hdu 1054 Strategic Game (二分图 最小顶点覆盖)
2014-09-05 10:41
603 查看
Strategic Game
Time Limit: 20000/10000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 65536/32768 K (Java/Others)Total Submission(s): 5047 Accepted Submission(s): 2306
Problem Description
Bob enjoys playing computer games, especially strategic games, but sometimes he cannot find the solution fast enough and then he is very sad. Now he has the following problem. He must defend a medieval city, the roads of which form a tree. He has to put the
minimum number of soldiers on the nodes so that they can observe all the edges. Can you help him?
Your program should find the minimum number of soldiers that Bob has to put for a given tree.
The input file contains several data sets in text format. Each data set represents a tree with the following description:
the number of nodes
the description of each node in the following format
node_identifier:(number_of_roads) node_identifier1 node_identifier2 ... node_identifier
or
node_identifier:(0)
The node identifiers are integer numbers between 0 and n-1, for n nodes (0 < n <= 1500). Every edge appears only once in the input data.
For example for the tree:
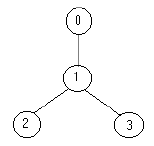
the solution is one soldier ( at the node 1).
The output should be printed on the standard output. For each given input data set, print one integer number in a single line that gives the result (the minimum number of soldiers). An example is given in the following table:
Sample Input
4 0:(1) 1 1:(2) 2 3 2:(0) 3:(0) 5 3:(3) 1 4 2 1:(1) 0 2:(0) 0:(0) 4:(0)
Sample Output
1 2
在网上搜树形DP的题做,搜到这题,想了一上午,也没找到DP方程,在网上搜了下题解,感觉那人的DP方程明显不对,照着他的方程敲了下,竟然a了,我以为我读错题了,又读了几遍,发现没读错,看到网上很多是用二分图做的,就找了份代码,跑了一下,发现与我的数据结果一样,才知道这题是用二分图,而不是树形DP,数据太水,坑啊
树形DP代码:
//203ms
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cstring>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
const int maxn=2000+100;
vector<int> son[maxn];
int dp[maxn][2];
void dfs(int u)
{
dp[u][1]=1;
for(int i=0;i<son[u].size();i++)
{
int v=son[u][i];
dfs(v);
dp[u][1]+=min(dp[v][0],dp[v][1]);
dp[u][0]+=dp[v][1];
}
return;
}
int main()
{
int n,x,m,y,root;
while(~scanf("%d",&n))
{
root=-1;
for(int i=0;i<=n;i++)
son[i].clear();
memset(dp,0,sizeof(dp));
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
{
scanf("%d:(%d)",&x,&m);
for(int j=0;j<m;j++)
{
scanf("%d",&y);
son[x].push_back(y);
if(root==-1)
root=x;
}
}
dfs(root);
printf("%d\n",min(dp[root][0],dp[root][1]));
}
return 0;
}数据:
6
3: (1) 1
1: (1) 2
2: (1) 4
4: (1) 6
6: (1) 5
5: (0)
取节点1和6就可以了,但是树形DP跑出来的结果是3
二分图还没学过,在网上找份代码http://blog.csdn.net/lulipeng_cpp/article/details/7692094
代码:
//625ms
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
#include<cstring>
#include<cstdio>
using namespace std;
const int MAX=1500;
vector<int> map[MAX];
bool used[MAX];
int link[MAX];
int n;
void preClear()
{
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
map[i].clear();
}
void storeMap() //存储二分图
{
preClear();
int i,j,row,col,num;
memset(map,false,sizeof(map));
for(j=0;j<n;j++)
{
scanf("%d:(%d)",&row,&num);
for(i=0;i<num;i++)
{
scanf("%d",&col);
//map[row][col]=true;
//map[col][row]=true;
//邻接表,双向图
map[row].push_back(col);
map[col].push_back(row);
}
}
}
bool can(int t) //确定是否存在增广路径
{
int tmp;
for(int i=0;i<map[t].size();i++)
{
tmp=map[t][i];
if(!used[tmp])
{
used[tmp]=true;
if(link[tmp]==-1 || can(link[tmp]))
{
link[tmp]=t;
return true;
}
}
}
return false;
}
int maxMatch()
{
int num=0;
memset(link,0xff,sizeof(link));
for(int i=0;i<n;i++) //从每一左顶点出发寻找增广路径
{
memset(used,false,sizeof(used));
if(can(i)) num++;
}
return num;
}
int main()
{
while(scanf("%d",&n)==1)
{
storeMap();
printf("%d\n",maxMatch()/2);
}
return 0;
}
相关文章推荐
- POJ 1463 ||HDU 1054 Strategic game(二分图最小顶点覆盖)
- hdu 1054 Strategic Game 最小顶点覆盖(二分图最大匹配)
- HDU 1054 Strategic Game(二分图 最小顶点覆盖)
- HDU 1054 Strategic Game 二分图 最小顶点覆盖
- HDU-1054 Strategic Game(二分图最小顶点覆盖)
- hdu 1054 Strategic Game 最小顶点覆盖(二分图最大匹配)
- 【最小顶点覆盖数 && 无向图】HDU - 1054 Strategic Game
- HDU 1054 Strategic Game-二分匹配&最小顶点覆盖
- HDU 1054 Strategic Game 最小顶点覆盖
- [hungary][最小顶点覆盖][二分图]hdu 1054
- hdu 1054 Strategic Game 二分图的匹配,最小点覆盖数
- HDU 1054 Strategic Game (最小顶点覆盖)
- HDU 1054 Strategic Game 二分图最小点覆盖
- HDU 1054 Strategic Game (最小顶点覆盖)
- HDU ACM 1054 Strategic Game 二分图最小顶点覆盖?树形DP
- hdu 1054 Strategic Game 二分图最小点覆盖
- HDU 1054 Strategic Game 最小顶点覆盖
- E - Strategic Game (HDU - 1054 )(最小顶点覆盖)(匈牙利算法模板)(树形DP)
- HDU - 1054 Strategic Game(二分图最小点覆盖/树形dp)
- HDU 1054 Strategic Game (二分图最小点覆盖)
