33 66
22 33 44 55 66 77 88 99
Arrays.binarySearch(a, 44): 2
a[2]: 44
Arrays.binarySearch(a, 45): -4
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
55 55 55 55 55 55 55 55
Arrays.equals(a,b): false
(2)顺序查找
The output is:
search(a, 44): 2
search(a, 50): -1
search(a, 77): 5
search(a, 100): -1
(3)折半查找
(4)反转
二.链式数据结构
(1)插入有序数组
(2)单向链表插入和删除
三.JAVA容器类
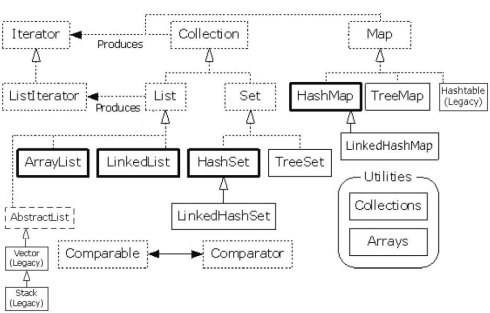
jdk1.4容器类关系图
虚线框表示接口。
实线框表示实体类。
粗线框表示最常用的实体类。
点线的箭头表示实现了这个接口。
实线箭头表示类可以制造箭头所指的那个类的对象。
容器类持有对象方式
1, Collection:只允许每个位置上放一个对象。它包括“以一定顺序持有一组对象”的List,以及“只能允许添加不重复对象”的Set。你可以用add()方法向Collection对象中加元素。
2, Map:一组以“键-值”(key-value)的形式出现的pair,Map也不接受重复的key值。你可以用put()方法往Map里面加元素。
Collection 和 Collections的区别
Collections是个java.util下的类,它包含有各种有关集合操作的静态方法,实现对各种集合的搜索、排序、线程安全化等操作。
Collection是个java.util下的接口,它是各种集合结构的父接口。继承自它的接口主要有Set 和List.
无论使用哪种Set,都需要定义equals(),但是只有在“要把对象放进HashSet”的情况下,才需要定义hashCode().因为HashSet是我们通常用的Set,所以通常也需要定义hashCode()。作为一种编程风格,你应该在覆写equals()的同时把hashCode()也覆写了。
LinkedList类
LinkedList使用双向链表来实现的,也就是每个对象,除了保存数据之外,还保存着在它前面和后面的那两个对象的reference,允许null元素。此外LinkedList提供额外的get,remove,insert方法在LinkedList的首部或尾部。这些操作使LinkedList可被用作堆栈(stack),队列(queue)或双向队列(deque)。
注意LinkedList没有同步方法。如果多个线程同时访问一个List,则必须自己实现访问同步。一种解决方法是在创建List时构造一个同步的List:
List list = Collections.synchronizedList(new LinkedList(...));
ArrayList类
ArrayList擅长对元素进行随机访问,可以把它想成“一个能够自动扩展的数组”。它允许所有元素,包括null。ArrayList没有同步。
size,isEmpty,get,set方法运行时间为常数。但是add方法开销为分摊的常数,添加n个元素需要O(n)的时间。其他的方法运行时间为线性。
每个ArrayList实例都有一个容量(Capacity),即用于存储元素的数组的大小。这个容量可随着不断添加新元素而自动增加,但是增长算法并没有定义。当需要插入大量元素时,在插入前可以调用ensureCapacity方法来增加ArrayList的容量以提高插入效率。
和LinkedList一样,ArrayList也是非同步的(unsynchronized)。
Vector类(legacy,遗留的)
Vector非常类似ArrayList。
ArrayList和Vector的区别
一.同步性:Vector是线程安全的,也就是说是同步的,而ArrayList是线程序不安全的,不是同步的。由Vector创建的Iterator,虽然和ArrayList创建的Iterator是同一接口,但是,因为Vector是同步的,当一个Iterator被创建而且正在被使用,另一个线程改变了Vector的状态(例如,添加或删除了一些元素),这时调用Iterator的方法时将抛出ConcurrentModificationException,因此必须捕获该异常。
二.数据增长:当需要增长时,Vector默认增长为原来一培,而ArrayList却是原来的一半.
Stack 类(legacy,遗留的)
Stack继承自Vector,实现一个后进先出的堆栈。Stack提供5个额外的方法使得Vector得以被当作堆栈使用。基本的push和pop方法,还有peek方法得到栈顶的元素,empty方法测试堆栈是否为空,search方法检测一个元素在堆栈中的位置。Stack刚创建后是空栈。
iterator()方法
Enumeration接口定义了可以对一个对象的类集中的元素进行枚举(一次获得一个)的方法。这个接口尽管没有被摈弃,但已经被Iterator所替代。
不论Collection的实际类型如何,它都支持一个iterator()的方法,该方法返回一个迭代子,使用该迭代子即可逐一访问Collection中每一个元素。
iterator()方法不必知道对象序列的具体实现,就能在序列中移动,选取其中的对象
用iterator()方法叫容器传给你一个Iterator对象。
List simple=new ArrayList();Iterator e= simple.iterator();
第一次调用Iterator的next()方法的时候,它会传给你序列中的第一个元素。
用next()方法获取序列中的下一个对象。
用hasNext()方法查询序列中是否还有其它对象。
用remove()方法删除迭代器所返回的最后一个元素。
Hashtable类(legacy,遗留的)
Hashtable继承Map接口,实现一个key-value映射的哈希表。任何非空(non-null)的对象都可作为key或者value。
添加数据使用put(key, value),取出数据使用get(key),这两个基本操作的时间开销为常数。
Hashtable通过initial capacity和load factor两个参数调整性能。通常缺省的load factor 0.75较好地实现了时间和空间的均衡。增大load factor可以节省空间但相应的查找时间将增大,这会影响像get和put这样的操作。
使用Hashtable的简单示例如下,将1,2,3放到Hashtable中,他们的key分别是”one”,”two”,”three”:
Hashtable numbers = new Hashtable();
numbers.put(“one”, new Integer(1));
numbers.put(“two”, new Integer(2));
numbers.put(“three”, new Integer(3));
要取出一个数,比如2,用相应的key:
Integer n = (Integer)numbers.get(“two”);
System.out.println(“two = ” + n);
由于作为key的对象将通过计算其散列函数来确定与之对应的value的位置,因此任何作为key的对象都必须实现hashCode和equals方法。
hashCode()是Object根类的方法(缺省情况下返回对象的内存地址),因此所有java对象都能生成hash code。
equals()是Object根类的方法,只是简单地比较两个对象的地址。
如果你用自定义的类当作key的话,要相当小心,按照散列函数的定义,如果两个对象相同,即obj1.equals(obj2)=true,则它们的hashCode必须相同,但如果两个对象不同,则它们的hashCode不一定不同,如果两个不同对象的hashCode相同,这种现象称为冲突,冲突会导致操作哈希表的时间开销增大,所以尽量定义好的hashCode()方法,能加快哈希表的操作。
如果相同的对象有不同的hashCode,对哈希表的操作会出现意想不到的结果(期待的get方法返回null),要避免这种问题,只需要牢记一条:要同时复写equals方法和hashCode方法,而不要只写其中一个。
HashMap类
HashMap和Hashtable类似,不同之处在于HashMap是非同步的,并且允许null,即null value和null key。但是将HashMap视为Collection时(values()方法可返回Collection),其迭代子操作时间开销和HashMap的容量成比例。因此,如果迭代操作的性能相当重要的话,不要将HashMap的初始化容量设得过高,或者load factor过低。
HashMap和Hashtable的区别
HashTable的应用非常广泛,HashMap是Hashtable的轻量级实现(非线程安全的实现),HashMap是新框架中用来代替HashTable的类,也就是说建议使用HashMap,不要使用HashTable。
1.HashTable的方法是同步的,HashMap未经同步,所以在多线程场合要手动同步HashMap这个区别就像Vector和ArrayList一样。
2.HashTable不允许null值(key和value都不可以),HashMap允许null值(key和value都可以)。
3.HashMap把Hashtable的contains方法去掉了,改成containsvalue和containsKey。因为contains方法容易让人引起误解。
4.HashTable使用Enumeration,HashMap使用Iterator。
hashCode()与equals()方法
hashCode()是Object根类的方法(缺省情况下返回对象的内存地址),因此所有java对象都能生成hash code。HashMap利用对象的hashCode()来进行快速的查找。
equals()是Object根类的方法,只是简单地比较两个对象的地址。
无论使用哪种Set,都需要定义equals(),但是只有在“要把对象放进HashSet”的情况下,才需要定义hashCode().因为HashSet是我们通常用的Set,所以通常也需要定义hashCode()。
如果你不覆写键的hashCode()和equals()的话,散列数据结构(HashSet,HashMap,LinkedHashSet,LinkedHashMap)就没法正确的处理键。
转载:http://blog.csdn.net/hsttmht/article/details/6989911
四.二叉树
tree = [A, B, D, G, E, C, F, H, I]
PreOrder Traversal: A B D G E C F H I
InOrder Traversal: D G B E A H F I C
PostOrder Traversal: G D E B H I F C A
LevelOrder Traversal: A B C D E F G H I
五.排序
(1)冒泡排序
(2)快速排序
还有其他排序方式,选择排序,堆排序。。。
(1)Arrays的使用
import java.util.Arrays;
public class TestArrays {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] a = {44, 77, 55, 22, 99, 88, 33, 66};
print(a);
Arrays.sort(a);
print(a);
int k = Arrays.binarySearch(a, 44);
System.out.printf("Arrays.binarySearch(a, 44): %d%n", k);
System.out.printf("a[%d]: %d%n", k, a[k]);
k = Arrays.binarySearch(a, 45);
System.out.printf("Arrays.binarySearch(a, 45): %d%n", k);
int[] b = new int[8];
print(b);
Arrays.fill(b, 55);
print(b);
System.out.println("Arrays.equals(a,b): " + Arrays.equals(a,b));
}
}The output is
44 77 55 22 99 88 33 66
22 33 44 55 66 77 88 99
Arrays.binarySearch(a, 44): 2
a[2]: 44
Arrays.binarySearch(a, 45): -4
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
55 55 55 55 55 55 55 55
Arrays.equals(a,b): false
(2)顺序查找
public class TestBinarySearch {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] a = {22, 33, 44, 55, 66, 77, 88, 99};
System.out.println("search(a, 44): " + search(a, 44));
System.out.println("search(a, 50): " + search(a, 50));
System.out.println("search(a, 77): " + search(a, 77));
System.out.println("search(a, 100): " + search(a, 100));
}
public static int search(int[] a, int x) {
// POSTCONDITIONS: returns an integer i;
// if i >= 0, then a[i] == x; otherwise x is not in a[];
for (int i=0; i<a.length; i++) { // step 1
// INVARIANT: x is not among a[0]...a[i-1] // step 2
if (a[i] == x) { // step 3
return i;
}
}
return -1; // step 4
}
}The output is:
search(a, 44): 2
search(a, 50): -1
search(a, 77): 5
search(a, 100): -1
(3)折半查找
public class TestBinarySearch {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] a = {22, 33, 44, 55, 66, 77, 88, 99};
System.out.println("search(a, 44): " + search(a, 44));
System.out.println("search(a, 50): " + search(a, 50));
System.out.println("search(a, 77): " + search(a, 77));
System.out.println("search(a, 100): " + search(a, 100));
}
public static int search(int[] a, int x) {
// POSTCONDITIONS: returns i;
// if i >= 0, then a[i] == x; otherwise i == -1;
int lo = 0;
int hi = a.length;
while (lo < hi) { // step 1
// INVARIANT: if a[j]==x then lo <= j < hi; // step 3
int i = (lo + hi)/2; // step 4
if (a[i] == x) {
return i; // step 5
} else if (a[i] < x) {
lo = i+1; // step 6
} else {
hi = i; // step 7
}
}
return -1; // step 2
}
}(4)反转
void reverse(int[] a) {
int n = a.length;
if (n < 2) {
return;
}
for (int i = 0; i < n/2; i++) {
swap(a, i, n-i-1);
}
}
void swap(int[] a, int i, int j) {
// swaps a[i] with a[j]:
int ai = a[i];
int aj = a[j];
a[i] = aj;
a[j] = ai;
}二.链式数据结构
(1)插入有序数组
void insert(int[] a, int n, int x) {
// preconditions: a[0] <= ... <= a[n-1], and n < a.length;
// postconditions: a[0] <= ... <= a
, and x is among them;
int i = 0;
while (i < n && a[i] <= x) {
++i;
}
System.arraycopy(a, i, a, i+1, n-i); // copies a[i..n) into a[i+1..n+1)
a[i] = x;
}(2)单向链表插入和删除
class Node {
int data;
Node next;
Node(int data) {
this.data = data;
}
}
Node insert(Node start, int x) {
if (start == null || start.data > x) {
start = new Node(x,start);
return start;
}
Node p=start;
while (p.next != null) {
if (p.next.data > x) break;
p = p.next;
}
p.next = new Node(x,p.next);
return start;
}
Node delete(Node start, int x) {
if (start == null || start.data > x) { // x is not in the list
return start;
} else if (start.data == x) { // x is the first element in the list
return start.next;
}
for (Node p = start; p.next != null; p = p.next) {
if (p.next.data > x) {
break; // x is not in the list
} else if (p.next.data == x) { // x is in the p.next node
p.next = p.next.next; // delete it
break;
}
}
return start;
}三.JAVA容器类

jdk1.4容器类关系图
虚线框表示接口。
实线框表示实体类。
粗线框表示最常用的实体类。
点线的箭头表示实现了这个接口。
实线箭头表示类可以制造箭头所指的那个类的对象。
容器类持有对象方式
1, Collection:只允许每个位置上放一个对象。它包括“以一定顺序持有一组对象”的List,以及“只能允许添加不重复对象”的Set。你可以用add()方法向Collection对象中加元素。
2, Map:一组以“键-值”(key-value)的形式出现的pair,Map也不接受重复的key值。你可以用put()方法往Map里面加元素。
Collection 和 Collections的区别
Collections是个java.util下的类,它包含有各种有关集合操作的静态方法,实现对各种集合的搜索、排序、线程安全化等操作。
Collection是个java.util下的接口,它是各种集合结构的父接口。继承自它的接口主要有Set 和List.
无论使用哪种Set,都需要定义equals(),但是只有在“要把对象放进HashSet”的情况下,才需要定义hashCode().因为HashSet是我们通常用的Set,所以通常也需要定义hashCode()。作为一种编程风格,你应该在覆写equals()的同时把hashCode()也覆写了。
LinkedList类
LinkedList使用双向链表来实现的,也就是每个对象,除了保存数据之外,还保存着在它前面和后面的那两个对象的reference,允许null元素。此外LinkedList提供额外的get,remove,insert方法在LinkedList的首部或尾部。这些操作使LinkedList可被用作堆栈(stack),队列(queue)或双向队列(deque)。
注意LinkedList没有同步方法。如果多个线程同时访问一个List,则必须自己实现访问同步。一种解决方法是在创建List时构造一个同步的List:
List list = Collections.synchronizedList(new LinkedList(...));
ArrayList类
ArrayList擅长对元素进行随机访问,可以把它想成“一个能够自动扩展的数组”。它允许所有元素,包括null。ArrayList没有同步。
size,isEmpty,get,set方法运行时间为常数。但是add方法开销为分摊的常数,添加n个元素需要O(n)的时间。其他的方法运行时间为线性。
每个ArrayList实例都有一个容量(Capacity),即用于存储元素的数组的大小。这个容量可随着不断添加新元素而自动增加,但是增长算法并没有定义。当需要插入大量元素时,在插入前可以调用ensureCapacity方法来增加ArrayList的容量以提高插入效率。
和LinkedList一样,ArrayList也是非同步的(unsynchronized)。
Vector类(legacy,遗留的)
Vector非常类似ArrayList。
ArrayList和Vector的区别
一.同步性:Vector是线程安全的,也就是说是同步的,而ArrayList是线程序不安全的,不是同步的。由Vector创建的Iterator,虽然和ArrayList创建的Iterator是同一接口,但是,因为Vector是同步的,当一个Iterator被创建而且正在被使用,另一个线程改变了Vector的状态(例如,添加或删除了一些元素),这时调用Iterator的方法时将抛出ConcurrentModificationException,因此必须捕获该异常。
二.数据增长:当需要增长时,Vector默认增长为原来一培,而ArrayList却是原来的一半.
Stack 类(legacy,遗留的)
Stack继承自Vector,实现一个后进先出的堆栈。Stack提供5个额外的方法使得Vector得以被当作堆栈使用。基本的push和pop方法,还有peek方法得到栈顶的元素,empty方法测试堆栈是否为空,search方法检测一个元素在堆栈中的位置。Stack刚创建后是空栈。
iterator()方法
Enumeration接口定义了可以对一个对象的类集中的元素进行枚举(一次获得一个)的方法。这个接口尽管没有被摈弃,但已经被Iterator所替代。
不论Collection的实际类型如何,它都支持一个iterator()的方法,该方法返回一个迭代子,使用该迭代子即可逐一访问Collection中每一个元素。
iterator()方法不必知道对象序列的具体实现,就能在序列中移动,选取其中的对象
用iterator()方法叫容器传给你一个Iterator对象。
List simple=new ArrayList();Iterator e= simple.iterator();
第一次调用Iterator的next()方法的时候,它会传给你序列中的第一个元素。
用next()方法获取序列中的下一个对象。
用hasNext()方法查询序列中是否还有其它对象。
用remove()方法删除迭代器所返回的最后一个元素。
Hashtable类(legacy,遗留的)
Hashtable继承Map接口,实现一个key-value映射的哈希表。任何非空(non-null)的对象都可作为key或者value。
添加数据使用put(key, value),取出数据使用get(key),这两个基本操作的时间开销为常数。
Hashtable通过initial capacity和load factor两个参数调整性能。通常缺省的load factor 0.75较好地实现了时间和空间的均衡。增大load factor可以节省空间但相应的查找时间将增大,这会影响像get和put这样的操作。
使用Hashtable的简单示例如下,将1,2,3放到Hashtable中,他们的key分别是”one”,”two”,”three”:
Hashtable numbers = new Hashtable();
numbers.put(“one”, new Integer(1));
numbers.put(“two”, new Integer(2));
numbers.put(“three”, new Integer(3));
要取出一个数,比如2,用相应的key:
Integer n = (Integer)numbers.get(“two”);
System.out.println(“two = ” + n);
由于作为key的对象将通过计算其散列函数来确定与之对应的value的位置,因此任何作为key的对象都必须实现hashCode和equals方法。
hashCode()是Object根类的方法(缺省情况下返回对象的内存地址),因此所有java对象都能生成hash code。
equals()是Object根类的方法,只是简单地比较两个对象的地址。
如果你用自定义的类当作key的话,要相当小心,按照散列函数的定义,如果两个对象相同,即obj1.equals(obj2)=true,则它们的hashCode必须相同,但如果两个对象不同,则它们的hashCode不一定不同,如果两个不同对象的hashCode相同,这种现象称为冲突,冲突会导致操作哈希表的时间开销增大,所以尽量定义好的hashCode()方法,能加快哈希表的操作。
如果相同的对象有不同的hashCode,对哈希表的操作会出现意想不到的结果(期待的get方法返回null),要避免这种问题,只需要牢记一条:要同时复写equals方法和hashCode方法,而不要只写其中一个。
HashMap类
HashMap和Hashtable类似,不同之处在于HashMap是非同步的,并且允许null,即null value和null key。但是将HashMap视为Collection时(values()方法可返回Collection),其迭代子操作时间开销和HashMap的容量成比例。因此,如果迭代操作的性能相当重要的话,不要将HashMap的初始化容量设得过高,或者load factor过低。
HashMap和Hashtable的区别
HashTable的应用非常广泛,HashMap是Hashtable的轻量级实现(非线程安全的实现),HashMap是新框架中用来代替HashTable的类,也就是说建议使用HashMap,不要使用HashTable。
1.HashTable的方法是同步的,HashMap未经同步,所以在多线程场合要手动同步HashMap这个区别就像Vector和ArrayList一样。
2.HashTable不允许null值(key和value都不可以),HashMap允许null值(key和value都可以)。
3.HashMap把Hashtable的contains方法去掉了,改成containsvalue和containsKey。因为contains方法容易让人引起误解。
4.HashTable使用Enumeration,HashMap使用Iterator。
hashCode()与equals()方法
hashCode()是Object根类的方法(缺省情况下返回对象的内存地址),因此所有java对象都能生成hash code。HashMap利用对象的hashCode()来进行快速的查找。
equals()是Object根类的方法,只是简单地比较两个对象的地址。
无论使用哪种Set,都需要定义equals(),但是只有在“要把对象放进HashSet”的情况下,才需要定义hashCode().因为HashSet是我们通常用的Set,所以通常也需要定义hashCode()。
如果你不覆写键的hashCode()和equals()的话,散列数据结构(HashSet,HashMap,LinkedHashSet,LinkedHashMap)就没法正确的处理键。
转载:http://blog.csdn.net/hsttmht/article/details/6989911
四.二叉树
public class BinaryTree<E> extends AbstractCollection {
protected E root;
protected BinaryTree<E> left, right, parent;
protected int size;
public BinaryTree() {
}
public BinaryTree(E root) {
this.root = root;
size = 1;
}
public BinaryTree(E root, BinaryTree<E> left, BinaryTree<E> right) {
this(root);
if (left != null) {
this.left = left;
left.parent = this;
size += left.size();
}
if (right != null) {
this.right = right;
right.parent = this;
size += right.size();
}
}
}
public class BinaryTree<E> extends AbstractCollection {
// insert lines 2-49 from Example 11.20 on page 212
public Iterator iterator() {
return new PreOrder();
}
abstract public class BinaryTreeIterator implements Iterator {
protected boolean rootDone;
protected Iterator lIt, rIt; // child iterators
public boolean hasNext() {
return !rootDone || lIt != null && lIt.hasNext()
|| rIt != null && rIt.hasNext();
}
abstract public Object next();
public void remove() {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException();
}
}
public class PreOrder extends BinaryTreeIterator {
public PreOrder() {//前序
if (left != null) {
lIt = left.new PreOrder();
}
if (right != null) {
rIt = right.new PreOrder();
}
}
public Object next() {
if (!rootDone) {
rootDone = true;
return root;
}
if (lIt != null && lIt.hasNext()) {
return lIt.next();
}
if (rIt != null && rIt.hasNext()) {
return rIt.next();
}
return null;
}
}
public class InOrder extends BinaryTreeIterator {
public InOrder() {//中序遍历
if (left != null) {
lIt = left.new InOrder();
}
if (right != null) {
rIt = right.new InOrder();
}
}
public Object next() {
if (lIt != null && lIt.hasNext()) {
return lIt.next();
}
if (!rootDone) {
rootDone = true;
return root;
}
if (rIt != null && rIt.hasNext()) {
return rIt.next();
}
return null;
}
}
public class PostOrder extends BinaryTreeIterator {//后序遍历
public PostOrder() {
if (left != null) {
lIt = left.new PostOrder();
}
if (right != null) {
rIt = right.new PostOrder();
}
}
public Object next() {
if (lIt != null && lIt.hasNext()) {
return lIt.next();
}
if (rIt != null && rIt.hasNext()) {
return rIt.next();
}
if (!rootDone) {
rootDone = true;
return root;
}
return null;
}
}
public class LevelOrder extends BinaryTreeIterator {//层次遍历
Queue<BinaryTree<E>> queue = new ArrayDeque<BinaryTree<E>>();
public boolean hasNext() {
return (!rootDone || !queue.isEmpty());
}
public Object next() {
if (!rootDone) {
if (left != null) {
queue.add(left);
}
if (right != null) {
queue.add(right);
}
rootDone = true;
return root;
}
if (!queue.isEmpty()) {
BinaryTree<E> tree = queue.remove();
if (tree.left != null) {
queue.add(tree.left);
}
if (tree.right != null) {
queue.add(tree.right);
}
return tree.root;
}
return null;
}
}
}tree = [A, B, D, G, E, C, F, H, I]
PreOrder Traversal: A B D G E C F H I
InOrder Traversal: D G B E A H F I C
PostOrder Traversal: G D E B H I F C A
LevelOrder Traversal: A B C D E F G H I
五.排序
(1)冒泡排序
private static void swap(int[] a, int i, int j) {
if (i == j) {
return;
}
int temp=a[j];
a[j] = a[i];
a[i] = temp;
}
}
public static void sort(int[] a) {
for (int i = a.length-1; i > 0; i--) { // step 1
for (int j = 0; j < i; j++) { // step 2
if (a[j] > a[j+1]) {
swap(a, j, j+1); // step 3
}
}
}(2)快速排序
public static void sort(int[] a) {
sort(a, 0, a.length);
}
private static void sort(int[] a, int p, int q) {
if (q - p < 2) {
return;
}
int m = partition(a, p, q); // step 2
sort(a, p, m); // step 4
sort(a, m+1, q); // step 5
private static int partition(int[] a, int p, int q) {
int pivot = a[p], i = p, j = q; // steps 1-2
while (i < j) { // step 3
while (i < j && a[--j] >= pivot) ; // step 4
if (i < j) {
a[i] = a[j]; // step 5
}
while (i < j && a[++i] <= pivot) ; // step 6
if (i < j) {
a[j] = a[i]; // step 7
}
}
a[j] = pivot; // step 8
return j;
}还有其他排序方式,选择排序,堆排序。。。
相关文章推荐
- Java2实用教程(第二版)程序代码——第二十六章 常见数据结构的Java实现
- 多种数据结构的Java实现(精)
- 数据结构的Java实现——顺序表
- java 利用 LinkedList类实现 数据结构 栈.......
- 严蔚敏《数据结构》中迷宫算法java实现
- 数据结构之应用 "栈(Stack)" 实现: 解析算术表达式及计算求值 (C#/Java) (转载)
- java数据结构之LinkedQueue(用链表实现的双端单向队列)
- Java数据结构之简单链表的定义与实现方法示例
- Java中如何实现Tree的数据结构算法
- java 利用 LinkedList类实现 数据结构 栈.......
- Java,数据结构,线性表,顺序实现
- java数据结构,实现栈/队列
- 利用java实现数据结构中常用的插入排序和快速排序算法
- Java中常用数据结构的实现类 Collection和Map
- 数据结构(LinkedList的java实现)
- 利用java实现数据结构中常用的插入排序和快速排序算法
- 多种数据结构的Java实现
- Java中常用数据结构的实现类 Collection和Map
- 数据结构的Java实现——栈和队列
- Java中常用数据结构的实现类 Collection和Map
