UVA - 1378 A Funny Stone Game (SG定理)
2014-08-28 15:18
405 查看
Description

The funny stone game is coming. There are n piles of stones, numbered with0, 1, 2,...,
n - 1. Two persons pick stones in turn. In every turn, each person selects three piles of stones numberedi,
j, k (i <
j, j
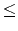
k and at least one stone left in pilei).
Then, the person gets one stone out of pilei, and put one stone into pile
j and pile k respectively. (Note: ifj =
k, it will be the same as putting two stones into pilej). One will fail if he can't pick stones according to the rule.
David is the player who first picks stones and he hopes to win the game. Can you write a program to help him?
The number of piles, n, does not exceed
23. The number of stones in each pile does not exceed 1000. Suppose the opponent player is very smart and he will follow the optimized strategy to pick stones.
1
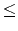
n
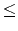
23) indicating the number of piles of stones. The second line contains
n non-negative integers separated by blanks, S0,...Sn-1 (0
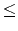
Si
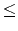
1000), indicating the number of stones in pile 0 to pilen - 1 respectively.
The last case is followed by a line containing a zero.
i,j and
k indicates which three piles David shall select at the first step if he wants to win. If there are multiple groups ofi,
j and k, output the group with the minimized lexicographic order. If there are no strategies to win the game,i,
j and k are equal to
-1.

The funny stone game is coming. There are n piles of stones, numbered with0, 1, 2,...,
n - 1. Two persons pick stones in turn. In every turn, each person selects three piles of stones numberedi,
j, k (i <
j, j
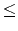
k and at least one stone left in pilei).
Then, the person gets one stone out of pilei, and put one stone into pile
j and pile k respectively. (Note: ifj =
k, it will be the same as putting two stones into pilej). One will fail if he can't pick stones according to the rule.
David is the player who first picks stones and he hopes to win the game. Can you write a program to help him?
The number of piles, n, does not exceed
23. The number of stones in each pile does not exceed 1000. Suppose the opponent player is very smart and he will follow the optimized strategy to pick stones.
Input
Input contains several cases. Each case has two lines. The first line contains a positive integern (1
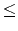
n
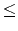
23) indicating the number of piles of stones. The second line contains
n non-negative integers separated by blanks, S0,...Sn-1 (0
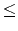
Si
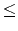
1000), indicating the number of stones in pile 0 to pilen - 1 respectively.
The last case is followed by a line containing a zero.
Output
For each case, output a line in the format `` Game t:ijk".t is the case number.i,j and
k indicates which three piles David shall select at the first step if he wants to win. If there are multiple groups ofi,
j and k, output the group with the minimized lexicographic order. If there are no strategies to win the game,i,
j and k are equal to
-1.
Sample Input
4 1 0 1 100 3 1 0 5 2 2 1 0
Sample Output
Game 1: 0 2 3 Game 2: 0 1 1 Game 3: -1 -1 -1 题意:有n堆石头,编号为0-n-1,第i堆初始有si个石头,两个游戏者轮流操作,每次可以选3堆i,j,k,使得i<j<=k,且第i堆至少还剩一个石子,然后从第i堆拿走一个石子 再往第j堆和第k堆各放一个石子(j和k可以一样),判断先手必胜还是必败,如果必胜,输出字典序最小的一个操作(i,j,k)。 思路:可以把每个石子看作是独立的游戏,然后我们从左到右重现排列成n-1,n-2.....0,这样方便我们SG状态的转移,所以我们就可以枚举每个i的后继状态sg[j]^sg[k]了,最后判断一下 操作一次后的SG值是不是为0,也就是必败#include <iostream> #include <cstdio> #include <cstring> #include <algorithm> using namespace std; const int maxn = 105; int n, a[maxn], sg[maxn], vis[maxn]; void init() { for (int i = 0; i <= 23; i++) { memset(vis, 0, sizeof(vis)); for (int j = 0; j < i; j++) for (int k = j; k < i; k++) vis[sg[k]^sg[j]] = 1; for (int j = 0; ; j++) if (!vis[j]) { sg[i] = j; break; } } } int main() { init(); int cas = 1; while (scanf("%d", &n) != EOF && n) { int ans = 0; for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) { scanf("%d", &a[i]); if (a[i] & 1) ans ^= sg[n-1-i]; } printf("Game %d: ", cas++); if (ans == 0) printf("-1 -1 -1\n"); else { int flag = 0; for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) { if (a[i] == 0) continue; for (int j = i+1; j < n; j++) { for (int k = j; k < n; k++) if ((ans^sg[n-1-i]^sg[n-1-j]^sg[n-1-k]) == 0) { printf("%d %d %d\n", i, j, k); flag = 1; break; } if (flag) break; } if (flag) break; } } } return 0; }
相关文章推荐
- 【UVA1378】A Funny Stone Game (博弈-求SG值-输出方案)
- uva 1378 A Funny Stone Game (博弈-SG)
- uva 1378 - A Funny Stone Game(组合游戏)
- sg函数_______A Funny Stone Game(uva 1378)
- uva 1378 A Funny Stone Game(博弈论)
- uva 1378 - A Funny Stone Game(组合游戏)
- Uva 1378 - A Funny Stone Game
- UVa 1378 A Funny Stone Game [博弈论 SG函数]
- UVA 1378 - A Funny Stone Game(博弈)
- UVA 1378 A Funny Stone Game (经典博弈)
- [UVA1378] A Funny Stone Game && SG函数
- uva 1378 A Funny Stone Game 博弈/组合游戏 sg定理
- LA 3668 A Funny Stone Game(博弈,SG定理)
- UVALive-7278 - Game of Cards【博弈】【sg定理】
- UVALive 3668 A Funny Stone Game(博弈)
- UVALive 3668 A Funny Stone Game
- [nim博弈扩展 sg函数] UVALive 3668 A Funny Stone Game
- UVA - 10561 Treblecross (SG定理)
- POJ 2599 A funny game#树形SG(DFS实现)
- hdu 2999 Stone Game, Why are you always there? (简单SG,有个优化)
