Android高手进阶 AIDL
2014-08-02 16:03
381 查看
在Android中, 每个应用程序都可以有自己的进程. 在写UI应用的时候, 经常要用到Service. 在不同的进程中, 怎样传递对象呢? 显然, Java中不允许跨进程内存共享. 因此传递对象, 只能把对象拆分成操作系统能理解的简单形式, 以达到跨界对象访问的目的. 在J2EE中,采用RMI的方式, 可以通过序列化传递对象.
在Android中, 则采用AIDL的方式. 理论上AIDL可以传递Bundle,实际上做起来却比较麻烦.
AIDL(AndRoid接口描述语言)是一种借口描述语言; 编译器可以通过aidl文件生成一段代码,通过预先定义的接口达到两个进程内部通信进程的目的.
如果需要在一个Activity中, 访问另一个Service中的某个对象, 需要先将对象转化成AIDL可识别的参数(可能是多个参数), 然后使用AIDL来传递这些参数, 在消息的接收端, 使用这些参数组装成自己需要的对象.
AIDL的IPC的机制和COM或CORBA类似,
是基于接口的,但它是轻量级的。它使用代理类在客户端和实现层间传递值. 如果要使用AIDL, 需要完成2件事情: 1. 引入AIDL的相关类.; 2. 调用aidl产生的class.
服务端的实现步骤:
首先看一下服务端,工程目录如下:
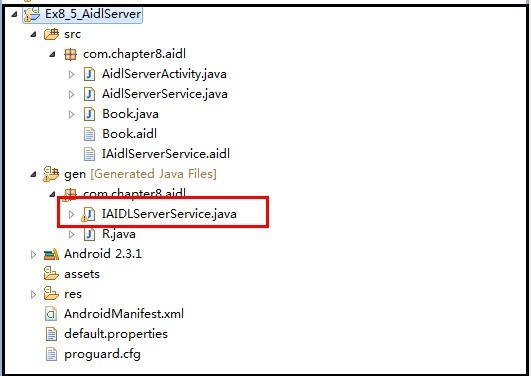
首先创建IaidlServerService.aidl文件,代码如下(一个简单方法,另一个返回对象方法),当我们点击保存时会在gen目录下生成对应的java文件,如上图红色部分:
package com.chapter8.aidl;
import com.chapter8.aidl.Book;
interface IAIDLServerService {
String sayHello();
Book getBook();
}
第二步:因为这个接口里有传递对象,所以对象要特殊处理一下,这里继承了Parcelable,Book.java代码如下:
[java] view
plaincopy
package com.chapter8.aidl;
import android.os.Parcel;
import android.os.Parcelable;
public class Book implements Parcelable {
private String bookName;
private int bookPrice;
public Book(){
}
public Book(Parcel parcel){
bookName = parcel.readString();
bookPrice = parcel.readInt();
}
public String getBookName() {
return bookName;
}
public void setBookName(String bookName) {
this.bookName = bookName;
}
public int getBookPrice() {
return bookPrice;
}
public void setBookPrice(int bookPrice) {
this.bookPrice = bookPrice;
}
public int describeContents() {
return 0;
}
public void writeToParcel(Parcel parcel, int flags) {
parcel.writeString(bookName);
parcel.writeInt(bookPrice);
}
public static final Parcelable.Creator<Book> CREATOR = new Creator<Book>() {
public Book createFromParcel(Parcel source) {
return new Book(source);
}
public Book[] newArray(int size) {
return new Book[size];
}
};
}
第三步:写一个与Book类对应的aidl,命名为Book.aidl,代码非常简单,代码如下:
[java] view
plaincopy
parcelable Book;
第四步:新建一个名为AidlServerService的Service.代码如下:
[java] view
plaincopy
package com.chapter8.aidl;
import com.chapter8.aidl.IAIDLServerService.Stub;
import com.chapter8.aidl.IAIDLServerService;
import android.app.Service;
import android.content.Intent;
import android.os.IBinder;
import android.os.RemoteException;
public class AidlServerService extends Service {
@Override
public IBinder onBind(Intent intent) {
return mBinder;
}
/**
* 在AIDL文件中定义的接口实现。
*/
private IAIDLServerService.Stub mBinder = new Stub() {
public String sayHello() throws RemoteException {
return "Hello";
}
public Book getBook() throws RemoteException {
Book mBook = new Book();
mBook.setBookName("Android应用开发");
mBook.setBookPrice(50);
return mBook;
}
};
}
第五步:在AndroidManifest.xml注册Service,代码如下:
[java] view
plaincopy
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<manifest xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
package="com.chapter8.aidl"
android:versionCode="1"
android:versionName="1.0">
<application android:icon="@drawable/icon" android:label="@string/app_name">
<activity android:name="AidlServerActivity"
android:label="@string/app_name">
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="android.intent.action.MAIN" />
<category android:name="android.intent.category.LAUNCHER" />
</intent-filter>
</activity>
<service android:name="AidlServerService"
android:process=":remote">
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="com.chapter8.aidl.IAIDLServerService"></action>
</intent-filter>
</service>
</application>
</manifest>
第六步:运行服务端工程,到设备上,好让客户端调用,服务端的Activity什么都没做.效果如下:
客户端的具体实现步骤:
第一步:新建客户端工程,目录结构如下:
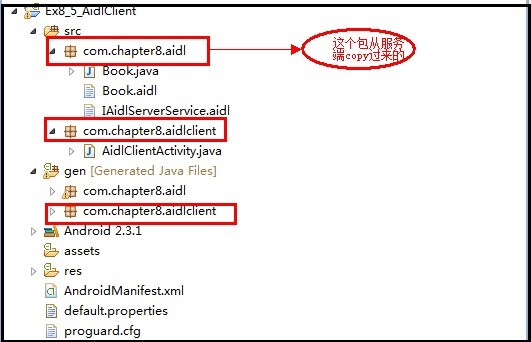
第二步:引入Aidl文件以及用到的类,如上面的com.chapter8.aidl包。直接从服务端里代码copy过来就OK.
第三步:修改main.xml布局文件,增加一个按钮,代码如下:
[java] view
plaincopy
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:orientation="vertical"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="fill_parent"
>
<TextView
android:id="@+id/textview"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="@string/hello"
/>
<Button
android:id="@+id/button"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="调用AIDL服务"
/>
</LinearLayout>
第四步:修改AidlClientActivity.java代码如下:
[java] view
plaincopy
package com.chapter8.aidlclient;
import com.chapter8.aidl.IAIDLServerService;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.content.ComponentName;
import android.content.Intent;
import android.content.ServiceConnection;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.os.IBinder;
import android.os.RemoteException;
import android.view.View;
import android.view.View.OnClickListener;
import android.widget.Button;
import android.widget.TextView;
public class AidlClientActivity extends Activity {
private TextView mTextView;
private Button mButton;
private IAIDLServerService mIaidlServerService = null;
private ServiceConnection mConnection = new ServiceConnection() {
public void onServiceDisconnected(ComponentName name) {
mIaidlServerService = null;
}
public void onServiceConnected(ComponentName name, IBinder service) {
mIaidlServerService = IAIDLServerService.Stub.asInterface(service);
//aidl通信
try {
String mText = "Say hello: " + mIaidlServerService.sayHello() + "/n";
mText += "书名: " + mIaidlServerService.getBook().getBookName()+"/n";
mText += "价格: " + mIaidlServerService.getBook().getBookPrice();
mTextView.setText(mText);
} catch (RemoteException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
};
@Override
public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.main);
//初始化控件
mTextView = (TextView)findViewById(R.id.textview);
mButton = (Button)findViewById(R.id.button);
//增加事件响应
mButton.setOnClickListener(new OnClickListener(){
public void onClick(View v) {
//bindService
Intent service = new Intent("com.chapter8.aidl.IAIDLServerService");
bindService(service, mConnection,BIND_AUTO_CREATE);
}
});
}
}
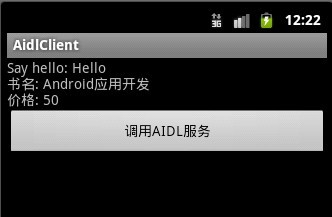
第五步:运行客户端工程,效果如下:
在Android中, 则采用AIDL的方式. 理论上AIDL可以传递Bundle,实际上做起来却比较麻烦.
AIDL(AndRoid接口描述语言)是一种借口描述语言; 编译器可以通过aidl文件生成一段代码,通过预先定义的接口达到两个进程内部通信进程的目的.
如果需要在一个Activity中, 访问另一个Service中的某个对象, 需要先将对象转化成AIDL可识别的参数(可能是多个参数), 然后使用AIDL来传递这些参数, 在消息的接收端, 使用这些参数组装成自己需要的对象.
AIDL的IPC的机制和COM或CORBA类似,
是基于接口的,但它是轻量级的。它使用代理类在客户端和实现层间传递值. 如果要使用AIDL, 需要完成2件事情: 1. 引入AIDL的相关类.; 2. 调用aidl产生的class.
服务端的实现步骤:
首先看一下服务端,工程目录如下:

首先创建IaidlServerService.aidl文件,代码如下(一个简单方法,另一个返回对象方法),当我们点击保存时会在gen目录下生成对应的java文件,如上图红色部分:
package com.chapter8.aidl;
import com.chapter8.aidl.Book;
interface IAIDLServerService {
String sayHello();
Book getBook();
}
第二步:因为这个接口里有传递对象,所以对象要特殊处理一下,这里继承了Parcelable,Book.java代码如下:
[java] view
plaincopy
package com.chapter8.aidl;
import android.os.Parcel;
import android.os.Parcelable;
public class Book implements Parcelable {
private String bookName;
private int bookPrice;
public Book(){
}
public Book(Parcel parcel){
bookName = parcel.readString();
bookPrice = parcel.readInt();
}
public String getBookName() {
return bookName;
}
public void setBookName(String bookName) {
this.bookName = bookName;
}
public int getBookPrice() {
return bookPrice;
}
public void setBookPrice(int bookPrice) {
this.bookPrice = bookPrice;
}
public int describeContents() {
return 0;
}
public void writeToParcel(Parcel parcel, int flags) {
parcel.writeString(bookName);
parcel.writeInt(bookPrice);
}
public static final Parcelable.Creator<Book> CREATOR = new Creator<Book>() {
public Book createFromParcel(Parcel source) {
return new Book(source);
}
public Book[] newArray(int size) {
return new Book[size];
}
};
}
第三步:写一个与Book类对应的aidl,命名为Book.aidl,代码非常简单,代码如下:
[java] view
plaincopy
parcelable Book;
第四步:新建一个名为AidlServerService的Service.代码如下:
[java] view
plaincopy
package com.chapter8.aidl;
import com.chapter8.aidl.IAIDLServerService.Stub;
import com.chapter8.aidl.IAIDLServerService;
import android.app.Service;
import android.content.Intent;
import android.os.IBinder;
import android.os.RemoteException;
public class AidlServerService extends Service {
@Override
public IBinder onBind(Intent intent) {
return mBinder;
}
/**
* 在AIDL文件中定义的接口实现。
*/
private IAIDLServerService.Stub mBinder = new Stub() {
public String sayHello() throws RemoteException {
return "Hello";
}
public Book getBook() throws RemoteException {
Book mBook = new Book();
mBook.setBookName("Android应用开发");
mBook.setBookPrice(50);
return mBook;
}
};
}
第五步:在AndroidManifest.xml注册Service,代码如下:
[java] view
plaincopy
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<manifest xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
package="com.chapter8.aidl"
android:versionCode="1"
android:versionName="1.0">
<application android:icon="@drawable/icon" android:label="@string/app_name">
<activity android:name="AidlServerActivity"
android:label="@string/app_name">
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="android.intent.action.MAIN" />
<category android:name="android.intent.category.LAUNCHER" />
</intent-filter>
</activity>
<service android:name="AidlServerService"
android:process=":remote">
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="com.chapter8.aidl.IAIDLServerService"></action>
</intent-filter>
</service>
</application>
</manifest>
第六步:运行服务端工程,到设备上,好让客户端调用,服务端的Activity什么都没做.效果如下:

客户端的具体实现步骤:
第一步:新建客户端工程,目录结构如下:

第二步:引入Aidl文件以及用到的类,如上面的com.chapter8.aidl包。直接从服务端里代码copy过来就OK.
第三步:修改main.xml布局文件,增加一个按钮,代码如下:
[java] view
plaincopy
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:orientation="vertical"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="fill_parent"
>
<TextView
android:id="@+id/textview"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="@string/hello"
/>
<Button
android:id="@+id/button"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="调用AIDL服务"
/>
</LinearLayout>
第四步:修改AidlClientActivity.java代码如下:
[java] view
plaincopy
package com.chapter8.aidlclient;
import com.chapter8.aidl.IAIDLServerService;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.content.ComponentName;
import android.content.Intent;
import android.content.ServiceConnection;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.os.IBinder;
import android.os.RemoteException;
import android.view.View;
import android.view.View.OnClickListener;
import android.widget.Button;
import android.widget.TextView;
public class AidlClientActivity extends Activity {
private TextView mTextView;
private Button mButton;
private IAIDLServerService mIaidlServerService = null;
private ServiceConnection mConnection = new ServiceConnection() {
public void onServiceDisconnected(ComponentName name) {
mIaidlServerService = null;
}
public void onServiceConnected(ComponentName name, IBinder service) {
mIaidlServerService = IAIDLServerService.Stub.asInterface(service);
//aidl通信
try {
String mText = "Say hello: " + mIaidlServerService.sayHello() + "/n";
mText += "书名: " + mIaidlServerService.getBook().getBookName()+"/n";
mText += "价格: " + mIaidlServerService.getBook().getBookPrice();
mTextView.setText(mText);
} catch (RemoteException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
};
@Override
public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.main);
//初始化控件
mTextView = (TextView)findViewById(R.id.textview);
mButton = (Button)findViewById(R.id.button);
//增加事件响应
mButton.setOnClickListener(new OnClickListener(){
public void onClick(View v) {
//bindService
Intent service = new Intent("com.chapter8.aidl.IAIDLServerService");
bindService(service, mConnection,BIND_AUTO_CREATE);
}
});
}
}
第五步:运行客户端工程,效果如下:


相关文章推荐
- Android高手进阶教程(二十五)之---Android 中的AIDL!!!
- Android高手进阶教程(二十五)之---Android 中的AIDL!!!
- Android高手进阶教程(二十五)之---Android 中的AIDL!!!
- Android高手进阶教程(二十五)之---Android 中的AIDL!!!
- Android高手进阶教程(二十五)之---Android 中的AIDL!!!
- Android高手进阶教程(二十五)之---Android 中的AIDL!!!
- Android高手进阶教程(二十五)之---Android 中的AIDL!!!
- Android高手进阶教程(二十五)之---Android 中的AIDL!!!
- Android高手进阶教程(二十五)之---Android 中的AIDL!!!
- Android高手进阶(一)AIDL跨进程调用
- Android高手进阶教程(二十五)之---Android 中的AIDL!!!
- 【读博笔记】读《 Android高手进阶教程(二十五)之---Android 中的AIDL!!! 》笔记
- Android高手进阶教程(二十五)之---Android 中的AIDL!!!
- Android高手进阶教程(九)之----Android Handler的使用!!!
- Android高手进阶教程(六)之----Android 中MenuInflater的使用(布局定义菜单)!
- Android高手进阶教程(十)之----Android PopupWindow的使用!!!
- Android高手进阶教程(十五)之---通过Location获取Address的使用!
- Android高手进阶教程(九)之----Android Handler的使用!!!
- Android 高手进阶教程(十三)之----Android 数据库SQLiteDatabase的使用!!
- Android高手进阶教程(十二)之----Android 在一个应用中如何启动另外一个已安装的应用!!!
