hdu-1022-Train Problem I
2014-12-13 14:51
267 查看
Train Problem I
Time Limit: 2000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 65536/32768 K (Java/Others)Total Submission(s): 22093 Accepted Submission(s): 8364
[align=left]Problem Description[/align]
As the new term comes, the Ignatius Train Station is very busy nowadays. A lot of student want to get back to school by train(because the trains in the Ignatius Train Station is the fastest all over the world ^v^). But here comes
a problem, there is only one railway where all the trains stop. So all the trains come in from one side and get out from the other side. For this problem, if train A gets into the railway first, and then train B gets into the railway before train A leaves,
train A can't leave until train B leaves. The pictures below figure out the problem. Now the problem for you is, there are at most 9 trains in the station, all the trains has an ID(numbered from 1 to n), the trains get into the railway in an order O1, your
task is to determine whether the trains can get out in an order O2.
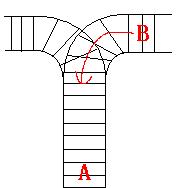
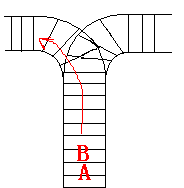
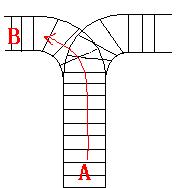
[align=left]Input[/align]
The input contains several test cases. Each test case consists of an integer, the number of trains, and two strings, the order of the trains come in:O1, and the order of the trains leave:O2. The input is terminated by the end of file.
More details in the Sample Input.
[align=left]Output[/align]
The output contains a string "No." if you can't exchange O2 to O1, or you should output a line contains "Yes.", and then output your way in exchanging the order(you should output "in" for a train getting into the railway, and "out"
for a train getting out of the railway). Print a line contains "FINISH" after each test case. More details in the Sample Output.
[align=left]Sample Input[/align]
3 123 321 3 123 312
[align=left]Sample Output[/align]
Yes. in in in out out out FINISH No. FINISH Hint
#include<stdio.h>
//#include<iostream>
#include<stack>
using namespace std;
char a[11],b[11];
int main()
{
int n;
bool teg[11];
while(~scanf("%d",&n))
{
stack<char> ss;
int i,t,k;
scanf("%s",a);
scanf("%s",b);
t=0;k=0;
for(i=0;i<n;++i)
{
ss.push(a[i]);
teg[k++]=1;
while(!ss.empty()&&ss.top()==b[t])
{
t++;
ss.pop();
teg[k++]=0;
}
}
if(ss.empty()&&t==n)
{
printf("Yes.\n");
for(i=0;i<k;++i)
{
if(teg[i]==true)
printf("in\n");
else
printf("out\n");
}
printf("FINISH\n");
}
else
printf("No.\nFINISH\n");;
}
return 0;
}//STL栈的应用:
push(x) 将x加入栈中,即入栈操作
pop() 出栈操作(删除栈顶),只是出栈,没有返回值
top() 返回第一个元素(栈顶元素)
size() 返回栈中的元素个数
empty() 当栈为空时,返回 true
相关文章推荐
- hdu 1022 Train problem I
- HDU 1022 ( Train Problem I )
- hdu 1022 Train Problem I(栈的操作);
- hdu1022 Train Problem I
- HDU 1022 Train Problem I
- HDU1022--Train Problem I
- hdu1022 Train Problem I
- hdu 1022 Train Problem I
- HDU-1022-Train Problem I(C++ && 简单堆栈)
- hdu 1022 Train Problem I(栈的应用+STL)
- hdu1022 Train Problem I(STL 栈的应用)
- HDU 1022 ( Train Problem I )
- HDU-1022-Train Problem I
- hdu 1022 Train Problem I
- HDU 1022 Train Problem I 栈
- HDU-1022-Train Problem I
- hdu 1022 Train Problem I 模拟
- hdu1022-Train Problem I
- [ACM] hdu 1022 Train Problem I(栈的使用)
- hdu 1022 Train Problem I
