第二十三次codeforces竞技结束 #279 Div 2
2014-12-04 02:19
585 查看
C题fst了…… 感觉状态不是很好…… 最近得好好复习考试了…… 可能得等寒假再捡回来编程了……
1 second
memory limit per test
256 megabytes
input
standard input
output
standard output
The School №0 of the capital of Berland has n children studying in it. All the children in this school are gifted: some of them are good at programming,
some are good at maths, others are good at PE (Physical Education). Hence, for each child we know value ti:
ti = 1, if the i-th
child is good at programming,
ti = 2, if the i-th
child is good at maths,
ti = 3, if the i-th
child is good at PE
Each child happens to be good at exactly one of these three subjects.
The Team Scientific Decathlon Olympias requires teams of three students. The school teachers decided that the teams will be composed of three children that are good at different subjects. That is, each team must have one mathematician, one programmer and one
sportsman. Of course, each child can be a member of no more than one team.
What is the maximum number of teams that the school will be able to present at the Olympiad? How should the teams be formed for that?
Input
The first line contains integer n (1 ≤ n ≤ 5000)
— the number of children in the school. The second line contains n integerst1, t2, ..., tn (1 ≤ ti ≤ 3),
where ti describes
the skill of the i-th child.
Output
In the first line output integer w — the largest possible number of teams.
Then print w lines, containing three numbers in each line. Each triple represents the indexes of the children forming the team. You can print both the teams,
and the numbers in the triplets in any order. The children are numbered from 1 to n in
the order of their appearance in the input. Each child must participate in no more than one team. If there are several solutions, print any of them.
If no teams can be compiled, print the only line with value w equal to 0.
Sample test(s)
input
output
input
output
题意是有n个人,他们分别精通1、2、3这三种技能,凑齐1、2、3可以组一个队伍,问这些人最多能组几个队伍并输出。
直接用3个数组存相应技能有哪些人会,然后从下标0开始凑队即可
2 seconds
memory limit per test
256 megabytes
input
standard input
output
standard output
During the lunch break all n Berland State University students lined up in the food court. However, it turned out that the food court, too, has a lunch break
and it temporarily stopped working.
Standing in a queue that isn't being served is so boring! So, each of the students wrote down the number of the student ID of the student that stands in line directly in front of him, and the student that stands in line directly behind him. If no one stands
before or after a student (that is, he is the first one or the last one), then he writes down number 0 instead (in Berland State University student IDs are numerated
from 1).
After that, all the students went about their business. When they returned, they found out that restoring the queue is not such an easy task.
Help the students to restore the state of the queue by the numbers of the student ID's of their neighbors in the queue.
Input
The first line contains integer n (2 ≤ n ≤ 2·105)
— the number of students in the queue.
Then n lines follow, i-th line contains the pair
of integers ai, bi (0 ≤ ai, bi ≤ 106),
where ai is
the ID number of a person in front of a student and bi is
the ID number of a person behind a student. The lines are given in the arbitrary order. Value 0 is given instead of a neighbor's ID number if the neighbor doesn't
exist.
The ID numbers of all students are distinct. It is guaranteed that the records correspond too the queue where all the students stand in some order.
Output
Print a sequence of n integers x1, x2, ..., xn —
the sequence of ID numbers of all the students in the order they go in the queue from the first student to the last one.
Sample test(s)
input
output
Note
The picture illustrates the queue for the first sample.
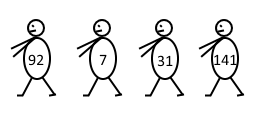
有一堆学生排队,他们每个人都有一个大于1的学号,然后队伍散了,每个人都来说自己前头和自己后头的人的学号,让你把队伍恢复出来。
我们不难发现,这些首尾相接的东西最终会串成两条链,分别为队伍中为奇数和队伍中为偶数的人们,然后把这个链组合起来即可
(0,a)说明a是第二个人,(b,0)说明b是倒数第二个人。
这个题目的要点在于队伍长度奇数和偶数时不同,需要判断。
1 second
memory limit per test
256 megabytes
input
standard input
output
standard output
Polycarpus participates in a competition for hacking into a new secure messenger. He's almost won.
Having carefully studied the interaction protocol, Polycarpus came to the conclusion that the secret key can be obtained if he properly cuts the public key of the application into two parts. The public key is a long integer which may consist of even a million
digits!
Polycarpus needs to find such a way to cut the public key into two nonempty parts, that the first (left) part is divisible by a as a separate number, and
the second (right) part is divisible by b as a separate number. Both parts should be positive integers
that have no leading zeros. Polycarpus knows values a and b.
Help Polycarpus and find any suitable method to cut the public key.
Input
The first line of the input contains the public key of the messenger — an integer without leading zeroes, its length is in range from 1 to 106 digits.
The second line contains a pair of space-separated positive integers a, b (1 ≤ a, b ≤ 108).
Output
In the first line print "YES" (without the quotes), if the method satisfying conditions above exists. In this case, next print two lines — the left and right
parts after the cut. These two parts, being concatenated, must be exactly identical to the public key. The left part must be divisible by a, and the right
part must be divisible by b. The two parts must be positive integers having no leading zeros. If there are several answers, print any of them.
If there is no answer, print in a single line "NO" (without the quotes).
Sample test(s)
input
output
input
output
input
output
吾辈的C题Fst了…… TLE@Test42
安心的读字符串处理就好了呀Q^Q 我为啥要string和longlong联用呢……Q^Q
关于当前字符串是否可以被某个数整除,我们每次都留下余数然后向后增加位数继续留下直至余数,即可~
A. Team Olympiad
time limit per test1 second
memory limit per test
256 megabytes
input
standard input
output
standard output
The School №0 of the capital of Berland has n children studying in it. All the children in this school are gifted: some of them are good at programming,
some are good at maths, others are good at PE (Physical Education). Hence, for each child we know value ti:
ti = 1, if the i-th
child is good at programming,
ti = 2, if the i-th
child is good at maths,
ti = 3, if the i-th
child is good at PE
Each child happens to be good at exactly one of these three subjects.
The Team Scientific Decathlon Olympias requires teams of three students. The school teachers decided that the teams will be composed of three children that are good at different subjects. That is, each team must have one mathematician, one programmer and one
sportsman. Of course, each child can be a member of no more than one team.
What is the maximum number of teams that the school will be able to present at the Olympiad? How should the teams be formed for that?
Input
The first line contains integer n (1 ≤ n ≤ 5000)
— the number of children in the school. The second line contains n integerst1, t2, ..., tn (1 ≤ ti ≤ 3),
where ti describes
the skill of the i-th child.
Output
In the first line output integer w — the largest possible number of teams.
Then print w lines, containing three numbers in each line. Each triple represents the indexes of the children forming the team. You can print both the teams,
and the numbers in the triplets in any order. The children are numbered from 1 to n in
the order of their appearance in the input. Each child must participate in no more than one team. If there are several solutions, print any of them.
If no teams can be compiled, print the only line with value w equal to 0.
Sample test(s)
input
7 1 3 1 3 2 1 2
output
2 3 5 2 6 7 4
input
4 2 1 1 2
output
0
题意是有n个人,他们分别精通1、2、3这三种技能,凑齐1、2、3可以组一个队伍,问这些人最多能组几个队伍并输出。
直接用3个数组存相应技能有哪些人会,然后从下标0开始凑队即可
Code:
#include <cmath>
#include <cctype>
#include <vector>
#include <cstdio>
#include <string>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <cstring>
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
int t[10086]={0};
int a[5]={0};
vector<int> q[5];
#define Max(a,b) ((a)>(b)?(a):(b))
#define Min(a,b) ((a)<(b)?(a):(b))
bool cmp(const int a, const int b)
{
return a > b;
}
int main()
{
int n=0; cin>>n;
for(int i=0;i<5;i++)q[i].clear();
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
{
scanf("%d",&t[i]);
a[t[i]]++;
q[t[i]].push_back(i+1);
}
int minv=min(a[1],min(a[2],a[3]));
printf("%d\n",minv);
for(int i=0;i<minv;i++)
{
printf("%d %d %d\n",q[1][i],q[2][i],q[3][i]);
}
return 0;
}B. Queue
time limit per test2 seconds
memory limit per test
256 megabytes
input
standard input
output
standard output
During the lunch break all n Berland State University students lined up in the food court. However, it turned out that the food court, too, has a lunch break
and it temporarily stopped working.
Standing in a queue that isn't being served is so boring! So, each of the students wrote down the number of the student ID of the student that stands in line directly in front of him, and the student that stands in line directly behind him. If no one stands
before or after a student (that is, he is the first one or the last one), then he writes down number 0 instead (in Berland State University student IDs are numerated
from 1).
After that, all the students went about their business. When they returned, they found out that restoring the queue is not such an easy task.
Help the students to restore the state of the queue by the numbers of the student ID's of their neighbors in the queue.
Input
The first line contains integer n (2 ≤ n ≤ 2·105)
— the number of students in the queue.
Then n lines follow, i-th line contains the pair
of integers ai, bi (0 ≤ ai, bi ≤ 106),
where ai is
the ID number of a person in front of a student and bi is
the ID number of a person behind a student. The lines are given in the arbitrary order. Value 0 is given instead of a neighbor's ID number if the neighbor doesn't
exist.
The ID numbers of all students are distinct. It is guaranteed that the records correspond too the queue where all the students stand in some order.
Output
Print a sequence of n integers x1, x2, ..., xn —
the sequence of ID numbers of all the students in the order they go in the queue from the first student to the last one.
Sample test(s)
input
4
92 31
0 7
31 07 141
output
92 7 31 141
Note
The picture illustrates the queue for the first sample.
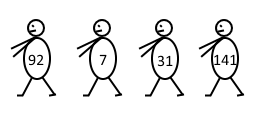
有一堆学生排队,他们每个人都有一个大于1的学号,然后队伍散了,每个人都来说自己前头和自己后头的人的学号,让你把队伍恢复出来。
我们不难发现,这些首尾相接的东西最终会串成两条链,分别为队伍中为奇数和队伍中为偶数的人们,然后把这个链组合起来即可
(0,a)说明a是第二个人,(b,0)说明b是倒数第二个人。
这个题目的要点在于队伍长度奇数和偶数时不同,需要判断。
Code:
#include <cmath>
#include <queue>
#include <cctype>
#include <cstdio>
#include <string>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <cstring>
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
int a[2000086]={0};
int b[2000086]={0};
int frt[2000086]={0};
int bnd[2000086]={0};
int ans[2000086]={0};
#define Max(a,b) ((a)>(b)?(a):(b))
#define Min(a,b) ((a)<(b)?(a):(b))
bool cmp(const int a, const int b)
{
return a > b;
}
int main()
{
int n=0; cin>>n;
int head,tail;
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
{
cin>>a[i]>>b[i];
frt[b[i]]=a[i];
bnd[a[i]]=b[i];
if(a[i]==0) head=b[i];
if(b[i]==0) tail=a[i];
}
int now=head,pos=1,tmp=0;
while(now)
{
ans[pos]=now;
now=bnd[now];
if(now) frt[now]=0;
pos+=2;
}
if(n%2==0)
{
now=tail,pos=n-2;
while(now)
{
ans[pos]=now;
now=frt[now];
pos-=2;
}
}
else
{
int pi;
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
{
if(frt[b[i]] && b[i]!=0)
{
pi=b[i];
while(frt[pi])
{
pi=frt[pi];
}
break;
}
}
int now=pi,pos=0,tmp=0;
while(now)
{
ans[pos]=now;
now=bnd[now];
if(now) frt[now]=0;
pos+=2;
}
}
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
{
printf("%d",ans[i]);
if(i<n-1)printf(" ");
}
return 0;
}C. Hacking Cypher
time limit per test1 second
memory limit per test
256 megabytes
input
standard input
output
standard output
Polycarpus participates in a competition for hacking into a new secure messenger. He's almost won.
Having carefully studied the interaction protocol, Polycarpus came to the conclusion that the secret key can be obtained if he properly cuts the public key of the application into two parts. The public key is a long integer which may consist of even a million
digits!
Polycarpus needs to find such a way to cut the public key into two nonempty parts, that the first (left) part is divisible by a as a separate number, and
the second (right) part is divisible by b as a separate number. Both parts should be positive integers
that have no leading zeros. Polycarpus knows values a and b.
Help Polycarpus and find any suitable method to cut the public key.
Input
The first line of the input contains the public key of the messenger — an integer without leading zeroes, its length is in range from 1 to 106 digits.
The second line contains a pair of space-separated positive integers a, b (1 ≤ a, b ≤ 108).
Output
In the first line print "YES" (without the quotes), if the method satisfying conditions above exists. In this case, next print two lines — the left and right
parts after the cut. These two parts, being concatenated, must be exactly identical to the public key. The left part must be divisible by a, and the right
part must be divisible by b. The two parts must be positive integers having no leading zeros. If there are several answers, print any of them.
If there is no answer, print in a single line "NO" (without the quotes).
Sample test(s)
input
116401024 97 1024
output
YES
116401024
input
2842545891539281719112818110001009 1000
output
YES
2842545891539
28171911281811000
input
12012 1
output
NO
吾辈的C题Fst了…… TLE@Test42
安心的读字符串处理就好了呀Q^Q 我为啥要string和longlong联用呢……Q^Q
关于当前字符串是否可以被某个数整除,我们每次都留下余数然后向后增加位数继续留下直至余数,即可~
Code:
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
char in[1048576], vis[1048576];
int main() {
int a, b, n, t(0), base(1), i; scanf("%s%d%d", in, &a, &b);
n = strlen(in);
for (i = 1; i < n; ++i) {
t = (t * 10 + in[i - 1] - '0') % a;
vis[i] = !t;
}
t = 0;
for (i = n - 1; i > 0; --i) {
(t += base * (in[i] - '0')) %= b;
if ((in[i] - '0') && !t && vis[i]) break;
(base *= 10) %= b;
}
if (!i) puts("NO");
else {
puts("YES");
for (int j = 0; j < i; ++j) putchar(in[j]);
putchar('\n'); puts(in + i);
}
}#import<bits/stdc++.h>
int a, b, c, n, p=1, i, d[1<<20];
char m[1<<20];
main() {
gets(m);
n = strlen(m);
scanf("%d%d", &a, &b);
for (i=n-1; i>=0; i--) {
d[i] = ((m[i] - '0') * p + d[i + 1]) % b;
p = p * 10 % b;
}
for (i=1; i<n; i++) {
c = (c * 10 + m[i - 1] - '0') % a;
if (!c && !d[i] && m[i] != '0') {
puts("YES");
printf("%.*s\n%s", i, m, m + i);
return 0;
}
}
puts("NO");
}
相关文章推荐
- 第十九次codeforces竞技结束 #275 Div 1
- 第七次codeforces竞技结束 #258 Div 2
- 第二十九次codeforces竞技结束 #293 Div 2
- 第十八次codeforces竞技结束 #272 Div 2
- 第二十一次codeforces竞技结束 #277 Div 2
- 第二十八次codeforces竞技结束 #291 Div 2
- 第三十二次codeforces竞技结束 #299 Div 2
- 第二十二次codeforces竞技结束 #278 Div 2
- 第十次codeforces竞技结束 #261 Div 2
- 第二十四次codeforces竞技结束 #281 Div 2
- 第三十次codeforces竞技结束 #296 Div 2
- 第三十一次codeforces竞技结束 #297 Div 2
- 第二十七次codeforces竞技结束 #288 Div 2
- 第十六次codeforces竞技结束 #269 Div 2
- 第三次codeforces竞技结束 #254 Div 2
- 第五次codeforces竞技结束 #256 Div 2
- 第三十三次codeforces竞技结束 #441 Div 2
- 第八次codeforces竞技结束 #259 Div 2
- 第二十五次codeforces竞技结束 #285 Div 2
- 第二十次codeforces竞技结束 #276 Div 2
