B. Fox And Two Dots
2015-02-03 15:53
316 查看
B. Fox And Two Dots
time limit per test
2 seconds
memory limit per test
256 megabytes
input
standard input
output
standard output
Fox Ciel is playing a mobile puzzle game called "Two Dots". The basic levels are played on a board of size n × m cells, like this:
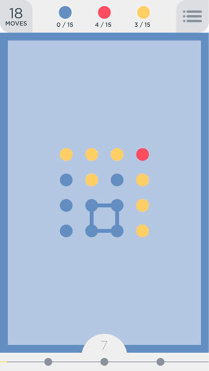
Each cell contains a dot that has some color. We will use different uppercase Latin characters to express different colors.
The key of this game is to find a cycle that contain dots of same color. Consider 4 blue dots on the picture forming a circle as an example. Formally, we call a sequence of dots d1, d2, ..., dk a cycle if and only if it meets the following condition:
These k dots are different: if i ≠ j then di is different from dj.
k is at least 4.
All dots belong to the same color.
For all 1 ≤ i ≤ k - 1: di and di + 1 are adjacent. Also, dk and d1 should also be adjacent. Cells x and y are called adjacent if they share an edge.
Determine if there exists a cycle on the field.
Input
The first line contains two integers n and m (2 ≤ n, m ≤ 50): the number of rows and columns of the board.
Then n lines follow, each line contains a string consisting of m characters, expressing colors of dots in each line. Each character is an uppercase Latin letter.
Output
Output "Yes" if there exists a cycle, and "No" otherwise.
Sample test(s)
input
output
input
output
input
output
input
output
input
output
Note
In first sample test all 'A' form a cycle.
In second sample there is no such cycle.
The third sample is displayed on the picture above ('Y' = Yellow, 'B' = Blue, 'R' = Red).
time limit per test
2 seconds
memory limit per test
256 megabytes
input
standard input
output
standard output
Fox Ciel is playing a mobile puzzle game called "Two Dots". The basic levels are played on a board of size n × m cells, like this:

Each cell contains a dot that has some color. We will use different uppercase Latin characters to express different colors.
The key of this game is to find a cycle that contain dots of same color. Consider 4 blue dots on the picture forming a circle as an example. Formally, we call a sequence of dots d1, d2, ..., dk a cycle if and only if it meets the following condition:
These k dots are different: if i ≠ j then di is different from dj.
k is at least 4.
All dots belong to the same color.
For all 1 ≤ i ≤ k - 1: di and di + 1 are adjacent. Also, dk and d1 should also be adjacent. Cells x and y are called adjacent if they share an edge.
Determine if there exists a cycle on the field.
Input
The first line contains two integers n and m (2 ≤ n, m ≤ 50): the number of rows and columns of the board.
Then n lines follow, each line contains a string consisting of m characters, expressing colors of dots in each line. Each character is an uppercase Latin letter.
Output
Output "Yes" if there exists a cycle, and "No" otherwise.
Sample test(s)
input
3 4 AAAA ABCA AAAA
output
Yes
input
3 4 AAAA ABCA AADA
output
No
input
4 4 YYYR BYBY BBBY BBBY
output
Yes
input
7 6 AAAAAB ABBBAB ABAAAB ABABBB ABAAAB ABBBAB AAAAAB
output
Yes
input
2 13 ABCDEFGHIJKLM NOPQRSTUVWXYZ
output
No
Note
In first sample test all 'A' form a cycle.
In second sample there is no such cycle.
The third sample is displayed on the picture above ('Y' = Yellow, 'B' = Blue, 'R' = Red).
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cmath>
#include <string>
#include <vector>
#include <set>
#include <map>
#include <queue>
#include <stack>
using namespace std;
const int INF = 0x7fffffff;
const double EXP = 1e-8;
const int MS = 55;
int n, m, cnt;
char cell[MS][MS];
int vis[MS][MS];
int dir[4][2] = { 0, 1, 1, 0, 0, -1, -1, 0 };
bool dfs(char c, int sx, int sy, int x, int y)
{
if (sx == x&&sy == y&&vis[sx][sy])
{
return cnt >= 4 ? true : false;
}
vis[x][y] = 1;
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++)
{
int tx = x + dir[i][0];
int ty = y + dir[i][1];
if (tx >= 0 && tx < n&&ty >= 0 && ty < m&&cell[tx][ty] == c&&vis[tx][ty] == 0 || (tx == sx&&ty == sy))
{
cnt++;
if (dfs(c, sx, sy, tx, ty))
return true;
cnt--;
}
}
return false;
}
bool solve()
{
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < m; j++)
{
memset(vis, 0, sizeof(vis));
cnt = 0;
if (dfs(cell[i][j], i, j, i, j))
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
int main()
{
cin >> n >> m;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
cin >> cell[i];
if (solve())
cout << "Yes" << endl;
else
cout << "No" << endl;
return 0;
}
相关文章推荐
- Codeforces Round #290 (Div. 2)B. Fox And Two Dots(dfs)
- 【codeforce-510B】fox and two dots
- Fox And Two Dots
- Fox And Two Dots(DFS)
- B. Fox And Two Dots
- Codeforces Round #290(Div.2) B.Fox And Two Dots
- 【Codeforces】-510B-Fox And Two Dots(dfs)
- Fox And Two Dots
- codeforces#290 B&&510 B Fox And Two Dots(简单dfs)
- Fox And Two Dots
- Fox And Two Dots (迷宫)
- 【CodeForces】510B - Fox And Two Dots(bfs)
- Codeforces Round #290 (Div. 2) B. Fox And Two Dots(DFS)
- codeforces#290 B&&510 B Fox And Two Dots(简单dfs)
- codeforces 510.B Fox And Two Dots (DFS好题)
- codeforces-510B-Fox And Two Dots【DFS】
- Fox And Two Dots
- B. Fox And Two Dots———简单DFS
- codeforce-B. Fox And Two Dots
- Codeforces-----510B Fox And Two Dots 搜索
