Codeforces #282 div2 ABC
2014-12-14 16:15
363 查看
A. Digital Counter
time limit per test
1 second
memory limit per test
256 megabytes
input
standard input
output
standard output
Malek lives in an apartment block with 100 floors numbered from
0 to 99. The apartment has an elevator with a digital counter showing the floor that the elevator is currently on. The elevator shows each digit of a number with
7 light sticks by turning them on or off. The picture below shows how the elevator shows each digit.

One day when Malek wanted to go from floor 88 to floor
0 using the elevator he noticed that the counter shows number
89 instead of 88. Then when the elevator started moving the number on the counter changed to
87. After a little thinking Malek came to the conclusion that there is only one explanation for this: One of the sticks of the counter was broken. Later that day Malek was thinking about the broken stick and suddenly he came up
with the following problem.
Suppose the digital counter is showing number n. Malek calls an integer
x (0 ≤ x ≤ 99)
good if it's possible that the digital counter was supposed to show
x but because of some(possibly none) broken sticks it's showing
n instead. Malek wants to know number of good integers for a specific
n. So you must write a program that calculates this number. Please note that the counter
always shows two digits.
Input
The only line of input contains exactly two digits representing number
n (0 ≤ n ≤ 99). Note that
n may have a leading zero.
Output
In the only line of the output print the number of good integers.
Sample test(s)
Input
Output
Input
Output
Input
Output
Note
In the first sample the counter may be supposed to show
88 or 89.
In the second sample the good integers are 00,
08, 80 and 88.
In the third sample the good integers are
03, 08, 09, 33, 38, 39, 73, 78, 79, 83, 88, 89, 93, 98, 99.
B. Modular Equations
time limit per test
1 second
memory limit per test
256 megabytes
input
standard input
output
standard output
Last week, Hamed learned about a new type of equations in his math class called Modular Equations. Lets define
i modulo j as the remainder of division of
i by j and denote it by
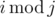
. A Modular Equation, as Hamed's teacher described, is an equation of the form
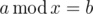
in which
a and b are two non-negative integers and
x is a variable. We call a positive integer
x for which
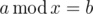
a
solution of our equation.
Hamed didn't pay much attention to the class since he was watching a movie. He only managed to understand the definitions of these equations.
Now he wants to write his math exercises but since he has no idea how to do that, he asked you for help. He has told you all he knows about Modular Equations and asked you to write a program which given two numbers
a and b determines how many answers the Modular Equation
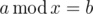
has.
Input
In the only line of the input two space-separated integers
a and b (0 ≤ a, b ≤ 109) are given.
Output
If there is an infinite number of answers to our equation, print "infinity" (without the quotes). Otherwise print the number of solutions of the Modular Equation
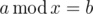
.
Sample test(s)
Input
Output
Input
Output
Input
Output
Note
In the first sample the answers of the Modular Equation are 8 and 16 since
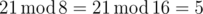
C. Treasure
time limit per test
2 seconds
memory limit per test
256 megabytes
input
standard input
output
standard output
Malek has recently found a treasure map. While he was looking for a treasure he found a locked door. There was a string
s written on the door consisting of characters '(', ')' and '#'. Below there was a manual on how to open
the door. After spending a long time Malek managed to decode the manual and found out that the goal is to replace each '#' with one or more ')' characters so that the final string
becomes beautiful.
Below there was also written that a string is called
beautiful if for each i (1 ≤ i ≤ |s|) there are no more ')' characters than '(' characters
among the first i characters of
s and also the total number of '(' characters is equal to the total number of ')' characters.
Help Malek open the door by telling him for each '#' character how many ')' characters he must replace it with.
Input
The first line of the input contains a string s (1 ≤ |s| ≤ 105). Each character of this string is one of the characters '(',
')' or '#'. It is guaranteed that
s contains at least one '#' character.
Output
If there is no way of replacing '#' characters which leads to a beautiful string print
- 1. Otherwise for each character '#' print a separate line containing a positive integer, the number of ')' characters this character must be replaced
with.
If there are several possible answers, you may output any of them.
Sample test(s)
Input
Output
Input
Output
Input
Output
Input
Output
Note
|s| denotes the length of the string
s.
time limit per test
1 second
memory limit per test
256 megabytes
input
standard input
output
standard output
Malek lives in an apartment block with 100 floors numbered from
0 to 99. The apartment has an elevator with a digital counter showing the floor that the elevator is currently on. The elevator shows each digit of a number with
7 light sticks by turning them on or off. The picture below shows how the elevator shows each digit.

One day when Malek wanted to go from floor 88 to floor
0 using the elevator he noticed that the counter shows number
89 instead of 88. Then when the elevator started moving the number on the counter changed to
87. After a little thinking Malek came to the conclusion that there is only one explanation for this: One of the sticks of the counter was broken. Later that day Malek was thinking about the broken stick and suddenly he came up
with the following problem.
Suppose the digital counter is showing number n. Malek calls an integer
x (0 ≤ x ≤ 99)
good if it's possible that the digital counter was supposed to show
x but because of some(possibly none) broken sticks it's showing
n instead. Malek wants to know number of good integers for a specific
n. So you must write a program that calculates this number. Please note that the counter
always shows two digits.
Input
The only line of input contains exactly two digits representing number
n (0 ≤ n ≤ 99). Note that
n may have a leading zero.
Output
In the only line of the output print the number of good integers.
Sample test(s)
Input
89
Output
2
Input
00
Output
4
Input
73
Output
15
Note
In the first sample the counter may be supposed to show
88 or 89.
In the second sample the good integers are 00,
08, 80 and 88.
In the third sample the good integers are
03, 08, 09, 33, 38, 39, 73, 78, 79, 83, 88, 89, 93, 98, 99.
#include <iostream>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string>
#include <cstring>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cmath>
#define N 1000#define ll __int64
using namespace std;
int vis[20]={2,7,2,3,3,4,2,5,1,2};
//电梯数字显示出现不同程度损坏,可能有一个或几个stick熄灭,算出每个数字存在的情况
<span style="font-family: Arial, Helvetica, sans-serif; font-size: 12px;">int main()</span>
{
int n;
while(~scanf("%d",&n))
{
int ans=1;
int a=n%10;
int b=n/10;
ans*=vis[a];
ans*=vis[b];
cout<<ans<<endl;
}
return 0;
}B. Modular Equations
time limit per test
1 second
memory limit per test
256 megabytes
input
standard input
output
standard output
Last week, Hamed learned about a new type of equations in his math class called Modular Equations. Lets define
i modulo j as the remainder of division of
i by j and denote it by
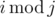
. A Modular Equation, as Hamed's teacher described, is an equation of the form
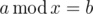
in which
a and b are two non-negative integers and
x is a variable. We call a positive integer
x for which
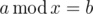
a
solution of our equation.
Hamed didn't pay much attention to the class since he was watching a movie. He only managed to understand the definitions of these equations.
Now he wants to write his math exercises but since he has no idea how to do that, he asked you for help. He has told you all he knows about Modular Equations and asked you to write a program which given two numbers
a and b determines how many answers the Modular Equation
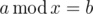
has.
Input
In the only line of the input two space-separated integers
a and b (0 ≤ a, b ≤ 109) are given.
Output
If there is an infinite number of answers to our equation, print "infinity" (without the quotes). Otherwise print the number of solutions of the Modular Equation
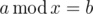
.
Sample test(s)
Input
21 5
Output
2
Input
9435152 272
Output
282
Input
10 10
Output
infinity
Note
In the first sample the answers of the Modular Equation are 8 and 16 since
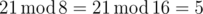
#include <iostream>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string>
#include <cstring>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cmath>
#define N 10000009
#define ll __int64
using namespace std;
//a=b+kx;因为数据比较大10^9,所有不能直接暴力,稍微转化一下
int main()
{
ll a,b;
while(~scanf("%I64d%I64d",&a,&b))
{
ll c=a-b;
if(a==b)
{
printf("infinity\n");
continue;
}
if(a<b)
{
printf("0\n");
continue;
}
ll ans=0;
for(int i=1;i*i<=c;i++)
{
if(c%i==0)
{
if(i>b)
{
ans++;
}
if( i*i<c && (c/i>b) )
ans++;
}
}
cout<<ans<<endl;
}
return 0;
}C. Treasure
time limit per test
2 seconds
memory limit per test
256 megabytes
input
standard input
output
standard output
Malek has recently found a treasure map. While he was looking for a treasure he found a locked door. There was a string
s written on the door consisting of characters '(', ')' and '#'. Below there was a manual on how to open
the door. After spending a long time Malek managed to decode the manual and found out that the goal is to replace each '#' with one or more ')' characters so that the final string
becomes beautiful.
Below there was also written that a string is called
beautiful if for each i (1 ≤ i ≤ |s|) there are no more ')' characters than '(' characters
among the first i characters of
s and also the total number of '(' characters is equal to the total number of ')' characters.
Help Malek open the door by telling him for each '#' character how many ')' characters he must replace it with.
Input
The first line of the input contains a string s (1 ≤ |s| ≤ 105). Each character of this string is one of the characters '(',
')' or '#'. It is guaranteed that
s contains at least one '#' character.
Output
If there is no way of replacing '#' characters which leads to a beautiful string print
- 1. Otherwise for each character '#' print a separate line containing a positive integer, the number of ')' characters this character must be replaced
with.
If there are several possible answers, you may output any of them.
Sample test(s)
Input
(((#)((#)
Output
1
2
Input
()((#((#(#()
Output
221
Input
#
Output
-1
Input
(#)
Output
-1
Note
|s| denotes the length of the string
s.
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string>
#include <cstring>
#include <algorithm>
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#define N 100009
using namespace std;
char str
;
vector<int> t;
int main()
{
while(~scanf("%s",str))
{
int a=0,b=0,c=0;
int num=0;
int len=strlen(str);
for(int i=0;i<len;i++)
{
if(str[i]=='(')
a++;
else if(str[i]==')')
b++;
else if(str[i]=='#')
c++;
}
int f=1;
for(int i=0;i<len;i++)
{
if(str[i]=='#')
{
if(c==1)
{
if(a<=b)// ‘)’个数大于或等于‘(’时,还存在‘#’
{
f=0;
break;
}
t.push_back(a-b);
num-=(a-b);
c--;
}
else
{
t.push_back(1);
num--;
b++;
c--;
}
}
else if(str[i]=='(')
num++;
else if(str[i]==')')
num--;
if(num<0)//在 # 结束之前出现未匹配')’个数大于‘(’的情况
{
f=0;
break;
}
}
if(num<0 ||f==0)//中途被标记或者 最后 # 结束之后存在
cout<<-1<<endl;
else
{
for(int i=0;i<t.size();i++)
cout<<t[i]<<endl;
}
}
return 0;
}
相关文章推荐
- Codeforces Round #429 (Div. 2) ABC
- Codeforces Round #319 (Div. 2) (ABCE题解)
- Codeforces Round #199 (Div. 2) (ABC)
- Codeforces Round #429 (Div. 2) ABC
- Codeforces Round #282 (Div2)
- Codeforces Round #226 (Div. 2) ABC
- Codeforces Round #324 (Div. 2)ABC
- Codeforces Round #429 (Div. 2) ABC
- Codeforces Round #282 (Div. 1) B. Obsessive String
- Codeforces Round #109 (Div. 1) 题解 【ABC】
- Codeforces Round #429 (Div. 2) ABC
- Codeforces Round #282 (Div. 2) c
- Codeforces Round #282 Div.1 B Obsessive String --DP
- Codeforces Round #282 (Div. 2) C. Treasure 贪心
- Codeforces Round #429 (Div. 2) ABC
- Codeforces Round #429 (Div. 2) ABC
- Codeforces Round #462 (Div. 2)题解ABC
- Codeforces Round #429 (Div. 2) ABC
- Codeforces Round #282 (Div. 2) B. Modular Equations&C. Treasure
- Codeforces Round #429 (Div. 2) ABC
