Java nio 学习笔记(五)
2014-06-26 17:42
134 查看
Java nio SocketChannel ServerSocketChannel 以及Selector实现的echo服务器和客户端(暂时有问题)
服务器端代码:
[java] view
plaincopy
import java.io.IOException;
import java.net.InetSocketAddress;
import java.nio.ByteBuffer;
import java.nio.channels.SelectionKey;
import java.nio.channels.Selector;
import java.nio.channels.ServerSocketChannel;
import java.nio.channels.SocketChannel;
import java.util.Calendar;
import java.util.Iterator;
public class TestServer {
public static void main(String[] args) {
new Thread(new EchoServer(1982)).start();
}
}
class EchoServer implements Runnable {
//要监听的端口号
private int port;
//生成一个信号监视器
private Selector s;
//读缓冲区
private ByteBuffer r_bBuf = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
public EchoServer(int port) {
this.port = port;
try {
s = Selector.open();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
@Override
public void run() {
try {
//生成一个ServerScoket通道的实例对象,用于侦听可能发生的IO事件
ServerSocketChannel ssc = ServerSocketChannel.open();
//将该通道设置为异步方式
ssc.configureBlocking(false);
//绑定到一个指定的端口
ssc.socket().bind(new InetSocketAddress(port));
//注册特定类型的事件到信号监视器上
ssc.register(s, SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT);
System.out.println("The server has been launched...");
while(true) {
//将会阻塞执行,直到有事件发生
System.out.println("监听新事件...");
s.select();
Iterator<SelectionKey> it = s.selectedKeys().iterator();
while(it.hasNext()) {
SelectionKey key = it.next();
//key定义了四种不同形式的操作
switch(key.readyOps()) {
case SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT :
dealwithAccept(key);
break;
case SelectionKey.OP_CONNECT :
break;
case SelectionKey.OP_READ :
dealwithRead(key);
break;
case SelectionKey.OP_WRITE :
break;
}
//处理结束后移除当前事件,以免重复处理
it.remove();
}
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
//处理接收连接的事件
private void dealwithAccept(SelectionKey key) {
try {
System.out.println("deal with new accept...");
ServerSocketChannel server = (ServerSocketChannel)key.channel();
SocketChannel sc = server.accept();
sc.configureBlocking(false);
//注册读事件
sc.register(s, SelectionKey.OP_WRITE);
System.out.println("deal with new accept2...");
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
//处理客户端发来的消息,处理读事件
private void dealwithRead(SelectionKey key) {
try {
SocketChannel sc = (SocketChannel)key.channel();
System.out.println("读入数据");
r_bBuf.clear();
sc.write(r_bBuf);
r_bBuf.flip();
System.out.println(r_bBuf.asCharBuffer().toString());
r_bBuf.clear();
System.out.println("处理完毕...");
try {
Thread.currentThread().sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
private String getCurrentTime() {
return Calendar.getInstance().toString();
}
}
client 端代码:
[java] view
plaincopy
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.net.InetSocketAddress;
import java.nio.ByteBuffer;
import java.nio.channels.SocketChannel;
public class TestClient {
public static void main(String[] args) {
new MiniClient("localhost", 1982);
}
}
class MiniClient {
private SocketChannel sc;
private ByteBuffer w_bBuf;
public MiniClient(String host, int port) {
try {
InetSocketAddress remote = new InetSocketAddress(host, port);
sc = SocketChannel.open();
sc.connect(remote);
if(sc.finishConnect()) {
System.out.println("已经与服务器成功建立连接...");
}
while(true) {
if(!sc.isConnected()) {
System.out.println("已经与服务器失去了连接...");
}
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
String str = br.readLine();
System.out.println("读入一行数据,开始发送...");
w_bBuf = ByteBuffer.wrap(str.getBytes());
w_bBuf.flip();
//向缓冲区中写入数据
sc.write(w_bBuf);
System.out.println("数据发送成功...");
w_bBuf.clear();
try {
Thread.currentThread().sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
} catch (IOException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
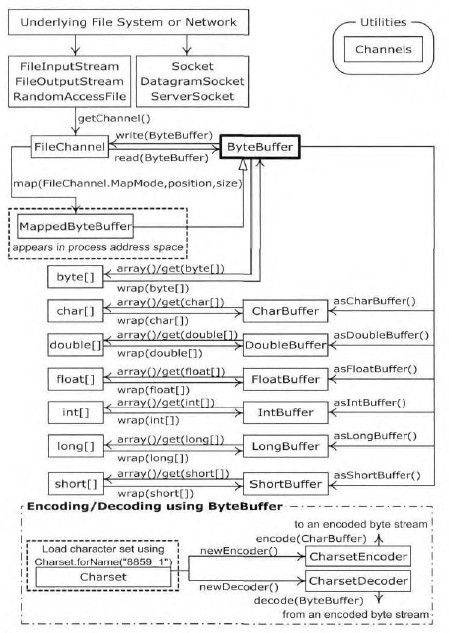
Thinking in java中的一个图片,刚找到的,比较清楚关系图。
服务器端代码:
[java] view
plaincopy
import java.io.IOException;
import java.net.InetSocketAddress;
import java.nio.ByteBuffer;
import java.nio.channels.SelectionKey;
import java.nio.channels.Selector;
import java.nio.channels.ServerSocketChannel;
import java.nio.channels.SocketChannel;
import java.util.Calendar;
import java.util.Iterator;
public class TestServer {
public static void main(String[] args) {
new Thread(new EchoServer(1982)).start();
}
}
class EchoServer implements Runnable {
//要监听的端口号
private int port;
//生成一个信号监视器
private Selector s;
//读缓冲区
private ByteBuffer r_bBuf = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
public EchoServer(int port) {
this.port = port;
try {
s = Selector.open();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
@Override
public void run() {
try {
//生成一个ServerScoket通道的实例对象,用于侦听可能发生的IO事件
ServerSocketChannel ssc = ServerSocketChannel.open();
//将该通道设置为异步方式
ssc.configureBlocking(false);
//绑定到一个指定的端口
ssc.socket().bind(new InetSocketAddress(port));
//注册特定类型的事件到信号监视器上
ssc.register(s, SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT);
System.out.println("The server has been launched...");
while(true) {
//将会阻塞执行,直到有事件发生
System.out.println("监听新事件...");
s.select();
Iterator<SelectionKey> it = s.selectedKeys().iterator();
while(it.hasNext()) {
SelectionKey key = it.next();
//key定义了四种不同形式的操作
switch(key.readyOps()) {
case SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT :
dealwithAccept(key);
break;
case SelectionKey.OP_CONNECT :
break;
case SelectionKey.OP_READ :
dealwithRead(key);
break;
case SelectionKey.OP_WRITE :
break;
}
//处理结束后移除当前事件,以免重复处理
it.remove();
}
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
//处理接收连接的事件
private void dealwithAccept(SelectionKey key) {
try {
System.out.println("deal with new accept...");
ServerSocketChannel server = (ServerSocketChannel)key.channel();
SocketChannel sc = server.accept();
sc.configureBlocking(false);
//注册读事件
sc.register(s, SelectionKey.OP_WRITE);
System.out.println("deal with new accept2...");
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
//处理客户端发来的消息,处理读事件
private void dealwithRead(SelectionKey key) {
try {
SocketChannel sc = (SocketChannel)key.channel();
System.out.println("读入数据");
r_bBuf.clear();
sc.write(r_bBuf);
r_bBuf.flip();
System.out.println(r_bBuf.asCharBuffer().toString());
r_bBuf.clear();
System.out.println("处理完毕...");
try {
Thread.currentThread().sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
private String getCurrentTime() {
return Calendar.getInstance().toString();
}
}
client 端代码:
[java] view
plaincopy
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.net.InetSocketAddress;
import java.nio.ByteBuffer;
import java.nio.channels.SocketChannel;
public class TestClient {
public static void main(String[] args) {
new MiniClient("localhost", 1982);
}
}
class MiniClient {
private SocketChannel sc;
private ByteBuffer w_bBuf;
public MiniClient(String host, int port) {
try {
InetSocketAddress remote = new InetSocketAddress(host, port);
sc = SocketChannel.open();
sc.connect(remote);
if(sc.finishConnect()) {
System.out.println("已经与服务器成功建立连接...");
}
while(true) {
if(!sc.isConnected()) {
System.out.println("已经与服务器失去了连接...");
}
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
String str = br.readLine();
System.out.println("读入一行数据,开始发送...");
w_bBuf = ByteBuffer.wrap(str.getBytes());
w_bBuf.flip();
//向缓冲区中写入数据
sc.write(w_bBuf);
System.out.println("数据发送成功...");
w_bBuf.clear();
try {
Thread.currentThread().sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
} catch (IOException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
Thinking in java中的一个图片,刚找到的,比较清楚关系图。

相关文章推荐
- Java NIO 学习笔记 - ByteBuffer (早期笔记)
- Java nio 学习笔记(三)
- Java nio 学习笔记(六)
- 【原创】java NIO FileChannel 学习笔记 新建一个FileChannel
- 【学习笔记】Java NIO
- java NIO 学习笔记
- Java NIO 学习笔记 - SocketChannel
- Java nio 学习笔记(三)
- Apache Mina学习笔记:Java NIO基础概念
- 【原创】java NIO FileChannel 学习笔记 FileChannel实现分析 即FileChannelImpl分析
- Java nio 学习笔记(一) Buffer(缓冲区)与Channel(通道)的相关知识
- Java nio 学习笔记(三)
- Java nio 学习笔记(六)
- Java nio 学习笔记 相关知识
- java NIO非阻塞式IO网络编程学习笔记(一)
- Java nio 学习笔记(二) Charset(字符集)与Selector(异步IO)的知识
- 转载:Java NIO 学习笔记 - ByteBuffer
- Java nio 学习笔记(一) Buffer(缓冲区)与Channel(通道)的相关知识
- Java学习笔记--NIO
- Java NIO 学习笔记 selector 行为机制分析(select操作 cancel操作)
