HDU 5120 Intersection(圆的面积交)
2015-01-17 20:00
375 查看
题目大意:给你两个圆环,让你求出来圆环的面积交,需要用到圆的面积交,然后容斥一下,就可以得到圆环的面积交。画一下图就会很清晰。
Total Submission(s): 526 Accepted Submission(s): 226
[align=left]Problem Description[/align]
Matt is a big fan of logo design. Recently he falls in love with logo made up by rings. The following figures are some famous examples you may know.

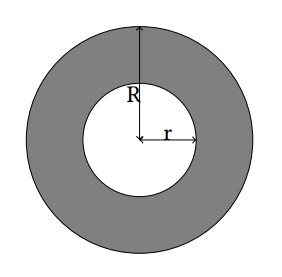
A ring is a 2-D figure bounded by two circles sharing the common center. The radius for these circles are denoted by r and R (r < R). For more details, refer to the gray part in the illustration below.
Matt just designed a new logo consisting of two rings with the same size in the 2-D plane. For his interests, Matt would like to know the area of the intersection of these two rings.
[align=left]Input[/align]
The first line contains only one integer T (T ≤ 105), which indicates the number of test cases. For each test case, the first line contains two integers r, R (0 ≤ r < R ≤ 10).
Each of the following two lines contains two integers xi, yi (0 ≤ xi, yi ≤ 20) indicating the coordinates of the center of each ring.
[align=left]Output[/align]
For each test case, output a single line “Case #x: y”, where x is the case number (starting from 1) and y is the area of intersection rounded to 6 decimal places.
[align=left]Sample Input[/align]
2
2 3
0 0
0 0
2 3
0 0
5 0
[align=left]Sample Output[/align]
Case #1: 15.707963
Case #2: 2.250778
[align=left]Source[/align]
2014ACM/ICPC亚洲区北京站-重现赛(感谢北师和上交)
Intersection
Time Limit: 4000/4000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 512000/512000 K (Java/Others)Total Submission(s): 526 Accepted Submission(s): 226
[align=left]Problem Description[/align]
Matt is a big fan of logo design. Recently he falls in love with logo made up by rings. The following figures are some famous examples you may know.

A ring is a 2-D figure bounded by two circles sharing the common center. The radius for these circles are denoted by r and R (r < R). For more details, refer to the gray part in the illustration below.

Matt just designed a new logo consisting of two rings with the same size in the 2-D plane. For his interests, Matt would like to know the area of the intersection of these two rings.
[align=left]Input[/align]
The first line contains only one integer T (T ≤ 105), which indicates the number of test cases. For each test case, the first line contains two integers r, R (0 ≤ r < R ≤ 10).
Each of the following two lines contains two integers xi, yi (0 ≤ xi, yi ≤ 20) indicating the coordinates of the center of each ring.
[align=left]Output[/align]
For each test case, output a single line “Case #x: y”, where x is the case number (starting from 1) and y is the area of intersection rounded to 6 decimal places.
[align=left]Sample Input[/align]
2
2 3
0 0
0 0
2 3
0 0
5 0
[align=left]Sample Output[/align]
Case #1: 15.707963
Case #2: 2.250778
[align=left]Source[/align]
2014ACM/ICPC亚洲区北京站-重现赛(感谢北师和上交)
#include <algorithm>
#include <iostream>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <iomanip>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string>
#include <queue>
#include <cmath>
#include <math.h>
#include <time.h>
#include <stack>
#include <map>
#include <set>
#define eps 1e-8
///#define LL long long
#define LL __int64
#define INF 0x3f3f3f
#define PI acos(-1)
#define mod 1000000007
using namespace std;
struct Point
{
double x, y;
};
double Distance(Point a, Point b)
{
return sqrt(((a.x-b.x)*(a.x-b.x) + (a.y-b.y)*(a.y-b.y))*1.0);
}
double area_of_overlap(Point c1, double r1, Point c2, double r2)
{
double a = Distance(c1, c2);
double b = r1;
double c = r2;
if((a >= b+c)) return 0.0;
if(a < abs(b-c))
{
double r = min(r1, r2);
return PI*r*r;
}
double cta1 = acos((a*a+b*b-c*c)/2.0/(a*b)),
cta2 = acos((a*a+c*c-b*b)/2.0/(a*c));
double s1 = r1*r1*cta1
-r1*r1*sin(cta1)*(a*a+b*b-c*c)/2/(a*b);
double s2 = r2*r2*cta2
-r2*r2*sin(cta2)*(a*a+c*c-b*b)/2/(a*c);
return s1+s2;
}
int main()
{
int T;
int Case = 1;
scanf("%d",&T);
while(T--)
{
double r1, r2;
Point a, b;
scanf("%lf %lf",&r1, &r2);
scanf("%lf %lf", &a.x, &a.y);
scanf("%lf %lf", &b.x, &b.y);
printf("Case #%d: ",Case++);
if(a.x == b.x && a.y == b.y)
{
printf("%.6lf\n",PI*(r2*r2-r1*r1));
continue;
}
double sum = 0;
sum += area_of_overlap(a, r2, b, r2);
sum -= area_of_overlap(a, r1, b, r2);
sum -= area_of_overlap(a, r2, b, r1);
sum += area_of_overlap(a, r1, b, r1);
printf("%.6lf\n",sum);
}
return 0;
}
/*
5
1 4
0 0 0 6
*/
相关文章推荐
- HDU-5120-Intersection【几何-相交圆面积】
- HDU 5120 Intersection——两圆面积并
- hdu 5120 Intersection (圆相交面积模板)
- hdu 5120 Intersection(求相交圆的面积)
- hdu 5120 Intersection(两圆相交面积)(模板)
- hdu 5120 Intersection (圆面积交)
- HDU 5120 Intersection 圆相交面积
- HDU 5120 Intersection 求两圆相交面积模板
- hdu 5120 Intersection 圆环面积交
- HDU5120 Intersection 【求圆的面积交】
- hdu 5120 Intersection 两环面积交
- hdu 5120 Intersection(求相交圆的面积)
- hdu 5120 Intersection (容斥原理+圆的相交面积模板)
- Hdu 5120 Intersection【计算圆环相交面积】
- hdu 5120 Intersection(求相交环面积)
- HDU 5120 Intersection (圆的面积交)
- hdu 5120 Intersection 两个圆的面积交
- hdoj 5120 Intersection 圆环面积求交
- HDU 5120 Intersection
- HDOJ 5120 Intersection【求圆与圆的交叉部分面积】
