基数排序
2015-01-17 16:47
267 查看
1.基数排序思想
基数排序(Radix Sorting) 又称为桶排序或数字排序:按待排序记录的关键字的组成成分(或“位”)进行排序。
基数排序和前面的各种内部排序方法完全不同,不需要进行关键字的比较和记录的移动。
借助于多关键字排序思想实现单逻辑关键字的排序。
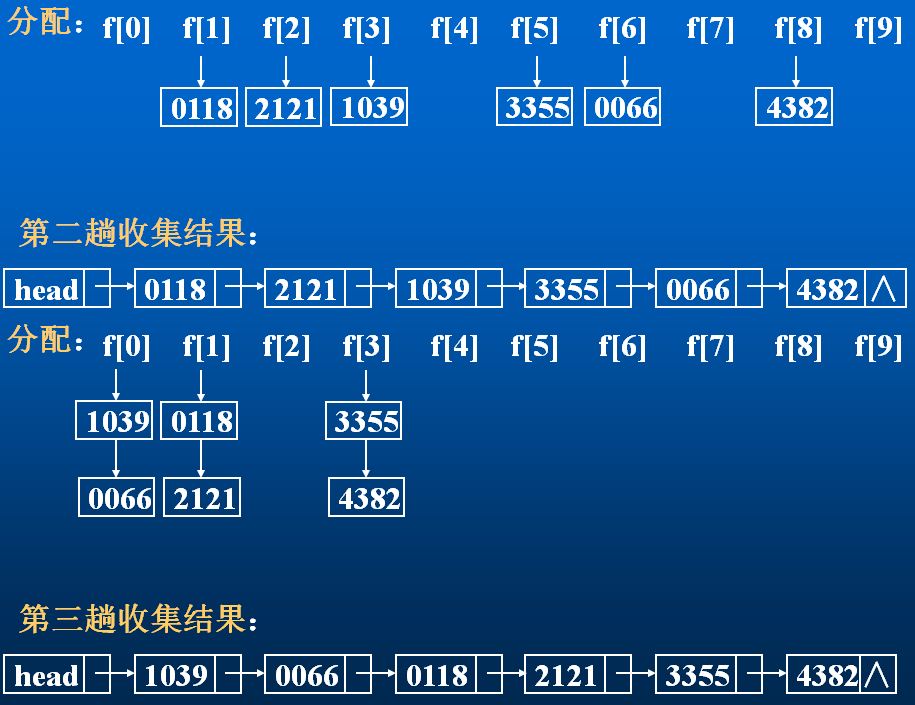
把带排序的数字看成‘0’-‘9’的字符串组成,从低位到高位,或者从高位到低位 根据数字先分配,
然后重新放一起。(字符串,带负数的暂时不讨论)
MSD(最高位优先法) LSD(最低位优先法)
2.排序示例


3.算法代码(LSD)
#include<stdio.h>
#include<string.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
int array[1011]; //待排数据
int temp[1011];//用于存放基数不同的数据
int count[11];//做下标用
int bits[5]={1,1,10,100,1000};//用于求各个位数上的数字
int MAXbit;//最高位数
int Figure(int a,int po)
{
return (a/bits[po])%10;
}
void Radix_Sort(int array[],int MAXbit,int n)
{
int i,j;
int t;
for(i=1;i<=MAXbit;i++)
{
memset(count,0,sizeof(count));
memset(temp,0,sizeof(temp));
for(j=0;j<n;j++)
{
count[Figure(array[j],i)]++;
}
for(j=1;j<=9;j++)
{
count[j]+=count[j-1];
}
for(j=n-1;j>=0;j--)
{
t=Figure(array[j],i);
temp[count[t]-1]=array[j];
count[t]--;
}
for(j=0;j<n;j++)
{
array[j]=temp[j];
}
}
}
int main()
{
int n;
int i;
while(scanf("%d",&n)!=EOF)
{
memset(array,0,sizeof(array));
for(i=0;i<n;i++)
{
scanf("%d",&array[i]);
}
Radix_Sort(array,3,n);
for(i=0;i<n;i++)
{
printf("%d ",array[i]);
}
printf("\n");
}
return 0;
}以上代码仅考虑最高3位数的情况。4.算法分析
设有n个待排序记录,关键字位数为d,每位有r种取值。则排序的趟数是d,排序的时间复杂度为: O(d(n+r)),空间复杂度为:O(n+r)。
相关文章推荐
- 常用排序算法之计数排序,基数排序与桶排序
- 基数排序
- 基数排序
- 分配排序---箱排序,基数排序与桶排序及排序选择方法
- C++基数排序(包含计数排序)
- 程序员必知的8大排序(四)-------归并排序,基数排序(java实现)
- 三种线性排序算法 计数排序、桶排序与基数排序
- 《算法导论》CLRS算法C++实现(六)P100 基数排序
- 【CLRS】《算法导论》读书笔记(三):计数排序(Counting sort)、基数排序(Radix sort)和桶排序(Bucket sort)
- 基数排序
- 三种线性排序算法 计数排序、桶排序与基数排序
- 基数排序
- 重提基数排序
- 基于静态链的基数排序
- 【数据结构与算法】内部排序之五:计数排序、基数排序和桶排序(含完整源码)
- 微软笔试题——基数排序
- 基数排序
- 计数,基数排序
- 基数排序
- 基数排序
