OpenStack Operations Guide 第八章 Lay of the Land
2014-11-26 18:13
169 查看
8.1 Using the OpenStack Dashboard for Administration
8.2 Command-Line Tools
8.2.1 Installing the Tools
8.2.2 Administrative Command-Line Tools
8.2.3 Getting Credentials
8.2.4 Inspecting API Calls
8.2.5 Servers and Services
8.2.6 Diagnose Your Compute Nodes
8.3 Network Inspection
8.4 Users and Projects
8.5 Running Instances
8.1 Using the OpenStack Dashboard for Administration
作为一个云管理员,你可以使用OpenStack dashboard来创建和管理projects,users,images,flavors。根据image服务的配置,用户可以为特定的project创建管理共享镜像。通常,策略都会设定允许管理员用户设置配额,创建管理策略。Dashboard在管理页面提供了系统面板与认证面板。OpenStack Admin User Guide会详细介绍如何使用dashboard:http://docs.openstack.org/user-guide-admin/content/ch_dashboard.html
8.2 Command-Line Tools
我们建议同时使用command-line和dashboard来管理您的云环境。一些有使用其他云技术的用户,可能会使用EC2兼容的API,和native API会有一些命名的不同。
我们建议使用Python Package Index(PyPI)安装客户端命令行工具。每个OpenStack项目都有自己的客户端:
python-novaclient
python-glanceclient
python-keystoneclient
python-cinderclient
python-swiftclient
python-neutronclient
8.2.1 Installing the Tools
root权限使用pip命令安装升级删除包
# pip install [--upgrade] <package-name>
# pip uninstall <package-name>
# pip install -e git+https://github.com/openstack/python-novaclient.git#egg=python-novaclient
如果你的云支持EC2 API,你应该也安装euca2ools或者其他EC2 API工具。
8.2.2 Administrative Command-Line Tools
在OpenStack服务安装的同时默认会有一些*-manage命令行工具:
nova-manage
glance-manage
keystone-manage
cinder-manage
不像上个章节介绍的工具,这些*-manage必须以root在控制节点上运行,因为他们必须要取配置文件(如/etc/nova/nova.conf)直接从数据查询,而不是通过OpenStack API endpoints。OpenStack的最终目标是把*-manage工具迁移到基于API的工具。
8.2.3 Getting Credentials
如果你想要使用命令行工具你必须拥有合适的credential。迄今为止获取credential最简单的方法就是使用OpenStack dashboard。选择project,access&security,api access,会看到两个按钮,下载OpenStack RC File和下载EC2 Credentials。运行openrc可以让你生成系统变量,如services endpoints和认证信息。根据登录用户的不同,下载的文件也不一样,如demo-openrc.sh admin-openrc.sh
脚本如下:
#!/bin/bash
# With the addition of Keystone, to use an openstack cloud you should
# authenticate against keystone, which returns a **Token** and **Service
# Catalog**. The catalog contains the endpoint for all services the
# user/tenant has access to--including nova, glance, keystone, swift.
# *NOTE*: Using the 2.0 *auth api* does not mean that compute api is 2.0.
# We use the 1.1 *compute api*
export OS_AUTH_URL=http://203.0.113.10:5000/v2.0
# With the addition of Keystone we have standardized on the term **tenant**
# as the entity that owns the resources.
export OS_TENANT_ID=98333aba48e756fa8f629c83a818ad57
export OS_TENANT_NAME="test-project"
# In addition to the owning entity (tenant), openstack stores the entity
# performing the action as the **user**.
export OS_USERNAME=demo
# With Keystone you pass the keystone password.
echo "Please enter your OpenStack Password: "
read -s OS_PASSWORD_INPUT
export OS_PASSWORD=$OS_PASSWORD_INPUT
注意:文件不会以文本保存你的密码。当时当你运行脚本时会提示然后保存在系统变量中。如果你不需要互交性的操作你可以把密码保存在脚本中,但是你需要考虑安全性。
选择下载EC2兼容credentials会生成一个ZIP文件,包含x509证书,解压会生成cacert.pem,cert.pem,ec2rc.sh,pk.pem文件。ec2sh.sh文件如下:
#!/bin/bash
NOVARC=$(readlink -f "${BASH_SOURCE:-${0}}" 2>/dev/null) ||\
NOVARC=$(python -c 'import os,sys; \
print os.path.abspath(os.path.realpath(sys.argv[1]))' "${BASH_SOURCE:-${0}}")
NOVA_KEY_DIR=${NOVARC%/*}
export EC2_ACCESS_KEY=df7f93ec47e84ef8a347bbb3d598449a
export EC2_SECRET_KEY=ead2fff9f8a344e489956deacd47e818
export EC2_URL=http://203.0.113.10:8773/services/Cloud
export EC2_USER_ID=42 # nova does not use user id, but bundling requires it
export EC2_PRIVATE_KEY=${NOVA_KEY_DIR}/pk.pem
export EC2_CERT=${NOVA_KEY_DIR}/cert.pem
export NOVA_CERT=${NOVA_KEY_DIR}/cacert.pem
export EUCALYPTUS_CERT=${NOVA_CERT} # euca-bundle-image seems to require this
alias ec2-bundle-image="ec2-bundle-image --cert $EC2_CERT --privatekey \
$EC2_PRIVATE_KEY --user 42 --ec2cert $NOVA_CERT"
alias ec2-upload-bundle="ec2-upload-bundle -a $EC2_ACCESS_KEY -s \
$EC2_SECRET_KEY --url $S3_URL --ec2cert $NOVA_CERT"
8.2.4 Inspecting API Calls / Using cURL for further inspection
可以通过加上--debug来显示OpenStack的API calls。如:
# nova --debug list
这个例子显示了客户端的HTTP请求以及endpoints的回复。
小贴士:Keyring Support可以保存你OpenStack中的密码到一个加密的文件中。默认是关闭的,如要开启请在环境变量中设置OS_CACHE=1 https://wiki.openstack.org/wiki/KeyringSupport 配置OS_CACHE的话,命令行工具每次操作与云的互交都会被认证,这样会增加命令运行时间,加大服务器的工作负载。
使用命令行工具的实际是调用OpenStack的API(通过HTTP的REST API)。在某些情况下你可能想直接与API互交或者因为某些有嫌疑的Bug。最好的方式就是使用cURL与其他工具结合,如jq,解析反应的JSON。
首先你要做的就是使用你的credentials来和云认证得到一个token。
你的credentials包括用户名,密码,租户(项目),你可以从openrc.sh文件中得到这些信息。Token允许你与其他的service endpoints互交,为不需要每次都获取授权。Token通常有24小时的声明周期,如果过去你会得到一个401未授权的警告,这时候你需要去在申请一个token。
1 查看你OpenStack服务的catalog
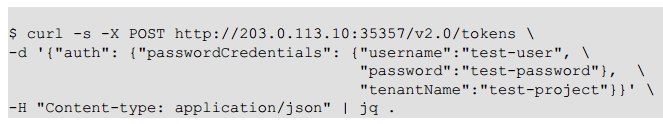
2 存储token到你的系统变量
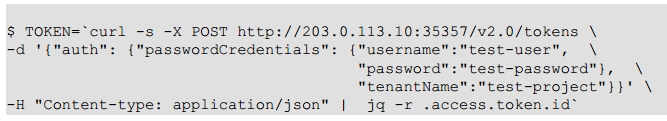
3 选择一个service endpoint,如compute,尝试一个请求,如列出实例
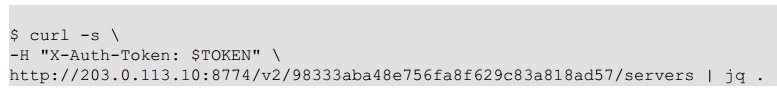
查看OpenStack API Reference:http://developer.openstack.org/api-ref.html
查看jq Manual:http://stedolan.github.io/jq/manual/
cURL命令中-s选项是用来方式显示进度表。-v帮你显示详细信息。
8.2.5 Servers and Services
这一小结会告诉你怎样去获得你云环境的概览。
首先你要学会发现那些服务器是属于你的OpenStack环境
# nova-manage service list | sort
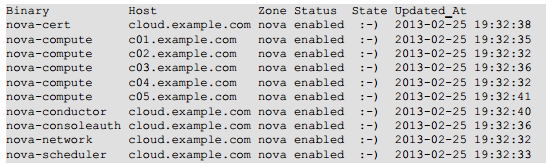
#cinder-manage host list | sort

#keystone catalog
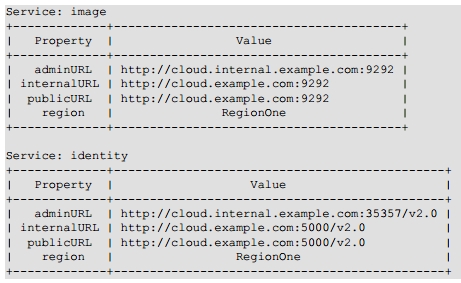
8.2.6 Diagnose Your Compute Nodes
你可以使用命令获取虚拟机的详细信息,如CPU使用率,内存,磁盘IO,网络IO等
#nova diagnostics <serverID>
根据hypervisor的不同,输出结果也不一样
Xen:
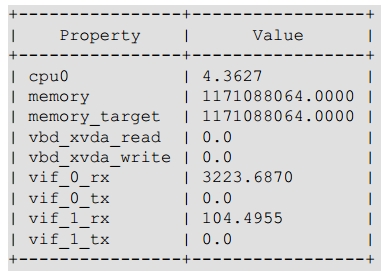
KVM:
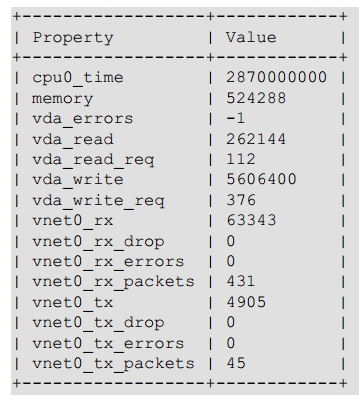
8.3 Network Inspection
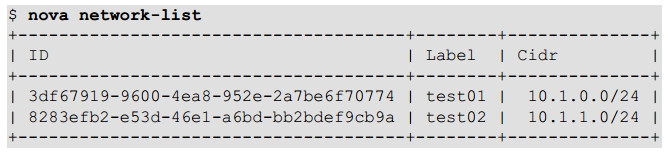
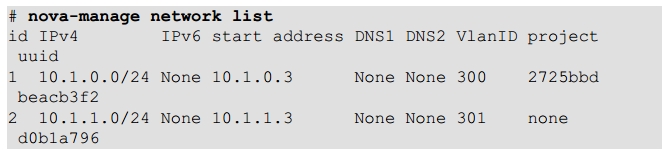
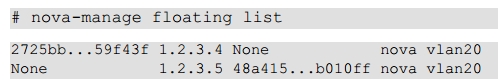
8.4 Users and Projects
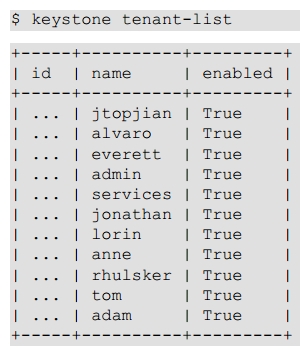
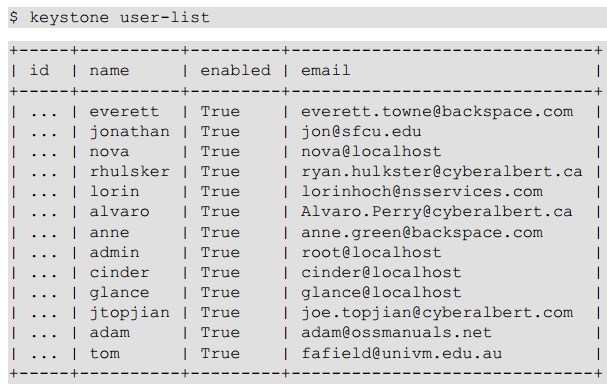
8.5 Running Instances
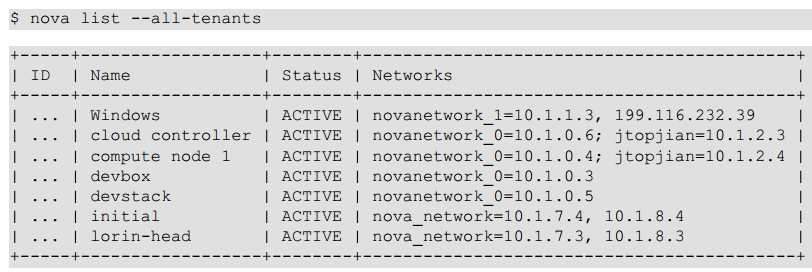
很遗憾这条命令没有告诉你更多具体的信息,如实例运行在哪个计算节点,用的哪个flavor,你可以用nova show <uuid>命令查看更详细的信息
8.2 Command-Line Tools
8.2.1 Installing the Tools
8.2.2 Administrative Command-Line Tools
8.2.3 Getting Credentials
8.2.4 Inspecting API Calls
8.2.5 Servers and Services
8.2.6 Diagnose Your Compute Nodes
8.3 Network Inspection
8.4 Users and Projects
8.5 Running Instances
8.1 Using the OpenStack Dashboard for Administration
作为一个云管理员,你可以使用OpenStack dashboard来创建和管理projects,users,images,flavors。根据image服务的配置,用户可以为特定的project创建管理共享镜像。通常,策略都会设定允许管理员用户设置配额,创建管理策略。Dashboard在管理页面提供了系统面板与认证面板。OpenStack Admin User Guide会详细介绍如何使用dashboard:http://docs.openstack.org/user-guide-admin/content/ch_dashboard.html
8.2 Command-Line Tools
我们建议同时使用command-line和dashboard来管理您的云环境。一些有使用其他云技术的用户,可能会使用EC2兼容的API,和native API会有一些命名的不同。
我们建议使用Python Package Index(PyPI)安装客户端命令行工具。每个OpenStack项目都有自己的客户端:
python-novaclient
python-glanceclient
python-keystoneclient
python-cinderclient
python-swiftclient
python-neutronclient
8.2.1 Installing the Tools
root权限使用pip命令安装升级删除包
# pip install [--upgrade] <package-name>
# pip uninstall <package-name>
# pip install -e git+https://github.com/openstack/python-novaclient.git#egg=python-novaclient
如果你的云支持EC2 API,你应该也安装euca2ools或者其他EC2 API工具。
8.2.2 Administrative Command-Line Tools
在OpenStack服务安装的同时默认会有一些*-manage命令行工具:
nova-manage
glance-manage
keystone-manage
cinder-manage
不像上个章节介绍的工具,这些*-manage必须以root在控制节点上运行,因为他们必须要取配置文件(如/etc/nova/nova.conf)直接从数据查询,而不是通过OpenStack API endpoints。OpenStack的最终目标是把*-manage工具迁移到基于API的工具。
8.2.3 Getting Credentials
如果你想要使用命令行工具你必须拥有合适的credential。迄今为止获取credential最简单的方法就是使用OpenStack dashboard。选择project,access&security,api access,会看到两个按钮,下载OpenStack RC File和下载EC2 Credentials。运行openrc可以让你生成系统变量,如services endpoints和认证信息。根据登录用户的不同,下载的文件也不一样,如demo-openrc.sh admin-openrc.sh
脚本如下:
#!/bin/bash
# With the addition of Keystone, to use an openstack cloud you should
# authenticate against keystone, which returns a **Token** and **Service
# Catalog**. The catalog contains the endpoint for all services the
# user/tenant has access to--including nova, glance, keystone, swift.
# *NOTE*: Using the 2.0 *auth api* does not mean that compute api is 2.0.
# We use the 1.1 *compute api*
export OS_AUTH_URL=http://203.0.113.10:5000/v2.0
# With the addition of Keystone we have standardized on the term **tenant**
# as the entity that owns the resources.
export OS_TENANT_ID=98333aba48e756fa8f629c83a818ad57
export OS_TENANT_NAME="test-project"
# In addition to the owning entity (tenant), openstack stores the entity
# performing the action as the **user**.
export OS_USERNAME=demo
# With Keystone you pass the keystone password.
echo "Please enter your OpenStack Password: "
read -s OS_PASSWORD_INPUT
export OS_PASSWORD=$OS_PASSWORD_INPUT
注意:文件不会以文本保存你的密码。当时当你运行脚本时会提示然后保存在系统变量中。如果你不需要互交性的操作你可以把密码保存在脚本中,但是你需要考虑安全性。
选择下载EC2兼容credentials会生成一个ZIP文件,包含x509证书,解压会生成cacert.pem,cert.pem,ec2rc.sh,pk.pem文件。ec2sh.sh文件如下:
#!/bin/bash
NOVARC=$(readlink -f "${BASH_SOURCE:-${0}}" 2>/dev/null) ||\
NOVARC=$(python -c 'import os,sys; \
print os.path.abspath(os.path.realpath(sys.argv[1]))' "${BASH_SOURCE:-${0}}")
NOVA_KEY_DIR=${NOVARC%/*}
export EC2_ACCESS_KEY=df7f93ec47e84ef8a347bbb3d598449a
export EC2_SECRET_KEY=ead2fff9f8a344e489956deacd47e818
export EC2_URL=http://203.0.113.10:8773/services/Cloud
export EC2_USER_ID=42 # nova does not use user id, but bundling requires it
export EC2_PRIVATE_KEY=${NOVA_KEY_DIR}/pk.pem
export EC2_CERT=${NOVA_KEY_DIR}/cert.pem
export NOVA_CERT=${NOVA_KEY_DIR}/cacert.pem
export EUCALYPTUS_CERT=${NOVA_CERT} # euca-bundle-image seems to require this
alias ec2-bundle-image="ec2-bundle-image --cert $EC2_CERT --privatekey \
$EC2_PRIVATE_KEY --user 42 --ec2cert $NOVA_CERT"
alias ec2-upload-bundle="ec2-upload-bundle -a $EC2_ACCESS_KEY -s \
$EC2_SECRET_KEY --url $S3_URL --ec2cert $NOVA_CERT"
8.2.4 Inspecting API Calls / Using cURL for further inspection
可以通过加上--debug来显示OpenStack的API calls。如:
# nova --debug list
这个例子显示了客户端的HTTP请求以及endpoints的回复。
小贴士:Keyring Support可以保存你OpenStack中的密码到一个加密的文件中。默认是关闭的,如要开启请在环境变量中设置OS_CACHE=1 https://wiki.openstack.org/wiki/KeyringSupport 配置OS_CACHE的话,命令行工具每次操作与云的互交都会被认证,这样会增加命令运行时间,加大服务器的工作负载。
使用命令行工具的实际是调用OpenStack的API(通过HTTP的REST API)。在某些情况下你可能想直接与API互交或者因为某些有嫌疑的Bug。最好的方式就是使用cURL与其他工具结合,如jq,解析反应的JSON。
首先你要做的就是使用你的credentials来和云认证得到一个token。
你的credentials包括用户名,密码,租户(项目),你可以从openrc.sh文件中得到这些信息。Token允许你与其他的service endpoints互交,为不需要每次都获取授权。Token通常有24小时的声明周期,如果过去你会得到一个401未授权的警告,这时候你需要去在申请一个token。
1 查看你OpenStack服务的catalog

2 存储token到你的系统变量

3 选择一个service endpoint,如compute,尝试一个请求,如列出实例

查看OpenStack API Reference:http://developer.openstack.org/api-ref.html
查看jq Manual:http://stedolan.github.io/jq/manual/
cURL命令中-s选项是用来方式显示进度表。-v帮你显示详细信息。
8.2.5 Servers and Services
这一小结会告诉你怎样去获得你云环境的概览。
首先你要学会发现那些服务器是属于你的OpenStack环境
# nova-manage service list | sort

#cinder-manage host list | sort

#keystone catalog

8.2.6 Diagnose Your Compute Nodes
你可以使用命令获取虚拟机的详细信息,如CPU使用率,内存,磁盘IO,网络IO等
#nova diagnostics <serverID>
根据hypervisor的不同,输出结果也不一样
Xen:

KVM:

8.3 Network Inspection



8.4 Users and Projects


8.5 Running Instances

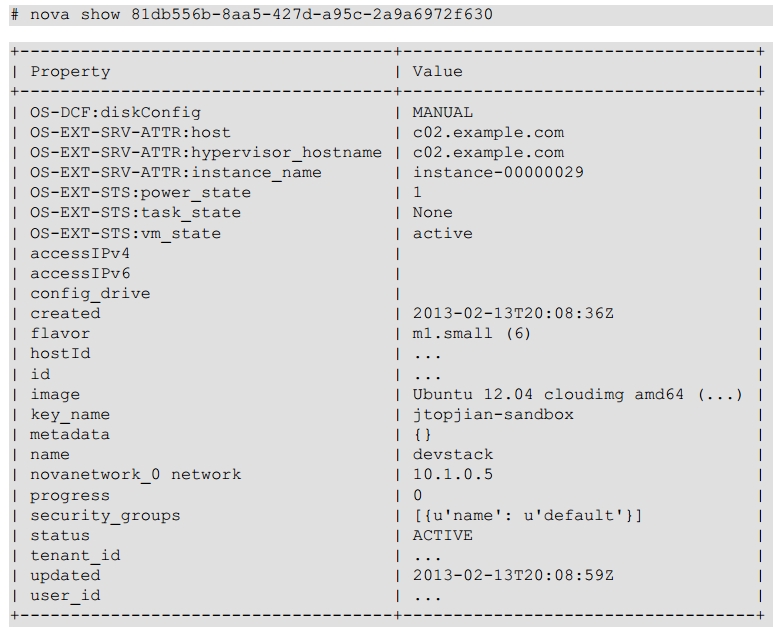
很遗憾这条命令没有告诉你更多具体的信息,如实例运行在哪个计算节点,用的哪个flavor,你可以用nova show <uuid>命令查看更详细的信息

相关文章推荐
- (翻译)正确实施DevOps-The Lay of the Land
- UVA - 10499 The Land of Justice
- UVA 10499-The Land of Justice
- HTTP:The Definitive Guide 1.8 Architectural Components of the Web
- H. (网预)The land of LandLord 第十一届北京邮电大学程序设计竞赛 - 热身赛 (1)
- uva 10499 - The Land of Justice
- 【原创】The solutional manual of the Verilog HDL: A Guide to Digital Design and Synthesis (2nd)—ch07-II
- the Marvelous Land of Oz 37.9%
- Running Xen: A Hands-On Guide to the Art of Virtualization
- Openstack Horizon and Django Compare the Working of authentication (Login)
- A step-by-step guide to the use of the Intel OpenCV library and the Microsoft DirectShow technology
- 新年的第一张碟:The Fat of the Land
- 1. MaxCounters 计数器 Calculate the values of counters after applying all alternating operations: increase counter by 1; set value of all counters to current maximum.
- UVa_10499 - The Land of Justice
- Counting the active session number and tune up concurrent performance of MapGuide/AIMS
- 【原创】The solutional manual of the Verilog HDL: A Guide to Digital Design and Synthesis (2nd)--ch03
- 【原创】The solutional manual of the Verilog HDL: A Guide to Digital Design and Synthesis (2nd)--ch09
- UVa 10499 - The Land of Justice
- Assume the coasting is an infinite straight line. Land is in one side of coasting, sea in the other.
- 10499 - The Land of Justice
