Ural1033 FloodFill 算法
2014-10-04 15:03
561 查看
1033. Labyrinth
Time limit: 1.0 secondMemory limit: 64 MB
Administration of the labyrinth has decided to start a new season with new wallpapers. For this purpose they need a program to calculate the surface area of the walls inside the labyrinth. This job is just for you!
The labyrinth is represented by a matrix N×N (3 ≤
N ≤ 33, you see, ‘3’ is a magic digit!). Some matrix cells contain a dot character (‘.’) that denotes an empty square. Other cells contain a diesis character (‘#’) that denotes a square filled by monolith block of stone wall. All squares are of the
same size 3×3 meters.
The walls are constructed around the labyrinth (except for the upper left and lower right corners, which are used as entrances) and on the cells with a diesis character. No other walls are constructed. There always will be a
dot character at the upper left and lower right corner cells of the input matrix.
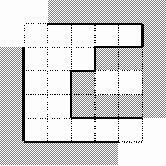
Your task is to calculate the area of visible part of the walls inside the labyrinth. In other words, the area of the walls' surface visible to a visitor of the labyrinth. Note that there's no holes to look or to move through
between any two adjacent blocks of the wall. The blocks are considered to be adjacent if they touch each other in any corner. See picture for an example: visible walls inside the labyrinth are drawn with bold lines. The height of all the walls is 3 meters.
Input
The first line of the input contains the single numberN. The next N lines contain N characters each. Each line describes one row of the labyrinth matrix. In each line only dot and diesis characters will be used and each line will be terminated with a new line character. There will be
no spaces in the input.
Output
Your program should print to the output a single integer — the exact value of the area of the wallpaper needed.Sample
| input | output |
|---|---|
5 ..... ...## ..#.. ..### ..... | 198 |
就是求图中粗黑色边缘墙的长度,然后计算墙的面积,每单位长度长3米,高也是3米。
思路:
看到了一种名字叫floodfill的算法,听起来好高端啊,和Photoshop里的魔术棒很像,但其实就是dfs活着bfs可以实现的。不过这道题是要根据这个算法计算,碰到墙壁就step++,计算边的长度。
值得注意的是,这个题起点和终点可能不连通。有必要的话遍历两次。我在这里出现了错误,刚开始统一的遍历两次,但是如果floodfill算法里不加判断的话,从1,1遍历过的,从n,n再遍历就要重复,因为刚进入floodfill算法时没有判断是否标记过而是直接计算的。计算结果就会多出几组数据如图。

本来挺水的一道题都没想的清清楚楚,真是弱爆了。。。~~~~(>_<)~~~~
好啦,贴代码。
//难点:周围还有墙。。。。 用广搜,当搜到边界或搜到#的时候计数加1
// 算法 :Foold_Fill 算法,其实就是dfs 或者bfs 求最大的联通块数,然后求表面积
//有这个填充算法为基础,类似photoshop的魔术棒选择工具就很容易实现了。
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdio>
#include<queue>
#include<cstring>
using namespace std;
char map[40][40];
bool vis[40][40];
int dx[]={0,0,1,-1};
int dy[]={1,-1,0,0};
int n;
int step;
void floodfill(int x,int y)
{
if(vis[x][y])return ;//忘记加这句话就WA。。。 ??????? 因为最后要从出口再进入的时候判断一下
vis[x][y]=1;
for(int i=0;i<4;i++)
{
int xx=x+dx[i],yy=y+dy[i];
if(map[xx][yy]=='#')
{
step++; //遇到墙壁就+1
}
else
{
if(!vis[xx][yy]) //触碰到了边界就继续转换方向
floodfill(xx,yy);
}
}
}
void dfs(int x,int y)
{
vis[x][y]=1;
int i,j;
for(i=0;i<4;i++)
{
if(map[x+dx[i]][y+dy[i]]=='#')step++;
else if(!vis[x+dx[i]][y+dy[i]] && map[x+dx[i]][y+dy[i]]=='.')
{
dfs(x+dx[i],y+dy[i]);
}
}
}
int main()
{
// freopen("q.in","r",stdin);
int i,j;
scanf("%d",&n);
memset(vis,true,sizeof(vis));
memset(map,'#',sizeof(map));
for(i=1;i<=n;i++)
{
for(j=1;j<=n;j++)
{
cin>>map[i][j];
if(map[i][j]=='.')vis[i][j]=false;
}
}
step=0;
// floodfill(1,1);
// floodfill(n,n);
dfs(1,1);
if(vis
==0)
dfs(n,n);
cout<<(step-4)*9<<endl;
}
相关文章推荐
- Ural-1076 Trash(最小费用最大流算法)
- 【manacher算法】HDU3294 URAL1297
- 算法练习:URAL 1495 One-two, One-two 2
- 【OpenCV入门教程之十五】水漫金山:OpenCV漫水填充算法(Floodfill)
- 二分图最大匹配(匈牙利算法) URAL 1721 Two Sides of the Same Coin
- Labyrinth (URAL 1033)
- 重学数据结构系列之——图论算法之FloodFill 算法
- 11基于opencv的漫水填充算法floodFill()
- FloodFill(洪水填充 )算法
- URAL 1033|Labyrinth|搜索
- ural 1297 最长回文串 manacher 算法
- [USACO2004][poj2375]Cow Ski Area(在特殊图上用floodfill代替强联通算法)
- 【OpenCV入门教程之十五】水漫金山:OpenCV漫水填充算法(Floodfill)
- Ural1109_Conference(二分图最大匹配/匈牙利算法/网络最大流)
- Ural 1033 Labyrinth(bfs)
- 【OpenCV入门教程之十五】水漫金山:OpenCV漫水填充算法(Floodfill)
- 【算法设计与数据结构】动态规划入门——URAL 1119 Metro
- URAL/1033 迷宫
- ural 1033. Labyrinth(dfs)
- URAL 1033 Labyrinth
