Beginner’s Guide to ALE and IDocs – a step-by-step approach
2015-02-05 11:04
671 查看
http://www.riyaz.net/sap/beginners-guide-to-ale-and-idocs-a-step-by-step-approach/18/
This article will help you understand the basics of ALE and IDocs via a simple do-it-yourself example. We will create a custom IDoc in one SAP system and then post some business data through it to another SAP system. Business data will be picked up from custom
data dictionary tables.
ALE – Application Link Enabling is a mechanism by which SAP systems communicate with each other and with non-SAP EDI subsystems. Thus it helps integration of distributed systems. It supports fail-safe delivery which implies that sender system does not have
to worry about message not reaching the source due to unavoidable situations. ALE can be used for migration and maintenance of master data as well as for exchanging transactional data.
The messages that are exchanged are in the form of IDocs or Intermediate Documents. IDocs act like a container or envelope for the application data. An IDOC is created as a result of execution of an Outbound ALE. In an Inbound ALE an IDOC serves as an input
to create application document. In the SAP system IDocs are stored in the database tables. They can be used for SAP to SAP and SAP to non-SAP process communication as long as the participating processes can understand the syntax and semantics of the data.
Complete documentation on IDOC is obtained by using transaction WE60.
Every IDoc has exactly one control record along with a number of data records and status records. Control record has the details of sender/receiver and other control information. Data records contain the actual business data to be exchanged while the status
records are attached to IDoc throughout the process as the IDoc moves from one step to other.
Now, let us understand the ALE Configuration by means of an example scenario below:
The Scenario

Data from custom tables (created in customer namespace) is to be formatted into an IDoc and sent from one SAP R/3
system to another using ALE service. We need to have two instances of SAP R/3 systems or we can simulate this on two clients of the same SAP R/3 system.
Create three tables as shown below.
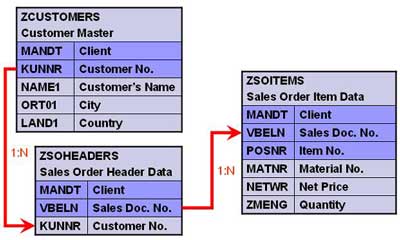
Creating Custom IDoc type and Message type
All the objects created should be present on both source as well as target system(s).
1. Create segments – Transaction WE31
Create a segment ZRZSEG1
Add all fields of table ZCUSTOMERS to it
Save the segment and go back
Release it using the menu path Edit -> Set Release
Similarly create two more segments given below
Seg. ZRZSEG2 – to hold all fields of table ZSOHEADERS
Seg. ZRZSEG3 – to hold all fields of table ZSOITEMS
2. Create Basic IDoc type – Transaction WE30
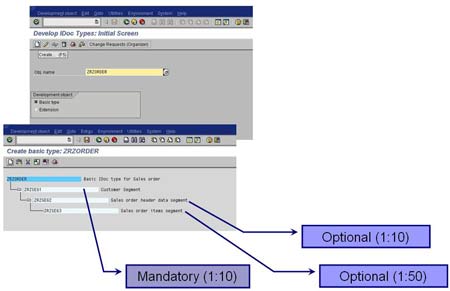
Create a Basic type ZRZORDER
Add the created segments in the hierarchy shown
Maintain attributes for each of the segments
Save the object and go back
Release the object using the menu path Edit -> Set Release
3. Create/Assign Message type – Transactions WE81/WE82
Go to WE81
Create a new Message type ZRZSO_MT
Save the object
Go to WE82 and create new entry
Assign the message type ZRZSO_MT to the basic type ZRZORDER
Also specify the Release Version
Save the object
Thus we have defined the IDoc structure which will hold the data to be transferred. In the next
part of the article we will understand the outbound settings, i.e. the settings to be done in the source system.
Beginner’s Guide to ALE and IDocs – a step-by-step approach
This article will help you understand the basics of ALE and IDocs via a simple do-it-yourself example. We will create a custom IDoc in one SAP system and then post some business data through it to another SAP system. Business data will be picked up from customdata dictionary tables.
ALE – Application Link Enabling is a mechanism by which SAP systems communicate with each other and with non-SAP EDI subsystems. Thus it helps integration of distributed systems. It supports fail-safe delivery which implies that sender system does not have
to worry about message not reaching the source due to unavoidable situations. ALE can be used for migration and maintenance of master data as well as for exchanging transactional data.
The messages that are exchanged are in the form of IDocs or Intermediate Documents. IDocs act like a container or envelope for the application data. An IDOC is created as a result of execution of an Outbound ALE. In an Inbound ALE an IDOC serves as an input
to create application document. In the SAP system IDocs are stored in the database tables. They can be used for SAP to SAP and SAP to non-SAP process communication as long as the participating processes can understand the syntax and semantics of the data.
Complete documentation on IDOC is obtained by using transaction WE60.
Every IDoc has exactly one control record along with a number of data records and status records. Control record has the details of sender/receiver and other control information. Data records contain the actual business data to be exchanged while the status
records are attached to IDoc throughout the process as the IDoc moves from one step to other.
Now, let us understand the ALE Configuration by means of an example scenario below:
The Scenario

Data from custom tables (created in customer namespace) is to be formatted into an IDoc and sent from one SAP R/3
system to another using ALE service. We need to have two instances of SAP R/3 systems or we can simulate this on two clients of the same SAP R/3 system.
Create three tables as shown below.

Creating Custom IDoc type and Message type
All the objects created should be present on both source as well as target system(s).
1. Create segments – Transaction WE31
Create a segment ZRZSEG1
Add all fields of table ZCUSTOMERS to it
Save the segment and go back
Release it using the menu path Edit -> Set Release
Similarly create two more segments given below
Seg. ZRZSEG2 – to hold all fields of table ZSOHEADERS
Seg. ZRZSEG3 – to hold all fields of table ZSOITEMS
2. Create Basic IDoc type – Transaction WE30

Create a Basic type ZRZORDER
Add the created segments in the hierarchy shown
Maintain attributes for each of the segments
Save the object and go back
Release the object using the menu path Edit -> Set Release
3. Create/Assign Message type – Transactions WE81/WE82
Go to WE81
Create a new Message type ZRZSO_MT
Save the object
Go to WE82 and create new entry
Assign the message type ZRZSO_MT to the basic type ZRZORDER
Also specify the Release Version
Save the object
Thus we have defined the IDoc structure which will hold the data to be transferred. In the next
part of the article we will understand the outbound settings, i.e. the settings to be done in the source system.
相关文章推荐
- Beginner’s Guide to ALE and IDocs – Part III
- Beginner’s Guide to ALE and IDocs – Part II
- Step By Step Guide to configure the “Replicating directory changes” for SharePoint 2010 and 2013
- How to Read and Understand a Scientific Paper: A Step-by-Step Guide for Non-Scientists
- HOW TO CONFIGURE LINUX DNS SERVER STEP BY STEP GUIDE EXAMPLE AND IMPLEMENTATION
- Mac OS X - A step-by-step guide to installing Go and building your first web service
- Step By Step Guide To Create Physical Standby Database Using RMAN Backup and Restore
- Step by step guide to set up master and slave machines
- Step by step guide to set up master and slave machines(转)
- A step-by-step guide to the use of the Intel OpenCV library and the Microsoft DirectShow technology
- Step By Step Guide To Create Physical Standby Database Using RMAN Backup and Restore (Doc ID 469493.
- Counter Hack Reloaded: A Step-by-Step Guide to Computer Attacks and Effective Defenses
- Step by step guide to set up master and slave machines on Windows
- THE DEAD-SIMPLE STEP-BY-STEP GUIDE FOR FRONT-END DEVELOPERS TO GETTING UP AND RUNNING WITH NODE.JS,
- The Beginner's Guide to Broadband and Wireless Internet
- A Simple Step-By-Step Guide To Apache Tomcat SSL Configuration
- Step-By-Step Guide To Create Physical Standby On Normal File System For ASM Primary using RMAN
- Step-by-Step Guide to Portal Development for Microsoft Dynamics CRM - 摘自网络
- Step by Step Guide to Add a SQL Job in SQL Server 2005
- 转 Step-by-step Introduction to Delegates and Lambda Expressions
