hdu4916 Count on the path
2014-08-09 19:48
363 查看
2014 Multi-University Training Contest 5 F题。
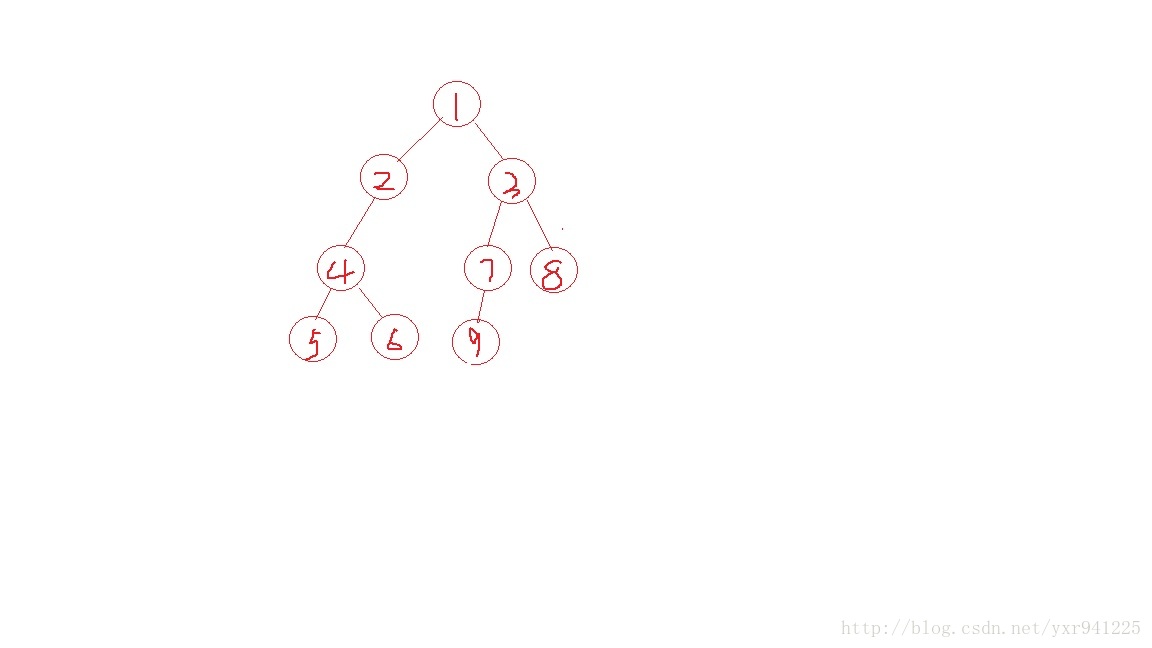
题目大意:给定一颗n个节点的树,q个查询,每次查询输入两个端点(u,v),代表树上一条从u->v的路径,求删掉这条路径上的点后,剩下的点中编号最小的点。
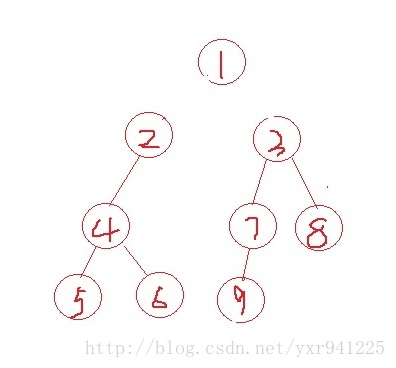
题目分析:可以这样想象:(1)我们以1这个节点为根,删掉根节点后形成若干个联通分量,很显然若路径中的两个端点在删掉根节点后还在同一个联通分量中,那么所求结果必然为1。这个可在预处理后O(1)实现(2)若两个端点不在同一个联通分量中,那么必然经过根节点,此时若纯暴力则时间复杂度可达O(n*q)之大,题目数据量非常大,必然死掉。 官方的题解给了做题的方向,可以用树形DP的思想,预处理求出每个节点的f[]值,f[u]代表从u到他所属的根节点(删除1之后的)除去路径上的点后编号最小的点值。
如下图所示,所求的值f[2]=4,f[3]=7,f[4]=5,f[5]=6,f[7]=8,f[8]=7,f[9]=8;
2所对应的根节点为2,f[2]=min(与2同属于一个联通分量且不在2到根节点的链上的,2以下的节点中编号最小的);
求出所有的f[]值后,还需知道各个联通分量中编号最小的点,因为当根节点1的儿子节点有多个,即有多个联通分量时 ,两个端点分属两个联通分量,最小值可能出现在别的联通分量中,但f[]值没有考虑到。 则我们需要保存编号最小的三个联通分量。
比较绕口,过后补上图解。
题目大意:给定一颗n个节点的树,q个查询,每次查询输入两个端点(u,v),代表树上一条从u->v的路径,求删掉这条路径上的点后,剩下的点中编号最小的点。
题目分析:可以这样想象:(1)我们以1这个节点为根,删掉根节点后形成若干个联通分量,很显然若路径中的两个端点在删掉根节点后还在同一个联通分量中,那么所求结果必然为1。这个可在预处理后O(1)实现(2)若两个端点不在同一个联通分量中,那么必然经过根节点,此时若纯暴力则时间复杂度可达O(n*q)之大,题目数据量非常大,必然死掉。 官方的题解给了做题的方向,可以用树形DP的思想,预处理求出每个节点的f[]值,f[u]代表从u到他所属的根节点(删除1之后的)除去路径上的点后编号最小的点值。
如下图所示,所求的值f[2]=4,f[3]=7,f[4]=5,f[5]=6,f[7]=8,f[8]=7,f[9]=8;
2所对应的根节点为2,f[2]=min(与2同属于一个联通分量且不在2到根节点的链上的,2以下的节点中编号最小的);
求出所有的f[]值后,还需知道各个联通分量中编号最小的点,因为当根节点1的儿子节点有多个,即有多个联通分量时 ,两个端点分属两个联通分量,最小值可能出现在别的联通分量中,但f[]值没有考虑到。 则我们需要保存编号最小的三个联通分量。
比较绕口,过后补上图解。


#include<iostream>
#include<cstdlib>
#include<cstdio>
#include<cstring>
#include<vector>
#include<stack>
#include<algorithm>
#include<queue>
struct node
{
int u,parent;
node(){}
node(int x,int y)
{
u=x,parent=y;
}
};
using namespace std;
const int maxn = 1000010;
stack<int >S;
queue<node >Q;
int pp[maxn];
int n,q,ecnt=0;
int next[maxn*2],e[maxn*2],head[maxn];
int cnt[maxn],f[maxn],x[5],y[5],other[maxn];
void addedge(int u,int v)
{
e[ecnt]=v;
next[ecnt]=head[u];
head[u]=ecnt++;
e[ecnt]=u;
next[ecnt]=head[v];
head[v]=ecnt++;
}
void dfs(int u,int fa)
{
f[u]=fa;
S.push(u);
while (!S.empty())
{
u=S.top();
int flag=0;
for (int i=head[u];i!=-1;i=next[i])
{
int v=e[i];
if (!f[v])
{
f[v]=fa;
S.push(v);
flag=1;
break;
}
}
if (!flag)
{
S.pop();
if (!S.empty())
{
int v=u;
u=S.top();
cnt[u]=min(v,cnt[u]);
cnt[u]=min(cnt[u],cnt[v]);
}
}
}
}
void bfs(int u,int parent)
{
Q.push(node(u,parent));
while (!Q.empty())
{
int x1=n+1,x2=n+1,y1=n+1,y2=n+1;
node tem=Q.front();
Q.pop();
u=tem.u;
parent=tem.parent;
for (int i=head[u];i!=-1;i=next[i])
{
int v=e[i];
if (v!=parent)
{
Q.push(node(v,u));
int yy=min(cnt[v],v);
if (yy<y1)
{
y2=y1;
x2=x1;
y1=yy;
x1=v;
}
else if (yy<y2)
{
y2=yy;
x2=v;
}
}
}
for (int i=head[u];i!=-1;i=next[i])
{
int v=e[i];
if (v==u)
continue;
other[v]=other[u];
if (v!=x1)
{
other[v]=min(other[v],y1);
}
else
{
other[v]=min(other[v],y2);
}
}
}
return ;
}
inline void scan(int &n)
{
char cc;
for (; cc = getchar(), cc<'0' || cc>'9';);
n = cc - '0';
for (; cc = getchar(), cc >= '0'&&cc <= '9';)
n = n * 10 + cc - '0';
}
int main()
{
while (scanf("%d%d",&n,&q)!=EOF)
{
int i,j,u,v,prex=0;
ecnt=0;
for (i=1;i<=n;i++)
{
head[i]=-1;
f[i]=0;
cnt[i]=n+1;
other[i]=n+1;
}
for (i=1;i<n;i++)
{
// scanf("%d%d",&u,&v);
scan(u);
scan(v);
addedge(u,v);
}
f[1]=1;
cnt[1]=n+1;
x[0]=x[1]=x[2]=0;
y[0]=y[1]=y[2]=n+1;
for (i=head[1];i!=-1;i=next[i])
{
dfs(e[i],e[i]);
}
for (i=head[1];i!=-1;i=next[i])
{
bfs(e[i],1);
int fa=min(cnt[e[i]],e[i]);
if (fa<y[0])
{
y[2]=y[1];
y[1]=y[0];
y[0]=fa;
x[2]=x[1];
x[1]=x[0];
x[0]=e[i];
}
else if (fa<y[1])
{
y[2]=y[1];
y[1]=fa;
x[2]=x[1];
x[1]=e[i];
}
else if (fa<y[2])
{
y[2]=fa;
x[2]=e[i];
}
}
for (i=2;i<=n;i++)
{
cnt[i]=min(other[i],cnt[i]);
}
for (i=0;i<q;i++)
{
// scanf("%d%d",&u,&v);
scan(u);
scan(v);
u^=prex;
v^=prex;
if (f[u]==f[v]&&(u!=1&&v!=1))
{
printf("1\n");
prex=1;
}
else
{
int tot=min(cnt[u],cnt[v]);
if (tot>y[0]&&(x[0]!=f[u]&&x[0]!=f[v]))
{
tot=y[0];
}
else if (tot>y[1]&&(x[1]!=f[u]&&x[1]!=f[v]))
{
tot=y[1];
}
else if (tot>y[2])
{
tot=y[2];
}
prex=tot;
printf("%d\n",tot);
}
}
}
return 0;
}
相关文章推荐
- HDU4916 Count on the path(树dp??)
- hdu4916 Count on the path,树dp
- Hdu 4916 Count on the path
- hdu 4916 Count on the path(树形dp)
- hdu 4916 Count on the path
- hdu 4916 Count on the path 树dp
- 【HDU】4916 Count on the path 树型DP
- HDU 4916 Count on the path
- Hdu 4916 Count on the path
- HDU 4916 Count on the path
- [HDOJ 4916] Count on the path [树+乱搞]
- HDU 4916(Count on the path-树上除链上的节点外最小值[强制在线])
- JavaWeb: 报错信息The superclass "javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet" was not found on the Java Build Path
- JavaWeb: 报错信息The superclass "javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet" was not found on the Java Build Path
- JavaWeb:报错信息The superclass "javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet" was not found on the Java Build Path
- The superclass "javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet" was not found on the Java Build Path
- The superclass "javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet" was not found on the Java Build Path 解决方法
- java web(jsp)-The superclass "javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet" was not found on the Java Build Path
- The superclass "javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet" was not found on the Java Build Path
- The superclass "javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet" was not found on the Java Build Path
